Circular Flow Diagram
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
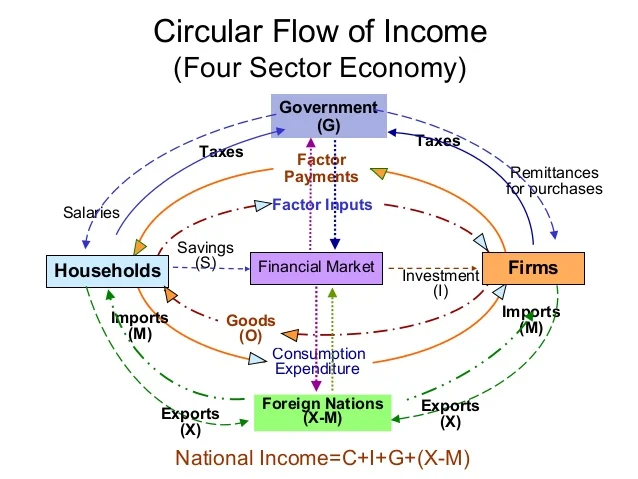
Circular flow of income
In any given time period (e.g. a year) the value of output produced is equal to the total income generated which itself is equal to the expenditure to produce the goods and resources.
These are methods for calculating GDP
value of output = total income = total expenditure
output method = income method = expenditure method
Circular flow in a closed system
Participants: Households and Firms.
Flow: Households provide factors of production (labour, capital) to firms. Firms pay wages, rent, and profits to households. Households use this income to buy goods and services from firms.
There is a continuous loop of economic activity within the domestic economy (the internal economic system of a country, focusing on activities that do not involve foreign trade).
Circular flow in an open economy
Participants: Households, firms, and foreign sector.
Flow: Includes all elements of a closed economy. Adds international trade = IMPORTS goods and services bought from other countries and EXPORTS goods and services sold to other countries.
Leakages
The outflow of money from the economy that reduce the amount of income circulating within it.
Savings (not spending it), Taxes (government’s money, taken out of income flow), Imports (spending on other countries and not to domestic economy) are all leakages.
If the leakages are greater than the injections, than the economy is shrinking.
Injections
The additions of money into the economy that help to increase the overall level of economic activity.
Investment (spending on goods to create jobs and increase production capacity), Government spending (spending on goods and services), and Exports (sales to foreign buyers bringing money into domestic economy from abroad) are all injections.
If injections are greater than leakages, the economy is growing.