Molecular Biology: Viruses + Vaccines
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i recommend turning on override answers in case you get the correct meaning but not wording :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
is a virus living or non-living?
non-living
what did Martinus Beijerinck do?
he coined the term “virus”
what did Wendell Stanley do?
he proved viruses were particulate
what did James Watson do?
he published a paper describing viral structure (also used electron microscope to confirm)
what unit are viruses measured in?
nanometers
each nanometer corresponds to what number of a meter?
one billionth of a meter
all viruses possess what features?
capsid and nucleic acid
what are the optional virus features?
lipid envelope and protein spikes
what is a capsid?
a crystalline protein coat
what makes up a capsid?
capsomeres
what is nucleic acid?
the virus’s core of either DNA or RNA
what is the lipid envelope?
a protective layer that encloses some viruses
what are protein spikes?
they are similar to a key as they help the virus to bind to a host cell’s receptors
what do we call a virus without an envelope?
naked
what is the name of this basic virus shape?
complex/mixed
what is the name of this basic virus shape?
spherical
what is the name of this basic virus shape?
polyhedral
what is the name of this basic virus shape?
helical
how are viruses classified?
by families
what are the four sections of classifying viruses into virus families?
genome, morphology, physical properties, and biological properties
what factors are there in classifying by genome?
DNA or RNA, number of chromosomes, double (ds) vs single (ss) stranded
what factors are there in classifying by morphology?
size, shape, symmetry, envelope
what factors are there in classifying by physical properties?
mass, pH stability, thermal stability
what factors are there in classifying by biological properties?
host range, pathogenicity
all virus family names end in what?
-viridae
why do viruses exist?
to replicate
where do viruses replicate?
inside of a host cell
what are the two cycles of virus replication?
lytic and lysogenic
true/false: viruses are usually not host specific.
false
the common cold, influenza, and rabies are all examples of which cycle?
the lytic cycle
herpes and chickenpox are examples of which cycle?
lysogenic
what is the first step in the lytic cycle?
attachment
what happens during attachment (lytic)?
the virus lands on the host cell and attaches to its receptors
what is the second step in the lytic cycle?
entry/penetration
what happens during entry/penetration (lytic)?
viral DNA or RNA enters the host cell, and the host’s DNA is destroyed
what is the third step of the lytic cycle?
replication/biosynthesis
what happens during replication/biosynthesis (lytic)?
viral DNA is replicated, transcription, translation
what is transcription?
when viral mRNA is made
what is viral mRNA?
the code to make more viral parts
what is translation?
when the mRNA travels to ribosomes, where viral proteins are made
what is the fourth step in the lytic cycle?
assembly/maturation
what happens during assembly/maturation (lytic)?
new viruses self-assemble in the cytoplasm
what is the fifth (last) step in the lytic cycle?
release/lysis
what happens during the release/lysis (lytic)?
the viral DNA shares a code to make an enzyme that causes the host’s cell membrane to lyse/burst. viruses are released, the host dies, and the cycle repeats
what is the first step in the lysogenic cycle?
attachment
what happens during attachment (lysogenic)?
the virus lands on the host cell and attaches to its receptors
what is the second step of the lysogenic cycle?
entry/penetration
what happens during entry/penetration (lysogenic)?
viral DNA or RNA enters the host cell and fuses with the host’s DNA
what is a provirus?
when the viral nucleic acid fuses with the host cell’s DNA
what happens between the second and third steps of the lysogenic cycle?
the latent period
what is the latent period?
a resting period where the infected cell performs mitosis (cell division) and makes copies of the provirus
what ends the latent period?
triggers
what are examples of triggers?
stress, sunburn, menstruation, pregnancy, aging
what is the third step of the lysogenic cycle?
replication/biosynthesis
what happens during replication/biosynthesis (lysogenic)?
viral DNA is replicated, transcription, translation
what is the fourth step in the lysogenic cycle?
assembly/maturation
what happens during assembly/maturation (lysogenic)?
