Ch. 8 Alkene Reactions & Synthesis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Alkene addition reaction types
You can add…
Halogen —> 1,2-dihalide
Hypohalous acid (HOX) —> halohydrin
H2O —> alkane
1 oxygen —> epoxide
2 hydroxyl group —> 1,2-diol
If the electrophile is a small atom (like H)
a carbocation intermediate will form
If the electrophile is a larger atom (like a halogen)
a 3-membered ring intermediate is formed
Four ways to prepare alkenes via elimination reactions
dehydrohalogenation, dehydration, dehydrogenation, dehalogenation
The preparation of alkenes is dominated by
elimination reactions (Ex. the loss of HBr from an alkyl halide to form an alkene, or the loss of H2O from an alcohol to form an alkene)
Dehydrohalogenation
“Lose-hydrogen-& halogen”
Removes hydrogen and adjacent halogen to form alkene using 1, 2, or 3 alkyl halides as a reactant and a strong base or strong bulky base

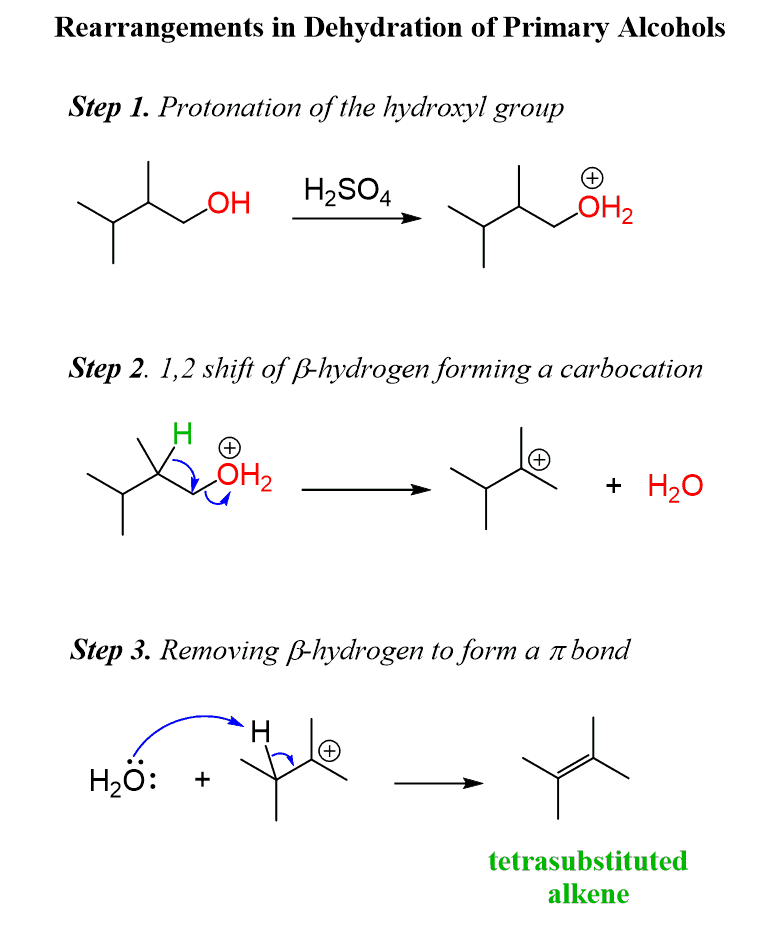
Dehydration
“Lose-water”
Loss of water from an alcohol to form an alkene using a strong acid (H2SO4), tertiary reactants best and carbocation intermediate formed so REARRANGEMENTS POSSIBLE!!!
