Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What 3 elements does the synapse consist of?
Presynaptic membrane - formed by the terminal button of an axon
Postsynaptic membrane - composed of a segment of dendrite or cell body
Synaptic cleft - space between presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane
What are neurotransmitters (NT)?
Endogenous chemical
Transmits signals across a synapse from one neurone to another target neurone, muscle cell or effector cell
Cause rapid excitatory or inhibitory effects.
What are neuromodulators (NM)?
Endogenous chemical
Released from one neurone but affects groups of neurones or effector cells that have the appropriate receptor
May not be released at synaptic sites
Often acts through second messengers
Effects are slower and longer-lasting
List the main neurotransmitters and neuromodulator classes
Acetylcholine (NT)
Monoamines (NT; NM): Catecholamines (dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine), Indolamines (serotonin)
Amino acids (NT; NM): Glutamate, GABA, Glycine
Peptides (NT; NM): Endorphins, Enkephalins
Lipid substances (NT): Anandamide, Leptin
Nucleosides (NM): Adenosine
Soluble gases: Nitric Oxide, Carbon Monoxide
NT and NM classes
Acetylcholine - NM or NT?
NT
NT and NM classes
Monamines - NM or NT? Examples?
NT and NM
Catecholamines - dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
Indolamines - serotonin
NT and NM classes
Amino acids - NM or NT? Examples?
NT and NM
Glutamate
GABA
Glycine
NT and NM classes
Peptides - NM or NT? Examples?
NM and NT
Endorphins
Enkephalins
NT and NM classes
Lipid substances - NM or NT? Examples?
NT
Anandamide
Leptin
NT and NM classes
Nucleosides - NM or NT? Examples?
NM
Adenosine
NT and NM classes
Soluble gases - NM or NT? Examples?
NM
Nitric oxide
Carbon monoxide
What are the major ‘slow’ neurotransmitters?
Acetylcholine
What are the main roles of acetylcholine in the human brain and body?
Peripheral nervous system – contraction of skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system
Brain – control of plasticity, arousal and reward
How is acetylcholine synthesised and stored?
Synthesised in presynaptic terminals from choline and acetyl-CoA
Stored in small synaptic vesicles
How is acetylcholine released into the synaptic cleft?
Action potential arrives ant presynaptic neurone
Presynaptic plasma membrane depolarises
ACh is released by vesicular exocytosis
How is acetylcholine removed from the synaptic cleft?
Rapidly removed by acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Choline is taken up by specific transporters
What types of receptors does acetylcholine act on?
Nicotinic receptors
Muscarinic receptors
What drugs stimulate and block nicotinic and muscarinic receptors?
Nicotinic receptors: stimulated by nicotine, blocked by curare
Muscarinic receptors: stimulated by muscarine, blocked by atropine
Nicotinic ACh Receptors
What type of receptors are nicotinic ACh receptors?
Ligand-gated ion channels
Nicotinic ACh Receptors
What happens when ACh binds to nicotinic receptors?
Opening of the central ion pore
Allowing Na⁺ influx
Causing depolarisation and excitation of the postsynaptic cell
Action potential generated
Muscarinic ACh Receptors
What type of receptors are muscarinic ACh receptors?
G protein–coupled receptors
Classified into five groups - M1 - M5
Muscarinic ACh Receptors
Which muscarinic receptors activate Gq/11 proteins and what is the effect?
M1, M3 and M5 receptors activate Gq/11:
When Ach binds to the receptor, the α subunit of the Gq/11 protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds and activates Phospholipase C (PLC)
PLC produces 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-3 phosphate (IP3)
This triggers Ca²⁺ release from the intracellular stores
Produces a slow depolarising EPSP
Leads to overall excitation of the postsynaptic neurone
Muscarinic ACh Receptors
Which muscarinic receptors activate Gi/o proteins and what is the effect?
M2 and M4 receptors activate Gi/o:
When Ach binds to the receptor, the the α subunit of the Gi/o protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds and inhibits adenylyl cyclase
Inhibit voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels
Leads to overall inhibition of the postsynaptic neurone
What is the main source of acetylcholine in the brain?
The Nucleus Basalis of Meynert in the basal forebrain
What are axons of neurones in the nucleus basalis of meynert known as?
Cholinergic fibers / neurones » release Ach
Where do cholinergic fibres from the Nucleus Basalis of Meynert project?
Neocortex
Hippocampus
Amygdala
What is the role of acetylcholine in the neocortex?
