RBT Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/224
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
225 Terms
1
New cards
Continuous Measurement
All instances of responses/bx detected during the observation period
Count
Frequency
Rate
Celeration
Duration
Latency
Interresponse Time (IRT)
Percentage
Trials-to-Criterion
Count
Frequency
Rate
Celeration
Duration
Latency
Interresponse Time (IRT)
Percentage
Trials-to-Criterion
2
New cards
Dimensions
Features that can be measured
3
New cards
Frequency
Count each time a bx occurs
4
New cards
Rate
Frequency/time
5
New cards
Duration
Length of time bx occurs
6
New cards
Latency
Time between an environmental event/antecedent and response
Ex. Time between an sd to when client starts following sd
Ex. Time between an sd to when client starts following sd
7
New cards
Interresponse Time (IRT)
Time between end of one response and beginning of next one
Ex. Time between two bites of food
Ex. Time between two bites of food
8
New cards
Percentage
Proportional quantity
Number of responses / Number of opportunities * 100
Number of responses / Number of opportunities * 100
9
New cards
Trials-To-Criterion
Number of response opportunities needed for a person to achieve pre-determined level of performance
10
New cards
Learning Opportunities (LOs)
Acquisition and maintenance tasks, tasks, analysis, mand training (command or ask), incidental teaching/PRT/NET (learn behavior).
11
New cards
Repeatability or countability
Bx can be counted
12
New cards
Temporal Extent
Duration
13
New cards
Temporal Locus
When bx occurs
14
New cards
Count
Number of responses emitted during an observation period
15
New cards
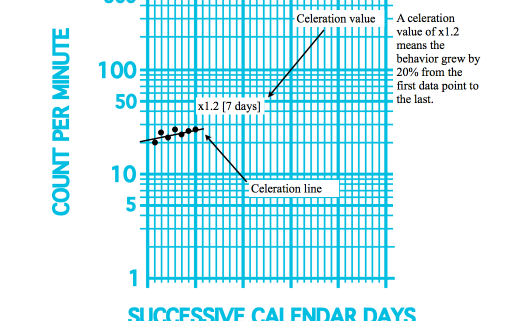
Celeration (Standard Celeration Chart)
Measure of the change in rate of responding per unit of time
Captures bx acceleration and deceleration
Captures bx acceleration and deceleration
16
New cards
Topography
Physical form or shape of a bx
17
New cards
Magnitude
Intensity of bx
18
New cards
Discontinuous Measurement
Measuring some instances of bx during an observation
19
New cards
Time Sampling
Observation is divided into intervals, presence or absence of bx recorded for each interval
20
New cards
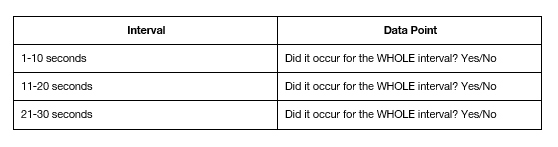
Whole-Interval Recording (Discontinuous, Time Sampling)
Measures continuous bx over brief intervals, record if a bx occurs throughout the ENTIRE interval
Report percentage of intervals where bx does occur during entire interval
Risks underestimation
Report percentage of intervals where bx does occur during entire interval
Risks underestimation
21
New cards
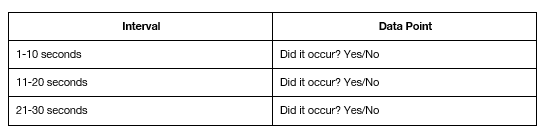
Partial-Interval Recording (Discontinuous, Time Sampling)
Measures INSTANCES of bx, record if a bx occurs at any point during interval
Does not capture duration
Recorded as percentage of intervals where bx occurred
Does not capture duration
Recorded as percentage of intervals where bx occurred
22
New cards
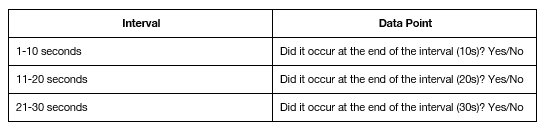
Momentary Time Sampling (Discontinuous, Time Sampling)
Measures presence or absence of bx within specific time intervals or at a specified/given time
Record if bx is occurring at the end of the interval
Reported as percentage of intervals where bx occurred
Records behavior when they occur at the particular moment the RBT was monitoring.
