Anatomy quiz #2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
1
New cards
How many ribs attach directly to the sternum (True ribs)
7
2
New cards
How many ribs attach indirectly to the sternum (False ribs)
3
3
New cards
How many floating ribs are there?
2
4
New cards
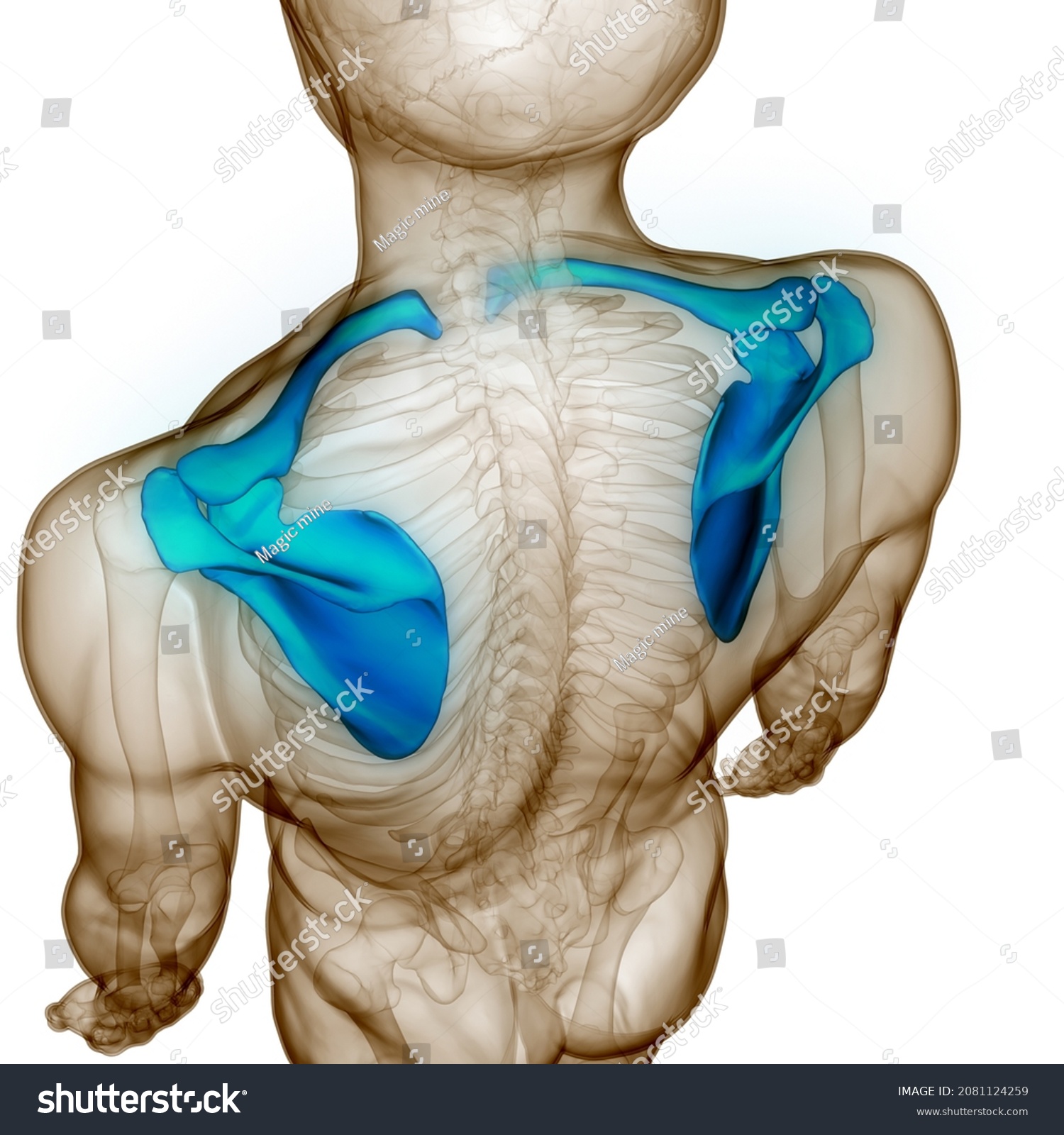
What is the Pectoral girdle comprised of?
the clavicle and the scapula
5
New cards
What does the pectoral girdle provide?
a rigid structure for muscles to pull against
6
New cards
Where is the pectoral girdle attached? (Anterior and Posterior)
Anterior attachment at sternoclavicular joint Posterior attachment is muscular
7
New cards
What does the pelvic girdle do?
