Muscle Contraction Types
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Muscle tension
Force generated by a muscular contraction
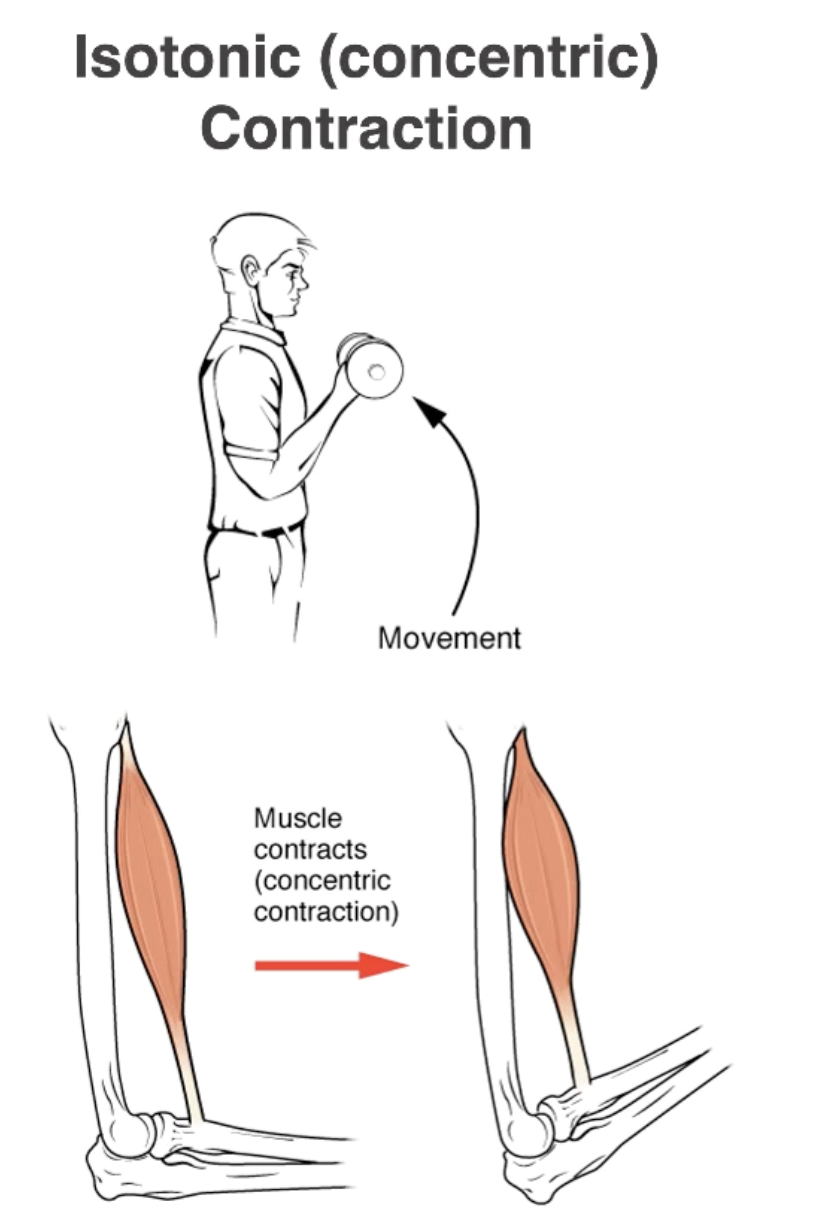
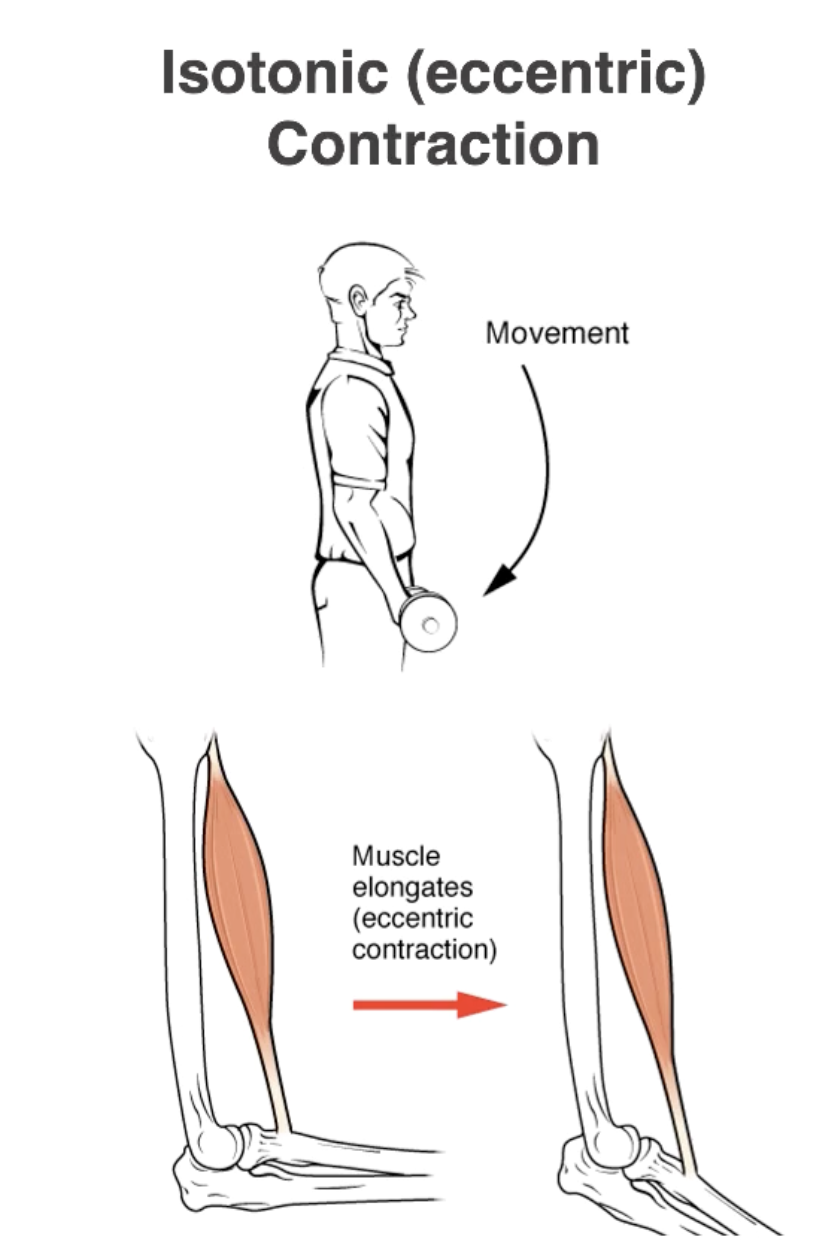
Isotonic Contractions
Iso - Same
Tonic - Tension
Tension in the muscle remains constant.
Length of the muscle changes.
Two types:
Concentric contraction (Shortens)
Eccentric contraction (Lengthens)
Concentric Contraction
