Chapter 4 A&P Notes
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review Epithelial Tissue Cards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the most abundant tissues in the body?
Connective tissue
What are the functions of connective tissue (5)?
binding
support
protection
insulation
transportation
How many types of connective tissues are there?
6
Adipose
Loose connective
Dense Regular
Cartilage
Bone/ Osseous
Blood
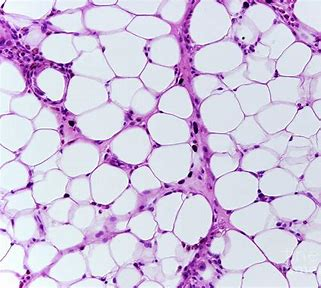
Adipose Tissue
Function and Location
it is closely packed fat cells
reserve food fuel, protects organs, and insulates against heat loss
Found under skin, breast, abdomen

Dense Regular
Function and Location
parallel collagen fibers w/ fibroblasts
attaches muscle to bones and bones to bones, withstands great tensile strength
found in tendons and ligaments
Cartilage
Three types
Function and Location
Hyaline:
supports and has cushioning properties
found in joints, nose
Fibrocartilage:
tensile strength, absorbs compressive shock
found in vertebral discs, knee discs
Elastic:
maintains shapes of structure. allows flexibility
found in external ear
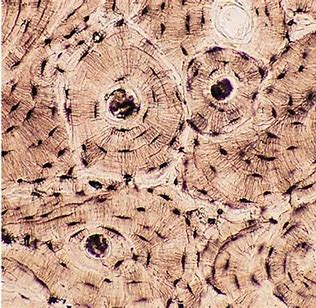
Bone Osseous
Function and Location
hard calcified matrix
bone supports and protects, act as levers for muscles, marrow is site of blood formation
found in bones
Blood
Function and Location
red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix
transports respiratory gases, nutrients, waste
found in blood vessels
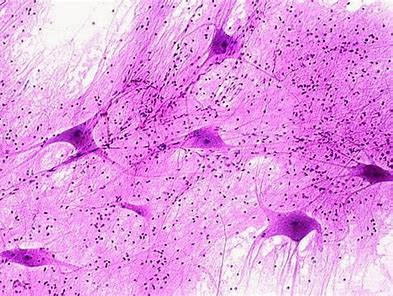
Nervous Tissue
Function and Location
made of neurons and neuroglia
transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors and effectors (glands/ muscles)
found in brain, spinal cord, nerves
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, smooth, cardiac

Skeletal
Desc Function, Location
long cylindrical, multinucleate, striations
voluntary movement, control facial expressions
found in skeletal muscles attached to bones or skin
Smooth
Desc, Function, Location
(4 sentences)
spindle shaped cells, central nuclei, no striations, form sheets
propels substances (urine, food, baby) along internal passageways
involuntary movement
found in walls of hollow organs (stomach, large intestine)
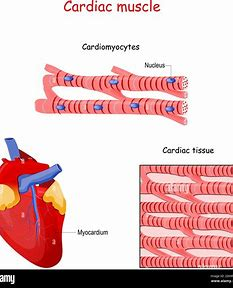
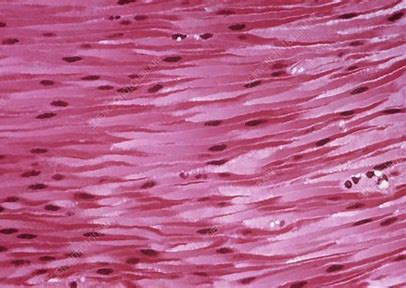
Cardiac
Desc, Function, Location
branching, striated, unicellular, form intercalated discs
propels blood into circulation, involuntary
found in walls of heart
What are the 4 types of epithelial membranes?
Hint: C, S, M, S
Cutaneous:
skin
Synovial:
line joint cavities (skeletal)
Mucous:
line body cavities OPEN to exterior (digestive: mouth) (respiratory: nose)
Serous:
moist membranes line cavities CLOSED to exterior
Ex: abdominal, thoracic, cranial