A&P Ch.1
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Anatomy
The study of structures and the relationships among them.
Gross anatomy
The study of body structures without the use of a microscope, focusing on the body level.
Histology
The study of body structures with the use of a microscope, focusing on the tissue level.
Physiology
The study of how body structures function.
Molecular physiology
The study of the functions of proteins and DNA.
Levels of Organization
The hierarchical organization of the body, including chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, system, and organism levels.
First level of Organization
Chemical : atoms and molecules
Second level of Organization
Cells : smallest units of living matter
Third level of Organization
Tissues : groups of specialized cells
Fourth level of Organization
Organs : structures with two or more different tissues having specific functions.
Fifth level of Organization
Organ Systems : related organs having a common function.
Sixth level of Organization
Organism : collection of integrated systems (a person)
Integumentary System
The system of the body that includes the skin and associated structures, protecting the body.
Skeletal System
The system of the body that includes bones, joints, and cartilage, supporting and protecting the body.
Muscular System
The system of the body that includes mainly skeletal muscle tissue, responsible for movement, posture, and heat generation.
Nervous System
The system of the body that includes the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and special senses, detecting changes in the environment and regulating the body.
Cardiovascular System
The system of the body that includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels, circulating blood for gas and nutrient exchange.
Respiratory System
The system of the body that includes the lungs and passageways for air, facilitating oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Lymphatic/Immune System
The system of the body that includes the spleen, lymph nodes and vessels, and immune cells, controlling interstitial fluid volume and providing immunity.
Endocrine System
The system of the body that includes hormone-producing glands and cells, regulating body activities through hormones.
Digestive System
The system of the body that includes the gastrointestinal tract and organs, breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
Urinary System
The system of the body that includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, filtering urinary waste and controlling water volume and acid/base balance.
Reproductive System
The system of the body that includes the male and female gonads and reproductive structures, responsible for fertilization and gestation of a new organism.
Palpation
The noninvasive technique of feeling body surfaces with the hands to assess certain aspects of body structure and function.
Auscultation
The noninvasive technique of listening to body sounds to evaluate the functioning of certain organs.
Percussion
The noninvasive technique of tapping on the body surface with the fingertips and listening to the resulting echo.
Characteristics of Living Things
Metabolism, responsiveness, movement, growth, differentiation, and reproduction.
Metabolism
sum of all chemical processes that occur in the body
Responsiveness
ability to detect and respond to changes in the external or internal environment
Movement
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells, or even organelles inside cells
Growth
an increase in size and complexity, due to an increase in the number and/or size of cells
Differentiation (development)
the change in a cell from an unspecialized to a specialized state
Reproduction
the formation of new cells for growth, repair, or replacement, or the production of a new individual
Homeostasis
The condition of equilibrium or balance in the body's internal environment.
To function and survive body cells require:
Precise chemical composition , perfect temperature , Narrow range of atmospheric pressure , Oxygen and Nutrients
Feedback system has three components:
Receptors, Control Center , and Effectors
Receptors
detects changes in the internal or external environment.
Control Center
receives and processes information from the receptor.
Effector
responds to the commands of the control center by either opposing or enhancing the stimulus.
Negative Feedback
A feedback system in which the response reverses the original stimulus.
Positive Feedback
A feedback system in which the response enhances the original stimulus.
Homeostatic Imbalances
Disorders and diseases that disrupt the structure or function of the body.
disorder
any abnormality of structure or function
Disease
illness (disruption generally caused by foreign “invader”) and characterized by recognizable set of signs and symptoms.
signs
what clinician can see (objective)
symptoms
what patient can feel (subjective)
Diagnosis
The art of distinguishing or determining the nature of one disease or disorder from another through medical history and physical examination.
Anatomical Position
A standardized position that allows precise anatomical reference, including standing erect, facing the observer, arms at the sides with palms turned forward, and feet flat on the floor.
Regional Names
Specific locations on the body.
Directional Terms
Terms used to precisely locate one part of the body relative to another.
Planes/Sections
Imaginary flat surfaces used to divide the body into different halves.
Body Cavities
Spaces within the body that protect, separate, and support internal organs.
Cranial
Brain cavity
Vertebral
contains spinal cord
Thoracic Cavity
The five organs in your thoracic cavity are your heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea and thymus.
pleural
contains lungs
Pericardial Cavity
encloses the heart and also surrounds the remaining thoracic organs (esophagus, trachea, and others)
Medial Mediastinum
contains the pericardial cavity
Abdominopelvic Cavity
seperated from thoracic cavity by the diaphram, a dome shaped muscle important in breathing. Has abdominal and pelvic cavities
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Serous Membranes
Membranes that protect cavities and organs within them.
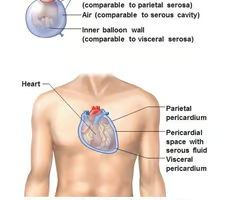
Visceral membrane
membrane closest to organ
Parietal membrane
outermost membrane
Radiography
Imaging technique that uses low-dose x-rays to visualize internal structures. The more dense the tissue, the whiter it appears
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Imaging technique that uses a powerful magnet to align protons in tissues and visualize images on a monitor, particularly useful for soft tissue.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
Imaging technique that takes X-rays in a series of sections to create a 3D image or video, providing detailed views of soft tissues and organs.
Ultrasound
Imaging technique that uses sound waves to bounce off internal structures, commonly used for pregnancy and visualizing organs and tumors.
Endoscopy
Imaging technique that uses a small camera to view internal cavities, commonly used for procedures like colonoscopy.
Facial
Face
Frontal
Forehead
Orbital
Eyes
otic
Ears
Nasal
Nose
Buccal
Cheeks
Oral
mouth
Mental
chin
Occipital
lower back of head
Cervical region
Entire neck; neck of something
Cephalic region
Entire head
Sternal
Sternum
Pectoral
Entire chest either side of sternum
Mammary
boobs
Umbilical
Belly button
Coxal
hips
pubic
pubic bone
Scapular
shoulder blades
Vertebal
spine
lumbar
not the lowest back but right above it
Axial region includes:
Makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk.
Appendicular region includes:
relating to the limbs and their attachments to the axis.
Acromial
point of the shoulder
Axillary
Armpit
Brachical
Entire upper arm
antecubital
where blood gets drawn
Olecranal
Elbow (dorsal)
Antebrachical
lower forearm
carpal
wrist
manual
whole hand
palmar
palm