Record if bx is occurring at the end of the interval
Reported as percentage of intervals where bx occurred
Records behavior when they occur at the particular moment the RBT was monitoring.
23
New cards
Planned Activity Check (Discontinuous, Time Sampling)
Measures bx of individuals in a group; At end of interval, measure number of students engaged in target activity
Variation of momentary time sampling
Variation of momentary time sampling
24
New cards
Artifact
Something that appears to exist because of the way it is examined or measured
25
New cards
Permanent Product
Measuring the effects of a bx produced on the environment
Not recommended to use as primary method of data collection
Ex postfacto
Not recommended to use as primary method of data collection
Ex postfacto
26
New cards
Baseline
Rate of bx prior to intervention
27
New cards
Behavioral Excesses
Bx that occur too frequently or intensely
Selt-stims, aggression, tantrums
Selt-stims, aggression, tantrums
28
New cards
Behavioral Deficits
Bx that occur at too low frequencies or intensity
Language, social bx, self-help skills
Language, social bx, self-help skills
29
New cards
Behavior Assessment
Process of identifying probable antecedent and consequent controlling variables
Discover recourses, environment, people, contingencies, maintenance and general factors, and possible reinforcers/punishers that surround potential target bx
Discover recourses, environment, people, contingencies, maintenance and general factors, and possible reinforcers/punishers that surround potential target bx
30
New cards
Fundamental Properties
Repeatability or Countability
Temporal Extent - Duration
Temporal Locus - When bx occurs
Temporal Extent - Duration
Temporal Locus - When bx occurs
31
New cards
Dead Man's Rule
If a dead man can do it, it's not a bx
32
New cards
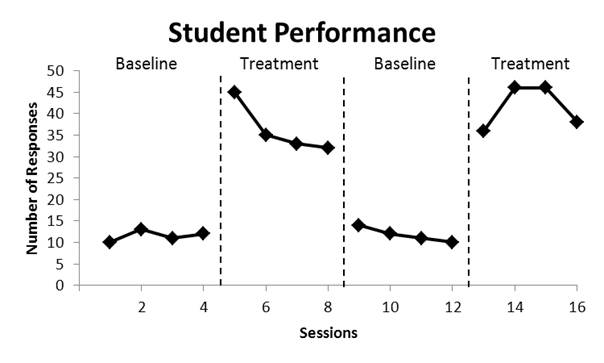
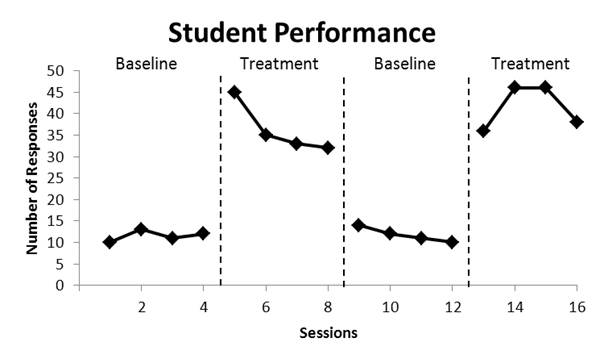
Phase Line
A dashed vertical line on a graph that indicates a change that may have an impact on bx. This can also indicate move from baseline (no modifications in environment) to intervention or from one intervention to another.
33
New cards
When to not connect dots on line graph
Points fall on either side of a condition change line
A significant span of time passed and bx was not measured
There was a discontinuity in time in the horizontal axis (eg. vacation)
Data were not collected, lost, etc.
It is follow-up or post-check data
Unless intersession time span same as the original experiment
Data points fall beyond the values described by the vertical axis
A significant span of time passed and bx was not measured
There was a discontinuity in time in the horizontal axis (eg. vacation)
Data were not collected, lost, etc.
