Microscopic Sedimentation Evaluation of Urine: Crystals, Casts, RBC/WBC, Epithelial Cells
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Sediment Examination
looking at cellular components of urine for the detection and evaluation of renal and urinary tract disorders and other systemic diseases
What is the urine collection method for viewing sedimentation?
cystocentesis
How much urine is collecting for sedimentation examination?
5-10 mL
Wet Mount
urine placed in plastic centrifuge tube or RTT
centrifuged at 1,000-2,000 rpm for 3-5 mins
supernatant is noted BEFORE pouring most of it out
use pipette to resuspend sediment from bottom of tube
place a drop onto slide and cover with a cover slip
examine under 10x and 40x w/ low light
What is noted BEFORE pouring it out?
supernatant
What objective(s) is used to examine the sediments?
10x and 40x to increase refractility of the cells
What is the time frame of when you should examine the urine?
30 mins after collection
What can be seen at 10x?
crystals and casts
How do you QUANITFY the specific structures seen ON 10x?
view 10 fields, quantify the numbers, find the average, and are reported per low powered field = /LPF
What can be seen at 40x?
leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelial cells, fat droplets, crystals, casts, sperm, debris, and bacteria
How do you QUANTIFY the specific structures seen ON 40x?
scan the ENTIRE cover slip and reported per high powered field = /HPF