Muscle Shortens
Eccentric Contraction
Muscle Lengthens
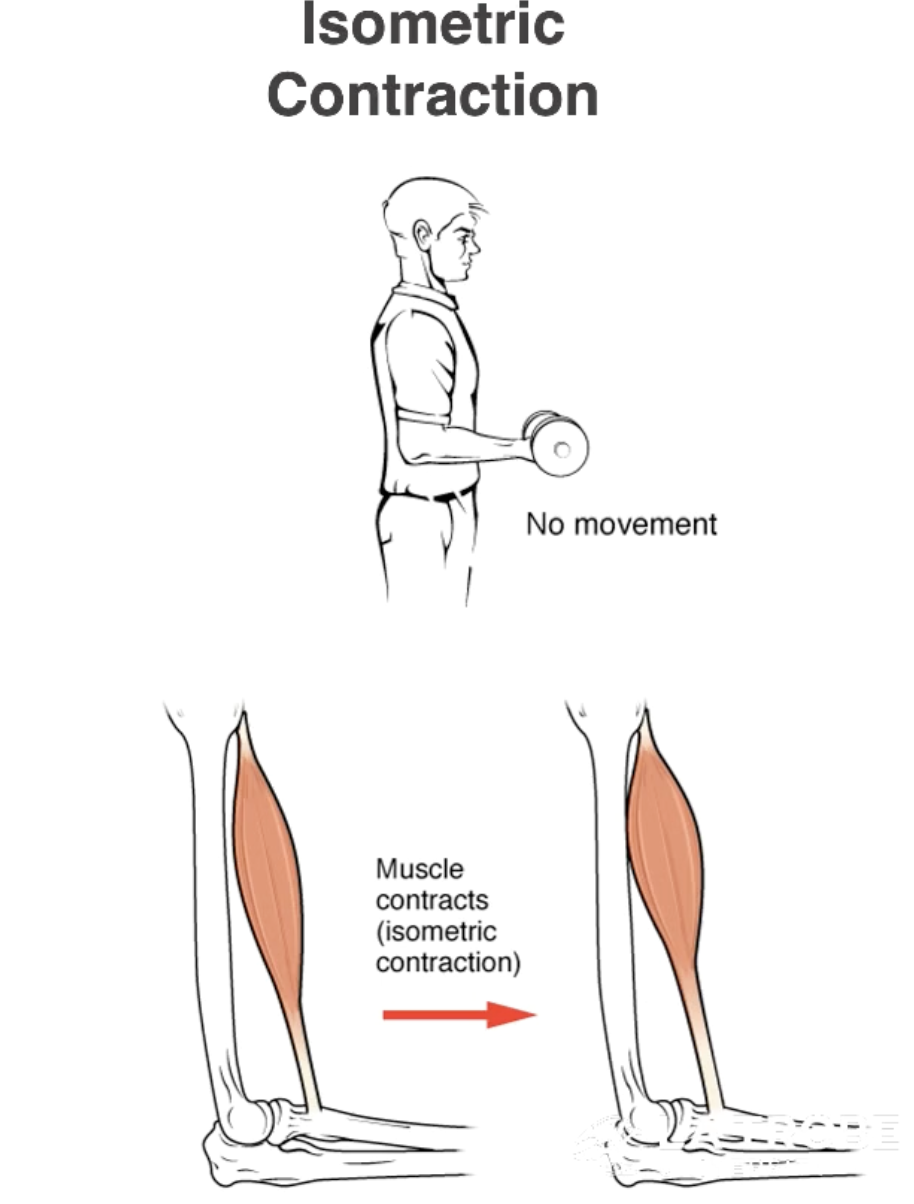
Isometric contraction
Iso - Same
Metric - Length
Tension in the muscle remains constant.
Length of the muscle remains constant.
Why does the muscle length not shorten for all contractions?
The connective tissues present ant tendons hold the muscle tight in position during all contractions.
Sarcomeres do get shorter
