Evolution Notes (Abiogenesis, Evidence of Evolution, Selection, Hardy-Wineberg Equilibrium, Speciation, Taxonomy)
Abiogenesis
Biogenesis: all life comes from other life
- No life just popped up out of nowhere-- it was created by other life
Abiogenesis: life arising from simple organic compounds
- Simple organic molecules (form from inorganic molecules) → must replicate → put the replicating molecules in a cell membrane → cells must evolve metabolism to be self-sufficient
- RNA world hypothesis = first genetic material was RNA, because:
- RNA is simple
- Can store info
- Can act like a protein+enzyme
- Codes for proteins
Spontaneous Generation: process by which living things come from nonliving things
- Dirty shirt+wheat+time = mice were created!
People and Experiments
| Francesco Redi | Lazzaro Spallanzani | Louis Pasteur |
|---|---|---|
| Didn’t believe in spontaneous generationSet up 3 experiments showing that maggots are not produced by meat, rather, maggots are attracted to the meat Life is being “brought” there | Used microscopes to find out what grew when food (broth) was exposed to airConclusion: access to air+food allows for the “life force” | Allowed broth to have access to air but not “floaty stuff” in the airBroth without floaty stuff did not spoil, but broth with floaty stuff did spoilConcluded that the things in air make the life |
How did early earth arise?
| Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis | Miller and Urey | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Evolution: amino acids/nucleotides turn into life forms, inorganic molecules can turn to organic molecules | Tested the hypothesis-- set up conditions like early earth with inorganic molecules, finds amino acids/inorganic molecules turned organic and life. Soon was disproved, found that the “conditions” were not accurate to the Hadean eon. |
Hadean Eon: very rough, asteroids bombarding earth, volcanos (A LOT), pretty much hell
- Life could have also been created in a hydrothermal vent
- Forms with lots of nutrients, heat, where water meets magma
- Because of chemosynthesis
Panspermia: life was delivered to Earth
Shallow clay tide pools allowed for molecules to be concentrated, clay allowed for first macromolecules as bonds formed
First life forms were prokaryotic, anaerobic, heterotrophic, unicellular
- No nucleus, no oxygen, consumed resources, one cell
Endosymbiosis-- eukaryotes developed from one prokaryote taking another prokaryote in, the prokaryote lives inside the cell and provides something
biogenesis = all life comes from life
- No life just popped up out of nowhere-- it was created by other life
Abiogenesis: life arising from simple organic compounds
Simple organic molecules (form from inorganic molecules) → must replicate → put the replicating molecules in a cell membrane → cells must evolve metabolism to be self-sufficient
- RNA world hypothesis = first genetic material was RNA, because:
- RNA is simple
- Can store info
- Can act like a protein+enzyme
- Codes for proteins
\n
Spontaneous Generation: process by which living things come from nonliving things
Dirty shirt+wheat+time = mice were created!
\n
People and Experiments and Stuff
| Francesco Redi | Lazzaro Spallanzani | Louis Pasteur |
|---|---|---|
| Didn’t believe in spontaneous generationSet up 3 experiments showing that maggots are not produced by meat, rather, maggots are attracted to the meat Life is being “brought” there | Used microscopes to find out what grew when food (broth) was exposed to airConclusion: access to air+food allows for the “life force” | Allowed broth to have access to air but not “floaty stuff” in the airBroth without floaty stuff did not spoil, but broth with floaty stuff did spoilConcluded that the things in air make the life |
\n
How did early earth arise?
\n
| Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis | Miller and Urey | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Evolution: amino acids/nucleotides turn into life forms, inorganic molecules can turn to organic molecules | Tested the hypothesis-- set up conditions like early earth with inorganic molecules, finds amino acids/organic moleculesSoon was disproved, found that the “conditions” were not as Miller and Urey didSuccess was not replicated with real Hadean conditionsShows that it’s possible to go from inorganic to organic |
\n
Hadean Eon: very rough, asteroids bombarding earth, volcanos (A LOT), pretty much hell
Life could have also been created in a hydrothermal vent
- Forms with lots of nutrients, heat, where water meets magma
- Because of chemosynthesis
\n
Panspermia: life was delivered to Earth
\n
Shallow clay tide pools allowed for molecules to be concentrated, clay allowed for first macromolecules as bonds formed
\n
First life forms were prokaryotic, anaerobic, heterotrophic, unicellular
No nucleus, no oxygen, consumed resources, one cell
\n
Endosymbiosis-- eukaryotes developed from one prokaryote taking another prokaryote in, the prokaryote lives inside the cell and provides something
Evidence of Evolution
What do we care about?