How are crystals and casts identified and reported?
number per low-power field (on 10x) by giving a range
How are RBCs, WBCs, epithelial cells, crystals, and casts reported?
a range per high-power field (40x)
How are Bacteria reported?
few, moderate, many OR 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+
need to specify what type it is
Dry Mount
centrifuge the urine
pour out the substance
use a pipette to grab pellet at bottom of tube
place small drop onto a slide
use another slide to smear the sample across to form a monolayer
allow sample to dry
stain the sample using Diff-Quik
Microscopic Evaluation Methods
wet mount and dry mounting
What is the MAIN difference between Wet and Dry Mount?
just place a cover slip over the slide vs spreading the sample to form a monolayer
How do Crystals Form?
urine that is static, supersaturated, solubility, or pH is altered
Where do Crystals Form?
any part of the urinary tract
What can the formation of Crystals result in?
calculi (stone) formation
What Influences Crystals to form?
pH, temperature, concentration, medication, time of collection, disease, state of patient, toxins
Crystalluria
crystals in urine
Urolithiasis
formation of urinary calculi
Grit/Sand
small pieces of calculi
How are CRYSTALS reported?
number per LPF (10x), few/moderate/many, or 1+/2+/3+/4+
What can Crystals tell you?
disorders predisposing P to uroliths
