ANSC 322 final
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
we select to improve
breeding values
we mate to improve
dominance and epistasis (GCV)
we manage to improve
environments
crossbreeding
the mating of sires of one breed or breed combination to dams of another breed or breed combination (mating different breeds)
genetic pyramaid
each level represents a generation.
line crossing
mating of animals of the same breed but different bloodlines
hybrid vigor
A phenomenon in which the hybrid state is selected because it has greater survival and reproductive success; also known as heterosis
hibrid vigor cant overcome
poor additive genetic effects
describe the difference between a crossbred and a composite
a crossbred is a first-generation hybrid with significant genetic variation whereas a composite is a stable, multigenerational population that breeds consistently
maternal heterosis
Advantage of the crossbred mother over the average of the purebred mothers
recombination
the genetic process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division
improving gene combination values often involves maximizing
heterozygosity
maintaining high levels of ________ __________ involved carefully planning mating systems
hybrid vigor
____________ have more hybrid vigor. ___________ breeding systems can be easier to maintain.
crossbreds, composite
heterosis is maximized by cross breeding
animals with very different genetics
besides hybrid vigor, an advantage of cross breeding is
breed complementation
breed complementation
combining desired traits from 2 or more breeds
what is the first known gene that, on its own, can cause a mental illness
GRIN2A
old animals have a more accurate
EBV
old animals increase
generation interval
genomic selection
modern breeding method that uses DNA markers (SNP) across a whole genome to predict an individual’s BV for specific traits.
to generate genomic predictions
add markers together
SNP markers
Single nucleotide polymorphisms used for genetic analysis.
SNP markers can help determine _______ traits
recessive
genomic testing reduces
generation interval
genomic testing is not good at detecting
rare genotypes (uncommon traits) because it needs large phenotypic databases
genomic testing may encourage
inbreeding
eugenics
science dealing with improving hereditary qualities
crossbreeding is the opposite of
inbreeding
heterosis is maximized with a
3-breed crossing system
composite
breed mix is the same in the sire and the dam and has been standardized into a predictable blend over crossbreeding generations
what were some of the first composites?
brangus, santa gertrudis, beefmaster
composites can create ________ calves while avoiding _______
uniform, inbreeding
the initial loss of heterosis occurs between what 2 generations
F1 and F2
in order to avoid inbreeding from a composite, scientists recommend the mix be based on how many sires from each breed (the more the better)
15-20
carrie buck was deemed ___________ so she was forcibly sterilized along with 70,000 others
feeble minded
what was the first eugenics law? when and were?
law against unfit marriages so unfit people will not reproduce together in Connecticut in 1895
generation interval
average age of parents when offspring are born
we want a _______ generation interval
low
