HNSC 2170: Unit 5 (Vitamins)
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What are vitamins?
Organic compounds vital to life and body functions.
How many classes of vitamins are there?
2: fat soluble and water soluble.
What are the fat soluble vitamins?
Vitamins A, D, E, K.
"KADE"
What are the water soluble vitamins?
1. B vitamins
2. Thiamin
3. Riboflavin
4. Niacin
5. Pantothenic acid
6. Biotin
7. Vitamin b6
8. Folate
9. Vitamin b 12
10. Vitamin C
How are fat soluble vitamins absorbed?
They dissolve in lipid and require bile for absorption.
Where are fat soluble vitamins stored?
In the liver or with other lipids in fatty tissues.
What can happen if fat soluble vitamins build up to toxic levels?
They can become toxic.
What is the first fat soluble vitamin recognized?
Vitamin A.
What are the three active forms of vitamin A in the body?
Retinol, retinal, and retinoic acid.
What is b-carotene?
A precursor to vitamin A found in plant-based foods.
What is the function of b-carotene?
It can be converted into active vitamin A in the body.
How much b-carotene is needed to supply 1ug of retinol?
Approximately 12ug.
What is the role of vitamin A?
vision, growth, reproduction
How are water soluble vitamins absorbed?
They are absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
Where are water soluble vitamins stored?
They are not stored in the body and are excreted in urine.
What is vitamin A deficiency?
Prevalent in developing countries, leading cause of preventable blindness in children.
What is vitamin A toxicity?
Caused by supplements and fortified foods, can weaken bones and cause malformations in fetus.
How is vitamin D synthesized in the body?
UV light converts a cholesterol compound in the skin into a vitamin D precursor, which is then converted to active vitamin D in the liver and kidneys.
What is the function of vitamin D?
Regulates blood calcium and phosphorus levels, maintains bone integrity.
What problems may be linked to low vitamin D levels?
High blood pressure, certain cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis.
How long does it take for symptoms of vitamin A deficiency to appear?
Over a year.
Who is most sensitive to vitamin A toxicity?
Children.
Can beta carotene cause vitamin A toxicity?
No, it is not converted efficiently enough to cause toxicity symptoms.
What can chronic intake of excess vitamin A do?