Dehydrogenation
“Lose-hydrogen”
Removal of H2 from alkane using heat and a catalyst (Pd or Pt) to form alkene, results in multiple products
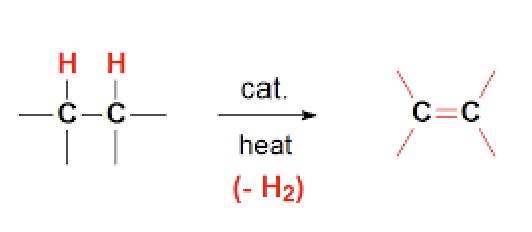
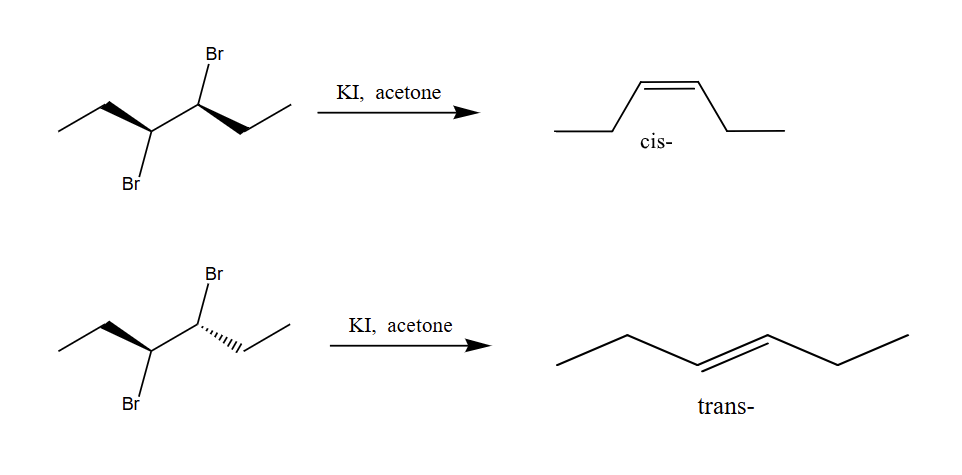
Dehalogenation of Vicinal Dibromides
“Lose halogen”
Both bromides removed by KI or ZN in CH3COOH (acetic acid), halogens are ANTI to each other…stereochemistry of reactants = stereochemistry of products (if reactant cis then product cis)
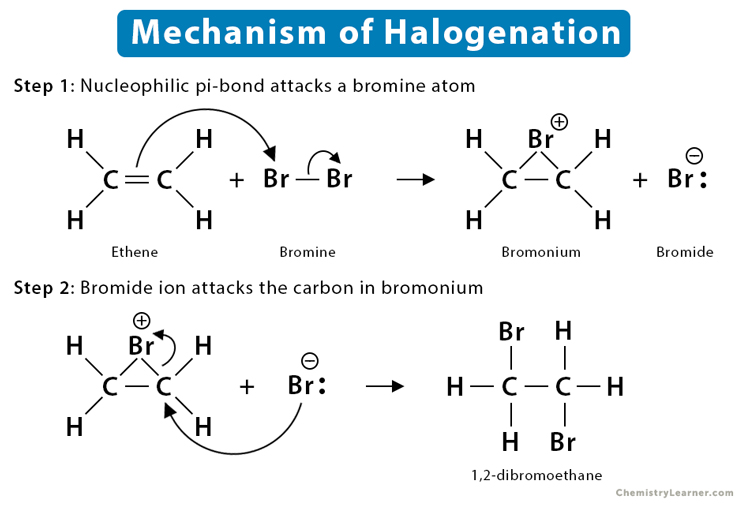
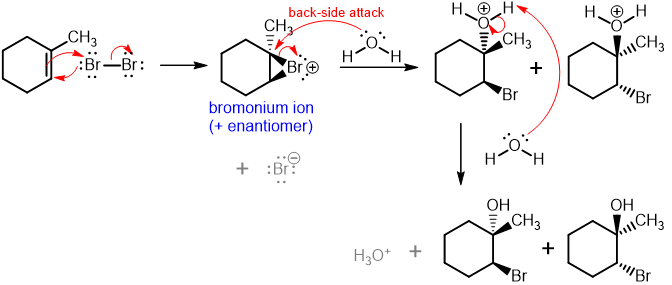
Halogenation of Alkenes
“Add halogen”
Addition of HX (Br or Cl) to form a 1,2-dihalide. Bromonium or chloronium ion intermediate forms. Anti-stereochemistry reaction: halogens attack from opposite faces (“backside attack”). No regiochemistry/Markovnikov product b/c adding same atom (H2)
Halohydrin
“Add halogen and hydroxide”
Addition of HO-X to alkene using halogen (Br or Cl) and water to form a Markovnikov halohydrin. Bromonium or chloronium ion intermediate forms. Bromohydrin in DMSO solvent and using NBS.
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
Addition of H and OH to an alkene using water and a strong acid (H2SO4 or H3PO4) to form Markovnikov alcohol, can also just be H3O+. Carbocation intermediates possible.
Oxymercuration-Demercuration Hydration of Alkenes
Addition of H and OH to alkene using mercuric acetate [Hg(OAc)2] with water (1st step) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (2nd step) to form Markovnikov alcohol. Forms mercurinium ion, but NOT carbocation intermediate!!