- Theory
Multidisciplinary explanation of a body of knowledge based off of rules, unifies different parts of the world, has a lot of support - Law
Establishing a relationship between multiple things, direct cause/effect - Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a potential explanation of a phenomenon, rooted in fact - Fact
Facts are observations shown to be true that can be disproven.
Early scientists tried to organize life.
- European baddies thought there was a great chain of being that linked species/life in an unchanging change (you can’t change a chain), connects terrestrial/divine life
- Life is static-it is what it is
- As european colonizers traveled across the world, they saw very similar unique organisms in very different places
- The ostrich (native to africa, similar birds found in South America (rhea) and Australia (emu))
- Collected the bones and saw similarities
- Saw traits/structures with no function
Cuvier attempted to say that fossils show some animals are extinct. This evidence all shows that life is evolving and changing!
Homologous structures = similar features of different organisms originating in a shared ancestor
Vestigial structures = useless structures that were once useful to an evolutionary ancestor
Macromolecule similarities can show similar blueprints/genes
Fossils are the only direct evidence of old organisms leading to modern species
Biogeography = how plants/animals are spread across the planet
- Before pangaea split, plants and animals could go everywhere, which is why some species are scattered along different continents
Evidence of evolution:
- Homologous structures
- Vestigial structures
- Macromolecules
- Fossil record
- Biogeography
- Embryology
Selection
Selection = the survival and reproduction of individuals with certain traits
Populations evolve b/c of selection, selection determines whether a trait is more/less common
Fitness = the ability to survive and reproduce
- Live vs die
- Did they mate?
- How many babies?
Fitness is dependent on how well an organism performs in their environment
- Can be influenced by phenotype/genotype
Artificial selection: humans select which traits move on
- Ex: food, dogs
Sexual selection: type of natural selection, traits that increase mating success or # of offspring pass through
Sexual selection leads to males being different from females
called sexual dimorphism -- males must compete for the attention of females or compete directly with other males
- female choice vs male competition
genetic drift = random selection- a trait survives because it was chosen at random
- sometimes called the bottleneck effect=only a few members survive to the next generation to pass on traits
selections can change traits in 3 different ways
- directional = selects for one extreme trait, against the other (shifting the curve)
- stabilizing = selects for the medium trait, against the extreme traits (just right!)
- disruptive = selects for both extreme traits, against the medium trait (leads to new species)
Natural selection: Nature selects traits that get passed on-- only the best traits (ensuring survival and reproduction) get passed on
- the only explanation for why organisms are specifically suited for specific thing
Jean Baptiste de Lemark = thought of the idea of the shared ancestor -- proposed the theory of species modification over time, traits gained over lifetime are passed to organism’s offspring
- why is this wrong? acquired characteristics do not change the DNA
Charles Darwin = “on the origin of species,” a naturalist, took a 5 year expedition of the world
His observations:
- observed fossils of extinct armadillos
- visited galapagos islands, intrigued by many of the organisms having similar characteristics to equador
- read thomas malthus who described how populations are controlled by death which balances population
- observed the finches in the Galapagos
- varied in size, beak size, and shape -- concluded that all finch descended from 1 species of finch (evolving to the food sources available on the island)
Darwin’s two theories:
- Descent with modification - all organisms descend from common ancestor, differences are modifications over time to ensure survival
- Modification by natural selection - nature chooses which traits to pass on
Evolution by natural selection:
- variation in a population -- the traits must be different/varied
- challenge in the environment (struggle) -- environment must have challenges to weed out the weak (disadvantaged traits)
- survivors reproduce and compete (differential fitness) -- the better traits will pass on to offspring
- the variation must be heritable -- the trait must be genetic
Hardy Wineberg Equilibrium
Gene pool = the total genetic information available in a population
Population genetics =
Genotype frequency = how often a specific genotype occurs in a population
Allele frequent = the proportion of a specific allele in a population
HWE says that:
- Nothing will mutate
- Nothing will migrate
- No genetic drift will occur
- No sexual selection (random mating)
- No natural selection
Under HWE, we can see whether or not genetic change has occurred.