genomic selection accelerates
the rate of genetic progress by decreasing generation interval
Dominance deviation:
d = heterozygous - midpoint
Additive effect:
a = midpont - homozygous recessive
a = homozygous dominant - midpoint
Midpoint:
(Homozygous dominant + Homozygous recessive) / 2
Mutations:
-Single point: SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
•ex: A -->T or G-->C
-Indels: gain or loss of nucleotides
-Nonsynonymous: changes the amino acid sequence
•Missense - amino acid(s) changed
•Nonsense - premature "STOP" codon --> truncated protein
-Synonymous: alters the DNA code, but not the amino acid sequence
•"Silent" mutations
•Occurs in protein coding region
-Regulatory: don't alter protein
•Alter the protein's expression (when the protein is expressed, where the protein is expressed, how much produced)
Uracil vs. Thymine:
-Uracil:
•Found in RNA
•Binds adenine more efficiently
•Less expensive energetically
•Less stable
-Thymine:
•Found in DNA
•More stable
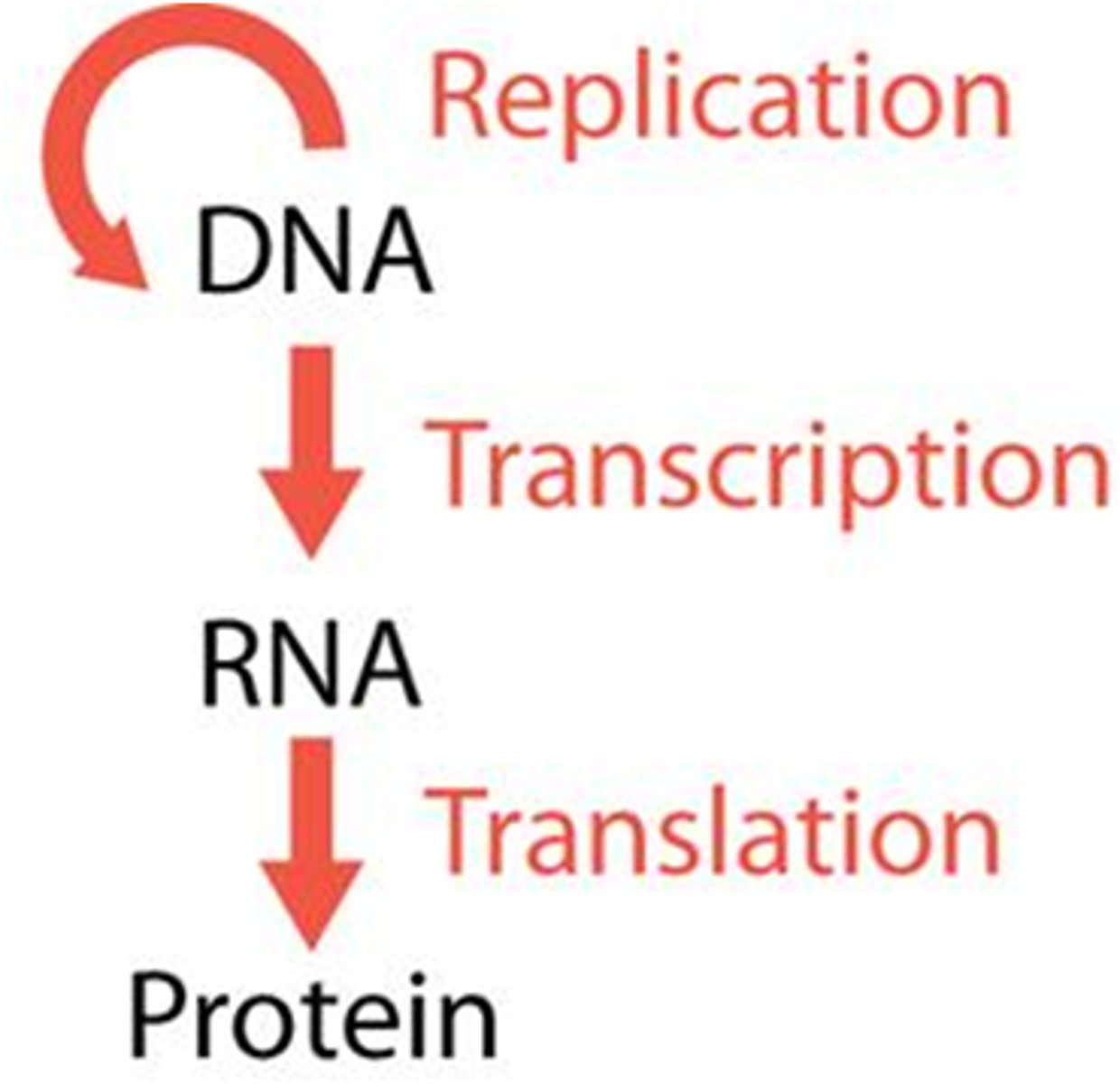
Centra Dogma:
-DNA cannot act as direct template for protein synthesis
-Requires an intermediary molecule: RNA
•mRNA (messenger RNA): contains the code for the sequence of amino acids
•tRNA (transfer RNA): carries the amino acid to the ribosome
•rRNA (ribosomal RNA): subunit of a ribosome
Autosomes:
-Non-sex chromosomes
-Chromosomes are composed of one giant strand of DNA
Primary Functions of DNA:
-Information needed to build and maintain and organism
-Hereditary - process of passing information from one generation to the next (most important)
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes:
-Prokaryotes: single cell and no nucleus --> DNA required for hundreds of cell types
-Eukaryotes: multi-cell with DNA in a nucleus --> DNA required for hundreds of cell types
Nucleotide:
-2 types of pentose sugars found in nucleic acids - ribose in RNA and 2-deoxyribose in DNA
•phosphate group + sugar group + nitrogenous base
Ribose vs. Deoxyribose:
-Second carbon has OH (ribose) vs. H (deoxyribose)
-Deoxyribose enables double helix --> longer strands (more stable), allow coiling
Nitrogenous bases:
-Purine = 2, Pyrimidine = 1 ring
-Thymine is found in DNA, uracil only in RNA
-Sugar attached to 1N (pyrimidine) or 9N (Purine)
-Nucleoside = base + sugar
•Cytidine, Uridine, Adenosine, Guanine, Thymidine
-Nucleotide = base + sugar + phosphate
•RNA: adenosine monophosphate
•DNA: deoxyadenosine monophosphate
-Nucleotides are synthesized by all living organisms
Origin of nucleotides:
-Come from our diet
-Recycled through salvage pathways
-Ultimate source is de-nouo synthesis through complex metabolic pathways
•using a lot of energy to make nucleotides
-Nucleotides are synthesized by ALL living organisms
Chromosomes:
-Humans have ~100 trillion cells
•6 feet of DNA per cell --> 600 trillion feet of DNA; because of that we must package it
-Chromosome --> higher order of DNA organization
-Chromosome pairs join at centromere
•Q-arm (bigger), P-arm (smaller)
DNA packaging:
-DNA must be packaged to fit into nucleus
-DNA is wrapped around histones
•DNA + histone = chromatin --> lower order of DNA organization
Chromatin:
-Euchromatin:
•Lightly packed
•Gene dense
•Active part of genome
-Heterochromatin:
•Densely packed
•Supercoiled
Genetic code:
-Nucleotides that code for an amino acid are called a codon