Weaken bones and contribute to hip fractures.
What should pregnant women be cautious of regarding vitamin A supplements?
High doses can cause malformations in the fetus.
What is the role of vitamin D in regulating blood calcium and phosphorus levels?
Maintaining bone integrity.
What are the well-established problems associated with vitamin D deficiency?
Impairment of calcium balance and bone health.
What is the leading cause of preventable blindness in children worldwide?
Vitamin A deficiency.
What is the chemical name for vitamin D?
Cholecalciferol.
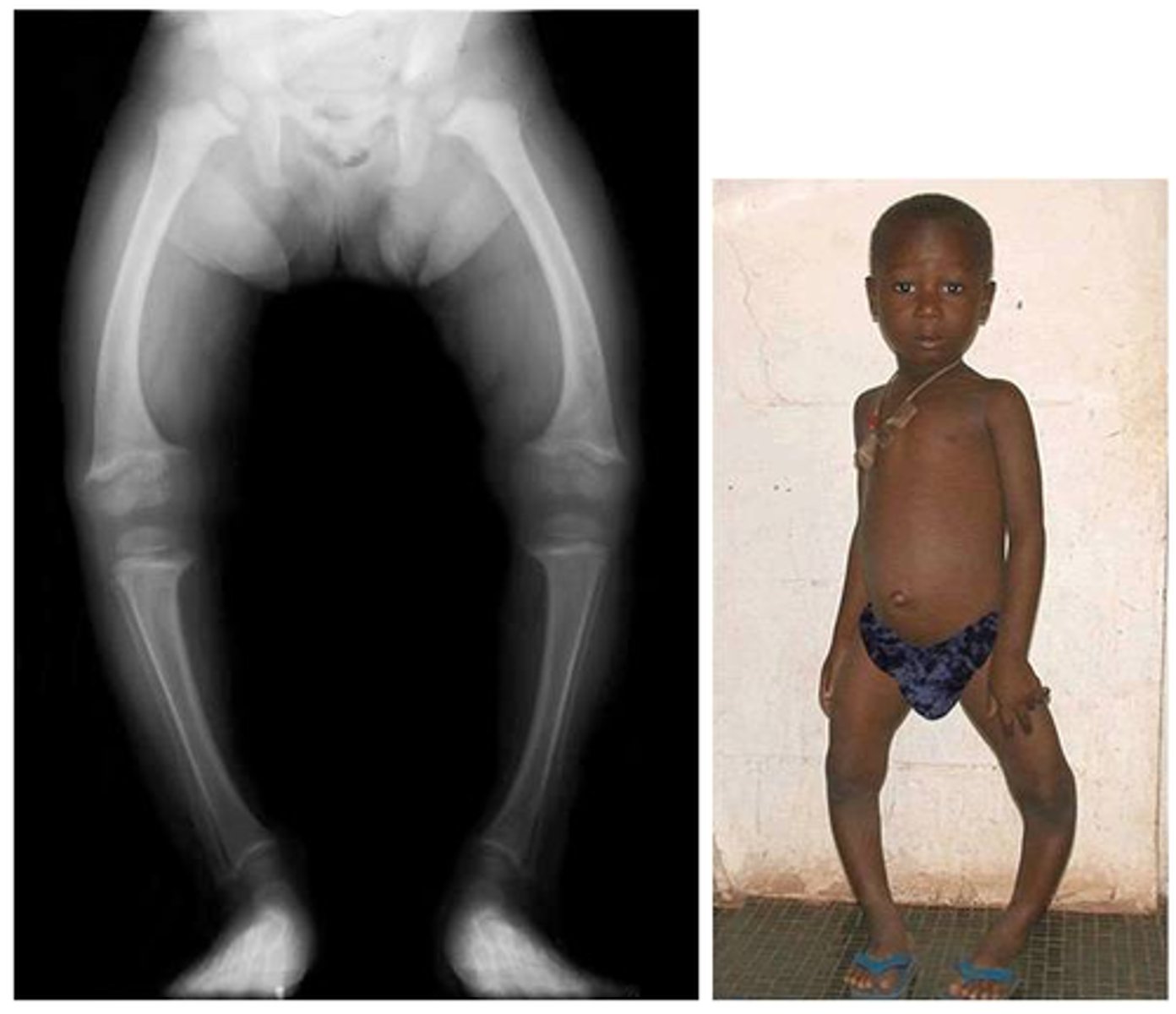
What are the two diseases resulting from vitamin D deficiency?
Rickets (in children) and osteomalacia (in adults).
What are the risk factors for vitamin D deficiency in older adults?
Lower intake, little UV light exposure, decreased activation ability
What are the major dietary sources of vitamin D in Canada?
Milk, fortified soy beverage, rice or almond beverage
What is the most potentially toxic vitamin?
Vitamin D
What is the main source of vitamin D toxicity?
Supplements
Is there a risk of vitamin D toxicity from sunlight?
No risk from sunlight
What factors affect the conversion of sunlight to active vitamin D?
Skin tone, sunscreen use, pollution, clothing, location, time of year
During which months does lack of direct sunlight prevent vitamin D activation in Manitoba?
November through March
What are some food sources of vitamin D?
Fortified milk, margarine, eggs, butter, fortified soy beverages, some fatty fish
Is breast milk a good source of vitamin D?
No, it is a low source
Is infant formula fortified with vitamin D?
Yes
What is the title of the document on the Government of Canada website that provides recommendations for vitamin D supplementation in breastfed infants?
Supplemental vitamin D is recommended for breastfed infants
What is another vitamin that is mentioned in the notes?
Vitamin E
What is the active form of Vitamin E?
Tocopherol
What is the gold standard form of Vitamin E?
Alpha-tocopherol
What is the main function of Vitamin E?
Acting as an antioxidant
Where is Vitamin E's antioxidant effect especially important?
Red blood cells and lungs
What is the potential benefit of Vitamin E in protecting against heart disease?
Protecting LDL from oxidation and reducing inflammation
Is there any benefit of Vitamin E supplements in the absence of deficiency?
