Genetics/inheritance
5.0(1)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:03 AM on 6/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Trait
a genetically determined characteristic
2
New cards
Alleles
One, two or more versions of DNA sequences
3
New cards
Dominant trait
Dominant traits are always expressed, even if only one copy of the dominant trait exists
4
New cards
Recessive trait
Recessive traits are only expressed if both alleles are recessive, if one is dominant the recessive trait is masked
5
New cards
homozygous
two identical pairs of alleles of a particular gene
6
New cards
heterozygous
two different alleles of a particular gene
7
New cards
Genotype
genetic information
8
New cards
Phenotype
set of observable physical traits
9
New cards
Law of domincance
\-In a heterozygote, a dominant allele will mas the expression of a recessive allele
\-The only way to express a recessive allele is as a homozygote (absence of dominant allele)
\-The only way to express a recessive allele is as a homozygote (absence of dominant allele)
10
New cards
Law of segregation
\-A diploid individual has 1 pair of alleles for each gene
\-When gametes are formed, this pair is randomly separated into 2 gametes.
\-Each gamete are haploid (contain 1 copy of each chromosome
\-which allele is passed to offspring is random
\-When gametes are formed, this pair is randomly separated into 2 gametes.
\-Each gamete are haploid (contain 1 copy of each chromosome
\-which allele is passed to offspring is random
11
New cards
Law of independent assortment
\-the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another
\-the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene
\-the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene
12
New cards
3 laws of inheritence
Law of independent assortment, Law of segregation, Law of domincance
13
New cards
Punnett square
a diagram used to predict genotypes of a cross
14
New cards
Incomplete dominance
a form of Gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene are partially expressed, often resulting in an intermediate or different phenotype
15
New cards
Representing alleles
exponents for the different dominant alleles
16
New cards
Example of co-dominance
ABO blood groups
17
New cards
Genes
The basic unit of heredity (made up of sequences of DNA) passed from parent to child.
18
New cards
Homologous chromosome
chromosomes that are present in the same chromosome pair
19
New cards
Sex chromosomes
two types of chromosomes, x and y, which determine the sex
20
New cards
Autosome (Chromosome)
the first 22 homologous pairs of human chromosomes that do not determine the sex of an individual
21
New cards
Co-dominance
a type of inheritence in which two alleles get expressed equally in the phenotype of a heterozygous individual
22
New cards
Incomplete dominance
when pairs of alleles are both expressed to form a new phenotype of a heterozygous individual
23
New cards
X-linked
a type of recessive inheritance which refers to genetic conditions associated with mutations in genes on the X chromosome (mostly in males)
24
New cards
Monohybrid cross
a mix between two sets of homozygous genotypes (completely dominant or completely recessive alleles) which result in opposite phenotypes for a certain genetic trait.
25
New cards
Pedigree
Shows a relationship between genetically related individuals, including the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene from one generation to the next
26
New cards
Pedigree rules (Females, Males, Shaded, Half-shaded, generation, numbering)
\-Females represented by circles
\-Males represented by squares
\-Shaded, means an individual is affected by the disease or disorder
\-Half-Shaded, means an individual is a carrier of the disease or disorder
\-Shows only phenotypes
\-Same generation on the same row
\-Roman numeral number generations
\-Arabic numerals number individuals in the same generation
\-Males represented by squares
\-Shaded, means an individual is affected by the disease or disorder
\-Half-Shaded, means an individual is a carrier of the disease or disorder
\-Shows only phenotypes
\-Same generation on the same row
\-Roman numeral number generations
\-Arabic numerals number individuals in the same generation
27
New cards
Types of inheritence from pedigree charts
autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, x linked dominant, x linked recessive
28
New cards
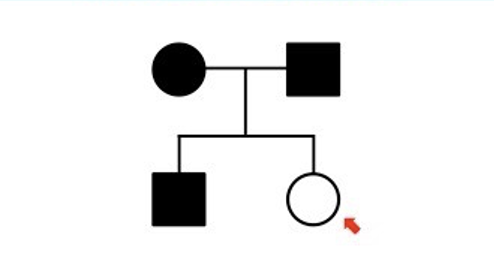
autosomal dominant
\-cannot be recessive as two affected parents cannot have an unaffected child
\-parents must be heterozygous
\-parents must be heterozygous
29
New cards
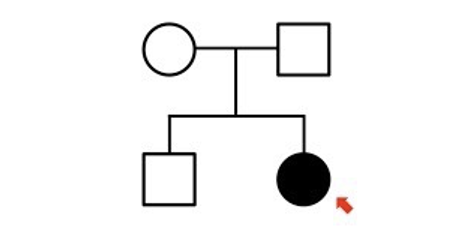
autosomal recessive
\-cannot be dominant as two unaffected parents cannot have an affected child
\-parents must be heterozygous
\-parents must be heterozygous
30
New cards
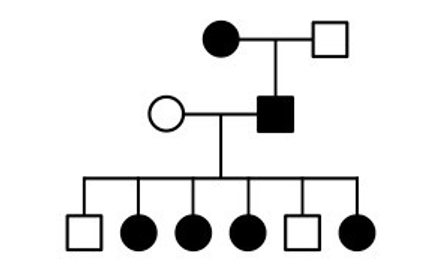
x linked dominant
\-affected daughters from an affected father suggest x linked dominance
\-sex linkage cannot be confirmed
\-sex linkage cannot be confirmed
31
New cards
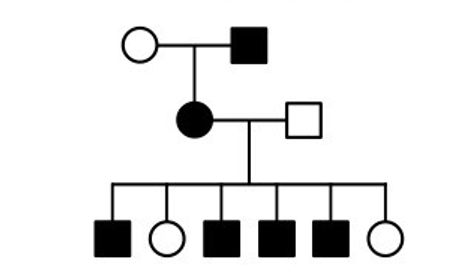
x linked recessive
\-affected sons from affected mothers suggests x-linked recessive
\-sex linkage cannot be confirmed
\-sex linkage cannot be confirmed
32
New cards
To identify **sex-linkage** look for:
\-Usually only males affected
\-Rarely seen, but females affected only when the father is affected
\-Rarely seen, but females affected only when the father is affected
33
New cards
To identify **autosomal recessive** look for:
\-Both males and females affected
\-Cases where two unaffected parents have an affected child
\-‘Skips’ generations
\-Cases where two unaffected parents have an affected child
\-‘Skips’ generations
34
New cards
To identify **autosomal dominant** look for:
\-Every affected individual has at least one affected parent
\-Both males and females affected
\-Seen in every generation
\-Both males and females affected
\-Seen in every generation
35
New cards
Blood types
A, B, AB, O
36
New cards
A heterozygous
I^A i
37
New cards
A homozygous
I^A, I^A
38
New cards
B heterozygous
I^B, i
39
New cards
B homozygous
I^B, I^B
40
New cards
O
i, i