estimate mineral composition of uroliths
evaluate effectiveness of medicine for urolithiasis
detect liver dz
detect metabolic dz
detect toxicity
Crystal: Amorphous
debris-like appearance
can be: urates, phosphates, or xanthine
no clinical significance
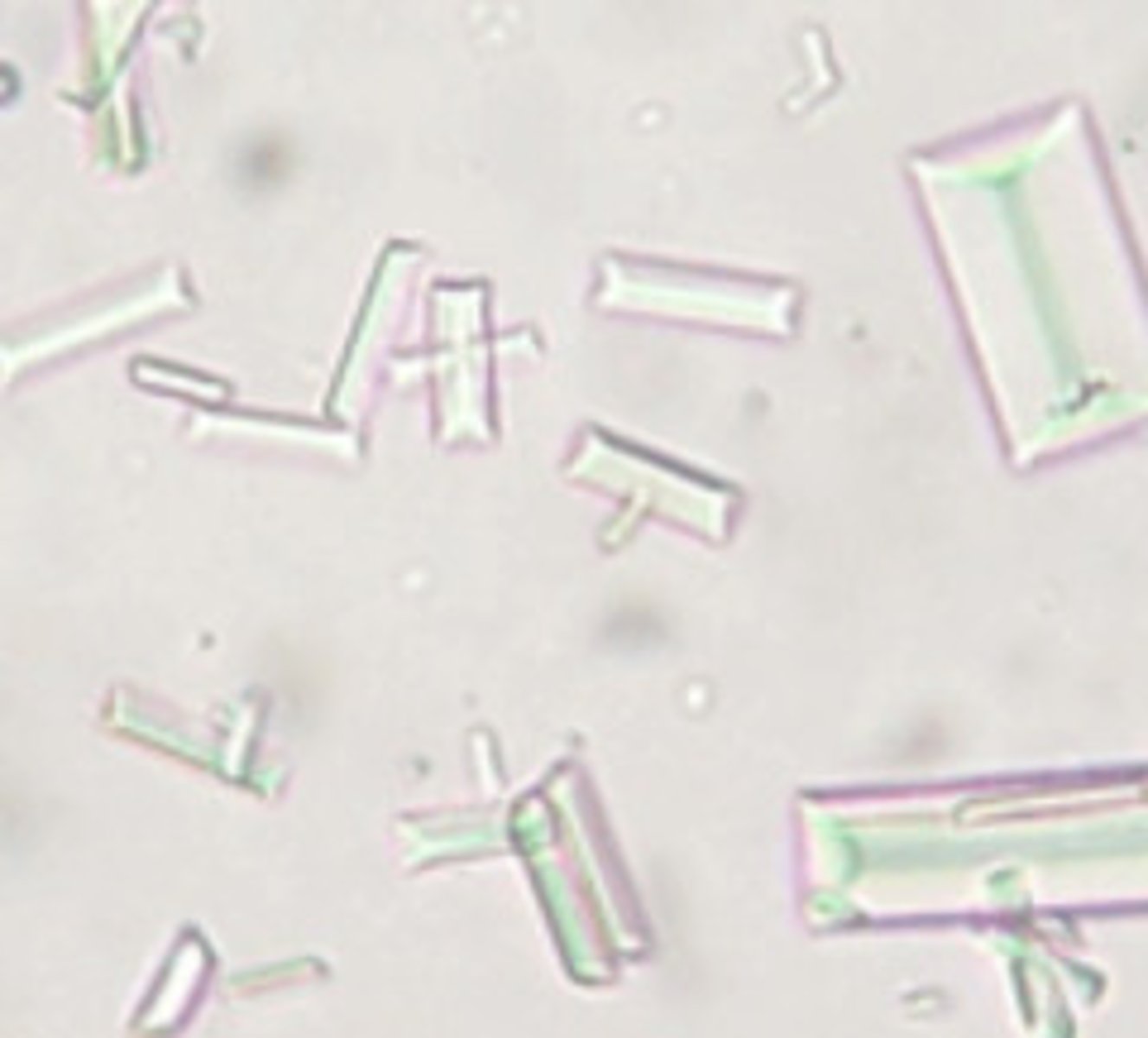
Crystal: Struvite
AKA magnesium ammonium phosphate OR triple phosphate
has 6-8 sided prisons w/ tapering sides
form in: stagnant/retained urine, chronic cystitis, "blocked cats"
Amorphous
Struvite
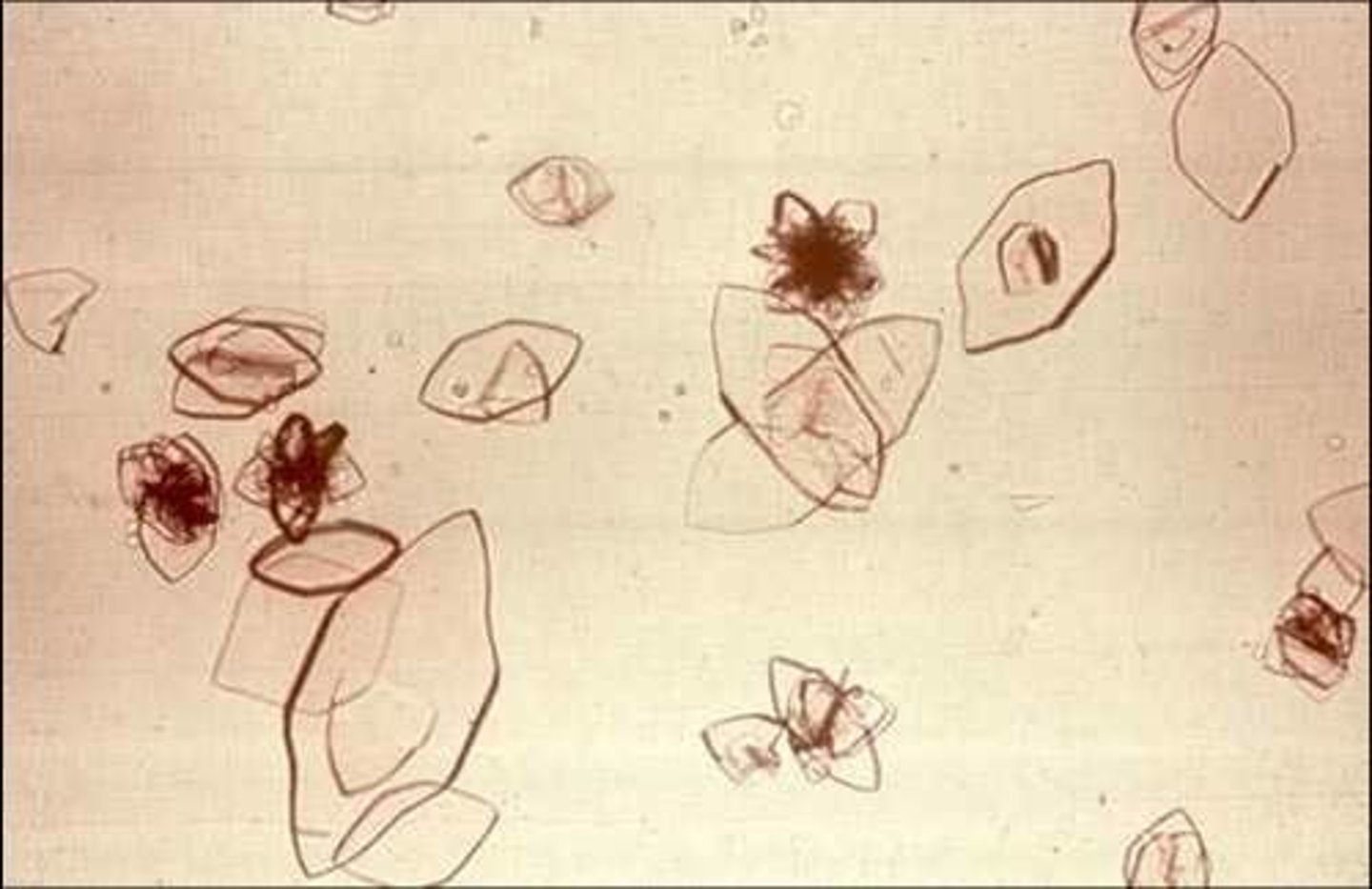
Crystal: Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate
has small squares w/ "x"
found in: acidic or neutral urine
common in small #'s in dogs and cats
Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate

Crystal: Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate
has elongated, flat, pointed ends OR "dumb bell"
forms in: ethylene glycol poisoning
time-dependent and occur 6-18 hrs after ingestion
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate
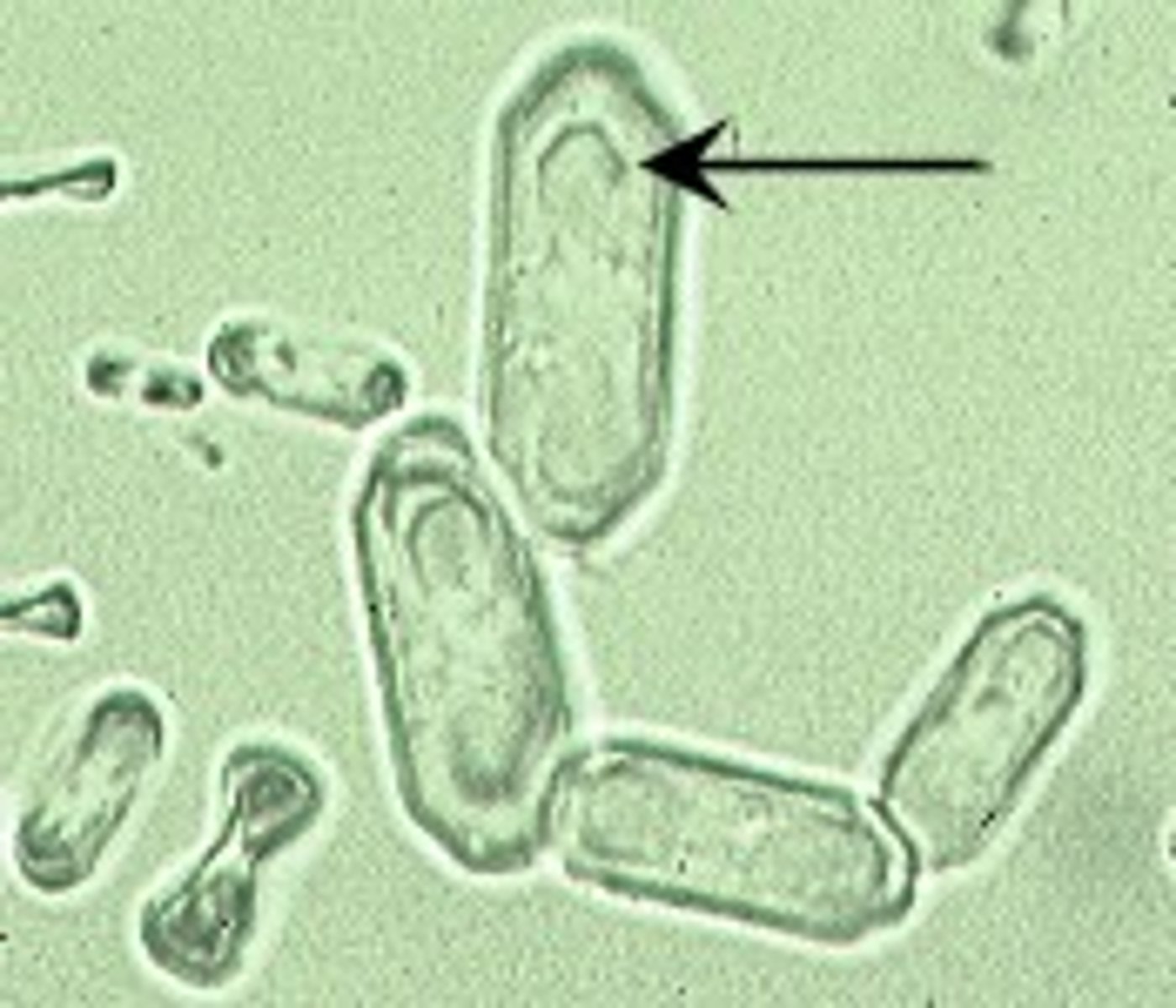
Crystal: Bilirubin
orange-reddish appearance w/ needle-like crystals
in LOW numbers is normal for dogs
in HIGH numbers in DOGS and OTHER ANIMALS = hemolysis or liver issues
Bilirubin
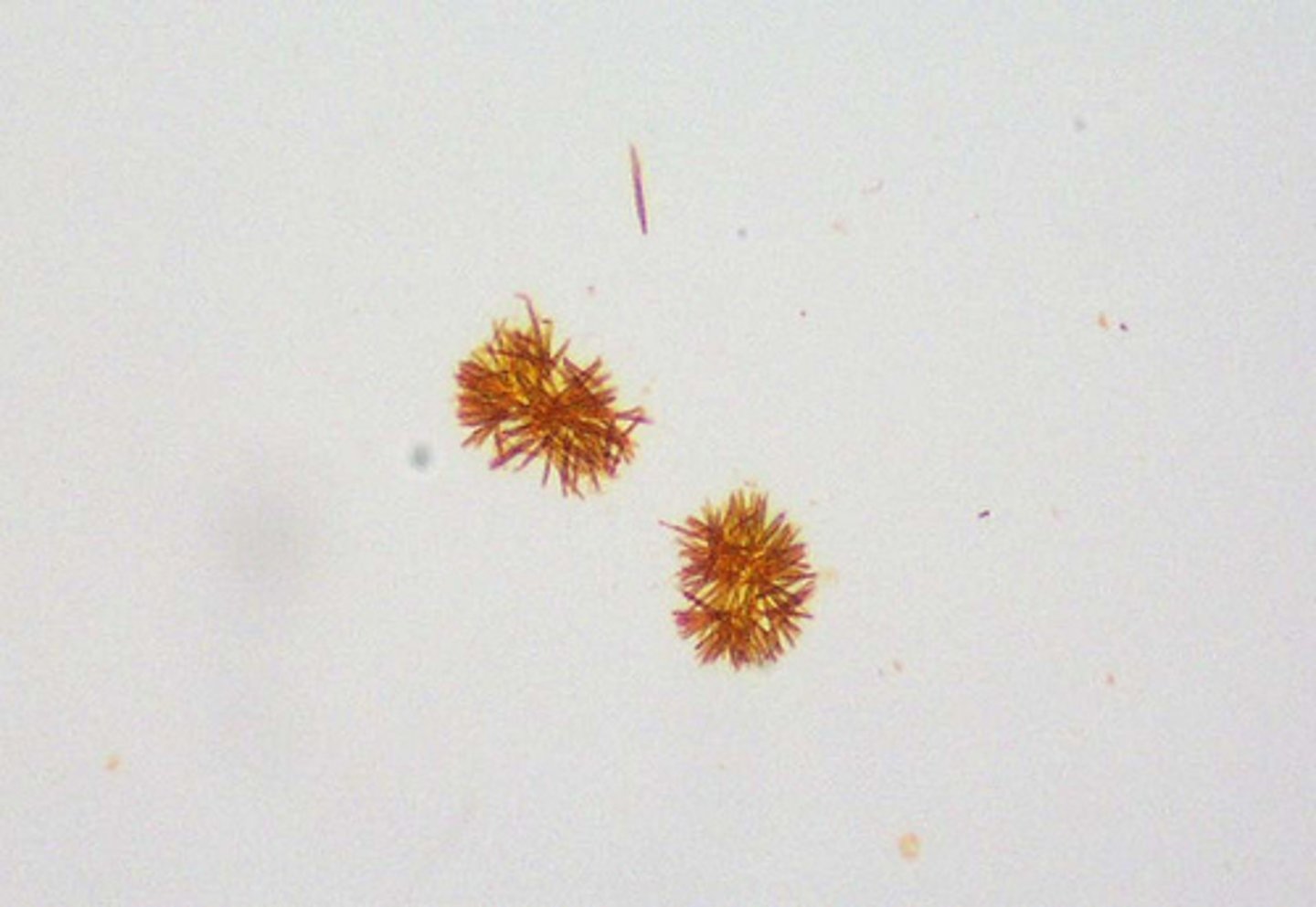
Crystal: Ammonium Biurate
AKA ammonium urate and nickname: thornapple crystal
brown, round w/ long irregular spikes appearance
present in severe liver disease