It is follow-up or post-check data
Unless intersession time span same as the original experiment
Data points fall beyond the values described by the vertical axis
34
New cards
Graph
Used to display and compare discrete sets of data that are not related to one another by a common under lying dimension by which the horizontal axis can be scaled
35
New cards
Parts of Line Graph
Horizontal and Vertical Axis
Condition Change Lines/Phase Lines
Condition Labels (Phase and Condition)
Data Points
Data Path
Figure Caption
Condition Change Lines/Phase Lines
Condition Labels (Phase and Condition)
Data Points
Data Path
Figure Caption
36
New cards
Cumulative Records
Shows number of responses on the ordinate (y-axis) and against time on abscissa (x-axis)
Cumulation of responses over time
There is no decrease on graph, steeper the slope, higher the rate of responses
Cumulation of responses over time
There is no decrease on graph, steeper the slope, higher the rate of responses
37
New cards
Ordinate
Y-axis
38
New cards
Abscissa
X-axis
39
New cards
Standard Celeration Chart
Charting changes in frequency of bx over time
40
New cards
Operational Definition
Defining bx specifically and observably
When offset and onset is
When offset and onset is
41
New cards
Interobserver Agreement (IOA)
Degree to which two or more independent observers report the same observed values after measuring the same events
42
New cards
Scatter Plot
Shows relative distribution of individual measures over in a dataset
Dots are not connected
Dots are not connected
43
New cards
5 Phases of Assessment
1. Screening
2. Defining problem or criteria for achievement
3. Pinpointing target bx's
4. Monitoring progress
5. Follow up
2. Defining problem or criteria for achievement
3. Pinpointing target bx's
4. Monitoring progress
5. Follow up
44
New cards
Indirect Assessments
Interviews, checklists
45
New cards
Direct Assessments
Tests
Direct Observation - only assessment method RBT's will use
Direct Observation - only assessment method RBT's will use
46
New cards
Assessment
Systematic collection of empirical datas, review, and use of info about educational programs undertaken for the purpose of improving student learning and development
47
New cards
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
The application of behavioral principles to everyday situations, that will, over time, increase or decrease targeted bx
48
New cards
Preference
Something that an individual is more likely to accept or approach relative to other stimuli
Something that is a reinforcer in one moment might be a preference in the next and vice versa
It all depends on what MOTIVATES the client
Something that is a reinforcer in one moment might be a preference in the next and vice versa
It all depends on what MOTIVATES the client
49
New cards
Reinforcer
Something that increases the likelihood of responding
Only a reinforcer if it results in an increase in a specific bx
Only a reinforcer if it results in an increase in a specific bx
50
New cards
Preference Assessment
Identify potential reinforcers that will motivate a child to work
Pairs yourself with reinforcement and provide an opportunity for the child to engage with you in a "fun" manner
Provides structure for staff to find motivating items by eliminating "trial and error" that occurs during delivery of potential reinforcers
Pairs yourself with reinforcement and provide an opportunity for the child to engage with you in a "fun" manner
Provides structure for staff to find motivating items by eliminating "trial and error" that occurs during delivery of potential reinforcers
51
New cards
Types of Preference Assessments
Free operant
Single Stimulus (Successive Choice)
Multiple Stimulus
Paired Stimulus (Present 2, make a choice)
Single Stimulus (Successive Choice)
Multiple Stimulus
Paired Stimulus (Present 2, make a choice)
52
New cards
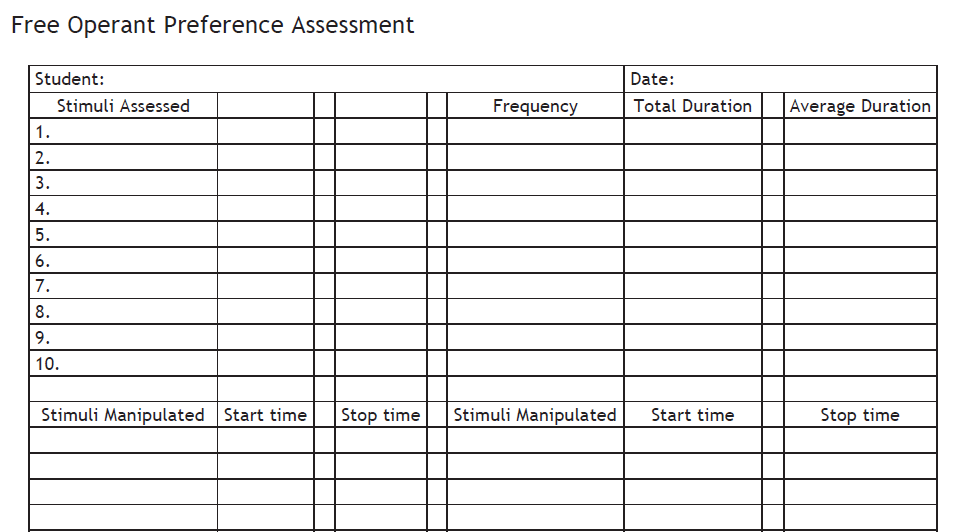
Free Operant Preference Assessment
Conducted with activities or toys and a stopwatch/timer
Measure duration of toy play during free play
Can be naturalistic or contrived (put specific toys out in different locations)
