Honors Chemistry Unit 2 Test
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Democritus
Greek philosopher who was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. (believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible)
Aristotle
Greek philosopher- believed that matter is infinitely divisible. Matter is composed of earth, wind (air), fire, water
Dalton
English chemist and schoolteacher who formulated a theory to describe the structure and chemical reactivity of matter in terms of atoms
Thomson
Discovered the Electron using the Cathode Ray Tube. Introduced the “Plum Pudding” model.
Rutherford
Discovered the nucleus of the atom using the Gold Foil Experiment
Millikan
Determined the mass and measured the charge of an electron using the Oil Drop Apparatus (1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom)
Chadwick
Confirmed the existence of the Neutron. Preformed the first artificial nuclear transformation, and the first artificial nuclear transformation
Goldstein
Observed that proton particles have a relative mass of 1
Schrödinger
Developed the equation for the probability of a single electron being found along a single axis. (he showed, through math, that waves can be used to describe electrons in atoms)
de Broglie
1929 discovery that electrons have properties of both waves and particles
Bohr
Created the Bohr model of the atom. It demonstrated that electrons occupy orbits at specific energies, Explained hydrogen spectral lines, and how electrons can be moved to a higher or lower energy level by the absorption or emission of energy (quantum leaps)
Heisenberg
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle: It is impossible to know the exact location and velocity of an electron. The better we know one, the less we know the other.