NORMAL in dalmations and bulldogs
Ammonium Biurate
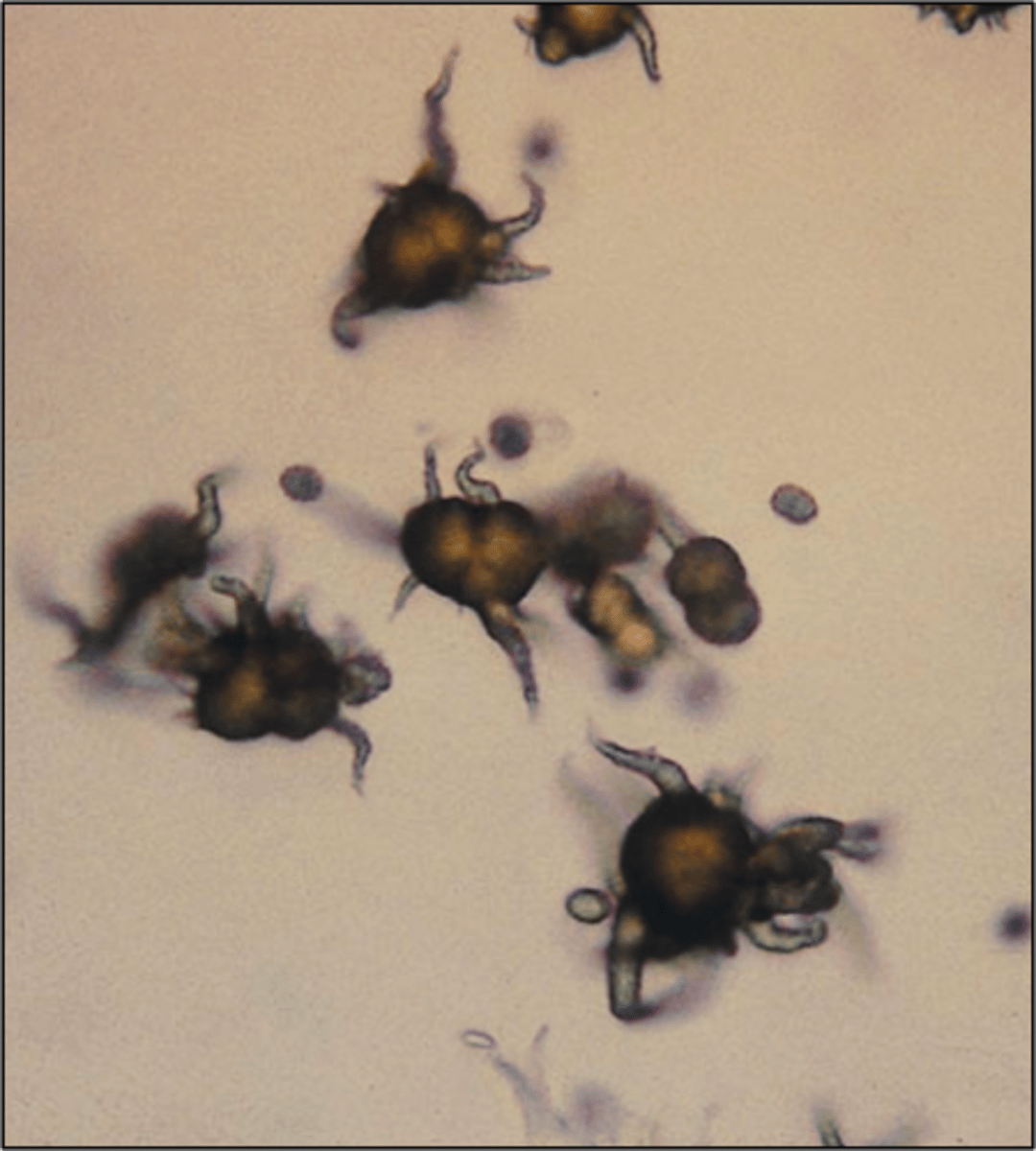
Crystal: Uric Acid
yellow or yellow-brown color and is pleiomorphic (many shapes)
COMMON in dalmations
UNCOMMON in other animals but represents liver dz
Uric Acid

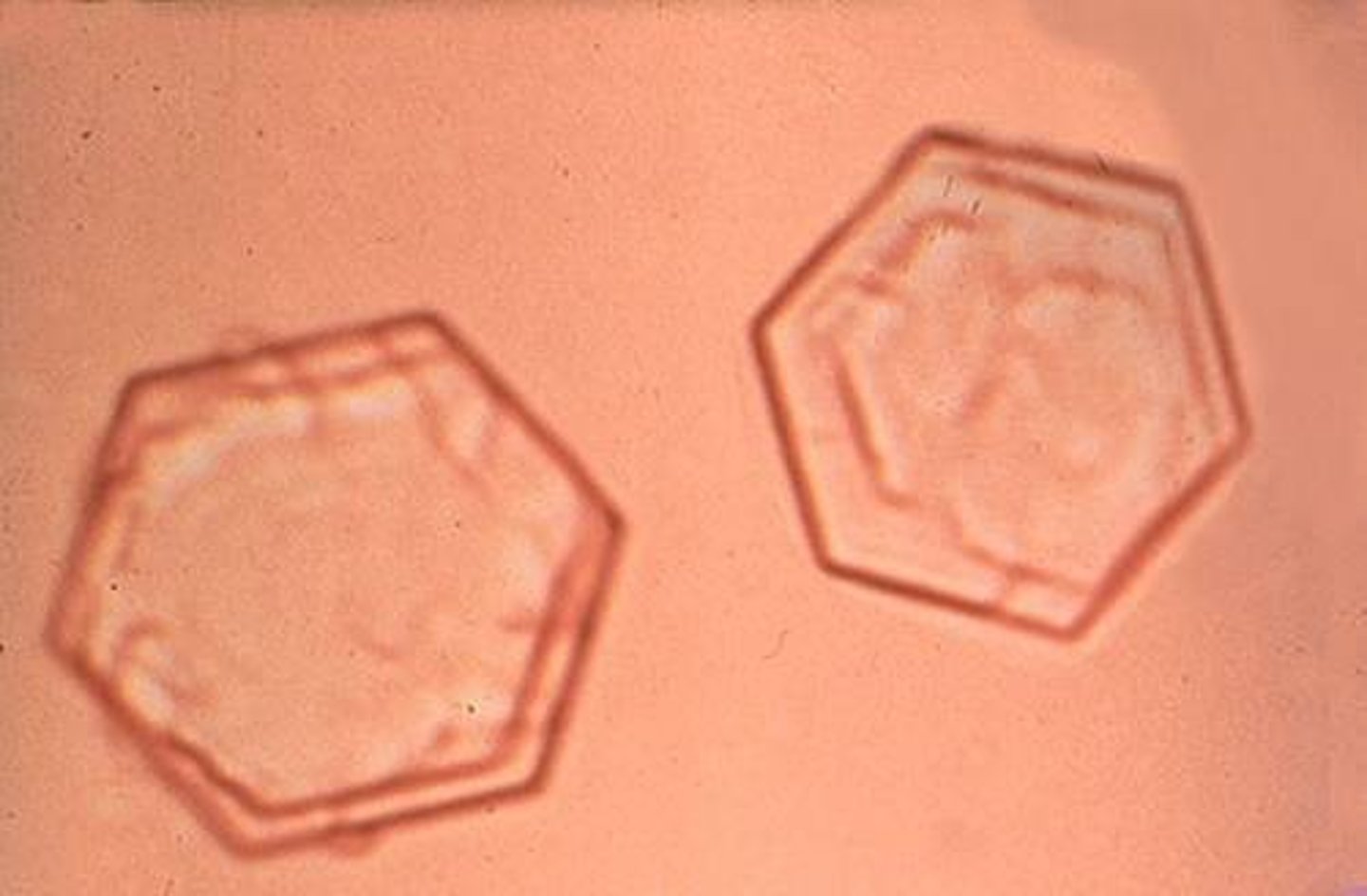
Crystal: Cystine
colorless, flat hexagons
COMMON in: MALE dachshunds, english bulldogs, newfoundlands, CATS- siamese
from an inherited defect in cystine metabolism
Cystine
What are the COMMON Crystals seen in Dalmations?
uric acid and ammonium biurate
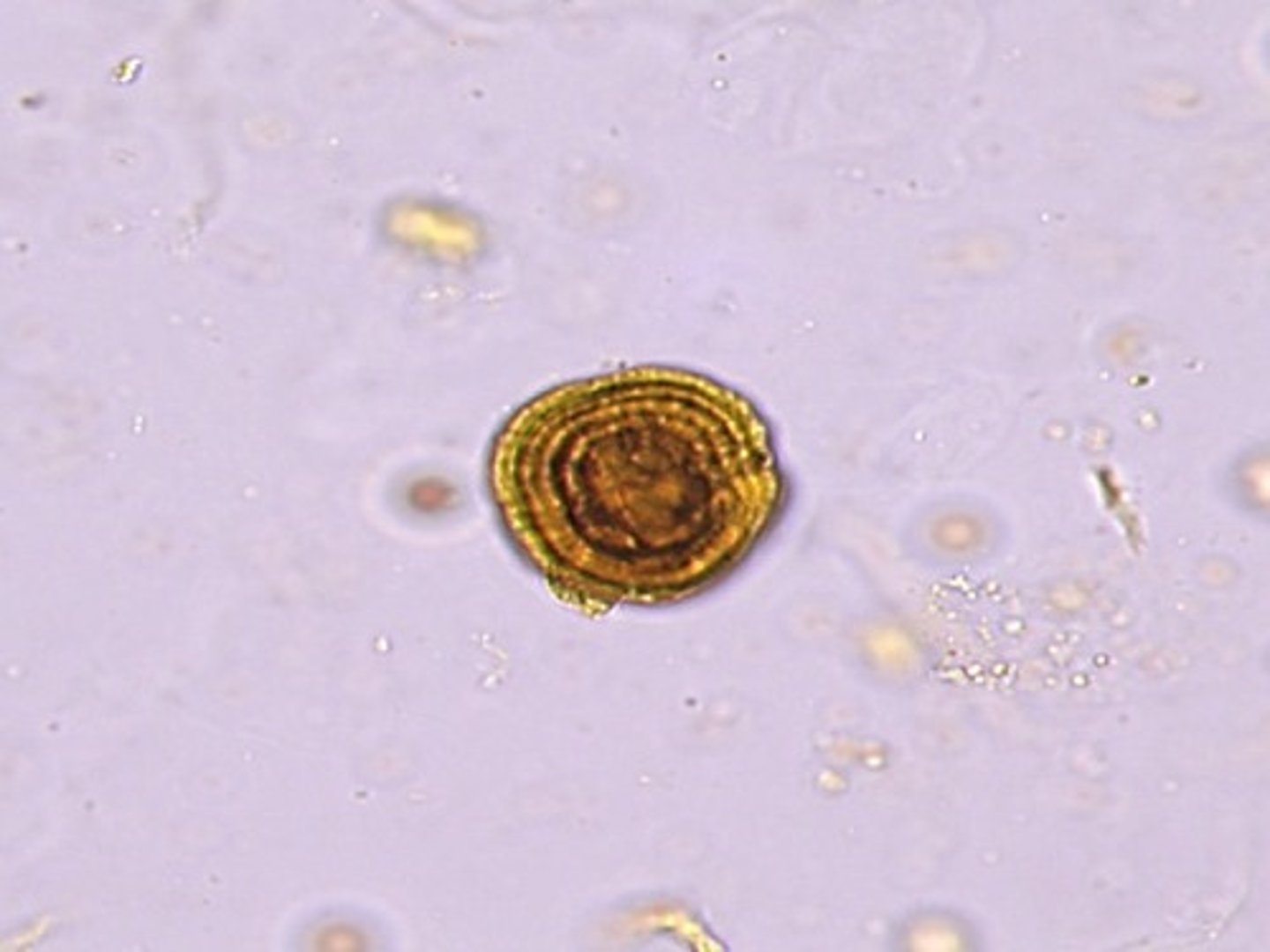
Crystal: Leucine
large, yellow spheres w/ concentric striations
indicate severe liver disease
Leucine
Crystal: Tyrosine
colorless OR yellow needles in groups or alone
IN CLUSTERS = severe liver disease
Tyrosine
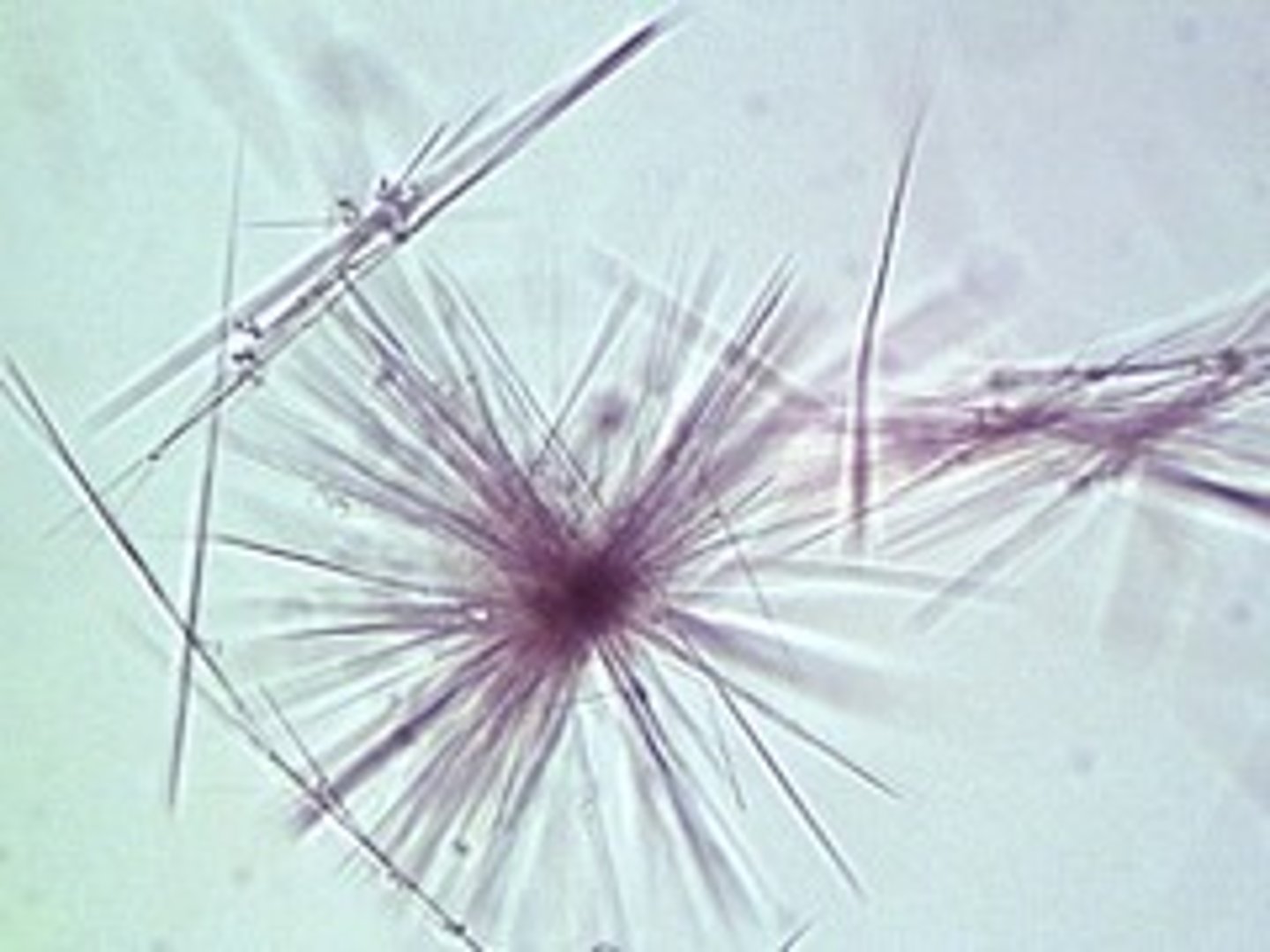
Crystal: Sulfonamide
varies in shape and color, haystack-like bundles or rediant spheres
from sulfa drugs
Sulfonamide
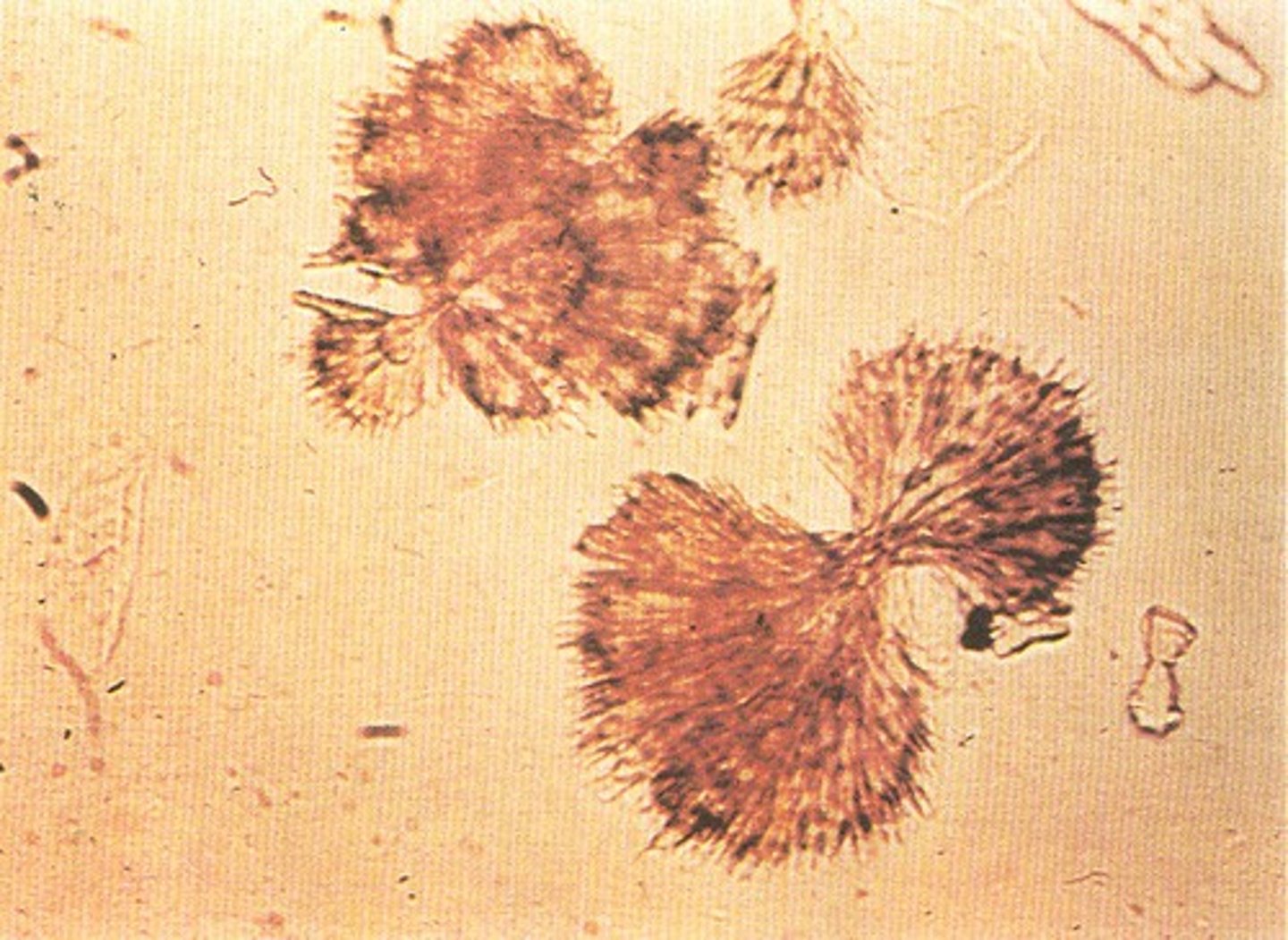
Crystal: Calcium Carbonate
varies in size, individual or cluster, yellow-brown, or colorless, large spheroids with radial striations or "dumb bell"
NOT in dogs or cats
COMMON in: horses, rabbits, guinea pigs, and goats (herbivores)
Calcium Carbonate
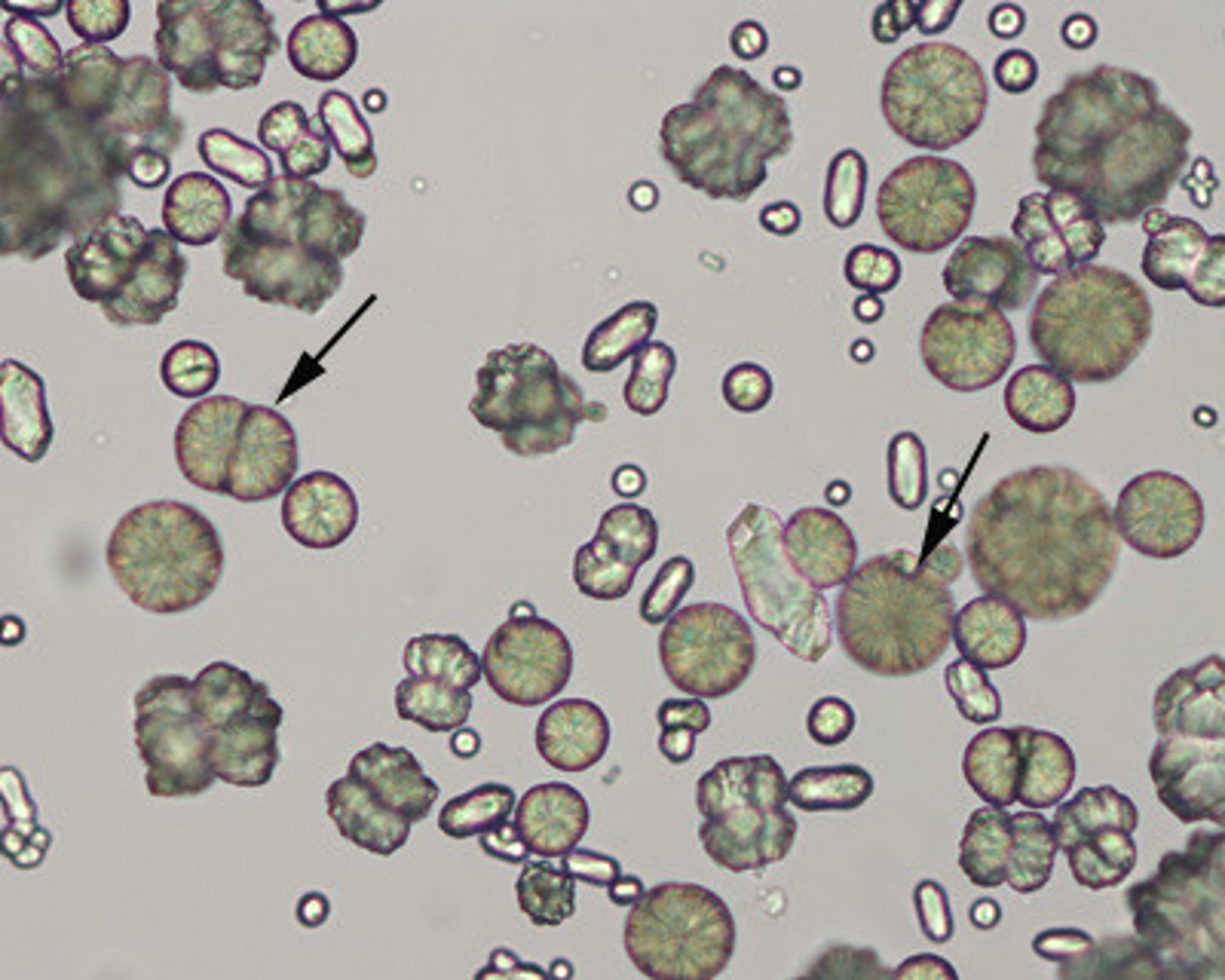
Casts
formed in lumen of distal and collecting tubules of kidney
Where is the concentration and acidity of urine the greatest in kidneys?
