Rutgers Functional Human Anatomy Lec 21 (Pregnancy & Embryonic development)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Prenatal development
- pre-embryonic development
- embryonic development
- fetal development
pre-embryonic development
- fertilization to implantation
- approx. 2 weeks
embryonic development
- implantation to end of 8th week of pregnancy
- 1st 2 months
fetal development
- 9th week to birth
- 3rd-9th month
- fetus
prenatal development known as
- gestation period (9 month period)
- 40 weeks
3 month trimesters:
1st, 2nd, 3rd
1st trimester
- rudiments of all organs appear
- most dangerous period in prenatal life (40% conceptions survive)
- 3 months (1-12 weeks)
4 events in 1st trimester
cleavage (sequence of cell division):
- blastocyst forms
implantation:
- embryo implants to endometrial lining
placentation:
- formation of placenta
embryogenesis:
- development of embryo
implantation in 1st trimester
- blastocyst further develops, creating 3 layers
- process called gastrulation and makes germ layers:
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
ectoderm forms
integumentary system
skeletal system
entire nervous system
part of endocrine system
respiratory system
digestive system
mesoderm forms
integumentary
skeletal
entire muscular
placentation (1st trimester)
Placental circulation:
- blood flow from fetus to placenta in paired umbilical arteries
- blood returns via single umbilical vein
amnion
innermost membrane of placental sac, encloses embryo/fetus
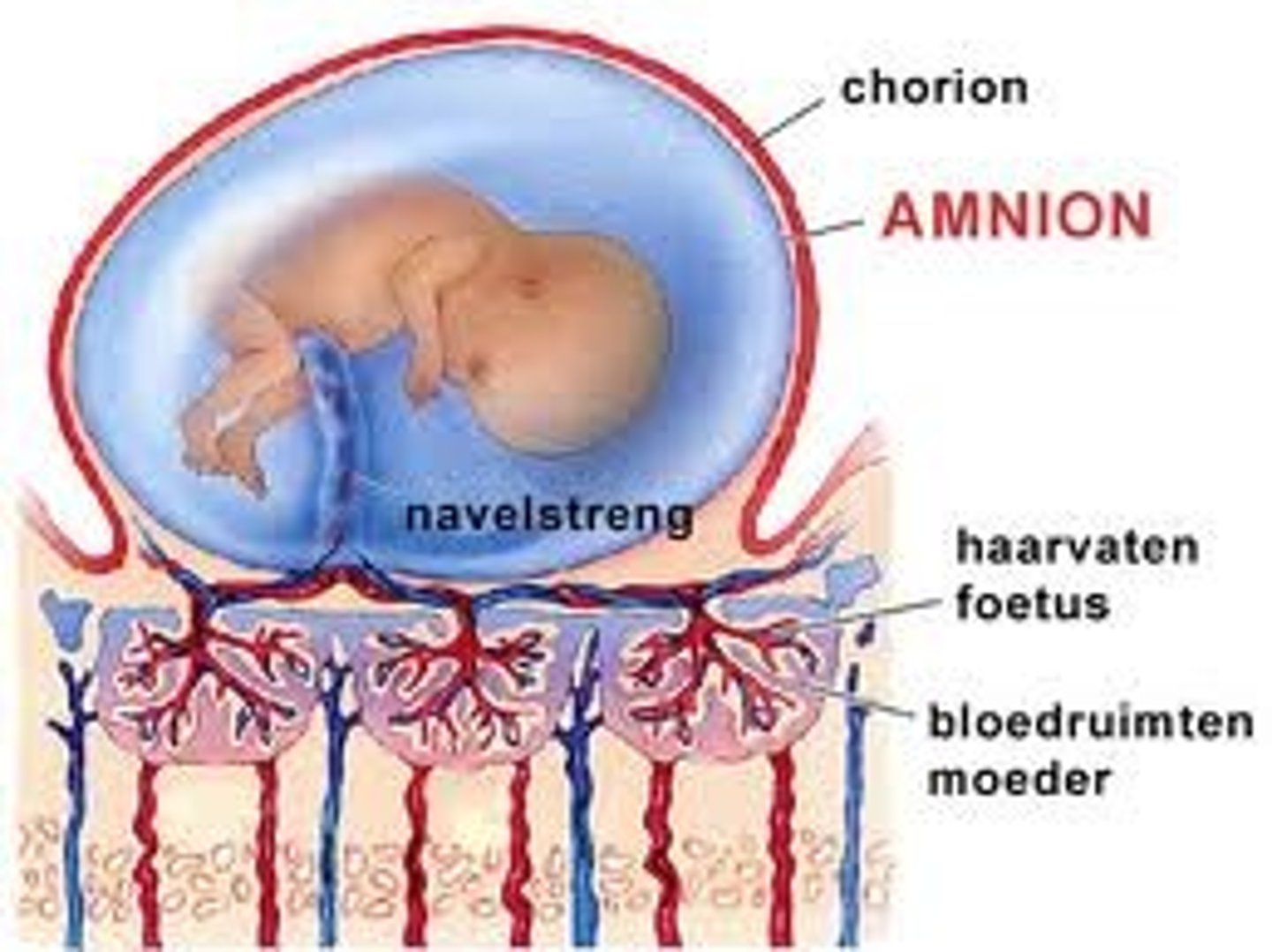
chorion
outer most membrane
contributes to formation of placenta
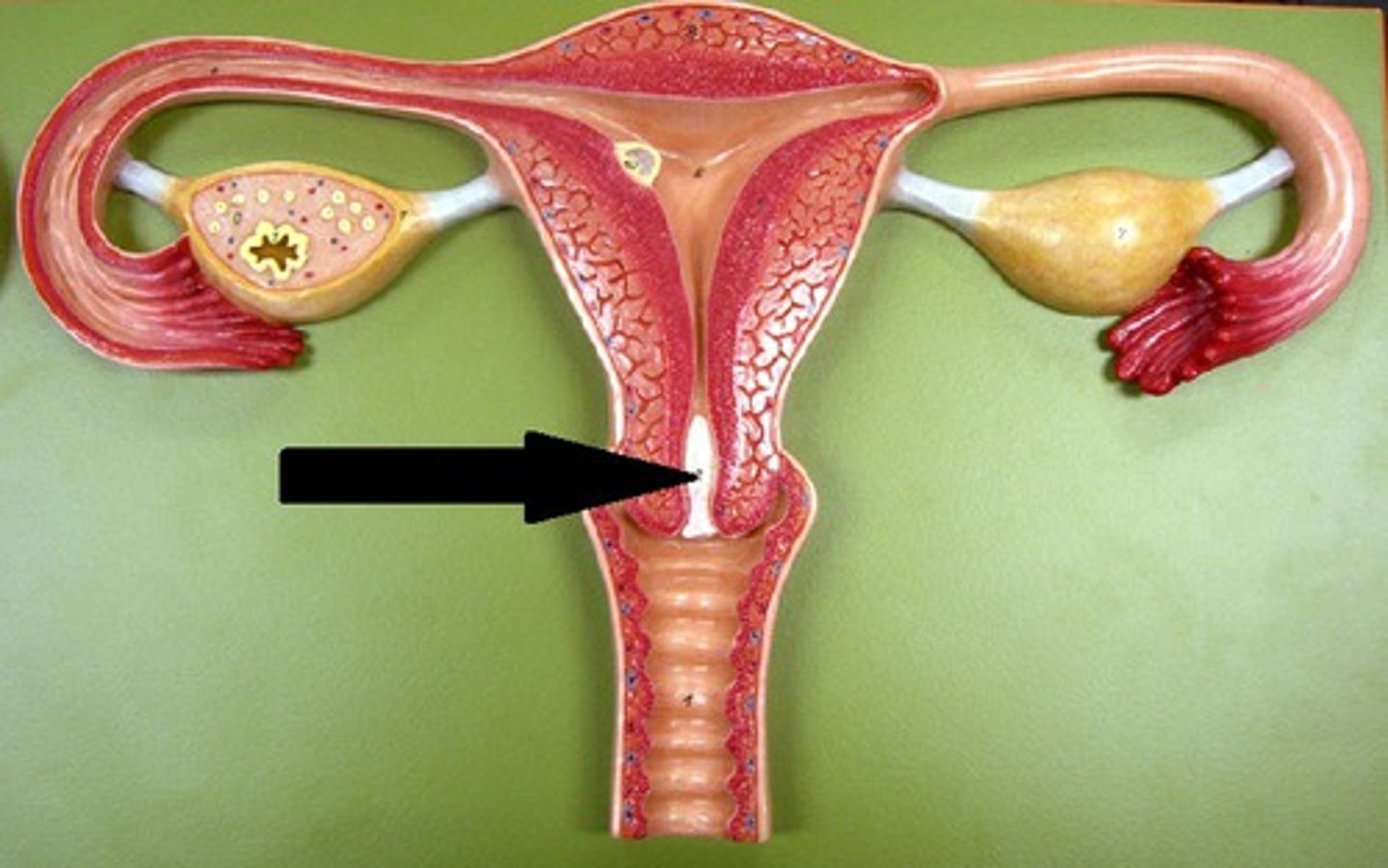
mucus plug
forms in area of cervix to prevent bacteria from entering