No, unless a deficiency is present
What can high doses of Vitamin E supplements cause?
Harm
Why is Vitamin E deficiency rare?
Found in many foods, stored in fatty tissue, and recycled by cells
Where may Vitamin E deficiency occur?
Premature infants born before transfer from mother
Is Vitamin E toxicity common?
No, it is rare
Are there adverse effects from naturally occurring Vitamin E in foods?
No
What is the likelihood of toxicity from Vitamin E supplements?
More likely than from naturally occurring sources
What types of foods are good sources of Vitamin E?
Vegetable oils, vegetables, fruits, fortified cereals/grains, meats, meat alternatives, and milk products
What happens to Vitamin E when foods are heat processed or oxidized?
Destroyed
Which types of foods retain little intact Vitamin E?
Processed, fast foods, deep fried foods, and convenience foods
Are water soluble vitamins stored in the body?
Most are not stored in the tissue to any great extent
What happens to excess water soluble vitamins?
Excreted in the urine
What is the risk of immediate toxicities with water soluble vitamins?
Less risk
What are the functions of B vitamins?
Act as coenzymes and involved in energy metabolism
Do B vitamin deficiencies occur together?
Yes, as many food sources contain a combination of B vitamins
What are some food sources of thiamin?
Legumes, enriched/whole grain cereals, sunflower seeds, pork
What is the role of thiamin in the body?
Critical role in energy metabolism and nerve cell membranes
What is the deficiency disease of thiamin called?
Beriberi
What are the symptoms of beriberi?