distal and collecting tubules
Formation of Casts
in the renal tubules, secreted proteins in acidic conditions form casts that are made of proteins from plasma and mucoprotein secreted by tubules
What are Casts made of?
protein from plasma and mucoprotein secreted by the tubules
What CAUSES the formation of DIFFERENT Casts to form?
from how quickly the filtrate is moving thru the tubules and how much tubular damage is present
How are Casts Reported?
numbers seen per low-power field (10x) and is classified by type
How many Casts are TYPICALLY seen and what KIND in NORMAL patients?
few-none and hyaline or granular
What does the presence of NUMEROUS Casts indicate?
generalized, acute, renal disease BUT not a reliable indicator
What Urine TYPE do Casts FORM IN?
acidic
What Urine TYPE do Casts DISSOLVE IN?
akaline
Cast: Hyaline
clear, colorless, transparent cylindrical w/ROUNDED sides
made of protein
considered "NORMAL"
seen in: hyperthermia, poor renal perfusion, or other mild kidney irritation
Hyaline
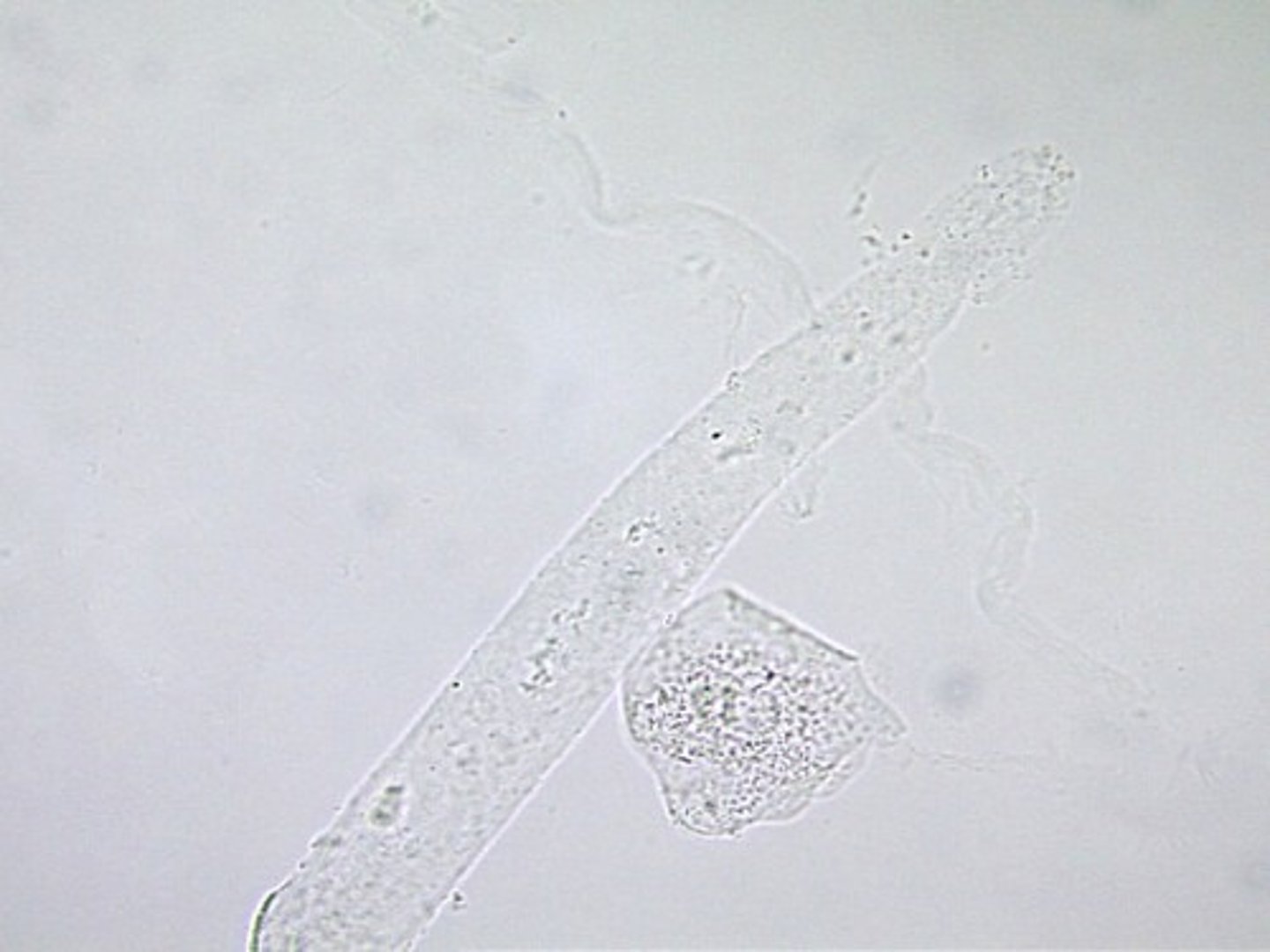
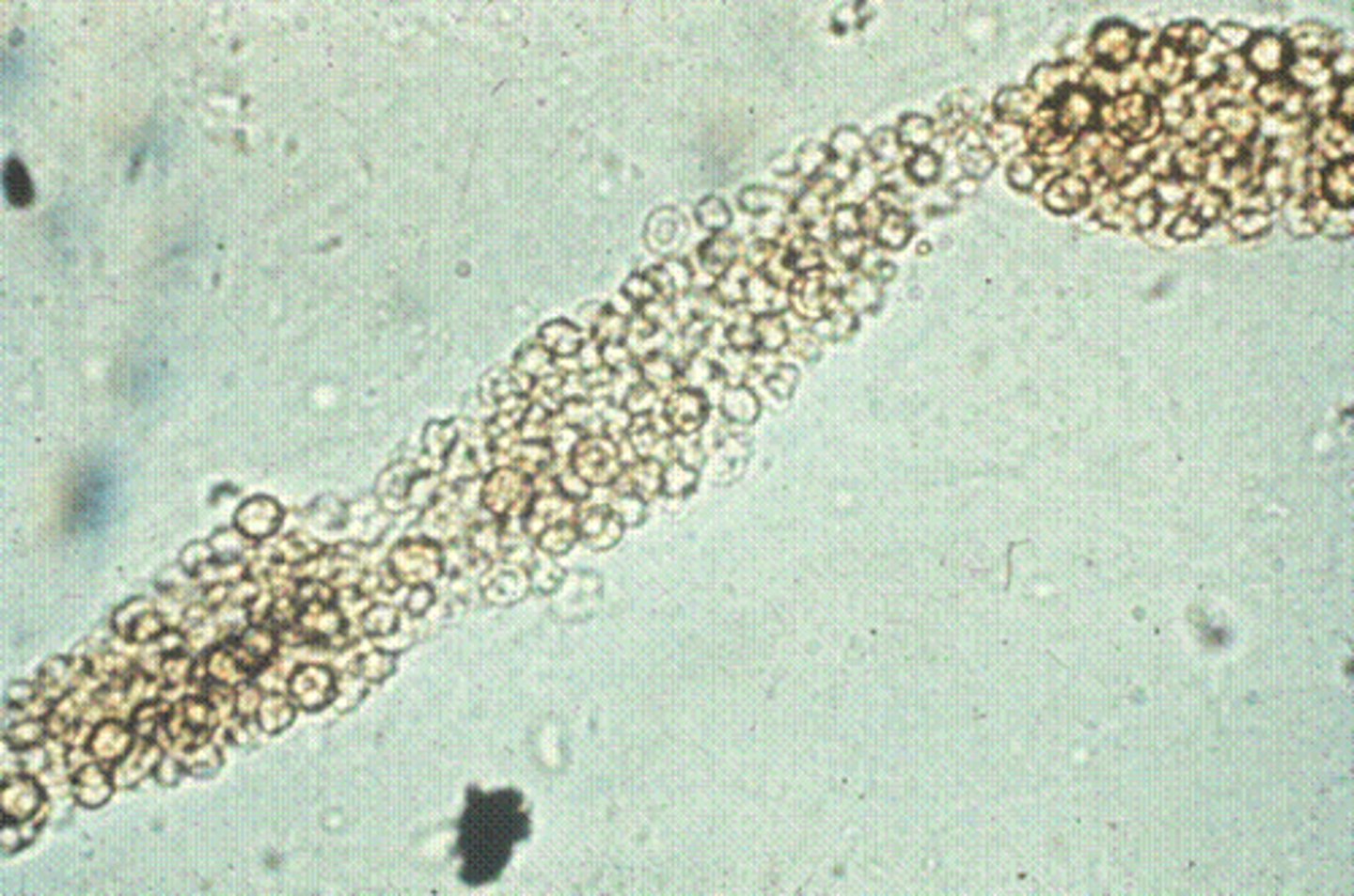
Cast: Cellular
either WBC or RBC
results from: ischemia, infarction, or nephrotoxicity
What does WBCs in Cellular Cast indicate?
inflammation in renal tubules
What does RBCs in Cellular Cast indicate?