If a client does not choose a toy, not what they are doing and for how long (duration). This includes self-stimulatory bx
In the Stimuli manipulates section, fill in the item or activity that the student chooses
Measure duration of toy play during free play
Can be naturalistic or contrived (put specific toys out in different locations)
If a client does not choose a toy, not what they are doing and for how long (duration). This includes self-stimulatory bx
In the Stimuli manipulates section, fill in the item or activity that the student chooses
53
New cards
Multiple Stimulus Preference Assessment
Conducted with edibles or items/activities
Measuring the order in which a client picks a toy (frequency or rank order)
Measuring the order in which a client picks a toy (frequency or rank order)

54
New cards
Multiple Stimulus w/ replacement (MS) Preference Assessment
Measures frequency in which a toy is chosen by replacing the toys in which the client did NOT choose
If client chooses toy 1 out of 3, replace toy 2 and 3 and repeat
If using MS with replacement, after the student selects an item, place that item back into the array.
If the student continues to pick the same item, do another session using MS without replacement so you can rank order the remaining items.
If client chooses toy 1 out of 3, replace toy 2 and 3 and repeat
If using MS with replacement, after the student selects an item, place that item back into the array.
If the student continues to pick the same item, do another session using MS without replacement so you can rank order the remaining items.

55
New cards
Multiple Stimulus without replacement (MSWO) Preference Assessment
Don't replace toy that client chooses and record the order in which toys or chosen (rank order)
Randomize array of remaining toys after every selection
Randomize array of remaining toys after every selection
56
New cards
Baseline
Current Level that a target bx occurs prior to intervention
Compared to after intervention data to determine effectiveness of intervention
Compared to after intervention data to determine effectiveness of intervention
57
New cards
Probe and baseline data
Both used to determine if a client has a specific skillset
58
New cards
Developmental Assessment
Norm-referenced developmental assessments provide info about how a child is developing compared to peers
Cognition, communication, motor, adaptive, and social skills are measured
Cognition, communication, motor, adaptive, and social skills are measured
59
New cards
Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Provide info about skills that are in your child's repertoire, including curriculum-based assessments
Determine what skills your child is able to perform as well as what skills your child should learn next
Determine what skills your child is able to perform as well as what skills your child should learn next
60
New cards
Examples of Developmental Assessments
Child Development Inventories (CDI)
Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales - II
Gilliam Autism Rating Scale (GARS)
Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales - II
Gilliam Autism Rating Scale (GARS)
61
New cards
Assessment of Basic Language and Learning Skills
ABLLS-R (Curriculum-based assessment)
ABLLS-R (Curriculum-based assessment)
Assessment of Basic Language and Learning Skills
An assessment tool, curriculum guide, and skills-tracking system used to help guide the instruction of language and critical learner skills for children with ASD or other developmental disabilities
• Cooperative and Reinforcer effectiveness
• Visual Performance
• Receptive Language
• Imitation
• Vocal Imitation
• Mands
• Tacts
• Intraverbals
• Spontaneous Vocalizations
• Syntax &Grammar
• Play and Leisure
• Soc. Interaction
• Group Instruction
• Follow Classroom Routines
• Gen. Responding
An assessment tool, curriculum guide, and skills-tracking system used to help guide the instruction of language and critical learner skills for children with ASD or other developmental disabilities
• Cooperative and Reinforcer effectiveness