new viruses self-assemble in the cytoplasm
what is the fifth (last) step in the lysogenic cycle?
release/lysis
what happens during the release/lysis (lysogenic)?
the viral DNA shares a code to make an enzyme that causes the host’s cell membrane to lyse/burst. viruses are released, the host dies, and the cycle repeats
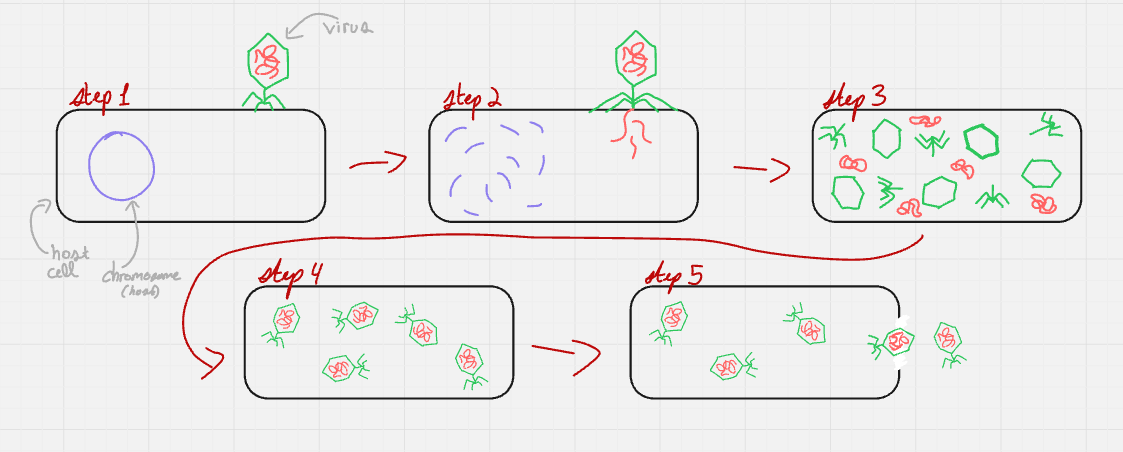
what cycle does this represent?
lytic
what cycle does this represent?
lysogenic
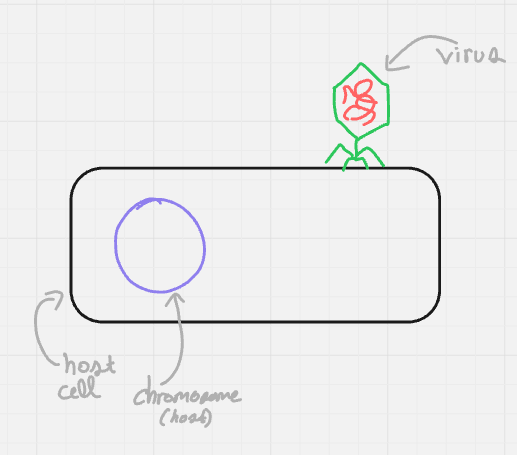
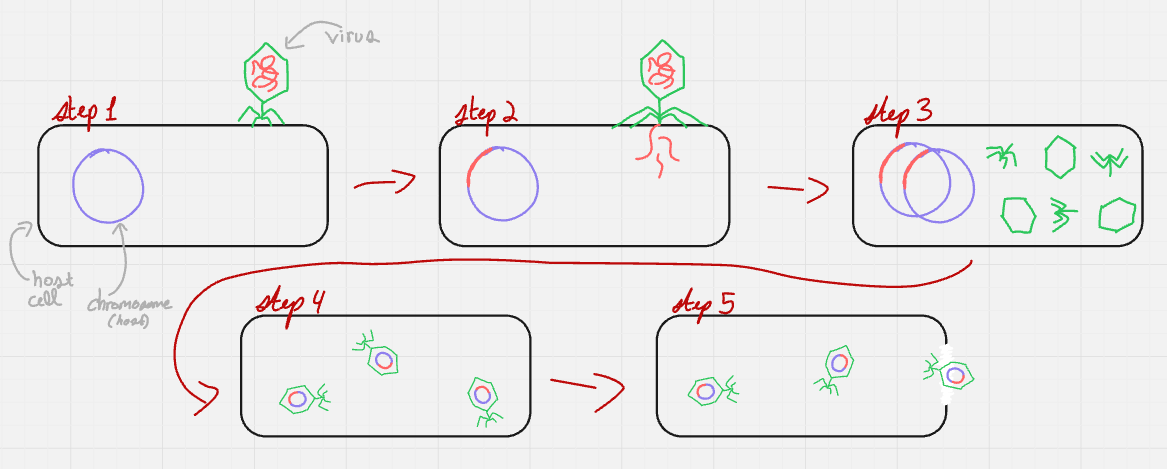
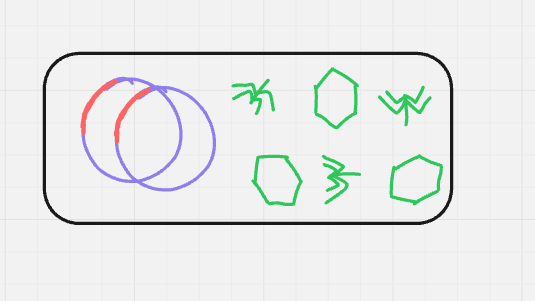
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lytic and lysogenic, attachment (1)
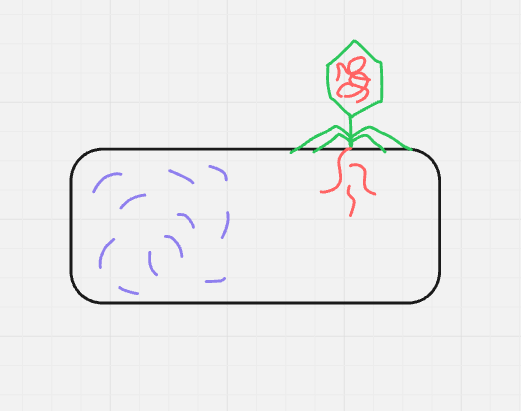
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lytic, entry/penetration (2)
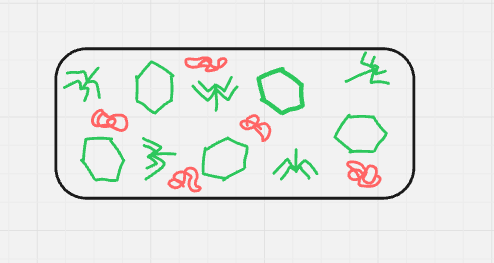
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lytic, replication/biosynthesis (3)
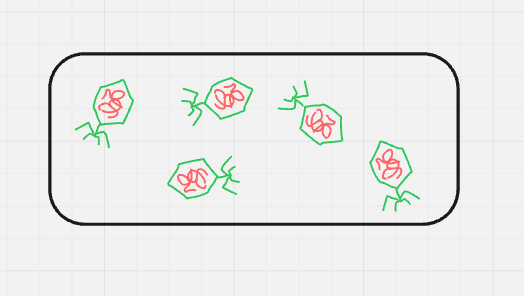
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lytic, assembly/maturation (4)
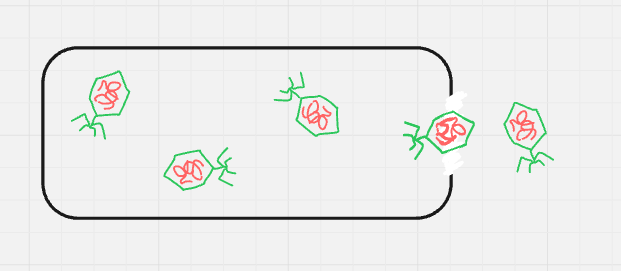
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lytic, release/lysis (5)
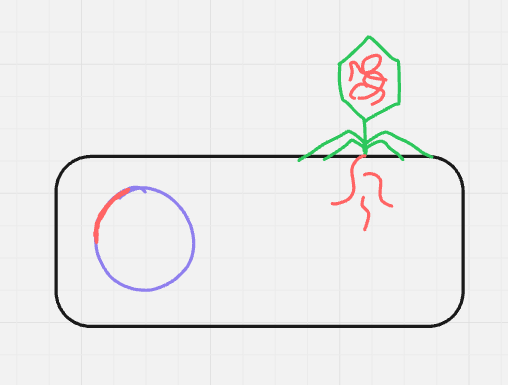
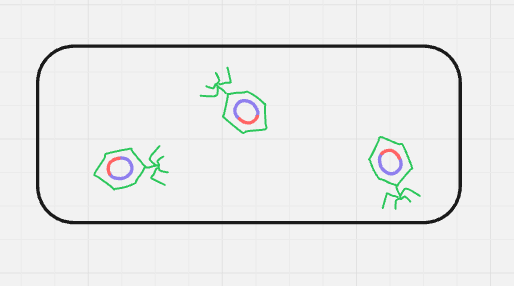
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lysogenic entry/penetration (2)