renal bleeding
Cellular RBC
Cellular WBC
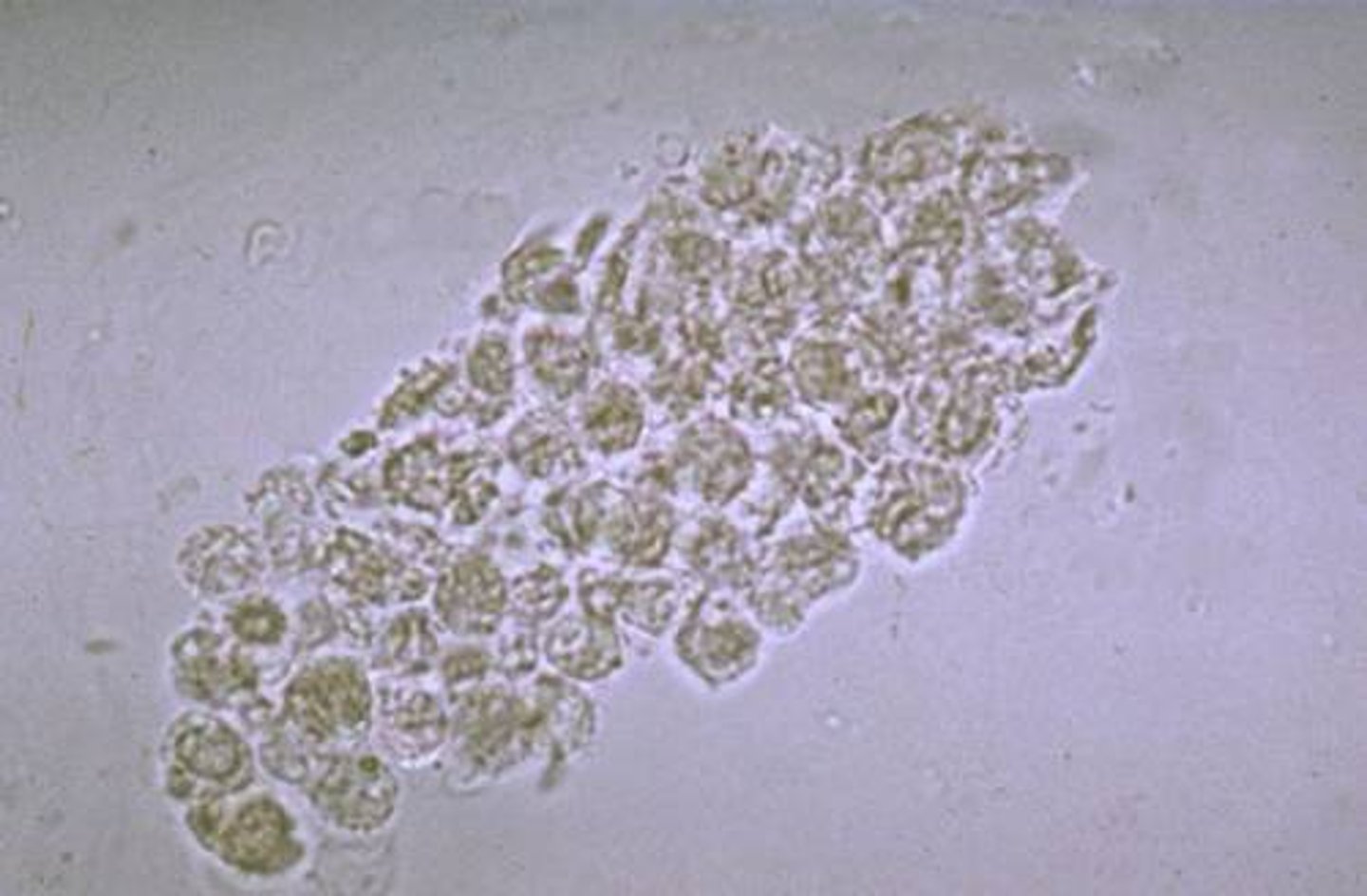
Cast: Granular
COMMON
a stage in the degeneration of cellular casts
if HIGH #'s = acute nephritis or severe kidney damage
Granular
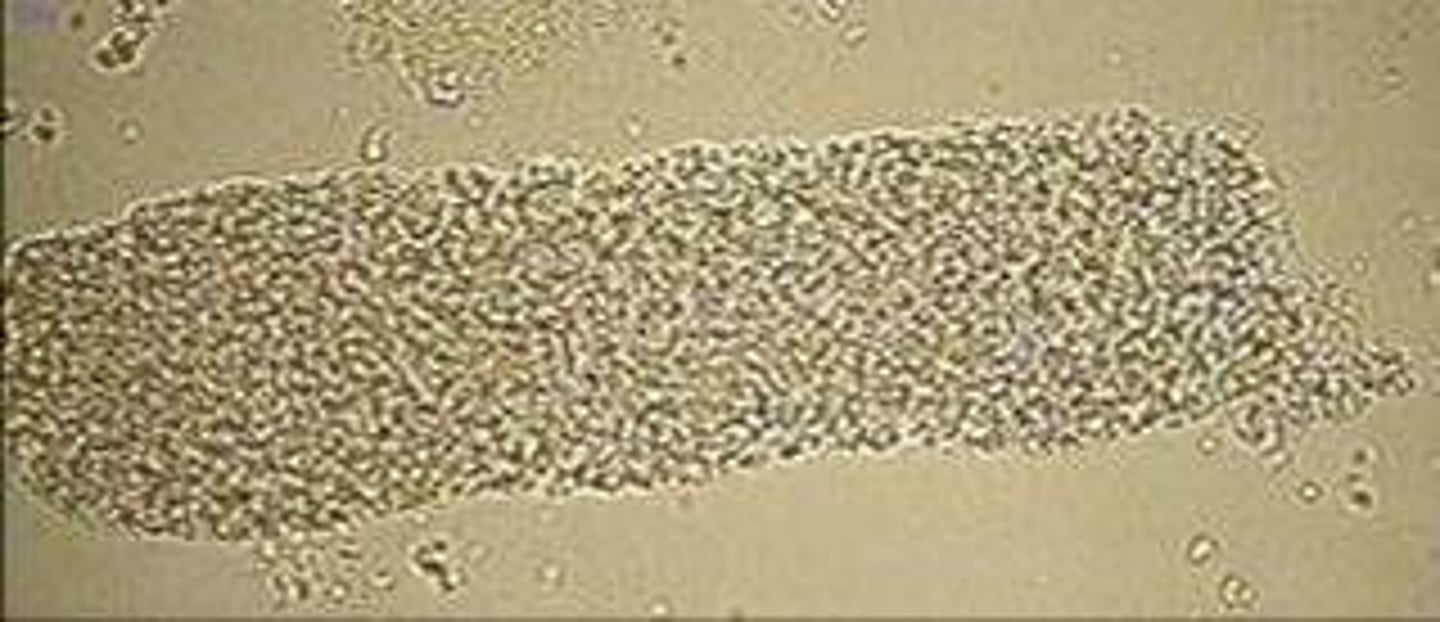
Cast: Waxy
smooth consistency, refractile, wide, squared off ends, brittle looking
a stage in the CONTINUE degeneration of granular cast
indicate tubular injury MORE severe than cellular or granular casts
ALWAYS pathogenic significance
Waxy
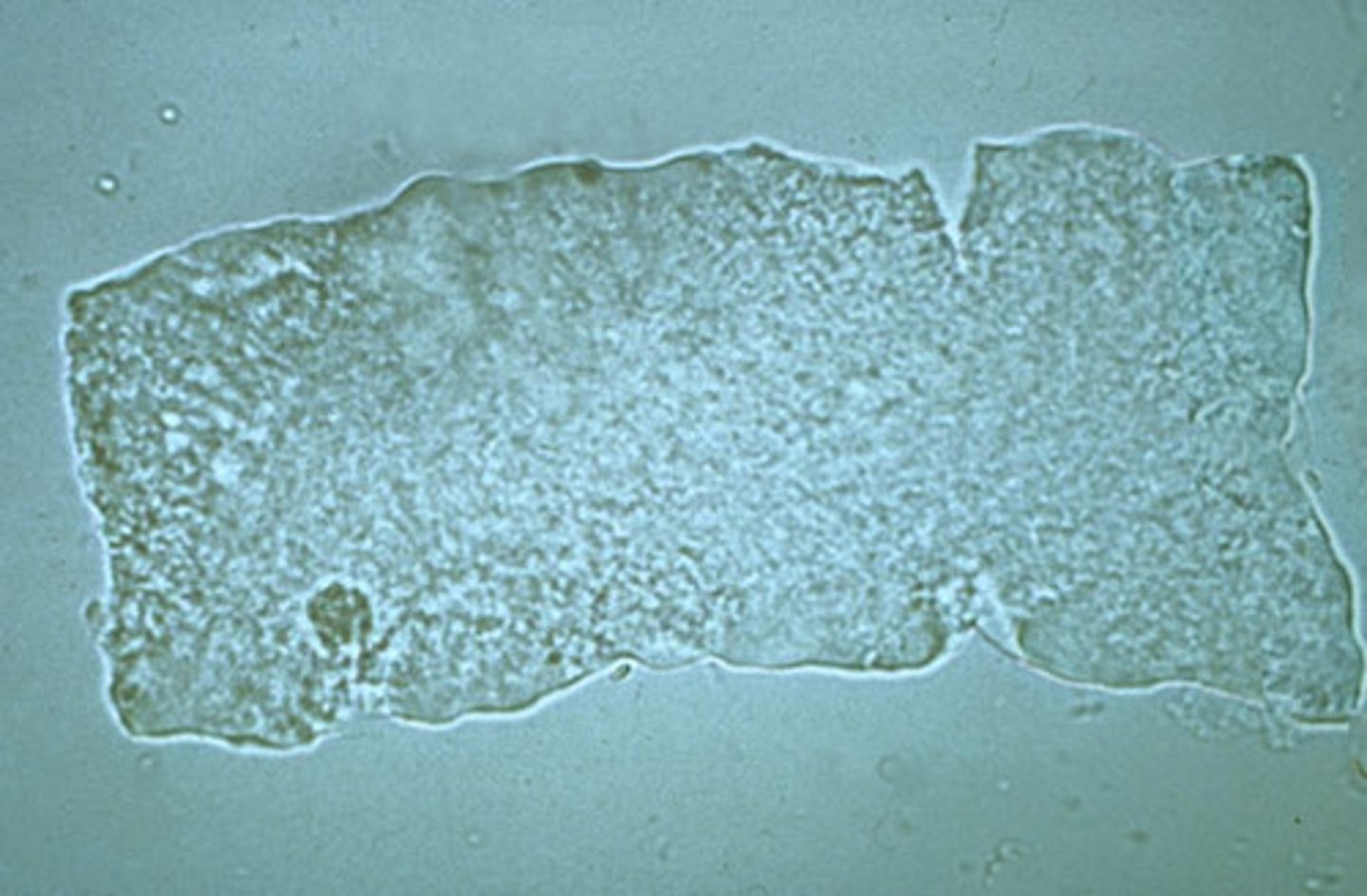
Cast: Fatty
refractile, lipid droplets inside
COMMONLY seen in CATS w/ renal disease
Fatty
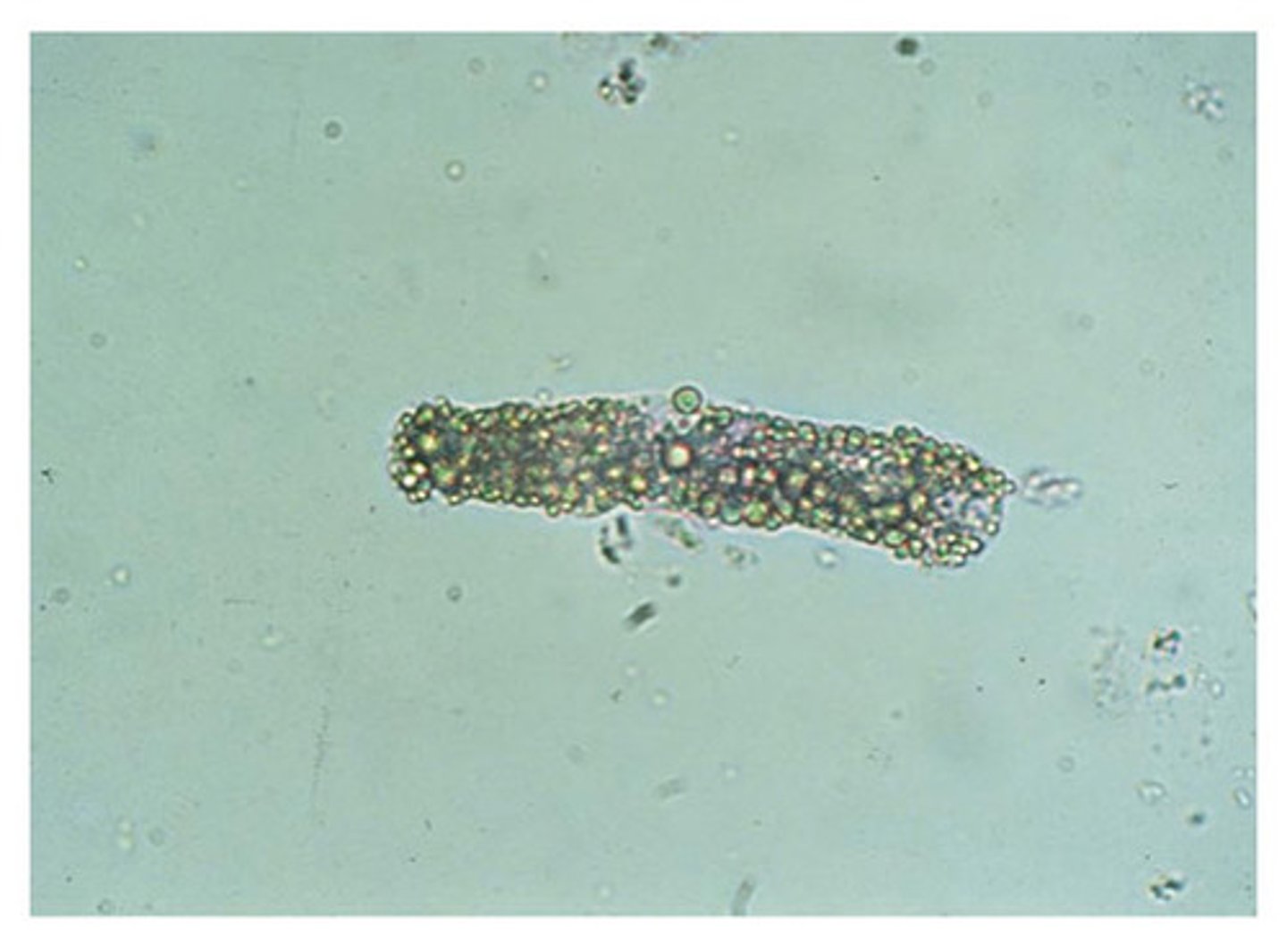
Urine: Erythrocytes
small, rounded, smooth-edged, somewhat refractile
SMALLER than WBCs
appearance is affected by: urine concentration, pH, time period of collection and examination
What are the different kinds of RBCs in urine?
intact, crenated, or lysed
Where do RBCs in Urine originate from?
any part of urinary tract that is inflamed or infected
RBCs in acidic or concentrated urine
shrink or crenate
RBCs in alkaline or diluted urine
swell and lyse
What do Hemolyzed RBCs release into the urine?
hemoglobin
How are Erythrocytes Reported?
numbers in average seen per high-power field (40x) and note clumping