Planck
The father of the quantum theory of energy. Planck’s Constant = 6.63 × 10^-34; He determined that atoms can emit quanta, which is the plural of quantum
Who found 1st subatomic particle - proving the atom is NOT the smallest particle of matter
Thompson
Bohr Model
An early model of atomic structure in which electrons travel around the nucleus in a number of stable orbits and electrons jump from one orbit to another based on conditions.
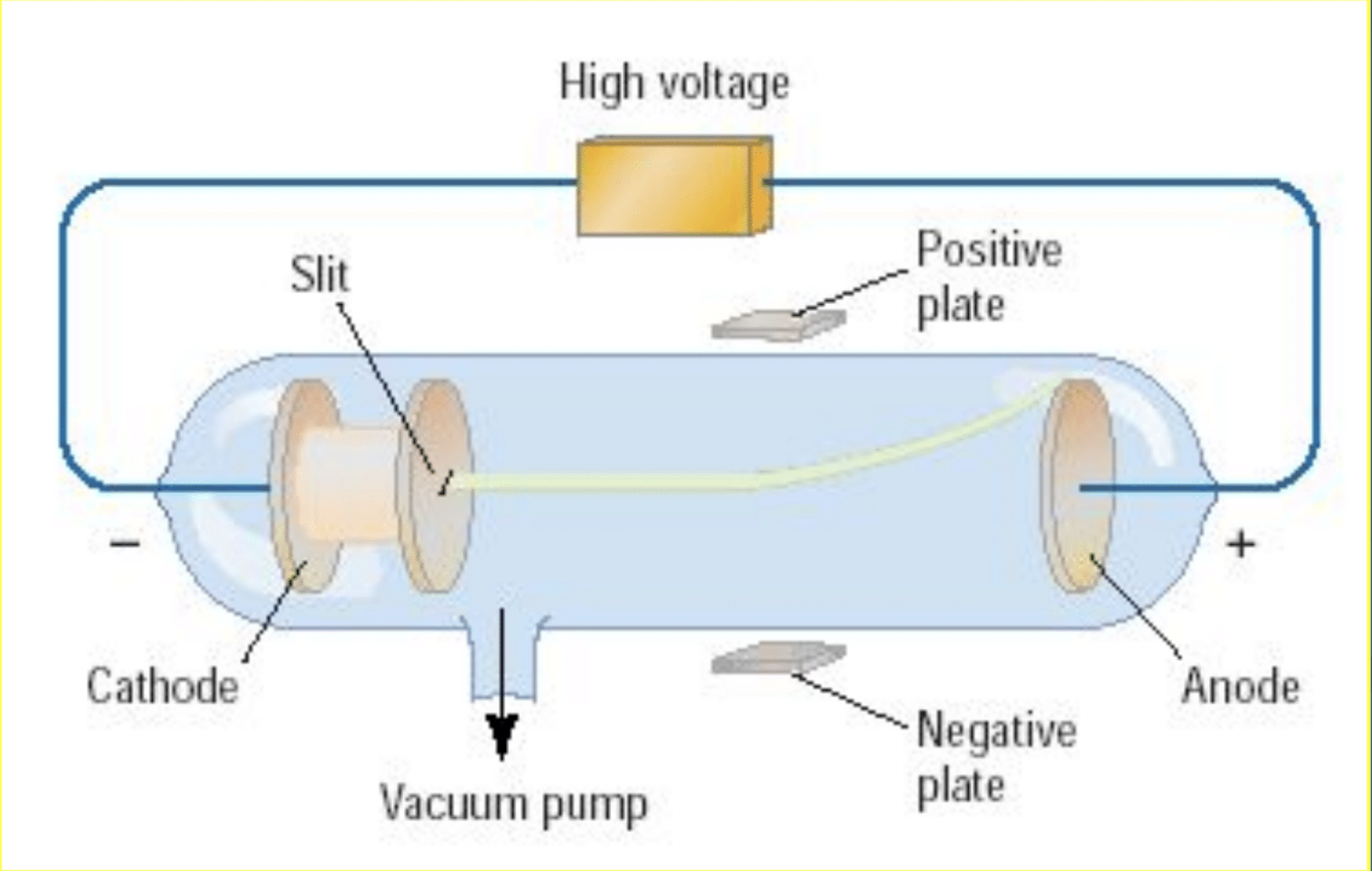
Cathode Ray Experiment
Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure
Still Valid?:
All elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms
Still Valid
Still Valid?:
Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element.
Still Valid
Still Valid?:
Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds
Still Valid
Still Valid?:
In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element.
Still Valid
Still Valid?:
All atoms of the same element have the same mass.
Not Valid
Who discovered the Laws of Definite/Indefinite Properties
Dalton
What is the Law of Definite Proportions
a chemical compound will always have the same proportions or amount of each element by weight, no matter what the amount is, or source.
What is the Law of Multiple Proportions
whenever the same two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
Protons
Located in the nucleus, positively charged, mass = 1 amu
Neutrons
Located in the nucleus, neutral charge, mass = 1 amu
Electrons
Located in the space around the nucleus, negatively charged, mass = 1/1840 amu
Nucleus
The positively charged center of the atom, consists of protons and neutrons, and it contains almost all of the atom’s mass.
Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom
Mass Number
Total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Isotopes
Two or more forms of one element that share the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons
Atomic Mass
The weighted average of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element
Average Atomic Mass Formula
AAM = (RA1)(M1) + (RA2)(M2)…
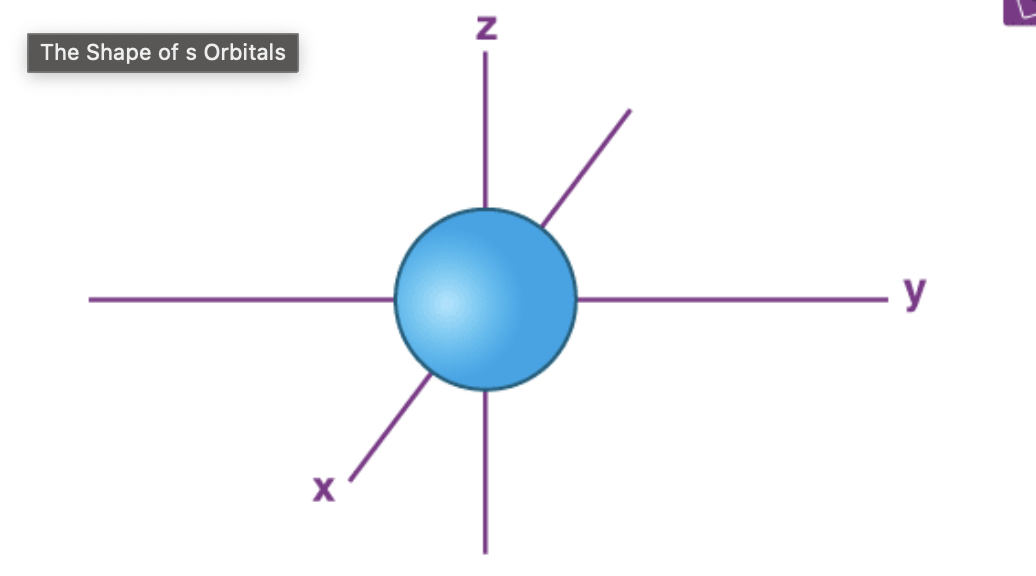
s Orbital Shape/Location
Spherical shape with the nucleus as its center,