![<p>Addition of H and OH to alkene using mercuric acetate [Hg(OAc)2] with water (1st step) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4) (2nd step) to form Markovnikov alcohol. Forms mercurinium ion, but NOT carbocation intermediate!!</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/94048e0b-974a-4d2d-bb9e-c1f8b2060a9b.png)
Hydroboration-Oxidation Hydration of Alkenes
“Adds hydrogen and boron”
ANTI-MARKOVNIKOV addition of H and OH to alkene using boran (BH3) and THF (1st step) and peroxide (H2O2) under basic conditions (NaOH) (2nd step). Transition state and triborane intermediate formed.

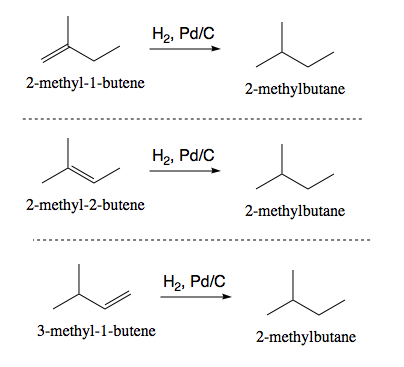
Catalytic-Hydrogenation Reduction of Alkenes
Forms alkane from alkene using H2 & a catalyst (Pd, Pt, Ni). No regioselectivity b/c H2 = no markovnikov product. Stereoselectivity b/c syn addition of H2.
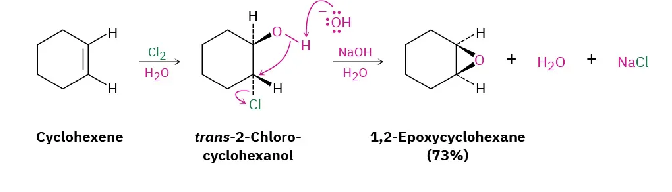
Epoxidation Oxidation of Alkenes
Forms epoxide (cyclic ether R—O—R in 3-membered ring) from oxidizing alkene with peroxyacid (RCO3H…Ex. mCPBA). Oxygen adds with syn-stereochemistry
Hydroxylation Oxidation of Alkenes
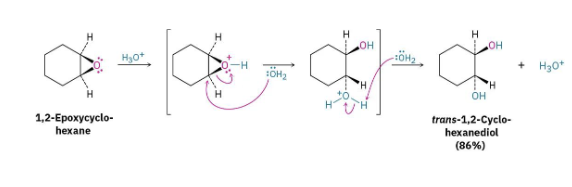
Forms 1,2-diol by using water (hydrolysis) and catalytic acid (H3O) on epoxide. Two OH groups added with anti-stereochemistry b/c being added to ring.
Hydroxylation using OsO4 Oxidation of Alkenes
Directly forms 1,2-diol without an epoxide intermediate by treating alkene with osmium tetraoxide (OsO4). Two OH groups added with syn-stereochemistry.

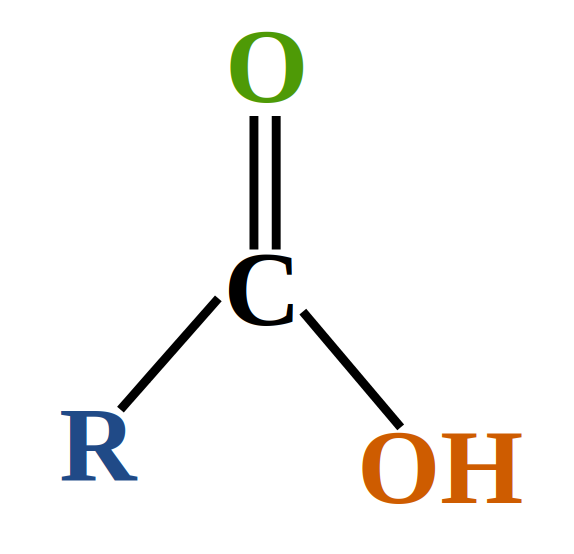
ketone