Urine: Leukocytes
mainly segmented neutrophils
LARGER than RBCs and SMALLER than epithelial cells
clumps are significant
WBCs in concentrate or acidic urine
shrink
WBCs in alkaline or diluted urine
swell
What do Leukocytes Indicate if Present in the Urine?
pyuria, nephritis, pyelonephritis, urteritis, cystitis, urethritis
Urine: Epithelial Cells
normal for some of these to be present in the urine
HIGH NUMBER = inflammation
What are the Different kinds of Epithelial Cells?
squamous, transitional, and renal
Squamous Epithelial Cells
from the urethra, vagina, or prepuce and found in using the free-catch or catherization method. NOT found in cystocentesis
Squamous
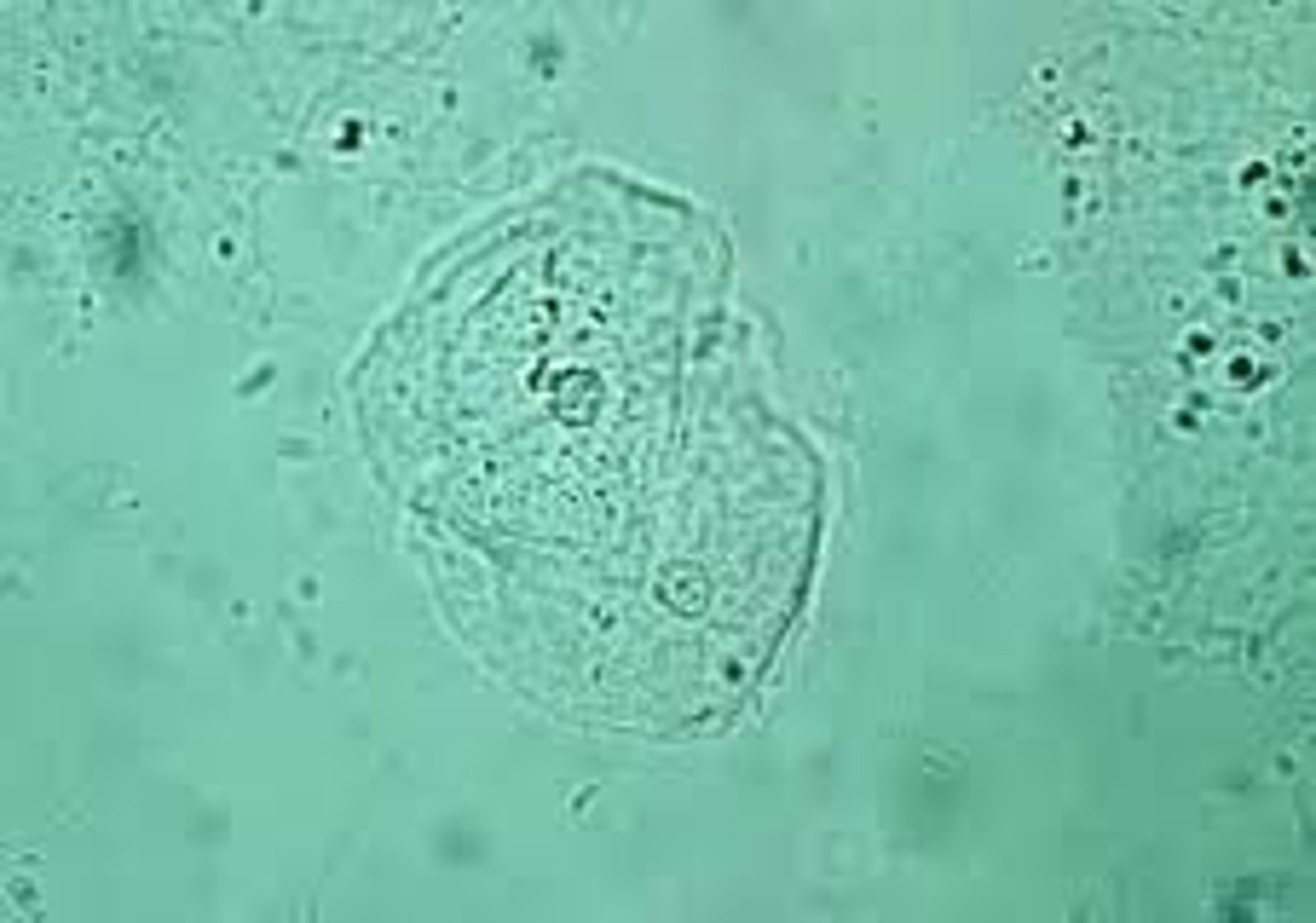
Transitional Epithelial Cells
line the ureters, renal pelvis, bladder, and proximal urethra and will be present in utilizing the catherization method
Transitional
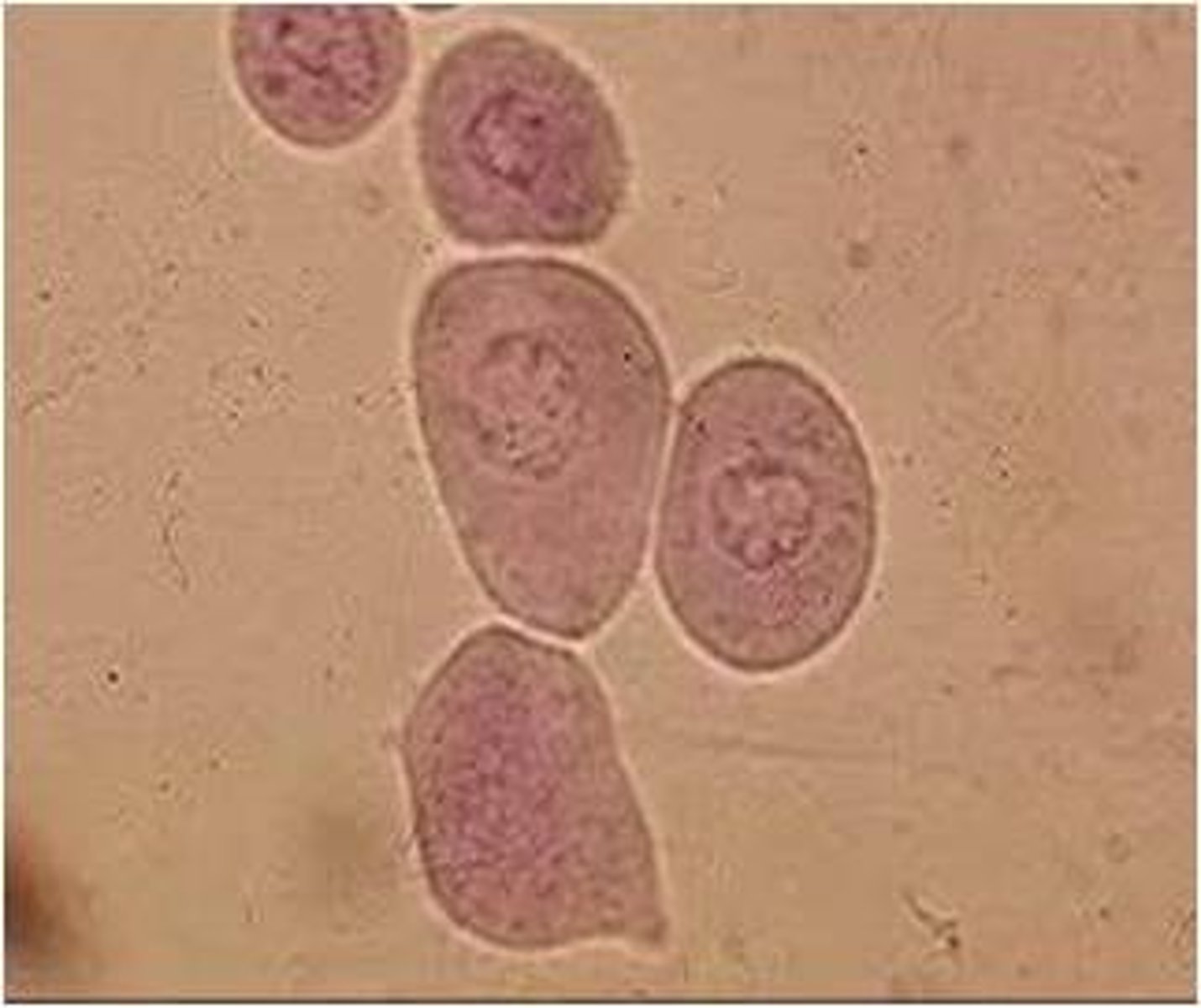
Renal Epithelial Cells
SMALLEST epithelial cell, comes from renal tubules, RARELY found EXCEPT as CASTS`
Order from Largest>Smallest of WBC, RBC, Bacteria, and Epithelial cells
epithelial> WBC> RBC> bacteria
Urine: Bacteria
can be insignificant or important pathogen, but in NORMAL urine is NOT present and in cystocentesis abnormal IF present.