Supports weight of the body from the vertebral column
8
New cards
What does the pelvic girdle do for lower organs?
Protects and supports
9
New cards
What is the primary function of your respritory system?
Gas exchange to support life
10
New cards
What is the secondary function of the lungs?
Provide energy for speech productuion
11
New cards
What is the trachea composed of?
Cartilage rings and a muscus membrane
12
New cards
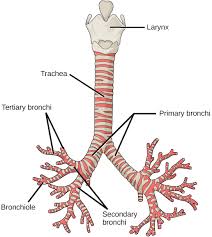
Where is the trachea located?
Inferior to the larynx
13
New cards
What is the name of the point where the trachea splits?
Carina
14
New cards
What does the trachea split into?
Bronchi
15
New cards
what do Terminal bronchioles divide into?
Alveolar ducts
16
New cards
Alveoli are sourrounded by what?
a network of capillaries
17
New cards
Alveoli are a location for what exchnage (membrane is permeable)?
Gas exchange
18
New cards
What is inspiration?
Air is drawn into the lungs and the thoracic cavity expands, decreasing air pressure in the lungs
19
New cards
What is expiration?
Air is expelled from the lungs, the thoracic cavity contracts, increasing the air pressure in the lungs
20
New cards
Where is plueral linkage and what does it do?
between the lungs and the ribs; it enables the lungs to expand and contract as the thorax changes volume
21
New cards
Parietal Pluera
Lines the inner surface of the thoracic cavity
22
New cards
Viceral pluera
Lines the outer surface of lungs
23
New cards
Why are the pluera useful?
Provide friction free movement, protection, and link lungs to the walls of thorax
24
New cards
What is boyles law?
Pressure and volume are inversely related
25
New cards
What is the diaphragm the primary muscle of?
Inspiration
26
New cards
What does the diaphragm separate?
The abdominal and thoracic cavities