-Codons consist of three adjacent nucleotides (triplet)
•Occur in DNA and RNA
•64 possible combos ([4 nucleotides]^3 = 64)
Protein reading frames:
-Proteins are large organic molecules whose function depends on precise folding
-Protein coding sequences are similar across species
-Reading frames:
•Add or delete 1-2 bases --> reading frame is upset; end up with non-functional proteins
•Add or delete 3 bases (or multiple of 3) --> add an amino acid, but rest of protein stays the same; can retain full biological activities
DNA replication:
-Structure of DNA suggests mode of replication
-A half DNA ladder is template for copying (semi-conservative)
-DNA replication is carried out by a highly complex array of proteins
•Helicase: unzips
•DNA primase: signals replication start site
•DNA polymerase: copies the sequence (only goes in one direction)
Mitochondrial genetic material:
-Function: generate energy to power cell
-Inherited from mother only
-Can be used to trace maternal lineage
-Has implications for cloning
Mendel's pea plants:
-High incidence of self-fertilization
-Mendel's stem length gene (Le/le)
•Recessive gene (le) --> shorter plants - latent factor
•Dominant gene (Le) --> tall plants - expressed factor
Law of segregation:
-In the formation of a gamete the two alleles at a locus separate and one is incorporated in each germ cell (one locus)
Law of independent assortment:
-The alleles of separate genes segregate (assort) independently (a loci)
Additive effects:
-Not all genes exhibit a dominant/recessive inheritance pattern
•Co-dominance
•No dominance
•Partial dominance (incomplete dominance)
Epistasis:
-Interaction among genes
ex: Dogs --> black/brown locus - Black (B) > chocolate (b)
•Extension locus: E (color expression coded by the black/brown locus enabled) - E > e (not expressed)
B_E_ = black
bbE_ = chocolate
_ _ee = yellow
Pleiotropy:
-A gene that affects multiple traits
ex: Belgian blue cattle --> myostatin gene affects double muscle and ease giving birth
Penetrance:
-The probability that a given phenotype will be expressed when the genotype known to produce the phenotype is present
ex: extra digit = D, five fingers = d
•6 fingers 70% of the time = 70% penetrance
Simple traits:
-Inheritance is determined by one or a few easily tracked genes
-Causes: defective protein, gene turned on/off at the wrong time
Sex-influenced inheritance:
-Mode of expression is different between males and females
ex: Sheep --> H = horns, h = no horns
•Male: HH = large horns, Hh = large horns, hh = no horns
•Female: HH = small horns, Hh = no horns, hh = no horns
Sex-linked inheritance:
-Traits linked to the sex chromosomes
ex: calico cats
•XO = orange, Xo = not orange
Phenotype possibilities:
XOXO = female orange
XOXo = female calico
XoXo = female not orange
XOY = male orange
XoY = male not orange
Sex-limited inheritance:
-Expression is limited to one sex
ex: any egg laying trait, milk expressing gene
-Opposite sex does carry the genes necessary to express the trait; never turned on
ex: bulls have gene to produce milk but it's never turned on
Q: Breeding values:
A) are influenced by allele frequency
B) equal transmitting ability * 2
C) are the additive genetic effect
D) are not known with certainty and must be estimated
E) all of the above
E)
Q: Heritability...