Loss of sensation in hands and feet, muscular weakness, abnormal heart action
What is Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome?
Severe thiamin deficiency seen in alcohol abusers
How does alcohol contribute to thiamin deficiency?
Displaces foods, impairs absorption, speeds up excretion
Are there symptoms of thiamin toxicity?
No reported symptoms
Is there a UL set for thiamin?
No
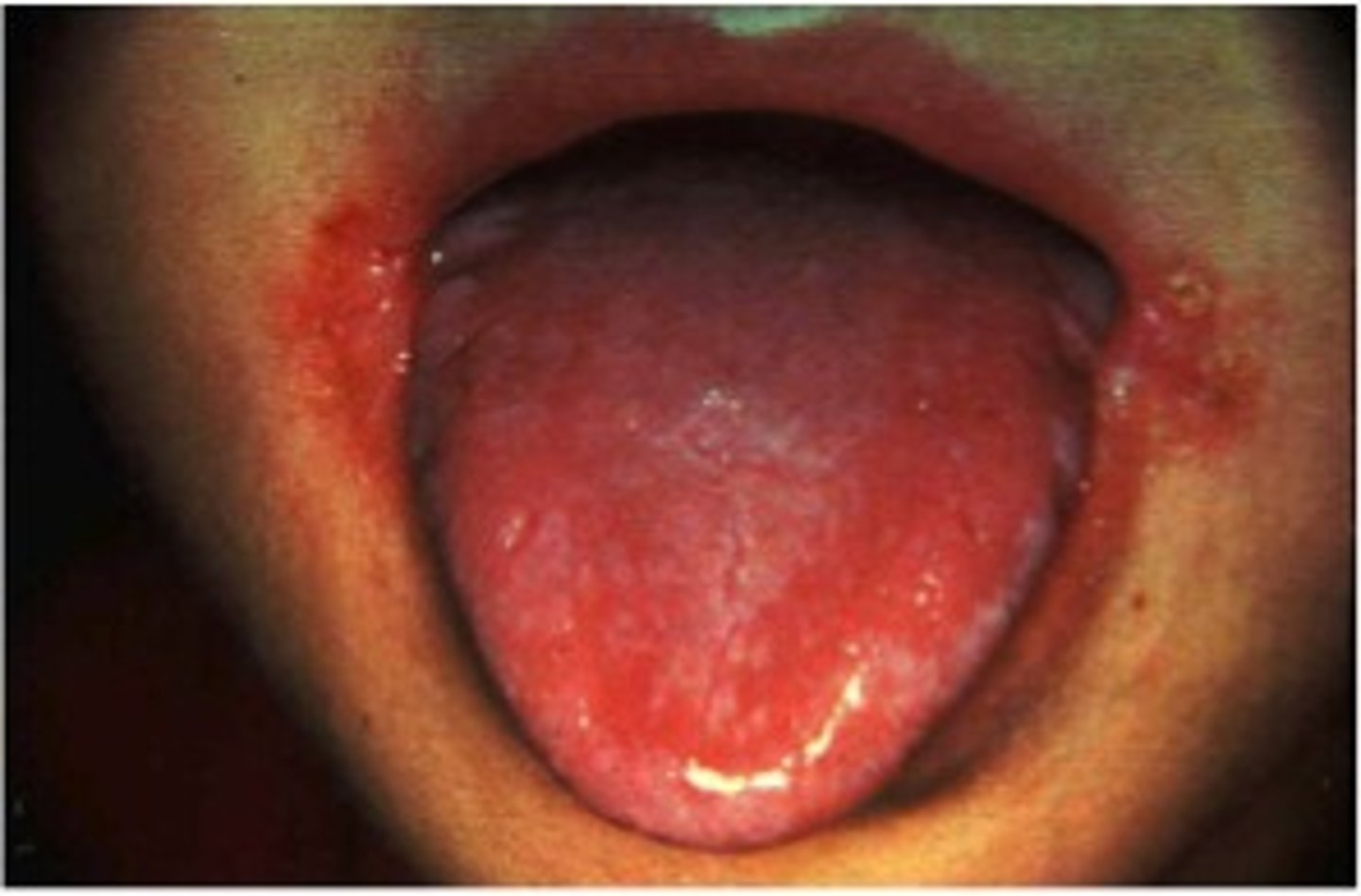
What are the functions of riboflavin?
Energy metabolism, vision, skin health
What is the deficiency disease of riboflavin called?
Ariboflavinosis
What are the symptoms of ariboflavinosis?
Sore throat, swollen mucous membranes, skin rash
Is there a UL set for riboflavin?
Yes, 35 mg/day
What are the food sources of riboflavin?
Milk products and enriched grain products.
Why is riboflavin deficiency often undetected?
Because the symptoms of thiamin deficiency are more severe.
Are there any reported symptoms of riboflavin toxicity?
No, there are no reported symptoms.
What is the UL for riboflavin?
There is no UL set at this time.
What are the functions of niacin?
Participates in the energy metabolism of all cells.
How is niacin created in the body?
Tryptophan (an amino acid) can be converted to niacin.
What are the food sources of niacin?
Almost all protein-containing foods and tryptophan.
What is the deficiency disease of niacin?
Pellagra.
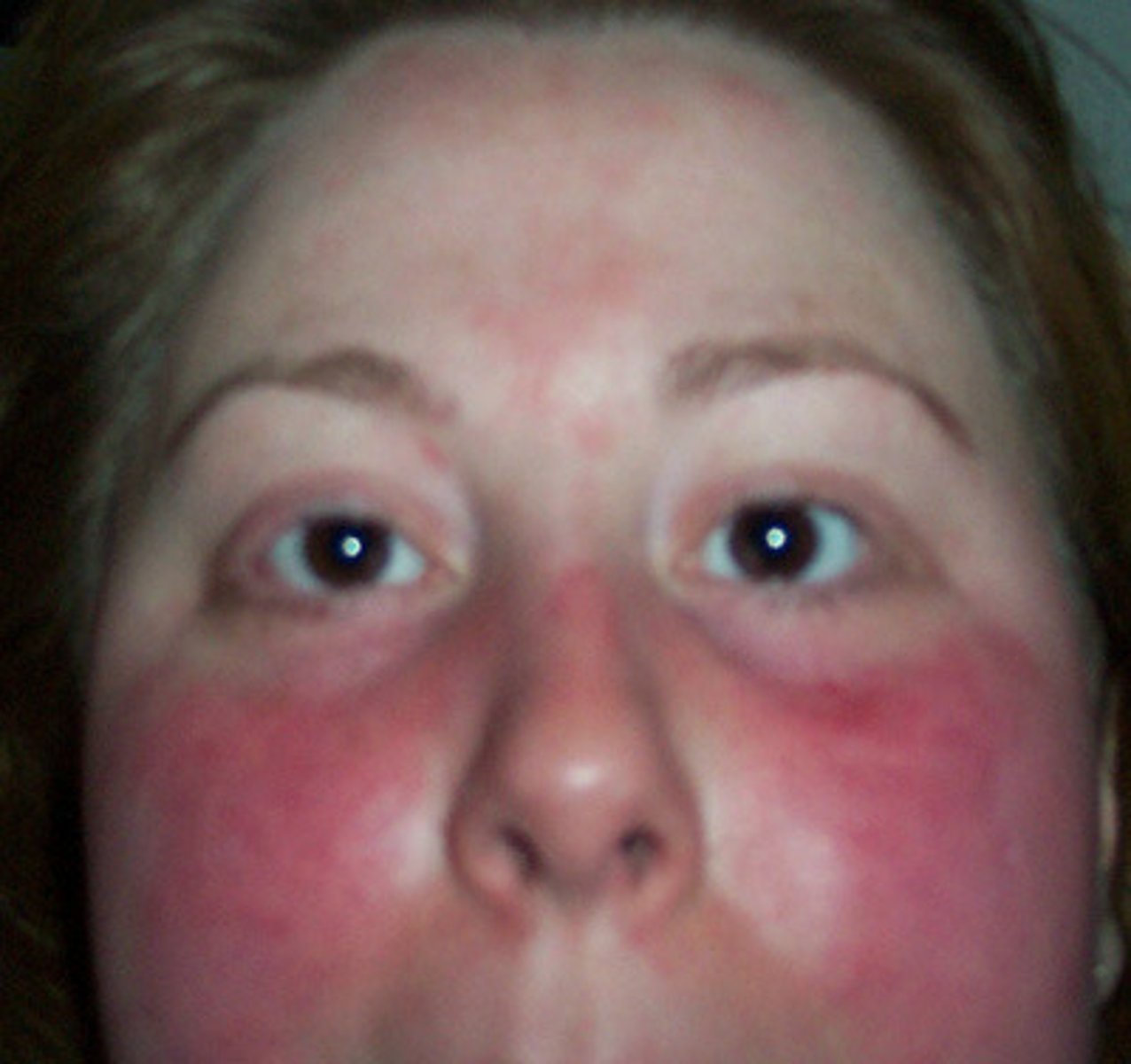
What is niacin toxicity typically linked to?
Supplement intake rather than food intake.
What is a symptom of niacin toxicity?
Niacin flush.
What should be monitored for in cases of niacin toxicity?
Liver damage.
How is niacin used as a medication?