embryogenesis (1st trimester)
- 12 weeks post-fertilization
organogenesis:
organs begin to form
2nd trimester
- development of organs and organ systems
- fetus looks human
- fetus covered by amnion
- fetus grows faster than placenta
3rd trimester
- rapid growth
- all fetal organs become functional
changes in uterus during gestation
- uterus increases in length (7.5cm to 30cm)
- contains almost 5L fluid
- uterus & contents weigh around 22 lbs
- maternal abdominal organs are pushed out of their normal positions
labor
series of strong, rhythmic uterine contractions
goal of labor
parturition:
expulsion (delivery) of fetus
3 stages of labor
dilation
expulsion
placental
dilation
- cervix dilates
- fetus pushed by muscular contractions into cervical canal
- amnion ruptures
expulsion
- movement of fetus through cervical canal and vagina
- delivery can be helped by episiotomy (cutting skin between vagina & anus) or cesarian section
placental
ejection of placenta (afterbirth)
breech presentation
birth position in which the buttocks, feet, or knees emerge first
premature labor
- labor begins before fetus completes normal development
- 23/24-36 weeks generally survive w/ care
- before 23/24 weeks generally dies (respiratory/cardiovascular/urinary system not developed enough)
neonatal period
from birth to 1st month
events in neonate during neonatal period
- lungs fill w/ air
- blood circulation changes w/ closing of ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale of heart
- heart rate drops from 120-140 bpm to 70bpm
- breathing rate drop from 30-60 breaths per min to normal rate (30)
- kidneys filters infant own blood
- digestive system becomes active
- metabolic rate increased to maintain warmth for few days after birth