27
New cards
Which side of the diaphragm is higher?
Right
28
New cards
What is the diaphragm innervated by?
Phrenic nerve
29
New cards
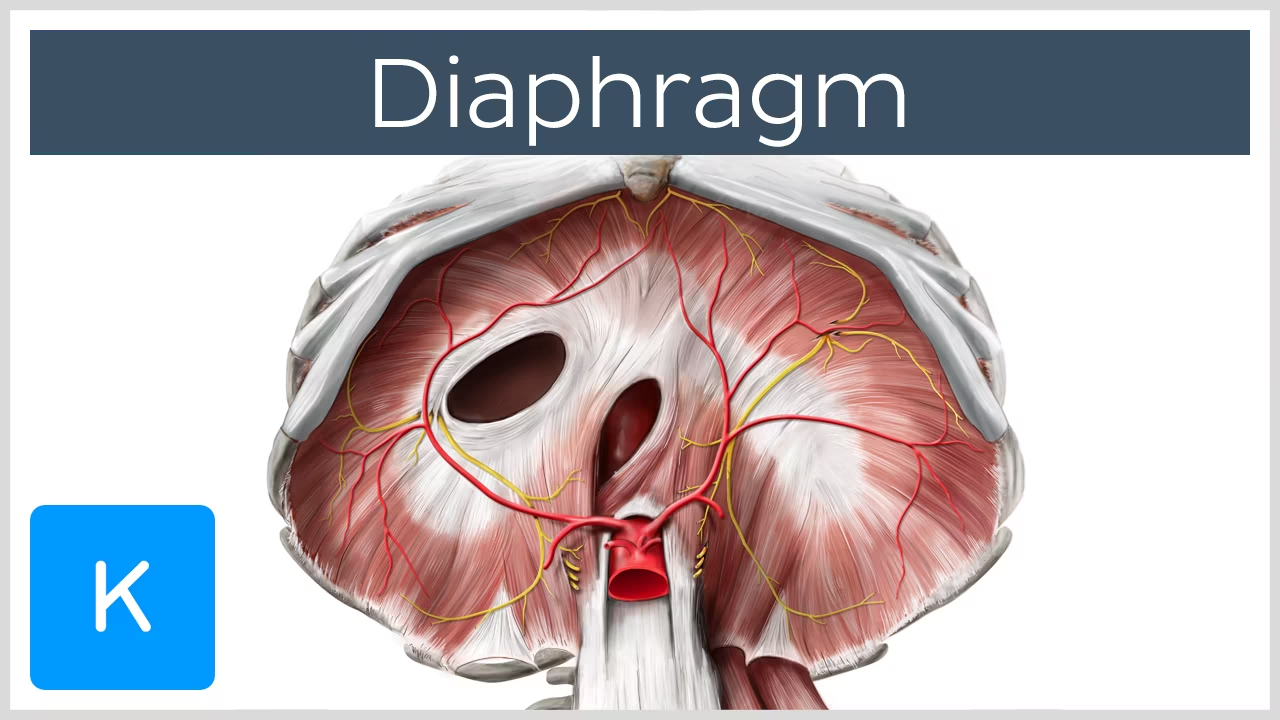
What is the white part in the middle of the diaphragm?
Central tendon
30
New cards
Where does the sternal portion of the diaphragm attach? (Muscular portion)
\
\n to xiphoid process
\n to xiphoid process
31
New cards
Where does the costal portion of the diaphragm attach? (Muscular portion)
to inner surface of cartilage of ribs 7 - 12
32
New cards
Where does the vertebral portion of the diaphragm attach? (Muscular portion)
to upper lumbar vertebrae (corpus of L1, transverse process of L1 – L5)
33
New cards
What is the only muscle contracted during tidal breathing?
Diaphragm
34
New cards
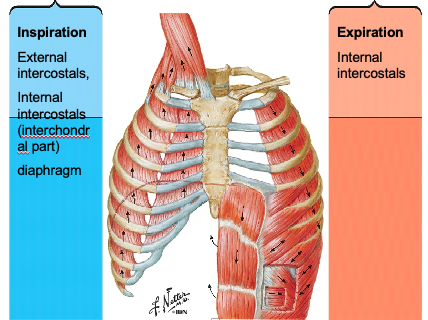
(Muscles of inspiration) where are external intercostals located and what direction do they go?
between the ribs, course downwards and inwards
35
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration) Where do the external intercostals origionate from?
Surface of ribs 1-11
36
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration) What are the external intercostals intervated by?
T1-T11
37
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration)Levator muscles in the back help do what?
Elevate the ribcage
38
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration) What are the levator muscles intervated by?
T2-T12
39
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration) What ribs does the Serratus posterior superior elevate?
2-5
40
New cards
(Muscles of inspiration) What innervates the Serratus posterior superior?
T1-T4
41
New cards
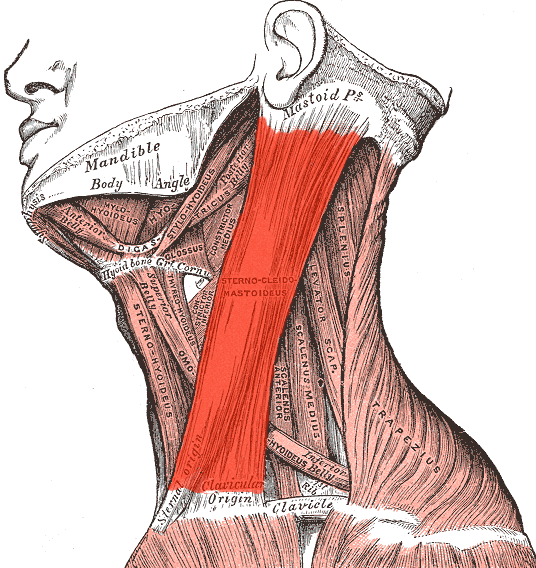
(inspiration) where does the Sternocleidomastoid originate from?