How to solve HWE problems:
p = allele frequency of dominant
q = allele frequency of recessive
p^2 = f(AA)
q^2 = f(aa)
2pq = f(Aa)
p = [2(AA)+Aa]/2(total)
q = [2(aa)+Aa]/2(total)
What is the question asking?
Allele frequency?
- Solve for P or Q
Evaluate the genotype frequency?
- Use HWE, solve for p^2, 2pq, or q^2
Did the population evolve?
- Compare p^2 = AA/total, 2pq=Aa/total, q^2 = aa/total
- If it matches, no evolution
- If it doesn’t match, yes evolution
Unknown genotypic frequency?
- Solve for q, square root HWE
\n
Always check your answers!
occurred
Speciation
Morphological species concept: external appearance is the most important criteria for classification of a new species
- some species look very alike and pose a problem
Biological species concept: a population that can interbreed successfully but cannot breed with other species
- some species are extinct, some are asexual
What is a species?
- a unique type of organism designated by genus name or specific epithet (designated by taxonomists). within sexual reproducers, one or more groups of individuals that can potentially interbreed, produce fertile offspring, and does not interbreed w/ other groups
- comes from speciation: formation of a new species, occurs when members of the same species become isolated and do not reproduce
let’s look at the fruit fly!
- fruit flies go towards fruit to reproduce-- migration brings a fruit to a new island with new climate (fruit flies with it)
- fruit flies adapt via natural selection to the new island
- island flies migrate back to the native flies-- they don’t recognize each other as options for reproduction because they are so different
- this is a speciation event
reproductive isolation: the separation of a species or population so members can no longer interbreed
- allopatric = population splits into 2 with some sort of barrier between, one adapts, they are different
- sympatric = speciation in same area (a mutation/genetic difference gives something a new trait
barriers to speciation = isolating mechanisms
- barriers to successful breeding between populations in the same area
- prezygotic = barriers before fertilization
- geographic isolation = physical separation of population that prevents reproduction
- habitat/ecological isolation = separation of populations due to them inhabiting different habitats (even if they are near each other, if one is aquatic and one is terrestrial, they cannot mate)
- temporal isolation = mating happens at different times, providing a timing separation, preventing reproduction
