Basic Immunology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
active vs passive immunity
pt produces Ab
follows immunization or infn
has memory
Ab transferred to pt ie gamma glob injections or placenta
no memory
natural vs adaptive immunity
non-specific
no memory ie PMNs, NK, stomach acid
specific
memory ie T cells, B cells
cellular vs humoral immunity
T cell / lymphokines
1ry defense for viral / fung infn (intracellular orgs)
delayed hypersensitivity ie transplant rejection
B cell / Ab
1ry defense for bact infn (extracellular org)
Ab dependent cellular cytotox (ADCC)
diagram of Ig
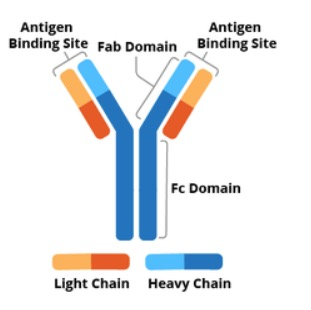
classes of Ig are based on
heavy chains
IgG
highest conc in serum (75% of total Ab conc)
4 subclasses which activate comp (except IgG4)
x-placenta
IgG 2 and 4 assoc w autoimmune d/o
IgG 1 and 3 “ “ dominant in infns
IgM
largest Ab (pentamer)
fixes comp the best!
prominent in early immune response (= acute infn)
5-10% of total Ab conc
IgA
predom Ab in secretions
serum (monomer) & secretory form (dimer)
1ry defense against some local infns at mucosal surface
2 subclasses
IgD
unknown fxn
present on B cell surface
IgE
allergEE
triggers release of histamines from mast cells
immune response curve
IgM followed by IgG → 2nd exposure to Ag → higher IgG response (anamnestic response)
Rosette test for T and B cells
a. incubate srbc w known # of purified lymph (srbc bind to E-rosette receptor CD2 on T cells
b. count rosetted lymphs; % of T cell is calculated
c. estimate B cells = 100% - calc % of T cells
d. estim of absolute counts: pt total lymph ct * % T or B cells
T cells
80% of circulating lymp cell
has TCR-1/2
CD2, 3+ (forms rosette w srbc)
CD4+ = T helper cell → release cytokines
CD8+ = T cytotoxic/suppressor cell
CD4 to CD8 ratio normal = 2:1
in AIDS pt → flipped 1:2
for viral infn & tumors, delayed hypersens rxn
B cells
5-15% of circulating lymph
has IgD or IgM & comp receptors (C3b) on surface
CD19, 20, 21+
Ab neutralize toxins, activate copm, act as opsonins