A) is the proportion of a population's variance due to additive genetic differences
B) is the proportion of an individual's variance due to additive genetic differences
C) is the proportion of a population's variance due to breeding value differences
D) is the probability a trait will be passed from parent to offspring
E) A and C
E)
Phenotype equation:
Phenotype = average + BV + dominance + epistasis + permanent environment + temporary environment
Estimated breeding value (EBV):
-EBV = 1/2 EBV of sire + 1/2 EBV of dam
-EBV = PTA of sire + PTA of dam
•PTA: Predicted transmitted ability
-EBV = additive genetic value
Gene combination value (GCV):
-GCV = dominance + epistasis
Genetic value:
-Genetic value = BV + GCV
Midpoint:
(Homozygous dominant + Homozygous recessive) / 2
Additive effect (a):
a = midpoint - homozygous recessive
a = homozygous dominant - midpoint
Dominance deviation (d):
d = heterozygous - midpoint
DNA replication:
-A structure of DNA suggests mode of replication
-A half DNA ladder is template for copying (semi-conservative)
-DNA replication is carried out by a highly complex array of proteins
Sense vs. Anti-sense:
-Sense strand: strand that corresponds to the mRNA sequence (5'-3')
-Antisense strand: serves as the template in the "template strand" (3'-5'); involved in gene regulation
•Template strand = antisense sequence
Transcription:
-Largely facilitated by RNA polymerase
•Uses the antisense strand
-Transcription factors:
•Proteins that bind DNA (humans have ~30,000 known)
•Bind to specific DNA sequences (usually 6-10 bps)
•Interaction with the environment to make sure that the correct gene is expressed
-Enhancer regions:
•~500 bp with multiple TF binding sites
-Helps encourage genes in that region to transcribe
-Enhances gene expression
Recombination:
-Genes on a chromosome are physically "linked"
-A "cross-over" event allows exchange of DNA between maternal and paternal chromosomes
-Creates new allele combinations
Linkage and reassortment:
-Linkage groups: genes close to each other are generally inherited together
-Linkage between two genes is often broken because of physical crossing over between homologous chromosomes
Gene regulation:
-Control of gene expression
•Control of transcription due to the structure of DNA and transcription factors
•Post-transcriptional - non-coding RNAs
-Gene regulation is important because:
•Protein synthesis is energetically expensive
•Different cell types require different proteins
Promoters:
-Start signals for RNA synthesis
-Function as the gene's ON/OFF switch
-Transcription start site is where RNA synthesis begins
Epigenetic control of gene regulation:
-Modifications to the DNA strand but not the DNA sequence
•Change transcriptional properties at the genome
•Can be inherited
•Altered for different cell types
•Modified by the environment
-Epigenetic causes:
•DNA methylation - CH3 is attached to cytosine bases when there is a guanine next to H
•Changes the shape of the DNA molecule
•Lots of DNA methylation at the beginning of the gene means the gene is probably off
Introns vs. Exons:
-Exon - protein coding region of the gene
•Only region of genes and the genome where the DNA sequence corresponds to the amino acid sequence