mastoid process of temporal bone
42
New cards
(inspiration) what does the Sternocleidomastoid elevate?
sternum and by association rib cage
43
New cards
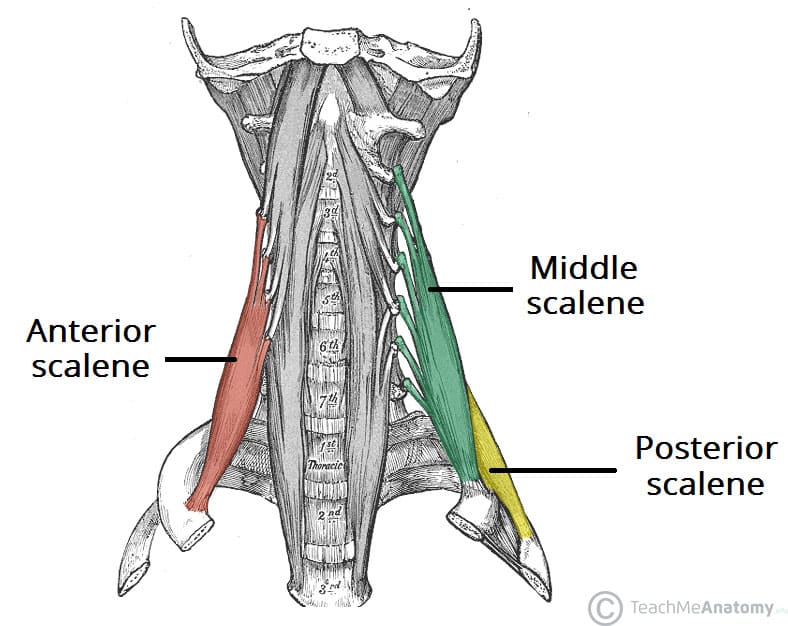
(inspiration) what do Scalenes (anterior, middle, posterior) elevate?
ribs 1 and 2
44
New cards
(inspiration) What are Scalenes (anterior, middle, posterior) innervated by?
C4-6
45
New cards
(inspiration) what does the Pectoralis major do?
Elevates sternum and therefore increases transverse \n dimension of rib cage
46
New cards
what is the pectoralis major innervated by?
C4-C7 and T1
47
New cards
what is the pectoralis minor innervated by?
C4-C7 and T1
48
New cards
true or false Expiration is passive at rest (requiring no active \n muscle contraction).
True
49
New cards