- behavioral isolation = attraction barrier between organisms, preventing reproduction
- mechanical isolation = genitalia does not fit
- insemination = getting past mechanical isolation
- gametic isolation = the sperm doesn’t get in the egg
- fertilization = getting past gametic isolation
- post-zygotic = barriers after fertilization
- reduced hybrid viability = offspring is stillborn, dies shortly after birth
- reduced hybrid fertility = offspring is sterile
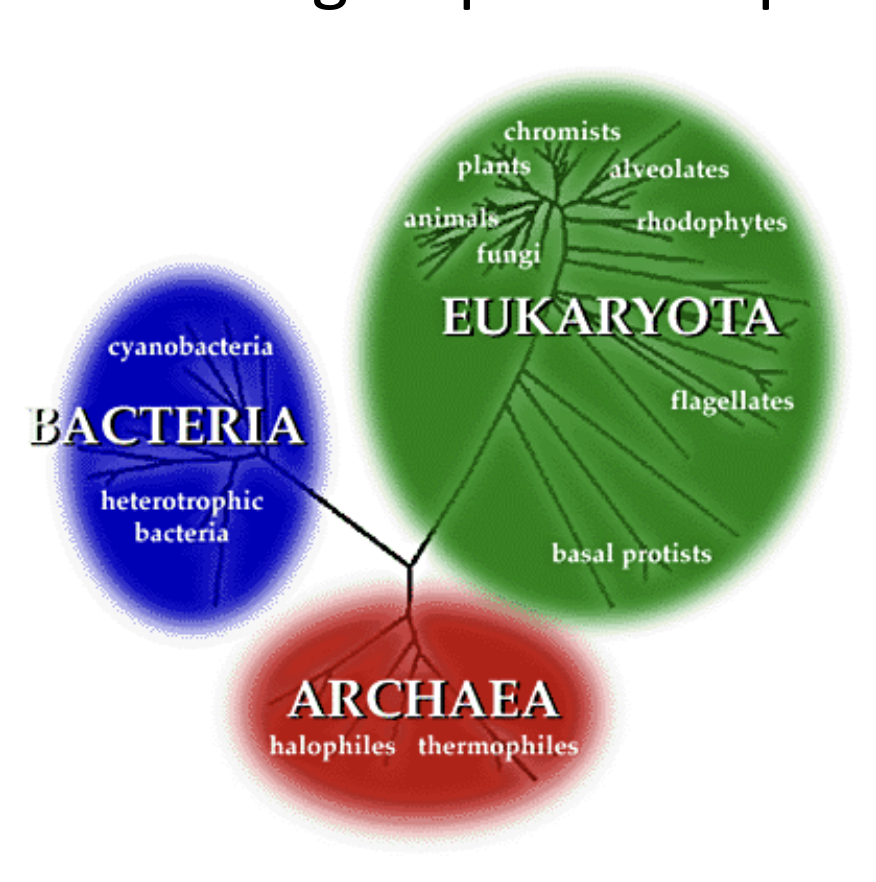
Taxonomy
Taxonomy - branch of biology that categorizes, names, and groups organisms according to evolution and observed traits

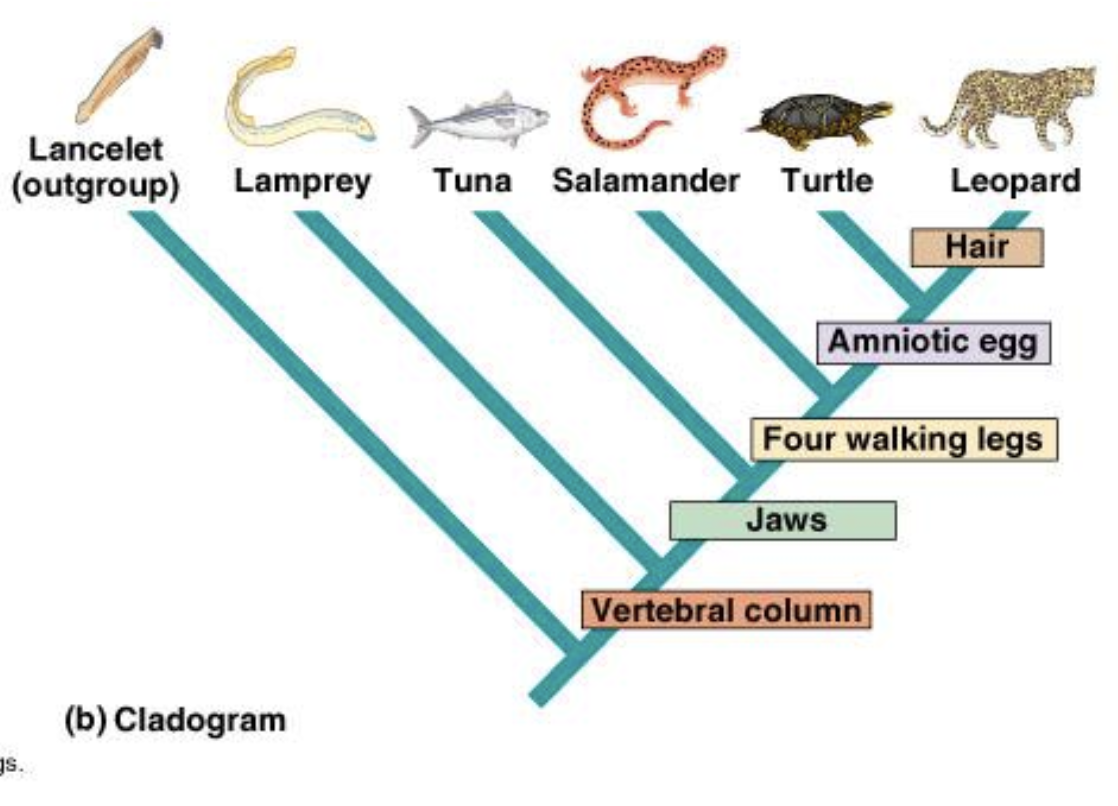
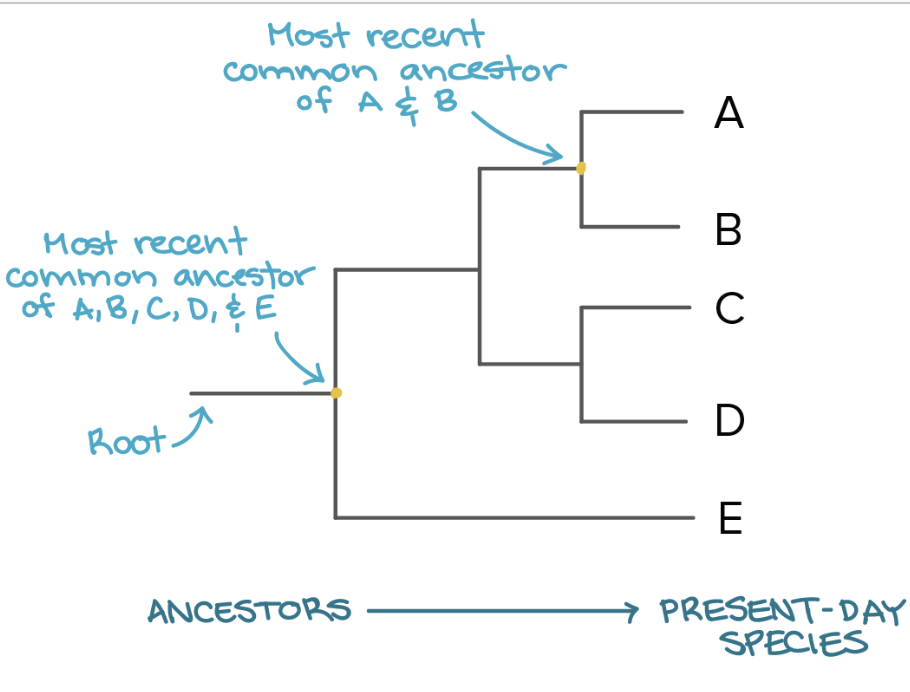
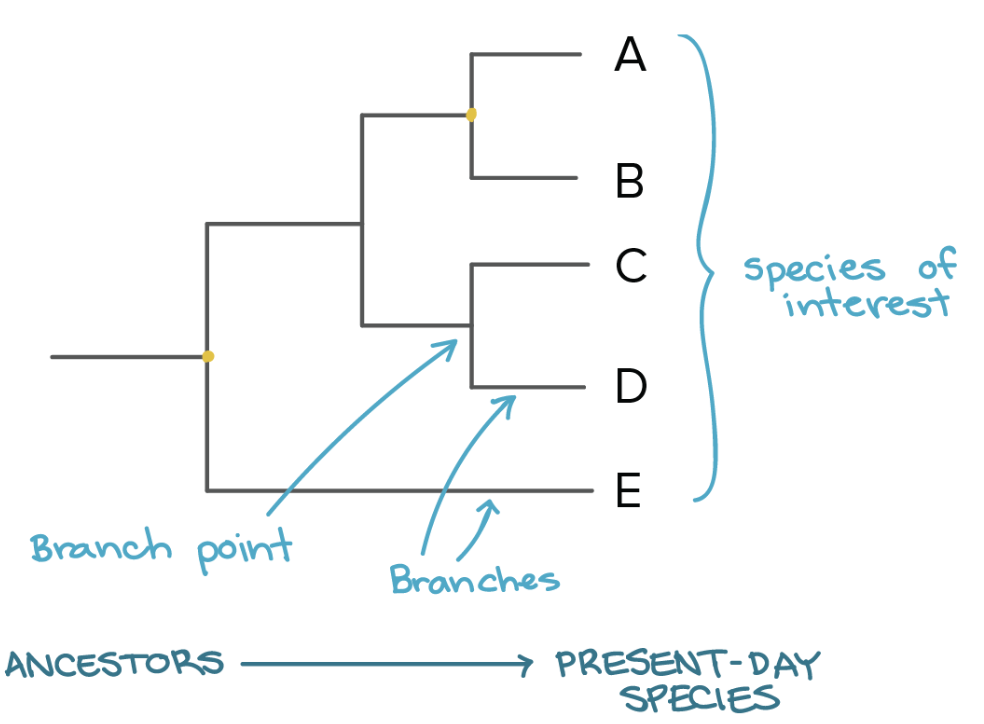
Our understanding of evolutionary history can help biologists develop phylogeny, or evolutionary history of a species.
Phylogenies are graphs with one axis, time, that map out the evolutionary history of an organism. Cladograms are another type of graph that are the hypothesis version of a phylogeny, cladograms have traits written on the graph.
 |  |
|---|
Species are more closely related if they have a more recent common ancestor.
Species are less closely related if they have a less recent common ancestor.
Parsimony = the simplest cladogram is the best (least amt of traits)