• Visual Performance
• Receptive Language
• Imitation
• Vocal Imitation
• Mands
• Tacts
• Intraverbals
• Spontaneous Vocalizations
• Syntax &Grammar
• Play and Leisure
• Soc. Interaction
• Group Instruction
• Follow Classroom Routines
• Gen. Responding
62
New cards
Assessment of Functional Living Skills
AFLS (Curriculum-Based Assessment)
AFLS (Curriculum-Based Assessment)
Assesses 6 modules: Basic Living Skills
Home Skills
Community Participation Skills
School Skills
Vocational Skills
Independent Living Skills
Each assessment module has 8 skills areas to access functional skills across different settings throughout learner's lifespan
Home Skills
Community Participation Skills
School Skills
Vocational Skills
Independent Living Skills
Each assessment module has 8 skills areas to access functional skills across different settings throughout learner's lifespan
63
New cards
Verbal Behavior Milestones Assessment and Placement Program
VB MAPP
VB MAPP
Criterion-Referenced Assessment Tool, curriculum guide, and skill tracking system to track LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT
64
New cards
65
New cards
Curriculum Based Assessment
Links instruction with assessment; based on CBA instrument, teachers, and other professional can specify instructional goals
1. Determine eligibility
2. Develop goals for instruction
3. Evaluate the student's progress in the curriculum
Direct observation and recording of a student’s performance in the local curriculum as the basis for gathering information to make instructional decisions.
Repertoire–list or number of skills or capabilities of an individual
identify those language and other critical skills that are in need of intervention in order for a child to become more capable of learning from his everyday experiences
1. Determine eligibility
2. Develop goals for instruction
3. Evaluate the student's progress in the curriculum
Direct observation and recording of a student’s performance in the local curriculum as the basis for gathering information to make instructional decisions.
Repertoire–list or number of skills or capabilities of an individual
identify those language and other critical skills that are in need of intervention in order for a child to become more capable of learning from his everyday experiences
66
New cards
Functional Assessment
Identify the function of a challenging behavior so an intervention can be put in place to reduce this behavior and/or increase more adaptive behaviors
Assessment in which gathers information on:
Clear description on the challenging bx (Behavior)
Antecedent
Consequence
Identify desirable bx that can replace challenging bx (Using words vs. Screaming)
Identify events or people that encourage challenging bx (Someone forgets to give lunch leading to yelling)
Development of hypothesis outlining potential functions of bx (reinforcing consequences)
A full history of interventions that have been previously implemented (success and failures)
Assessment in which gathers information on:
Clear description on the challenging bx (Behavior)
Antecedent
Consequence
Identify desirable bx that can replace challenging bx (Using words vs. Screaming)
Identify events or people that encourage challenging bx (Someone forgets to give lunch leading to yelling)
Development of hypothesis outlining potential functions of bx (reinforcing consequences)
A full history of interventions that have been previously implemented (success and failures)
67
New cards
Functional Assessment Methods
Direct Observation - Observer records ABC. frequency, interval, graphs
Informant Methods - Interviews and Questionnaires (FAST, MAS)
Functional Analysis - Antecedents and consequences are manipulated to understand their effects
Informant Methods - Interviews and Questionnaires (FAST, MAS)
Functional Analysis - Antecedents and consequences are manipulated to understand their effects
68
New cards
Functional Analysis
An analysis of the purposes (functions) of problem behavior wherein antecedents and consequences representing those and the person’s natural routines are observed.