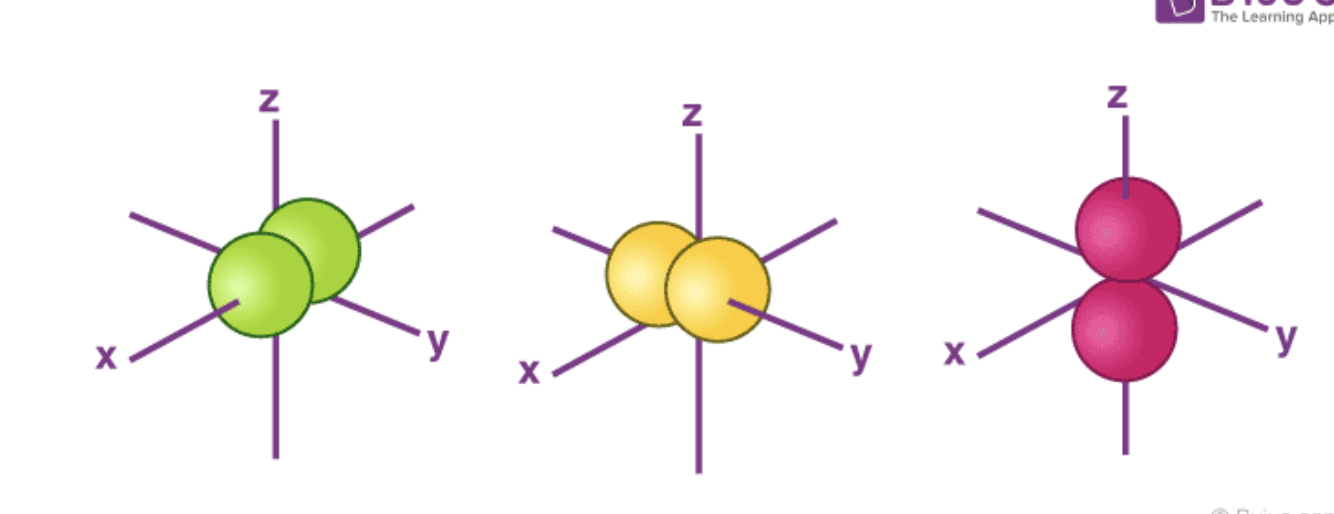
p Orbital Shape/Location
Two lobes that lie on either side of the plane and pass through the nucleus. (Dumbell Shaped)
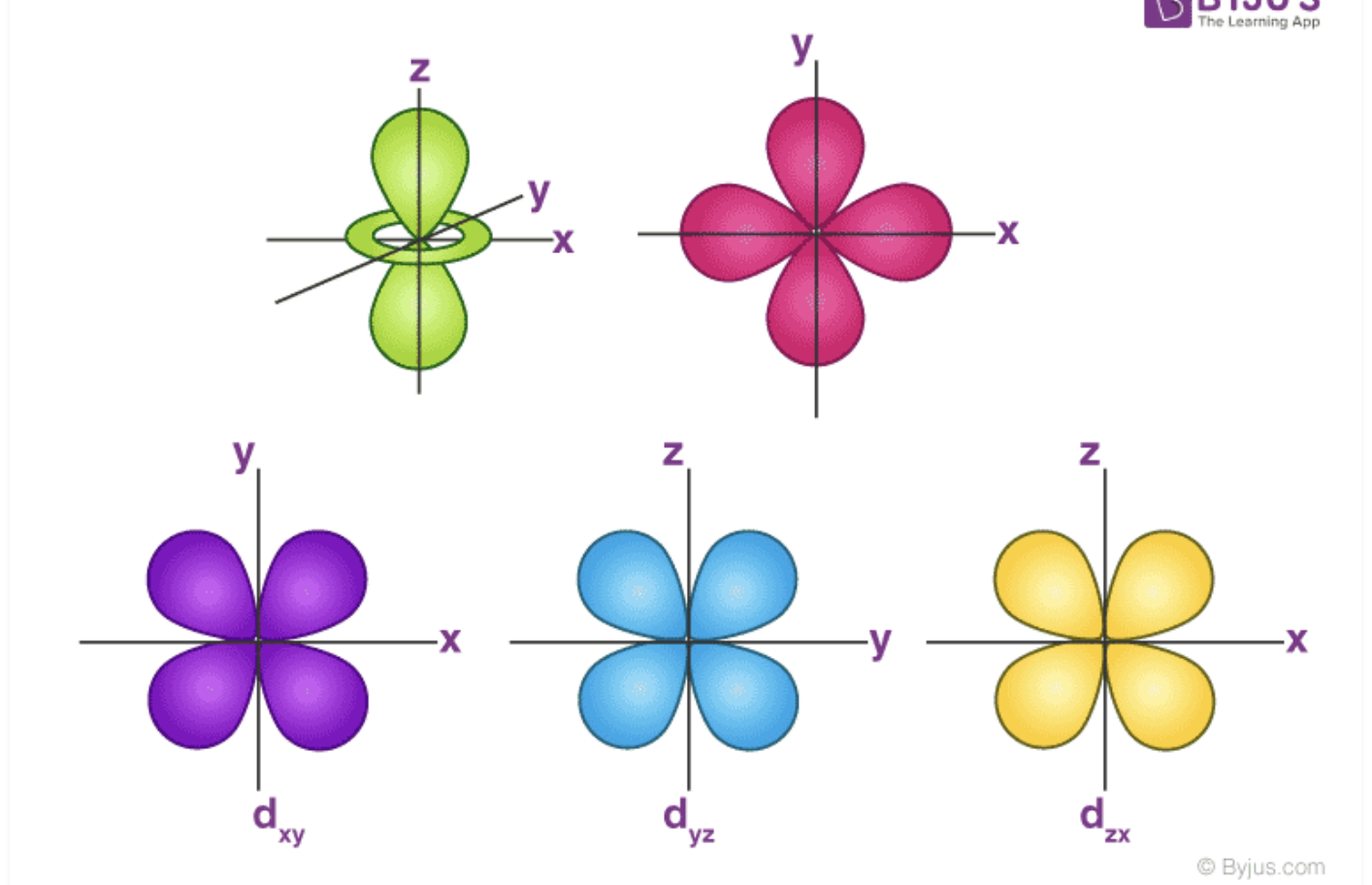
d Orbital Shape/Location
Shaped like two perpendicular dumbbells that lie on either side of the plane and pass through the nucleus
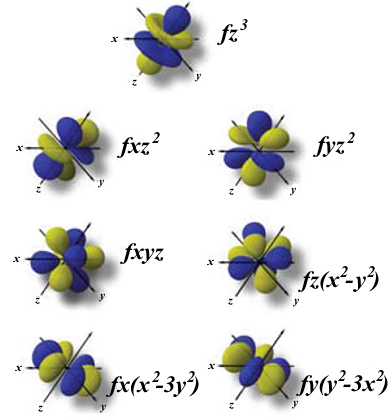
f Orbital Shape/Location
F orbital is found to be tetrahedral in shape. In total, 17 electrons can be accommodated in an f orbital.