•Only region that contains codons
-Introns - non-protein coding region of the gene
•Included in the primary RNA transcription but then spliced out
Hardy-Weinberg equation:
-In the absence of forces that change gene and genotype frequencies, they will remain stable
p = frequency of 'A' allele
q = frequency of 'a' allele
p^2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (AA)
q^2 = frequency of homozygous genotype (aa)
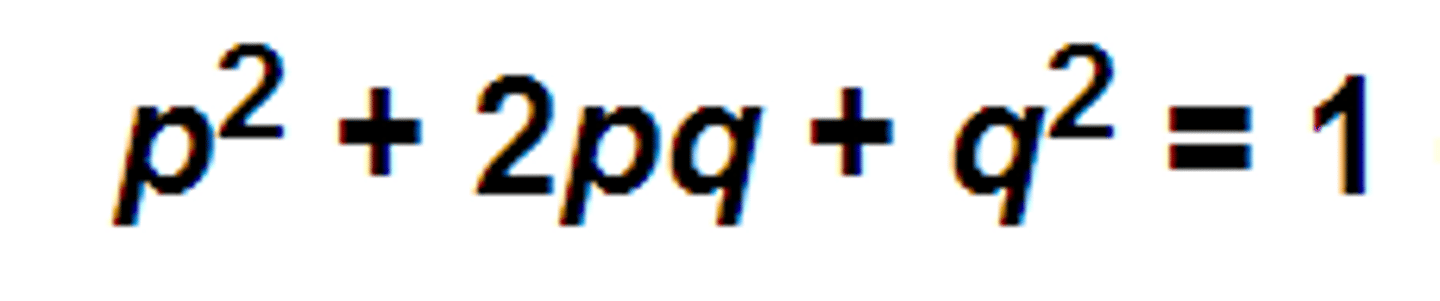
Factors that alter Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
-Selection:
•Which individuals will become parents of the next generation
•Increase the frequency of favorable allele (goal)
•Favored allele becomes 100% --> it's fixed
-Non-random mating:
•Mating is determining which males you're going to mate to any selected females
•Random mating: selected males have an equal opportunity to mate with any selected females
•Any systematic mating plan is nonrandom
-Migration:
•Movement of individuals into or out of a population
-Mutation:
•Altering DNA to create a new allele; occur naturally
•Usually associated with a loss or reduction in gene function
-Drift:
•A random change in gene frequencies
•Associated with a small population
Quantitative traits:
-Quantitative traits are controlled by genes at multiple loci
-Phenotype = genotype + environment
Additive effect:
-Additive effects = breeding value
•Part of animal's genotype that is due to transmittable gene effects
Quantitative trait locus (QTL):
-Major gene
-One locus can be extended to many loci
-We will never know the effect of every single gene, so we must used an estimated breeding value (EBV)
•EBV: used to represent the total genetic merit of an animal
-Transmitting ability (TA) or a Progeny difference (PD) - 1/2 of breeding value b/c a parent can only pass on a random sample of 1/2 of their genes
The new model:
P = BV + GCV + Ep + Et + G*E
•We select to improve breeding value
•We mate to improve dominance and epistasis (GCV)
•We manage to improve environments
Old model vs. New Model:
-Old model: phenotype = genotype + environment
-New mode: phenotype + environment + G*E
Expression of quantitative traits:
-Continuous measures: a measure could fall any place along a given scale
ex: milk production, height
-Distinct classes: a measure falls into a distinct category
•Constrained by a biological integer (can't have half sizes)
•Measures we put on a scale
-Threshold traits: a measure that falls into 1 category or another
Heritability:
-Heritability (h^2) is the proportion of phenotypic variation in a population due to genetic differences
-You have to have variation for there to be heritability when breeding
Narrow sense heritability: h2 = (σ2 BV / σ2 P)
Broad sense heritability: H2 = (σ2 BV + σ2 GCV) / (σ2 P)
Narrow sense vs. Broad sense heritability:
-Narrow sense = to the proportion of variance due to transmittable genetic effects
h2 = (σ2 BV / σ2 P)
-Broad sense = to the proportion of variance due to all genetic effects H2 = (σ2 BV + σ2 GCV) / (σ2 P)
Calculating EBV:
-EBV = h^2 * selection differential
•h^2 = narrow sense heritability
•selection differential: difference between selected individuals and average