69
New cards
Functions of Bx
SEAT
Sensory - Self-stims, Bx feels good or meets sensory needs
Escape - from person, task, environment, etc
Attention - Desire for attention from peers and adults (can be person-specific)
Tangible - Specific item or activity (Could have been denied access)
Sensory - Self-stims, Bx feels good or meets sensory needs
Escape - from person, task, environment, etc
Attention - Desire for attention from peers and adults (can be person-specific)
Tangible - Specific item or activity (Could have been denied access)
70
New cards
Skill Acquisition Plan
A written plan that identifies an individual's strengths and deficits
Name of client
Objectives for each skill/program
Definition of target bx
Materials/setting
Instructional method
Ways to respond to correct/incorrect responses
Plans for generalization and maintenance
Behavioral objective
Instructional objective (Related to formal instruction)
Name of client
Objectives for each skill/program
Definition of target bx
Materials/setting
Instructional method
Ways to respond to correct/incorrect responses
Plans for generalization and maintenance
Behavioral objective
Instructional objective (Related to formal instruction)
71
New cards
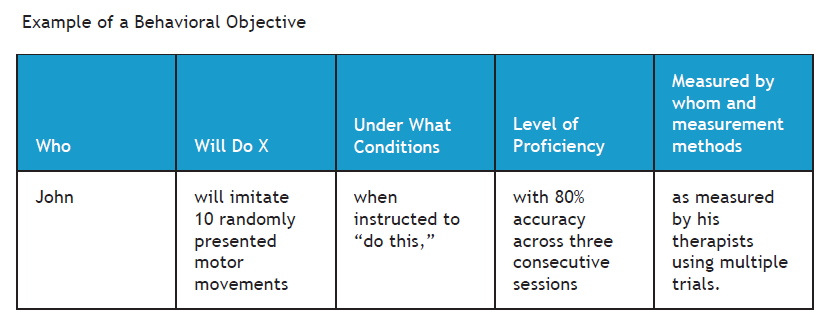
Behavioral Objective
Precise specification of a behavioral goal including 3 essential elements:
A statement of the condition in which bx will occur (location, when)
A statement of expected bx
A statement of criteria for attainment
A statement of the condition in which bx will occur (location, when)
A statement of expected bx
A statement of criteria for attainment
72
New cards
Instructional Method
Lets therapist know how instructions and materials are presented
Discrete Trial Method
Chaining
Shaping
Naturalistic Teaching Methods
Prompting/Prompt Fading
Discrete Trial Method
Chaining
Shaping
Naturalistic Teaching Methods
Prompting/Prompt Fading
73
New cards
"Train and Hope" Method
“Train and hope” refers to teaching individuals a desired skill within a treatment session and hoping that the individual will generalize the use of that skill without implementation of a predetermined plan or strategy to facilitate generalization.
74
New cards
Generalization
A skills is considered generalized when it occurs across various settings, people and stimuli, as well as overtime
Involves systematic planning
Involves systematic planning
75
New cards
Contingency
The reinforcement or punishment that occurs after a bx has been expressed
Dependent and temporal relation between operant bx and its controlling variables
What increases or decreases the probability of operant bx
Dependent and temporal relation between operant bx and its controlling variables
What increases or decreases the probability of operant bx
76
New cards
Natural Maintaining Contingencies
A naturally existing contingency, in layman's terms, “natural consequence” happens without the manipulation of the behavioral analysts.
Good for generalization
Good for generalization
77
New cards
Possible ways to plan for generalization
Natural Maintaining Contingencies
Program Common Stimuli
Train loosely
Train in multiple settings
Train with multiple people
Vary sd or cues
Program Common Stimuli
Train loosely
Train in multiple settings
Train with multiple people
Vary sd or cues
78
New cards
Program Common Stimuli
Identifying salient features in the environment where the target response should occur and bringing those into the teaching environment.