Null cells (NK, K)
large lymph, 5-15%
no TCR or Ig on surface
CD16, 56+
kills virus infd cells & tumor cells
can distinguish healthy cells w MHC class I
NK cells: cytotoxic w/o MHC restriction
killer cells: Ab dependent cellular cytotoxicity
_ is mediator of immune complex at a tissue injury
neutrophils recruited by cytokines > release lysosomal enzymes > inflammation
C3b and Fc rcp are present on
B cells and monocytes
normal T to B cell ratio
8:1 ; B cells produce a lot of Ab, they do the job
or 80% T cell, 20% B cell (from ascp boc)
complement fxn
control inflammation
activates phagocytes (chemotaxis)
lyses target cells (foreign org)
opsonization - enhances phagocytic binding by coating foreign org & attaching to complement receptors on neutrophils & monocytes
classical complement pathway
bind in order except at beginning C1, 4, 2, 3
a fragments = go into plasma
b = attach to cell (except C2a and C2b)
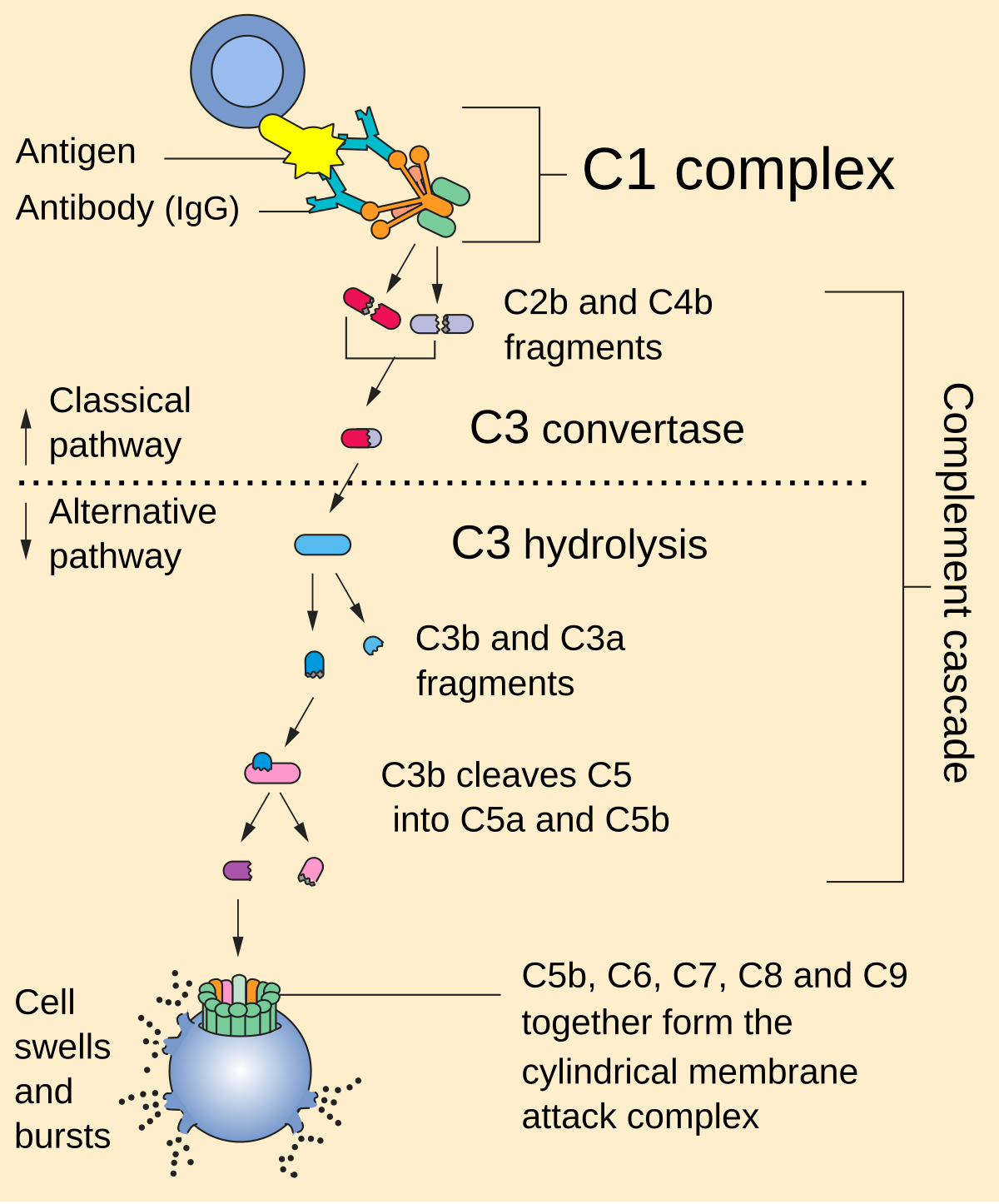
alternative complement pathway
starts w C3 → involves C3 again → C5 → MAC complex
activated by LPS, polysacc
involves factors B & D and control factors H&I
both complement cascades require
Ca and Mg++
complement ctrl proteins
classical
C1 esterase inhibitor
C4 binding protein
alternative
factor I - degrades C3b
factor H - completes w factor B
hypersensitivity rxn types I & II
I = immediate, anaphylactic
IgE-sens mast cells → histamine ie bee sting, hay fever, asthma
II = Ab-dep
Ab attaches to Ag → cell death
ie tx rxn, AIHA, hashimotos, Goodpasture’s dz
hypersensitivity rxns III & IV
III = large formation of immune complex, not cleared by lymphs
ie Rhematoid arthritis, SLE, serum sickness
IV = delayed sens-T cells release IL; monocyte & lymp infiltration
takes >12 hr to develop
ie contact dermatitis, TB, leprosy, GVHD
tests for allergy (or for cellular immunity)
skin tests, RIST, RAST
eosinophils in nasal secretions
allergic rxns
phagocytic wbc
neutro, eos, mono
lymph & baso are NOT phagocytic