However overall muscle length with the tendons and connective tissue can vary dependent on the contraction
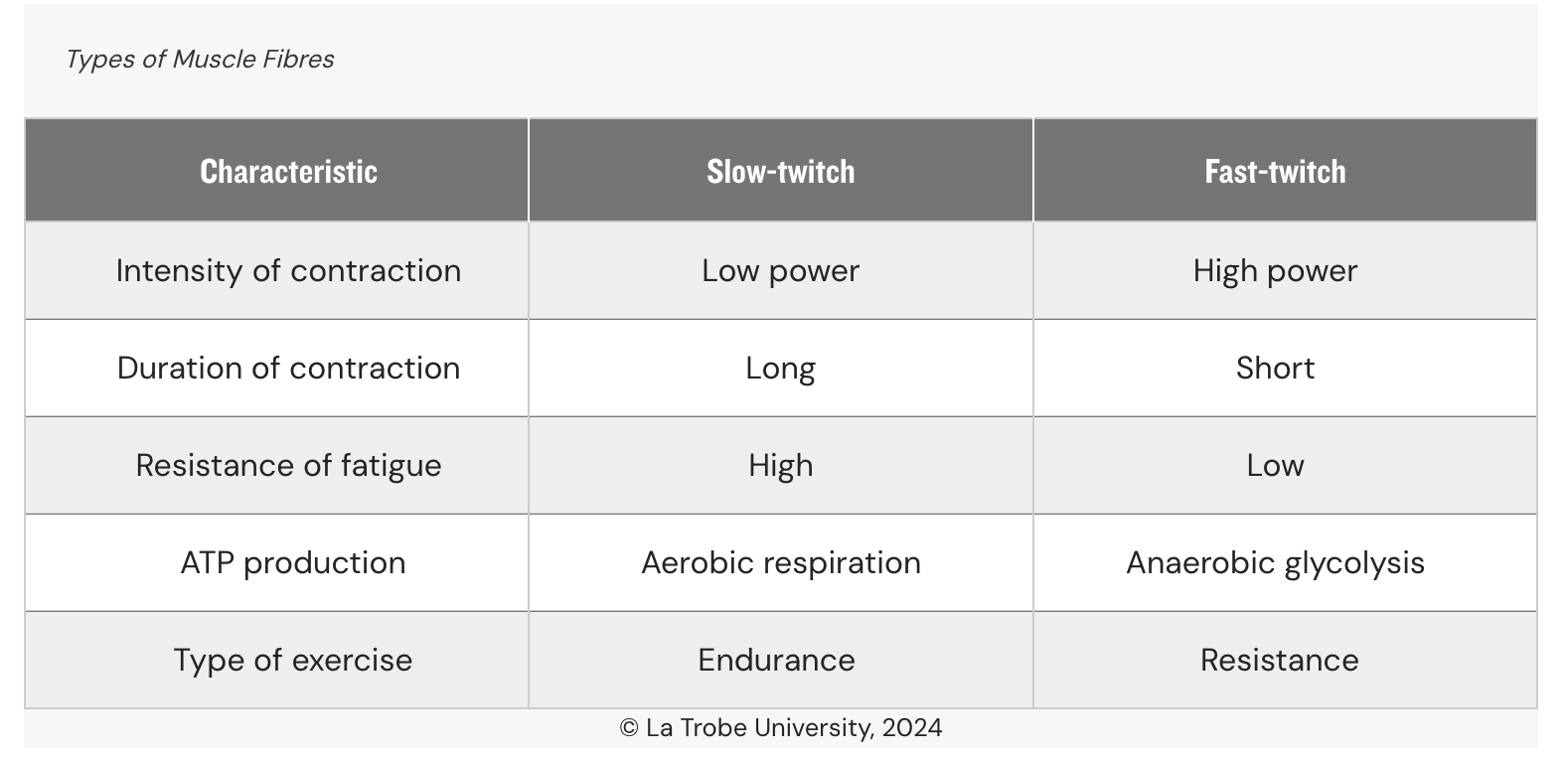
Muscle Fibre types:
Slow Twitch Fibres
Contract very slowly
Aerobically respirate to product ATP
Need more oxygen
Can function for long periods sans fatigue
Suitable for endurance exercise
Muscle Fibre types:
Fast Twitch Fibres
Contract very quickly
Anaerobic glycolysis to product ATP
Do not need much mitochondria
Do not need oxygen to contract
