motivation and emotion unit 8
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
biological basis of emotions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what does the cannon-bard theory state? 1 pt
the thalamus and hypothalamus are responsible for the emotional experience and emotional behavior respectively
what did papez state about emotions? 1 pt
emotional experiences are related to the activity of lower regions of the brain and a series of interocnnected nuclei that are activated sequentially five rise to our most primary emotions AKA limbic system
what are the three first brain theories? 3 pts
reptilian brain- responsible for automatic behaviors necessary for survival such as breathing
ancient mammalian brain- responsible for the conservation of the individual and species, and includes behaviors such as avoidance and escape, and the pursuit of pleasure
new mammalian brain- responsible for rational strategies and verbal ability that allows understanding the complexity of the experiential, physiological, and behavioral aspects of emotion
what are the limbic circuit structures? 5 pts
amygdala
insula
cingulate gyrus
orbitofrontal cortex
hippocampus
what are the different limbic structures and their associated functions and emotions? 5 pts
amygdala- activates behavioral and physiological responses of emotions, associated with fear
insula- processes bodily sensations and integrates sensory information, associated with disgust. NB: stimulation can cause nausea
cingulate gyrus- evaluates experiences from an emotional perspective and motivates behavior, associated with fear
orbitofrontal cortex- regulates motivation and emotion, organizes behavior, and controls responses, associated with anger. NB: damage can lead to apathy
hippocampus- plays a role in learning emotional reactions through its connections with other brain structures
CHAI O
what is the two system view of fear and anxiety? 2 pts
there is a distinction between the circuits underlying 2 classes of responses elicited by threats:
behavioral responses + physiological changes
conscious feeling reflected in self-reports
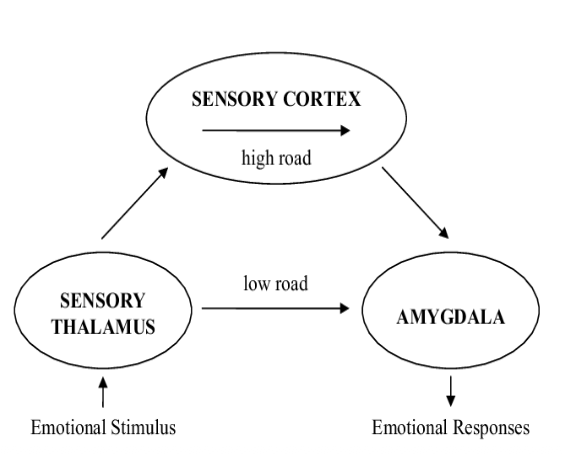
what is the role of the amygdala in fear conditioning? 2 pts
unconscious and innate- a direct thalamus→ amygdala route that processes sensory aspects of incoming stimuli and transmits the info directly to the amygdala for a rapid conditioned fear response, enabling immediate reactions
conscious and rational- allows for a more complex analysis of the incoming stimuli and offers a more adequate but slower emotional response and generates the conscious feeling
what is damasio’s somatic marker hypothesis? 1 pt
our rational processes require emotional information which relies on our bodily sensations to function effectively and adatively
what is damasio’s somatic marker theory based on? 1 pt
it is based on observations of individuals with damahe to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex who exhibit normal intellectual functioning but severe behavioral challanges particularly in decision-making and future planning
what are the three shared aspects of activation? 3 pts
non specific- no specific patterns associated with specific emotions
unidimensional- degree of activation depends on the amount of energy
unidirectional- correlation between intensity of the subjective experience and the physiological parameters
what does the theory of activation in emotions state? 1 pt
this theory states that activation is synonymous with cortical desynchronization which oscillated between sleep and maximum arousal.
what does the neuropsychological approach to activation state? 1 pt
the level of activation depends on the intensity of the stimulation that reaches the cortex through the ascending reticular activating system
what does the locationist approach of emotions state? 1 pt
different emotion categories have their roots in different mechanisms in the brain:
anger- orbitofrontal cortex
sadness- anterior cingulate gyrus
fear- amygdala
disgust- insula
what does the contructionist approach of emotions state? 1 pt
emotions are psychological events that emerge from more basic psychological processes (they are constructed) and the psychological function of the brain is determined by a network of brain regions