Electron Configuration
describes where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. (Ex: electron configuration of lithium, 1s²2s¹)
Ground State
the lowest energy state of an atom or other particle.
Excited State
When an electron temporarily occupies an energy state greater than its ground state,
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
It is impossible to know the exact location and velocity of an electron. The better we know one, the less we know the other.
Aufbau principle
electrons enter the lowest energy level first.
Pauli Exclusion principle
Orbitals can only have two electrons at once, and they must have opposite spins
Hund’s Rule
When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, they don’t pair up until they have to.
What are the exceptions to the filling order of electron configuration
Chromium and Copper.
Chromium steals a 4s electron to make its 3d sublevel half full.
Copper steals a 4s electron to fill its 3d sublevel
Photoelectric effect
a phenomenon that occurs when light shone onto a metal surface causes the ejection of electrons from that metal
Valence Electrons
The electrons in an atom's outermost electron shell
Stable Electron Configurations
The most stable electron configurations occur in the noble gasses. (or the ones that have full energy levels)
Hydrogen Spectra
The line spectrum emitted by a hydrogen atom when an excited hydrogen atom returns to its ground state
Chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes, Cl-35 and Cl-37. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45. Which of these two isotopes of chlorine is more abundant?
Chlorine- 35
Atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element
Atomic Mass Unit
one-twelfth the mass of a carbon atom having six protons and six neutrons
The range in size of most atomic radii is approximately
5 × 10–11 m to 2 × 10–10 m
Evidence about Dalton’s atomic theory has shown that
Atoms are divisible
Why did J. J. Thomson reason that electrons must be a part of the atoms of all elements?
Charge-to-mass ratio of electrons was the same, regardless of the gas used.
Which hypothesis led to the discovery of the proton?
When a neutral hydrogen atom loses an electron, a positively-charged particle should remain.
An element has an atomic number of 76. The number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of the element are ____.
76 protons and 76 electrons
Isotopes of the same element have different
Mass numbers
How many protons, electrons, and neutrons does an atom with atomic number 50 and mass number 125 contain?
50 protons, 50 electrons, 75 neutrons
Protium
1/1 H
Deuterium
2/1 H
Tritium
3/1 H
What unit is used to measure weighted average atomic mass?
amu
The atomic mass of an element depends upon the
mass and relative abundance of each isotope of that element
What is the relative charge of a proton?
1+
How many protons are present in an atom of Be-9?
4
Atomic Orbital
region of high probability of finding an electron
What is the lowest energy level called?
The ground state
Photon
discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy
Quantum
energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another
Frequency
number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time
Wavelength
distance between wave crests
Spectrum
separation of light into different wavelengths
Atomic Emission Spectrum
frequencies of light emitted by an element
What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy level?
5
What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level?
s, p, and d only
What is the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an oxygen atom?
6
Which type of electromagnetic radiation includes the wavelength 10^-7m?
visible light
According to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, if the position of a tiny moving particle is known, the
velocity of the particle cannot be exactly determined.
How can the position of a very tiny particle be determined?
by analyzing its interactions with another particle
In an s orbital, the probability of finding an electron a particular distance from the nucleus can best be determined by the
quantum mechanical model.
What frequency are 20 mm microwaves?
15 GHz
What is the wavelength of a 92.9 MHz radio wave?
3.2 m
All electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum at
The same speed