During exercise or breathing beyond tidal, \n expiration is aided by
active muscle contractions
50
New cards
Internal intercostals are the primary muscles of what?
forced exhalation
51
New cards
what are internal intercoastals innervated by?
T2-T11
52
New cards
what is the Abdominal aponeurosis used for?
has various attachments for muscles
53
New cards
what is the midline of the abdominal aponeurosis called?
linea alba
54
New cards
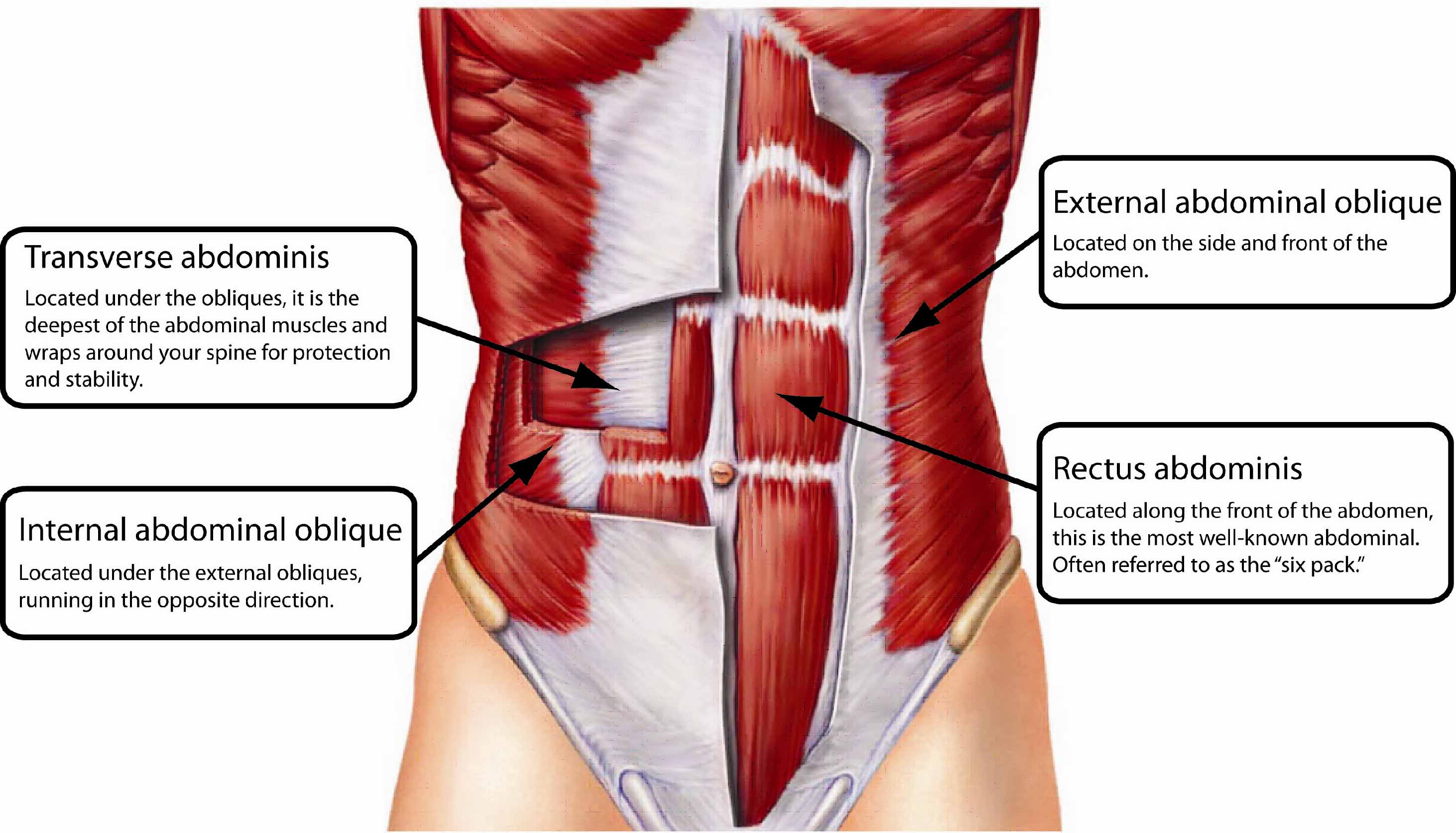
what is thr origin of the Rectus abdominis
Pubic crest and pubic symphysis
55
New cards
What is the rectus abdominis innervated by?
T7-T12
56
New cards
what action does the rectus abdominis perform?
Flexes trunk, aids forced expiration and \n raise intra-abdominal pressure
57
New cards
What is the deepest abdominal muscle?
