Philosophy Final Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is Deontology?
duty/obligation (religious, non religious)
What is Divine Command Theory?
morality is determined by whether or not God commands it vs Categorical Imperative-if everyone can do this, (duty to society)
What is Consequentialism?
right and wrong is determined by outcome
What is Utilitarianism?
an ethical theory that determines right from wrong by focusing on the outcome (focusing on increasing happiness and well being of large amounts of people)
What is Teleology?
What is something’s nature or purpose?
What is Autonomy?
the state of being independent or free, especially in regards to one's actions or well
What is Justice?
refers to fairness or balance in all relationships
What is Beneficence?
first the most good (the act of doing what is best for others)
What is Non-Malfeasance?
doing no harm (means “to do no harm”)
What are the “Forms?”
not the material world known to us through sensation, possess the highest and most fundamental kind of reality
Be able to reproduce Plato’s Cave diagram, describe each element and discuss the meaning of each component. Be able to apply the components of the diagram to a modern context.
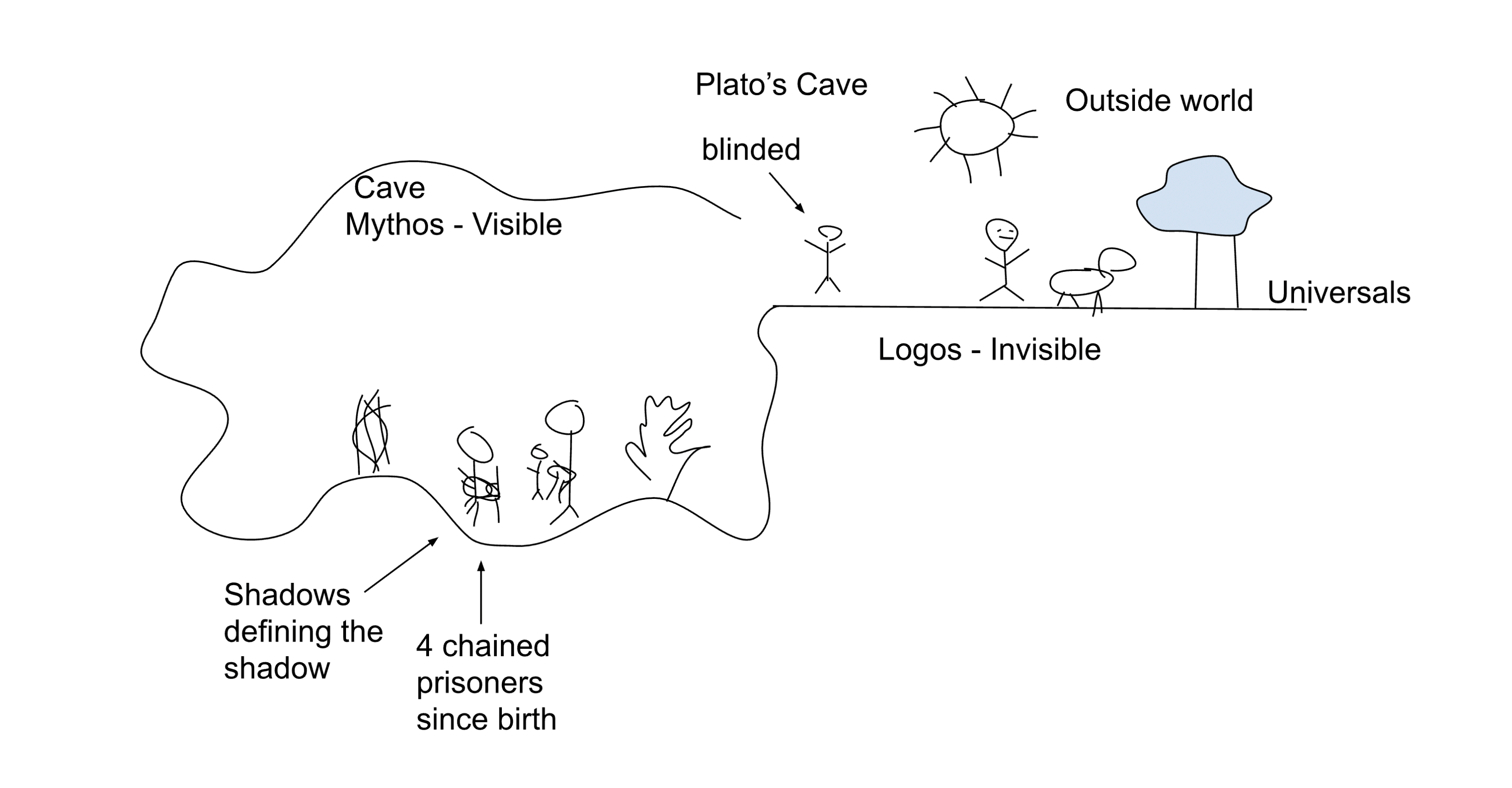
What does The Fire represent?