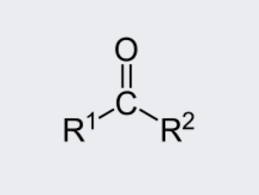
carboxylic acid
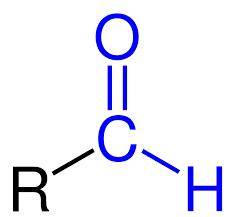
aldehyde
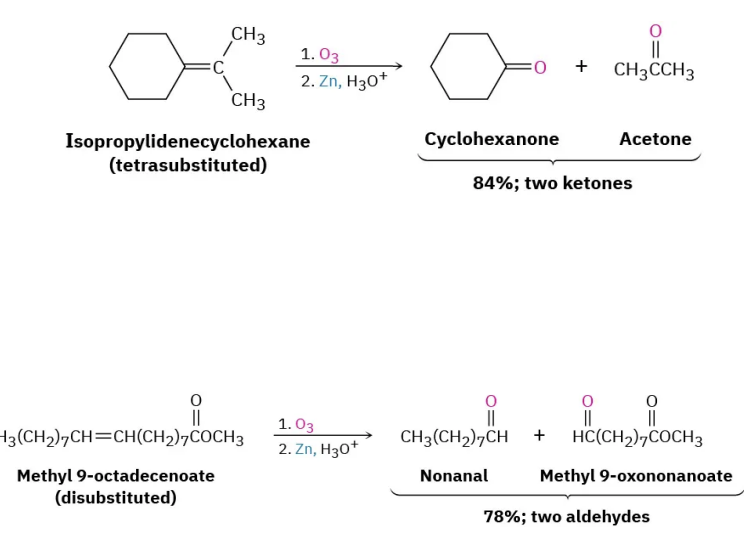
Cleavage to Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation of Alkenes
Forms 2 carbonyl containing fragments from alkene C=C bonds cleaved by a strong oxidizing agent: ozone (O3), potassium permanganate (KMnO4)…can be mild, and periodic acid (HIO4)…ozonolysis. Oxygen double-bonds to each cleaved carbon.
tetrasubstituted = 2 ketones
trisubstituted = 1 ketone, 1 aldehyde
disubstituted = 2 aldehydes
Under oxidizing conditions aldehydes oxidize further into carboxylic acids.
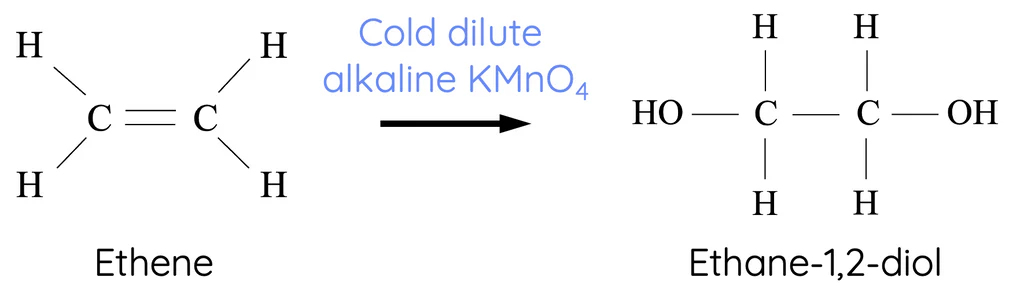
Mild Oxidation of Alkenes
KMnO4, NaOH (aq), cold = CIS 1,2-diol
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes
KMnO4, H2SO4 (aq), heat = ketones, carboxylic acids, and sometimes CO2
Carbenes
neutral molecule thats only ever a reaction intermediate, electron deficient, highly reactive, behaves as electrophile when reacting with alkenes, stereospecific
Dichlorocarbene formed by reaction of chloroform (CHCl3) with strong base (Ex. KOH). When dichlorocarbene reacts with alkene, dichlorocyclopropane forms.
Simmons-Smith Rxn uses a carbenoid instead.

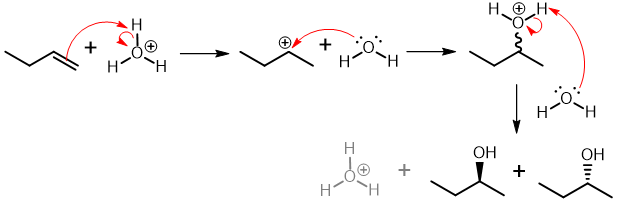
Addition of H2O to Achiral Alkene
R & S enantiomers result, cation has plane of symmetry, transition states are mirror images and equally likely to occur
Addition of H2O to Chiral Alkene
# of chiral centers found by 2^n, if 2 chiral centers then 4 possible stereoisomers, unequal amounts of products