Transverse abdominis
58
New cards
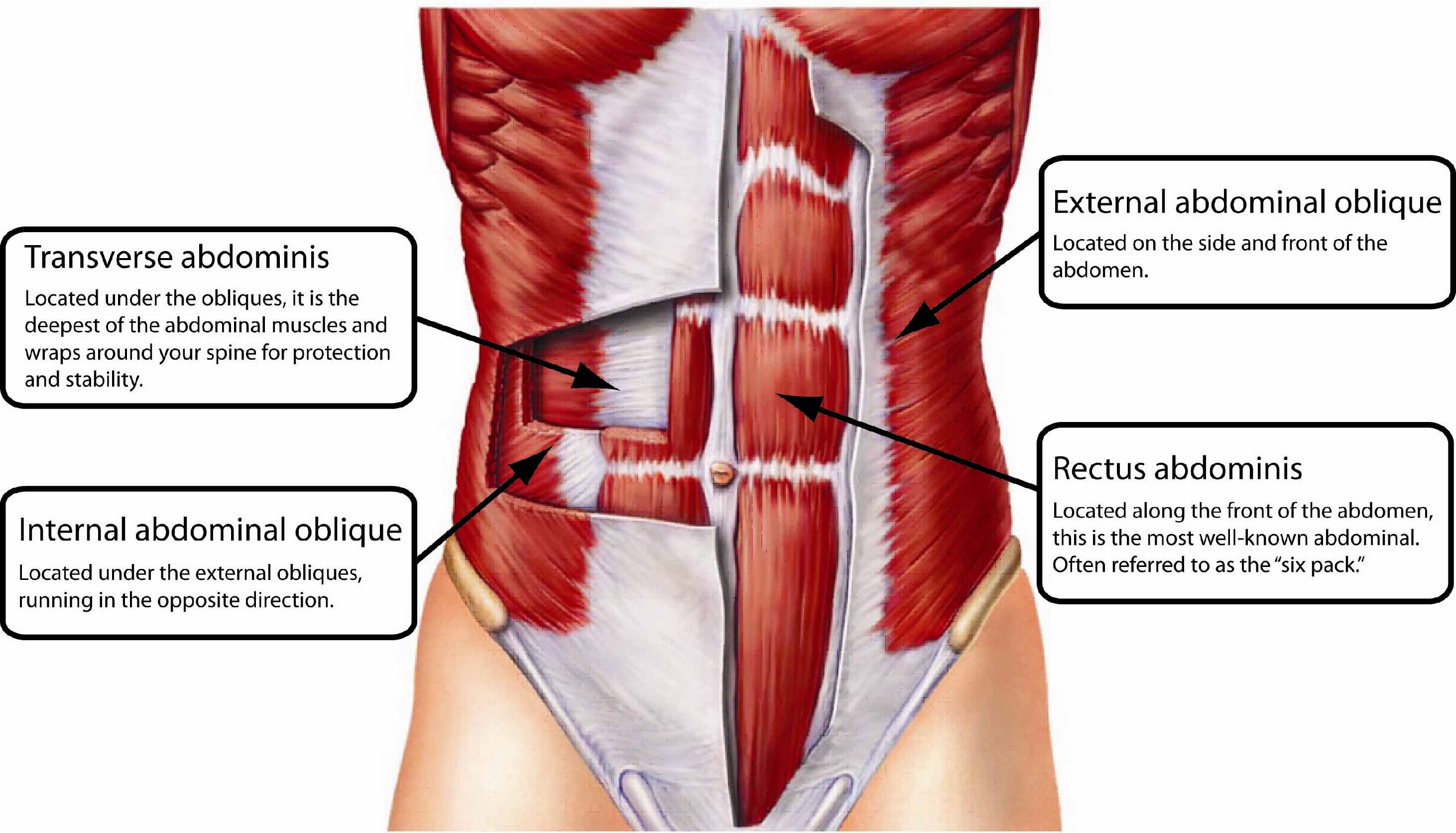
what is the origin of the transverse abdominis
vertebral column
59
New cards
whats is the transverse abdominis innervated by?
T7-T12
60
New cards
What action does the transverse abdominis perform?