The fire behind the prisoners is the source of light, casting shadows on the cave wall. It represents a limited, artificial source of understanding. While it provides illumination, it is still within the confines of the cave and does not show the true nature of the objects.
Fire symbolizes the partial truths that influence our understanding of reality.
What do The Puppeteers represent?
The puppeteers are individuals who manipulate the shadows and control what the prisoners see. They represent those who control information and shape the prisoners' (or society’s) understanding of reality, often for self-interest or power.
Meaning: The puppeteers are analogous to authorities, media, or powerful institutions that manipulate information and perceptions.
What does The Escape represent?
One of the prisoners escapes the cave and slowly ascends into the world above, where he comes to understand that the shadows on the wall were mere illusions, and that true knowledge lies outside of the cave.
The journey from ignorance to knowledge
What does the The Sun represent?
Once the freed prisoner exits the cave, he is confronted by the bright light of the sun, which initially blinds him. Over time, he adjusts and realizes that the sun represents the source of true knowledge and understanding.
Meaning: The sun symbolizes the Form of the Good, which Plato considers the ultimate truth or reality.
Plato’s Line: Be able to reproduce the diagram and explain Plato’s rationale to find the most profound understanding of reality in rationality and reason as opposed to empirical experience.
The forms are unchanging ideas/realities, while the physical world is flawed and imperfect copy of the forms
Plato argues that sensory perception gives us opinions or beliefs (unreliable)and doesnʻt lead to true knowledge. Which is reflected of the line (imagination and belief)
Rational thought and intellectual reason enable us to move beyond the world of appearances to grasp universal truths about nature of reality. Math, logic, and philosophy are examples of disciplines where the mind works with abstract concepts and eternal truths.
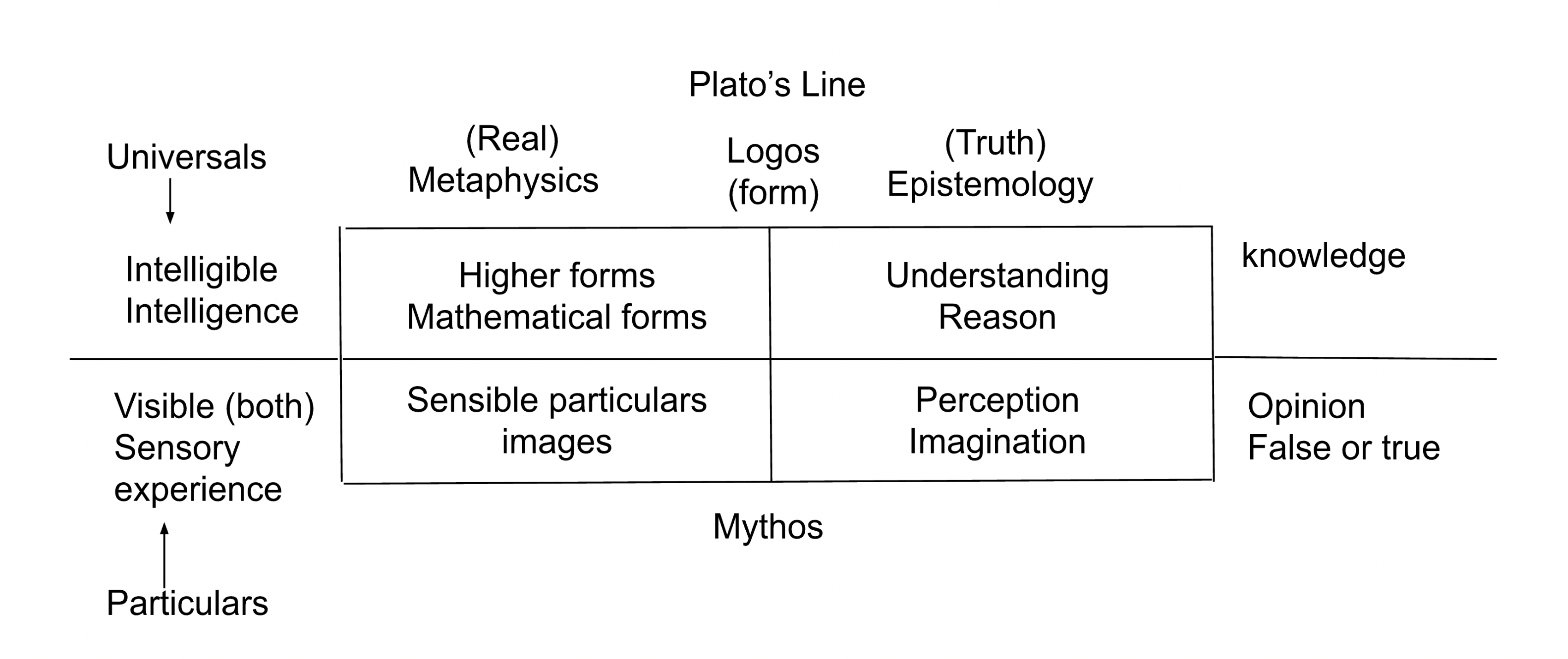
What is Logos?
principle of rationality; ordering the principles of the universe
What is Mythos?
sensory experience/common sense
What is Rationalism?
knowledge is based on logic and reason
What is Empiricism?
knowledge is based on experience and experimentation
Be able to clearly articulate Aristotle’s philosophy of universals and particulars, substance and accidents, his description of “causes” (Material cause, Formal cause, Efficient cause, Final cause) and the connection of movement to the defining of reality and importance of Potentiality and Actuality
What is Universal?