Cholinergic fibers extend to the neocortex
Ach activates muscarinic M1 receptors here which enhances the processes that are involved in memory consolidation:
Muscarinic M1 receptors are Gq/11-coupled receptors
Activation by ACh leads to PLC activation → IP₃ and DAG production → Ca²⁺ release
This causes slow depolarising EPSPs and increased neuronal excitability
Increased excitability supports synaptic plasticity, which is essential for memory consolidation
What are the roles of acetylcholine in the hippocampus and amygdala?
Cholinergic fibers project to the hippocampus and amygdala:
Hippocampus – regulate memory formation
Amygdala – regulate emotions
What other brain regions contain cholinergic neurones which release ACh?
Interneurones in the striatum
Dorsal lateral tegmental nucleus in the midbrain
Which regions of the brain do cholinergic neurones of the dorsal lateral tegmental nucleus in the midbrain project to?
Thalamus - regulates sensory processing
Cerebellum - regulates movement coordination
Why do drugs acting on CNS cholinergic receptors have peripheral nervous system (PNS) effects?
Because both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors mediate activity in the autonomic nervous system
Example of a nicotinic receptor agonist
What CNS effects can nicotinic receptor agonists (e.g. nicotine) cause?
E.g. nicotine
Convulsions
Example of a muscarinic receptor agonist
What CNS effects do muscarinic receptor agonists have?
What CNS effects do muscarinic receptor agonists have?
E.g. Amanita mushrooms
CNS:
Vertigo
Confusion
Weakness
Coma at higher doses
PNS:
Salivation
Sweating
Pupil contraction
Dyspnoea
Abdominal pain
Diarrhoea
Example of muscarinic receptor antagonists
What CNS effects do muscarinic receptor antagonists have?
What PNS effects do muscarinic receptor antagonists have?
e.g. Atropine, Scopolamine
CNS:
Drowsiness
Euphoria
Amnesia
Fatigue
Dreamless sleep
Excitement
Hallucinations
PNS:
Pupil dilation
Decreased salivation
Decreased secretion in the pharynx and respiratory tract
Increased heart rate
Decreased gut motility and secretion
Decreased bladder tone
What do anticholinesterase inhibitors do?
Block ACh degradation
Causing accumulation of ACh in synapses
Why are anticholinesterase inhibitors considered dangerous?
They are very toxic and can be used as chemical weapons
What therapeutic use do anticholinesterase inhibitors have?
Some are used as therapeutic agents in Myasthenia gravis
What are the CNS effects of anticholinesterase inhibitors?
Slurred speech
Confusion
Loss of reflexes
Convulsions
Sometimes coma at higher doses.
What are the PNS effects of anticholinesterase inhibitors?
Pupil constriction
Watery nasal discharge
Bronchiolar secretion (wheezing)
Nausea
Vomiting
Cramps
Diarrhoea
Involuntary urination
Sweating
Twitching
What is dopamine?
Neurotransmitter
Of the catecholamine family
What are the main roles of dopamine in the human brain and body?
Control of movement
Emotional response
Control of pleasure and pain
How is dopamine synthesised and stored?
Synthesised in the presynaptic terminals of dopaminergic neurones from amino acid tyrosine
Stored in large dense core vesicles
How is dopamine released?
Released by vesicles exocytosis
What happens when dopamine binds to its receptors?
Produces either excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic effects depending on the type of postsynaptic receptor
How is dopamine removed from the synaptic cleft?
removed by dopamine transporters
How is dopamine degraded?
degraded by the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO)
What type of receptors are dopamine receptors?
G protein-coupled receptors
What are the two main families of dopamine receptors?
D1-like dopamine receptors (D1, D5)
D2-like dopamine receptors (D2, D3, D4)
D1-like Dopamine Receptors
What G protein do D1-like dopamine receptors activate?
Gs
D1-like Dopamine Receptors
Intracellular signalling pathway
When dopamine binds to the D1-like receptor, the α subunit of the Gs protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds to and activates adenylyl cyclase
Leads to stimulation of various voltage-gated channels
Leads to overall excitation of the postsynaptic neurone
D1-like Dopamine Receptors
What is the overall effect of D1-like dopamine receptor activation?
Stimulation of various voltage-gated channels
Leading to overall excitation of the postsynaptic neurone
D2-like Dopamine Receptors
What G protein do D2-like dopamine receptors activate?
Gi/o
D2-like Dopamine Receptors
Intracellular signalling pathway
When dopamine binds to the D2-like receptor, the the α subunit of the Gi/o protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds and inhibits adenylyl cyclase
Inhibit various voltage-gated channels
Leads to overall inhibition of the postsynaptic neurone
How is dopamine action terminated at the synapse?
By re-uptake across the presynaptic membrane mediated by dopamine transporters
This is an energy dependent process
How is the ion gradient required for dopamine transport generated?