Compresses abdomen
61
New cards
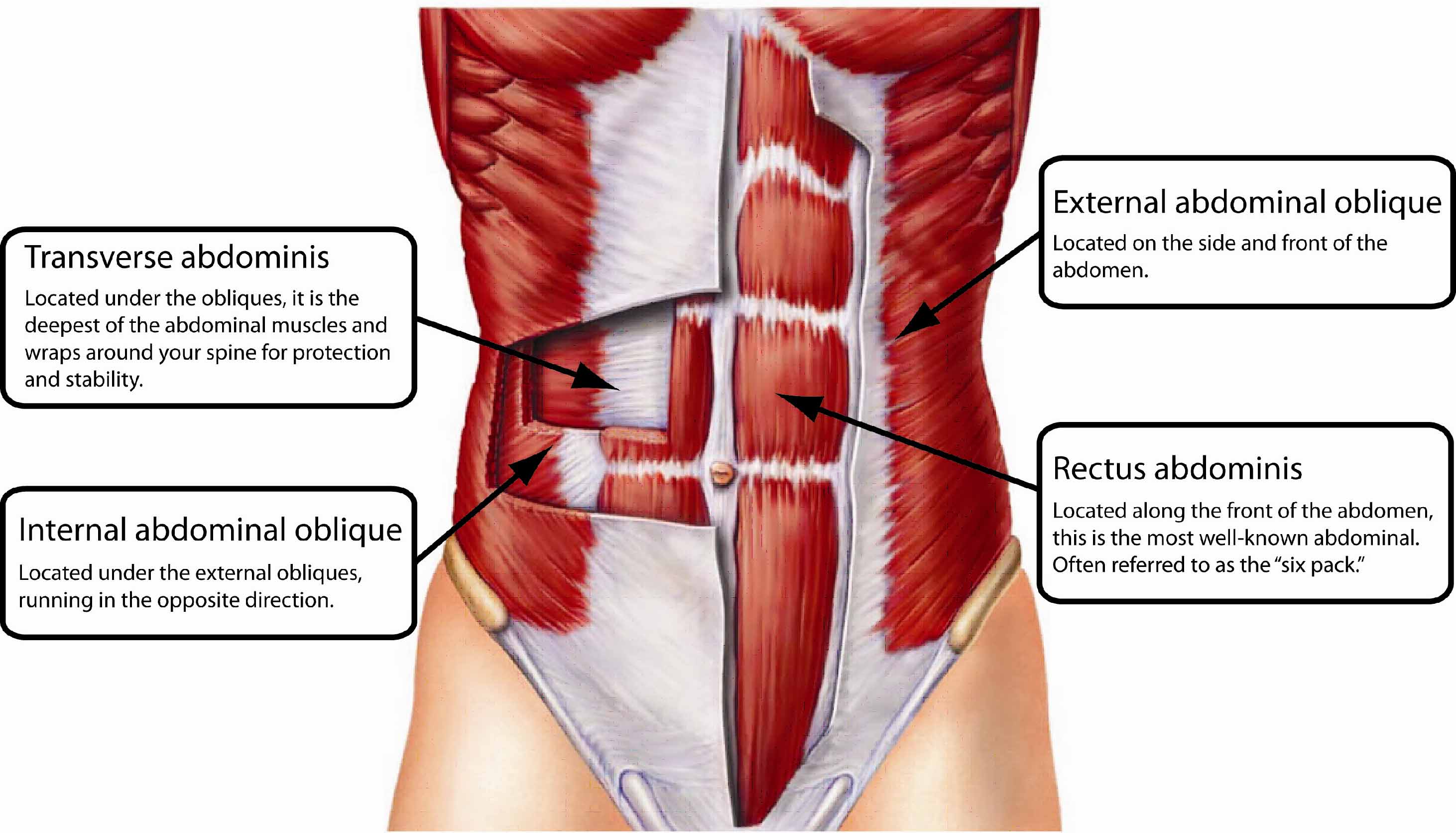
what is the origin of the Internal oblique abdominis?
anterior two thirds of iliac crest
62
New cards
what is the internal oblique abdominis innervated by?
T7-T12
63
New cards
what action does the internal oblique abdominis perform?
Supports abdominal wall, assists forced \n respiration, aids raising intra-abdominal pressure \n and, with muscles of other side, abducts and \n rotates trunk.
64
New cards
Which abdominal muscle is most superficial?
External Oblique abdominis
65
New cards
What is the external oblique abdominis innervated by?
T7-T12
66
New cards
What direction does the external obliques follow?
Courses downward and medially (generally \n opposite internal oblique abdominis
67
New cards
what is the origin of the external obliques?
lower borders of ribs 5-12
68
New cards
what action does the external obliques perform?
compress abdominal contents
69
New cards
what does the Serratus posterior inferior do?
Muscle of forced exhalation
70
New cards
where is the Serratus posterior inferior located?
Originate on the spinous process of T11 – L3 Insert into lower margins of ribs 7-12
71
New cards
what is the Serratus posterior inferior innervated by?
T9-T12
72
New cards
where is the Latissimus dorsi located?
The back
73
New cards
what does the Latissimus dorsi do?
Stabilizes posterior wall for expiration.