Renal
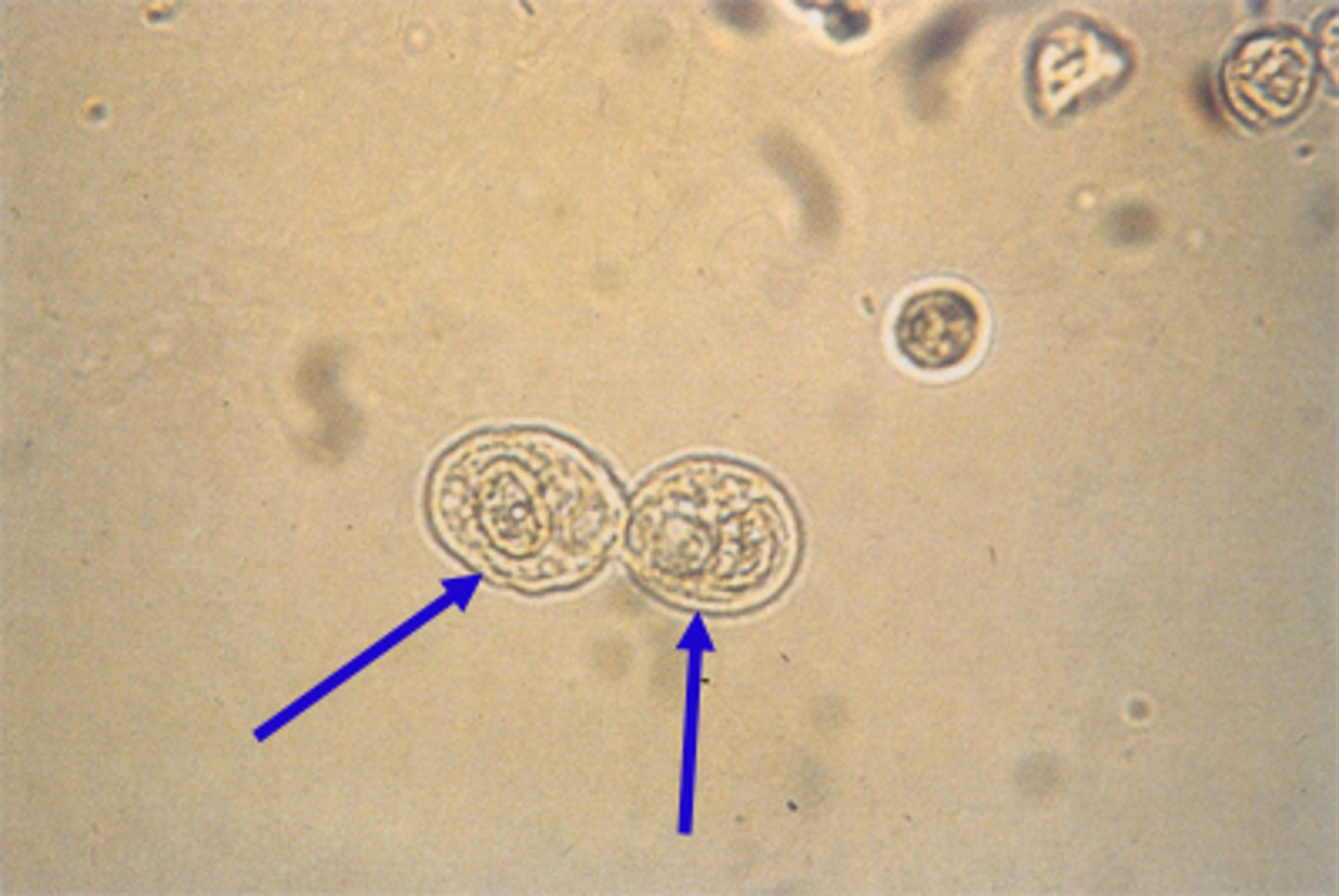
What is the name for Round Bacteria?
cocci
What is the name for Rod-Shaped Bacteria?
bacilli
How are Bacteria Reported?
few/moderate/many or 1+/2+/3+/4+
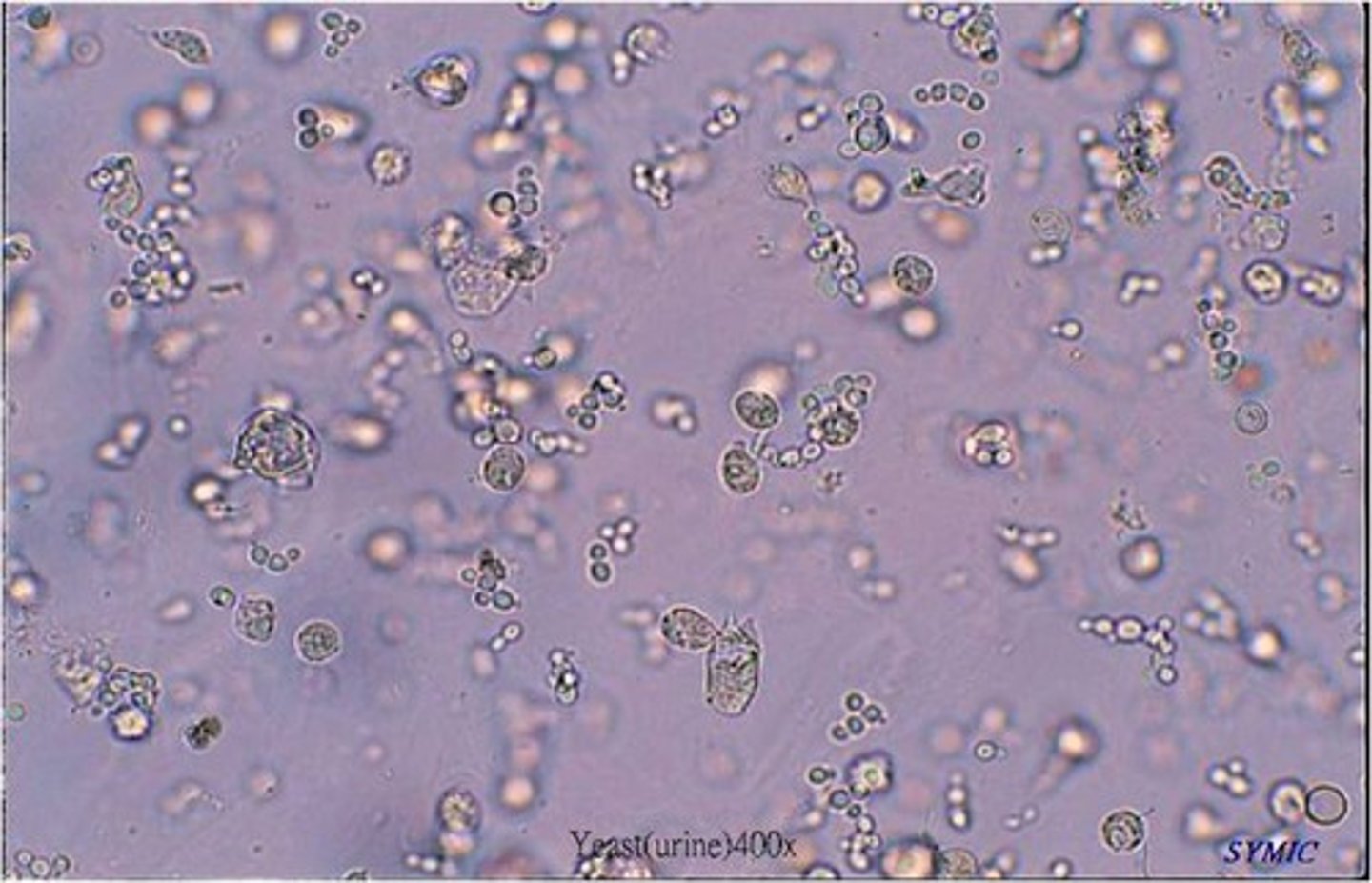
Filamentous Mold
Budding Yeast