general concepts or properties that can be predicated of many individual things (help us understand and organize world
What is Particulars?
individual, concrete things in world that exemplify universals (universals only exist in particulars)
What is Substance?
in what exists in itself (ousia)
What is Accidents?
Qualities that inhere in a substance but not essential to its existence
Material:
what is it made of?
Formal:
what form does the material take?
Efficient:
who or what caused this thing to exist?
Final:
nature/purpose of this thing? Why does it exist? (teleological)
Actuality:
What something is now? (pine cone)
Potentiality:
What something will become? (pine tree)
What is the ultimate good for Aristotle? How does he determine this? and why is this teleological? How did Aristotle come to this conclusion?
Central to his ethics is eudaimonia (happiness) which aristotle argues is highest good and ultimate purpose of human life.
What is Rational vs Non Rational?
Intellect vs Emotion
What is Vegetative vs Appetitive
concerned with basic biological vs concerned with desires and emotions
What is an example of a Valid Syllogism?
All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.
What is Validity?
“If” premises are believed to be true can’t it be false?
What is a Counterexample?
All men are mortal. Socrates is mortal. Therefore, Socrates is a man.
not all mortal things are men, there are other mortal creatures
What are the fallacies we learned?
• Affirming the Consequent: If P then Q, Q therefore P
• Post Hoc : “post hoc ergo propter hoc” means, literally, “after this therefore because of this.”
• Straw Man – Find one weak part or minutiae of opponent’s argument or reframe argument into a weakened form in order to “knock it down” .
• Ad Hominem – Attack the speaker not the statement.
• Appeal to Popularity/Authority/Force/Fear/Pity
• Fallacy of Many Questions – “How many school shootings should we tolerate before we change the gun laws?”
What is the primary argument of the skeptics? (In light of Aristotle/Plato)
No certainty if there’s true, good, real because limited by sensory experience
What is the nature of the “Good” according to the Pyrrhonists?
Suspension of judgement which includes moral questions that were good or bad. If you want to achieve (ataraxia), you cannot be troubled by conflicting beliefs. Tranquility can be achieved through suspending judgement and not being troubled by conflicting beliefs.
What is Materialism?
view that everything in universe is made of thoughts, feelings, and consciousness (matter)
Real and good:
1. Good: tied to pleasure but not pursuing any and every desire
Knowledge can be gained through observation of nature
2. Reality: rejected, gods, spirits, and souls