79
New cards
Positive Reinforcement (Sr+)
Presentation of stimulus that increases bx
80
New cards
Negative Reinforcement (Sr-)
Removal of stimulus that increase bx
eg. Client asks for a break from work, bt removes break, increases chances of client manding
eg. Client asks for a break from work, bt removes break, increases chances of client manding
81
New cards
Three-Term Contingency
Antecedent, Bx, Consequence
82
New cards
Skinner Box
behavior that is followed by pleasant consequences is likely to be repeated, and behavior followed by unpleasant consequences is less likely to be repeated
83
New cards
Skinner Box - Reflexive Motivation
Worsening set of circumstances
Instructors and demands can become the reflexive MO's-, indicating a painful or undesirable is about to occur
BTs should reduce value of escape and engage with child. Pair yourself with "good" things and make activities more fun than stopping them
Reflexive MOs- : Tone indicated a shock was coming for rats in experiment
Instructors and demands can become the reflexive MO's-, indicating a painful or undesirable is about to occur
BTs should reduce value of escape and engage with child. Pair yourself with "good" things and make activities more fun than stopping them
Reflexive MOs- : Tone indicated a shock was coming for rats in experiment
84
New cards
Primary Reinforcer
Unconditioned Reinforcers
Biological Needs - Water, food, sleep, shelter/warmth, sex, and touch
Biological Needs - Water, food, sleep, shelter/warmth, sex, and touch
85
New cards
Secondary Reinforcers
Conditioned Reinforcers; Stimuli that acquire their reinforcing properties only as a function of events in an individual's life
Tangible (toys)
Social (attention, praise)
Activity (games, movies)
Generalized Sr - money, credit cards, tokens
Back-up Sr - What is received after exchanging generalized sr (tokens)
Tangible (toys)
Social (attention, praise)
Activity (games, movies)
Generalized Sr - money, credit cards, tokens
Back-up Sr - What is received after exchanging generalized sr (tokens)
86
New cards
Premack Principle/Grandma's Rule
more probable behaviors will reinforce less probable behaviors
First brush teeth then play games
First eat vegetables then dessert
First brush teeth then play games
First eat vegetables then dessert
87
New cards
Rapport
Closeness, empathy, and mutual liking for an individual
Establish yourself as a reinforcer
Establish yourself as a reinforcer
88
New cards
Freebies
Providing reinforcement that child likes without conditions or demands
non-contingent
non-contingent
89
New cards
Steps to Establish Yourself as a Reinforcer
1. Pairing yourself with positive reinforcement (sanitize environment, don't give free access to preferred items, conduct preference assessments, give freebies at a high rate)
2. Assess if pairing procedure worked (Do they look forward to seeing you? Frequently walk or turn away to see if they want your attention)
3. Introduction of demands: If... Then (First few demands introduced will teach child to request for item or be simple/mastered demands)
2. Assess if pairing procedure worked (Do they look forward to seeing you? Frequently walk or turn away to see if they want your attention)
3. Introduction of demands: If... Then (First few demands introduced will teach child to request for item or be simple/mastered demands)
90
New cards
Operant Conditioning
the modification of behavior via reinforcement and punishment
91
New cards
Stimulus-Stimulus Pairing
How to develop secondary reinforcers
Neutral stimulus (doesn't affect bx) is paired with primary or learned reinforcer. over time, neutral stimulus acquires reinforcing properties
Food + therapist saying "good job" -> client learns "good job" accompanies good things
Neutral stimulus (doesn't affect bx) is paired with primary or learned reinforcer. over time, neutral stimulus acquires reinforcing properties
Food + therapist saying "good job" -> client learns "good job" accompanies good things
92
New cards
Generalized Reinforcers
Learned reinforcers that have become effective for a wide range of bx under a variety of circumstances
Developed when coupled with primary or learned reinforcers
eg. tokens, social recognition
Developed when coupled with primary or learned reinforcers
eg. tokens, social recognition
93
New cards
Types of Reinforcers
STATE
Social (verbal, recognition)
Tangible (toys)
Activity (past times)
Token
Edible (food)
Social (verbal, recognition)
Tangible (toys)
Activity (past times)
Token
Edible (food)
94
New cards
Satiation
Having enough of something preferred to the point its no longer preferred/ Satisfied
95
New cards
Direct Reinforcement
Reinforcer is obtained through the completion of the task
More effective than indirect -> Do direct when possible
More effective than indirect -> Do direct when possible
96
New cards
Indirect Reinforcement
Reinforcer is delivered through social mediation upon the completion of the task
Therapist presents reinforcer
Less effective than direct -> Do direct when possible
Therapist presents reinforcer
Less effective than direct -> Do direct when possible
97
New cards
Continuous Reinforcment
Reinforcement given each instance of response
98
New cards
Intermittent Reinforcement/ Variable Schedules of Reinforcement
Bx requirement for reinforcement varies (could be more than 1 each time or in a range)
99
New cards
Fixed Ratio Schedule
Reinforcement delivered after a fixed number of responses
FR2 - Reinforcement given after 2 correct responses
FR2 - Reinforcement given after 2 correct responses
100
New cards
Fixed Interval Schedule
Reinforcement delivered after a fixed amount of time
FI5 - Reinforcement given after 5 minutes of correct bx (sitting and writing for 5 minutes)
FI5 - Reinforcement given after 5 minutes of correct bx (sitting and writing for 5 minutes)