Na+/K+ ATPases use energy from ATP hydrolysis to create a concentration gradient of ions across the presynaptic membrane
How does dopamine enter the presynaptic neurone during reuptake?
Co-transport of Na+ and Cl- ions and dopamine from the synaptic cleft
What is the role of potassium ions in dopamine transport?
K+ ions bind to the transporter allowing it to return to the outward position
Release of K+ ions into the synaptic cleft equilibrates the ionic gradient across the pre-synaptic membrane
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
What is the main source of dopamine in the brain?
neurones located in the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
What is the Mesolimbic Dopamine pathway?
Neurones in the VTA which axons extend to limbic areas e.g. Nucleus Accumbens
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
Function of dopamine released in the nucleus accumbens by the mesolimbic dopamine pathway
Regulates the mood and reward centres
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
Effects of diseases and drugs which increase dopamine release in the mesolimbic pathway
Positive psychotic symptoms
Aggressive and hostile behaviours.
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
What is the Mesocortical Dopamine pathway?
Neurones in the VTA which axons extend to the prefrontal cortex
Mesolimbic & Mesocortical Pathways
Function of dopamine released in the prefrontal cortex by the mesocortical dopamine pathway
regulates attention and memory
Nigrostriatal Pathway
What is another major source of dopamine in the brain?
Substantia Nigra in the midbrain
Nigrostriatal Pathway
Where do substantia nigra neurones project?
To the striatum of the basal ganglia region
Nigrostriatal Pathway
What is the function of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway?
regulation of motor function
Nigrostriatal Pathway
What are the effects of dopamine deficiency in this pathway?
Rigidity
Akinaesia or bradykinaesia
Tremor
Akathisia and dystonia (symptoms of Parkinson’s disease)
Nigrostriatal Pathway
What are the effects of hyperactivity in this pathway?
Chorea
Dyskinesias
Tics
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
What is the third main source of dopamine in the brain?
Arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
Where does dopamine released from the arcuate nucleus act?
It is released into the portal blood system and travels to the anterior pituitary
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
What is the effect of dopamine on the anterior pituitary?
It acts on prolactin-secreting cells (lactotrophs) to suppress prolactin release
What drugs act as dopamine receptor agonists and mimetics?
DA transporter inhibitors:
Amphetamine - causes release of dopamine
Cocaine - prevents reuptake of dopamine
» drugs of abuse
What dopamine precursor is used therapeutically?
L-DOPA
Treatment for Parkinson’s disease
What are dopamine receptor antagonists used for?
anti-schizophrenic or anti-psychotic drugs (D2 antagonists)
What is noradrenaline?
AKA norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter
Of the catecholamine family
What are the main roles of noradrenaline in the human brain and body?
Autonomic nervous system control – sympathetic nervous system
CNS – control of alertness, rest cycles, attention and memory
How is noradrenaline synthesised and stored?
Synthesised in the presynaptic terminals of adrenergic neurones from amino acid tyrosine
Stored in large dense core vesicles
How is noradrenaline released?
By vesicle exocytosis
How does noradrenaline act at the synapse?
It binds to specific adrenergic receptors
Produces either excitatory or inhibitory postsynaptic effects depending on the postsynaptic receptor
How is noradrenaline removed and degraded?
Removed by adrenergic transporters
Degraded by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
What type of receptors does noradrenaline bind to?
Adrenergic receptors » G protein-coupled receptors
How are adrenergic receptors classified?
α receptors: α1 and α2
β receptors: β1, β2 and β3
α1 receptors
What G protein are α1 receptors coupled to?
Gq/11
α1 receptors
Intracellular signalling pathway
When NA binds to the α1 receptor, the α subunit of the Gq/11 protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds and activates Phospholipase C (PLC)
PLC produces 2 second messengers: diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol-3 phosphate (IP3)
This triggers Ca²⁺ release from the intracellular stores
Produces a slow depolarising EPSP
Leads to overall excitation of the postsynaptic neurone
α2 Receptors
What G-protein are α2 Receptors coupled to?
Gi/o
α2 Receptors
Intracellular signalling pathway
When NA binds to the α2 receptor, the the α subunit of the Gi/o protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds and inhibits adenylyl cyclase
Leads to the inhibition of various voltage-gated channels
Leads to overall inhibition of the postsynaptic neurone
β Receptors
What G-protein are β Receptors coupled to?
Gs
β Receptors
Intracellular signalling pathway
When NA binds to the β receptor, the the α subunit of the Gs protein separates from the βγ subunits
The α subunit binds to and stimulates adenylyl cyclase
This leads to the activation of various voltage-gated channels
Leads to overall excitation of the postsynaptic neurone
How is the activity of NA terminated at the synapse?