To lower blood lipids.
What are the functions of pantothenic acid and biotin?
Both play a role in energy metabolism.
Are deficiencies of pantothenic acid and biotin common?
No, they are rare.
What are the functions of vitamin B6?
Participates in over 100 reactions in body tissues and metabolism of protein and amino acids.
What are some food sources of Vitamin B6?
Meats, fish, and poultry
What is the potential relationship between low vitamin B6 intake and heart disease?
Some evidence suggests an increased incidence of heart disease, but more research is needed
What is the danger of large doses of Vitamin B6 from supplements?
It can be dangerous
What is the function of folate (folic acid)?
Plays an important role in cell division
Which individuals are at risk of folate deficiency?
Pregnant women, elderly, alcoholics, and smokers
What are the potential effects of folate deficiency?
Associated with neural tube defects and increased risk of abnormalities in the brain and spinal cord at birth
What is the recommended daily intake of synthetic folate for women of childbearing age?
400ug/day from supplements or enriched foods
What foods have been fortified with folic acid in Canada?
White flour, enriched pasta, and corn meal
What is the concern regarding folate toxicity?
It can mask Vitamin B12 deficiency by resolving macrocytic anemia
What are some potential interactions with folate absorption in the elderly?
Many medications, such as antacids, aspirin, oral contraceptives, and anticonvulsant medications
What is the effect of decreased folate absorption in alcoholics?
Increased risk of folate deficiency