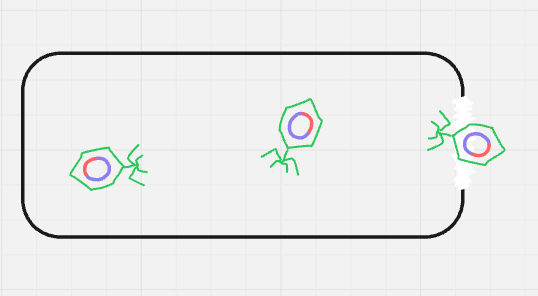
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lysogenic, replication/biosynthesis (3)
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lysogenic, assembly/maturation (4)
what cycle + step is this? (format: cycle name, step name (#))
lysogenic, release/lysis (5)
what does budding mean?
when the virus pushes out of the host’s membrane without using enzymes
what nucleic acid does influenza have?
RNA
true/false: influenza is enveloped.
true
true/false: influenza has surface proteins/protein spikes.
true
how many types of influenza are there?
four
what type of influenza does not infect humans?
influenza D
what type of influenza is the most virulent/dangerous?
influenza A
how many types of protein spikes does influenza A have?
two
what does the protein spike “H” stand for?
hemagglutinin
what does the protein spike “N” stand for?
neuraminidase
how many types of hemagglutinin (H) are there?
18
how many types of neuraminidase (N) are there?
11
what does hemagglutinin (H) do?
helps the virus attach to the host cell
what does neuraminidase (N) do?
helps the virus to be released when replicated
how is influenza A classified?
by subtypes
how are the subtypes created?
based on the combination of H and N proteins
true/false: influenza A is host specific.
false
how is influenza B classified?
by lineages
what are the two lineages of influenza B?
Yamagata and Victoria
what part of influenza makes us need an annual flu vaccine?
the RNA
why does having RNA instead of DNA make a difference for the influenza vaccine?
RNA is extremely error prone, and it has high mutation rates
what is antigenic drift?
the natural mutation over time of known strands of influenza
what is antigenic shift?
when two different strands of a virus combine to form a new subtype
why is antigenic shift more dangerous than drift?
it is unpredictable
what is a vaccine?
a means of producing immunity against pathogens by the introduction of live, killed, or altered antigens that stimulate the body to produce antibodies against more dangerous forms
what is an antigen?
a foreign object
what does efficacy mean?
the ability to produce a desired or intended result
what does vaccine efficacy mean?
the percent reduction in disease when comparing vaccinated and unvaccinated groups
what is herd immunity?
when enough people become immune to a disease, it makes its spread less likely
what is immunity?
the ability of an organism to resist a particular infection or toxin by the action of specific antibodies