Can function for short periods, fatigue quickly
Rapid/forceful contractions
Suitable for resistant exercise
Muscles get thicker

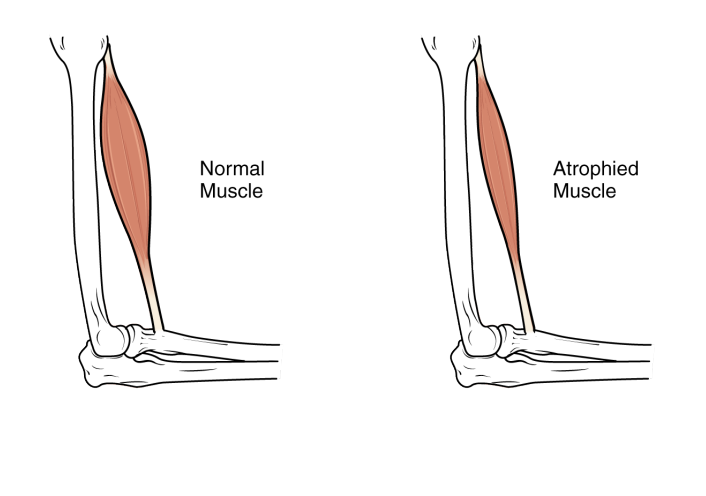
Sarcopenia
Muscle gets weaker and smaller, atrophies.
Age-related condition, irreversible.
Muscle cells begin to die with age, replaced with connective and adipose tissue.
Ability to produce powerful contractions declines
Can be delayed to some extent with age