Same as dopamine
What is the main source of NA in the brain?
Locus Coeruleus, located in the Pons region of the Brain Stem
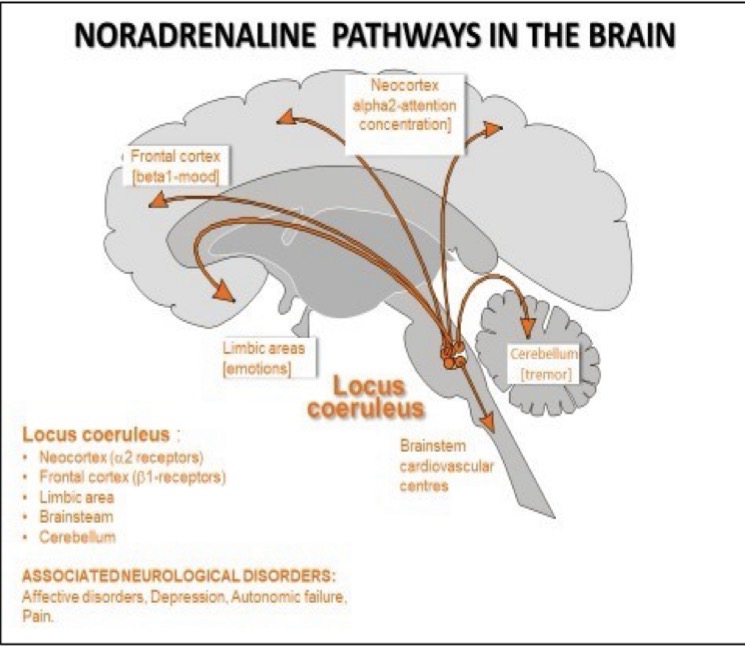
Where do neurones in the Locus Coeruleus nucleus project their axons to AKA where is NA released in the brain?
Neocortex
Limbic system
Diencephalon
Medulla oblongata
Spinal cord
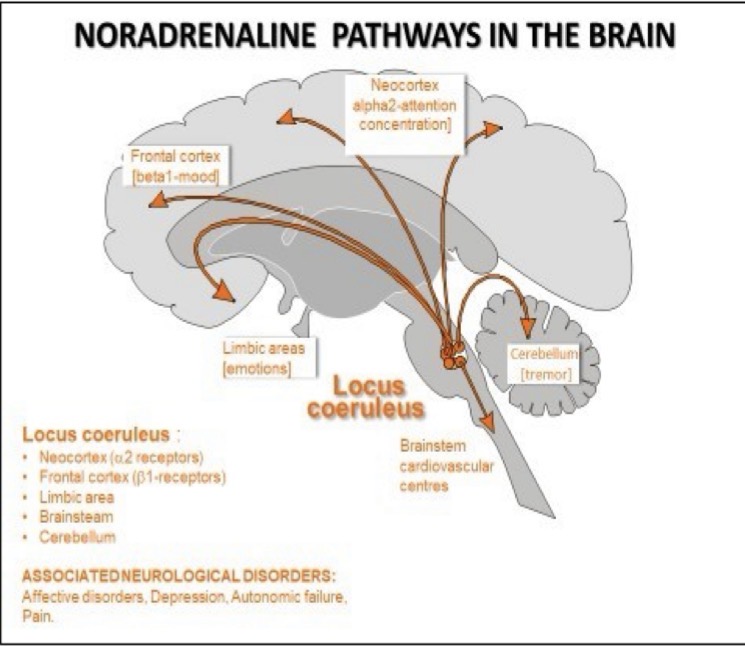
Function of NA in the neocortex
Regulate attention and concentration
Via activation of a2 receptors
Function of NA in the frontal cortex
Regulate mood
Via activation of B1 receptors
Function of NA in limbic areas
Regulate emotions
Function of NA in the medulla oblongata
Regulate cardiovascular centres
NA Receptor Agonists and Mimetics
NA transporter inhibitors
e.g. Amphetamine, Cocaine
Regulate wakefulness and alertness
MOA (moamine oxidase) inhibitors
Impairs cognitive processes = euphoria, insomnia, hallucinations, delusions
NA Receptors Antagonists
Beta blockers
What is serotonin (5-HT)?
Neurotransmitter
Of the indolamine category
Role of serotonin in the human brain and body
Controls mood, appetite, sleep
Regulates cognitive functions e.g. memory, learning
How is serotonin synthesised?
In presynaptic terminals of serotonergic neurones from amino acid tryptophan
Stored in large dense core vesicles