ANAT 100 - Module 11
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
1
New cards
Accessory Organs
Provide enzymes that breakdown food and bile to digest dietary fats
* liver, gallbladder, pancreas
* liver, gallbladder, pancreas
2
New cards
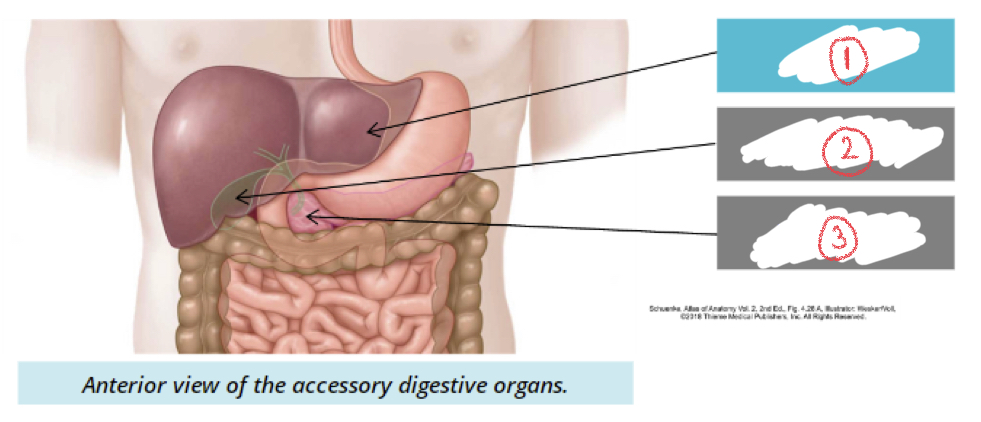
1. Liver
2. Gallbladder
1. Pancreas
3
New cards
Liver
* produces bile for digestion of fats
* Stores glycogen
* Metabolizes toxins, drugs, alcohol in blood
* Stores glycogen
* Metabolizes toxins, drugs, alcohol in blood
4
New cards
Gallbladder
Storage and release of bile
5
New cards
Pancreas
* mixed gland → endocrine and exocrine functions
* Control blood glucose
* Secretes digestive enzymes into intestine
* Control blood glucose
* Secretes digestive enzymes into intestine
6
New cards
4 lobes of the liver
1. Right lobe
2. Left lobe
3. Quadrate lobe
4. Caudate lobe
7
New cards
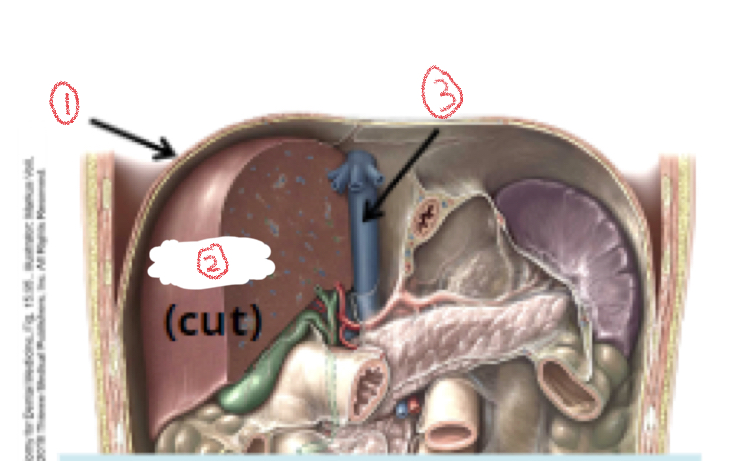
1. Diaphragm
2. Liver
3. inferior vena cava
8
New cards
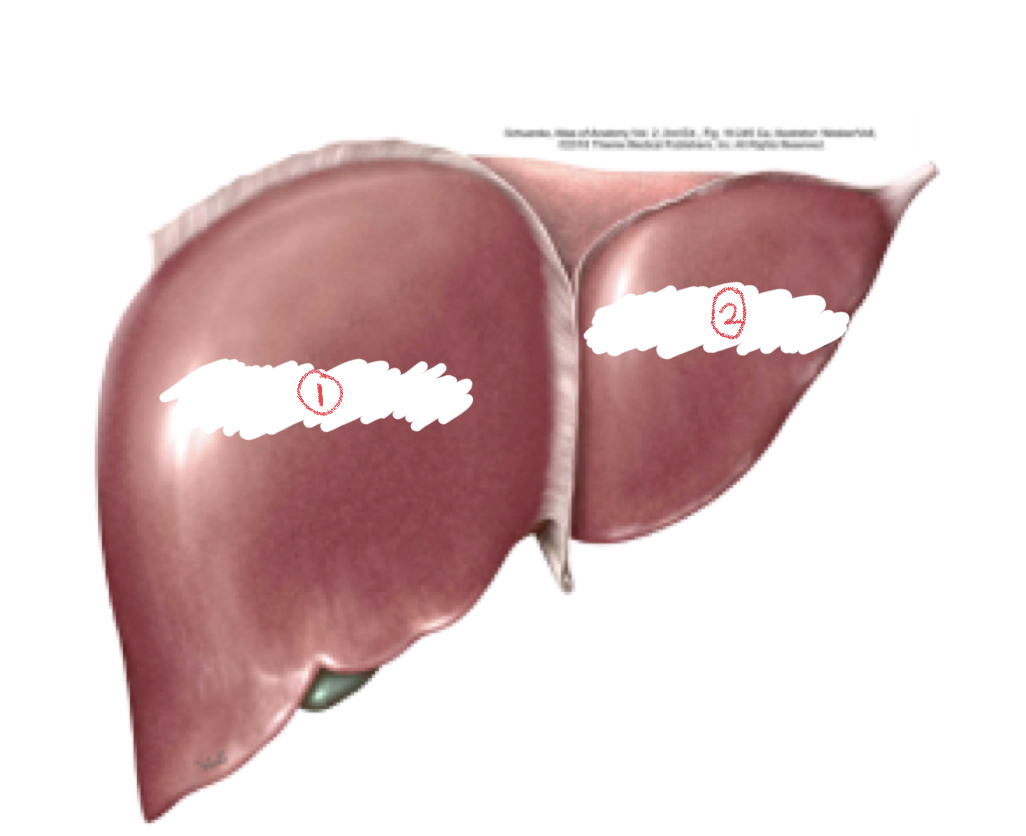
1. Right lobe
2. Left lobe
9
New cards
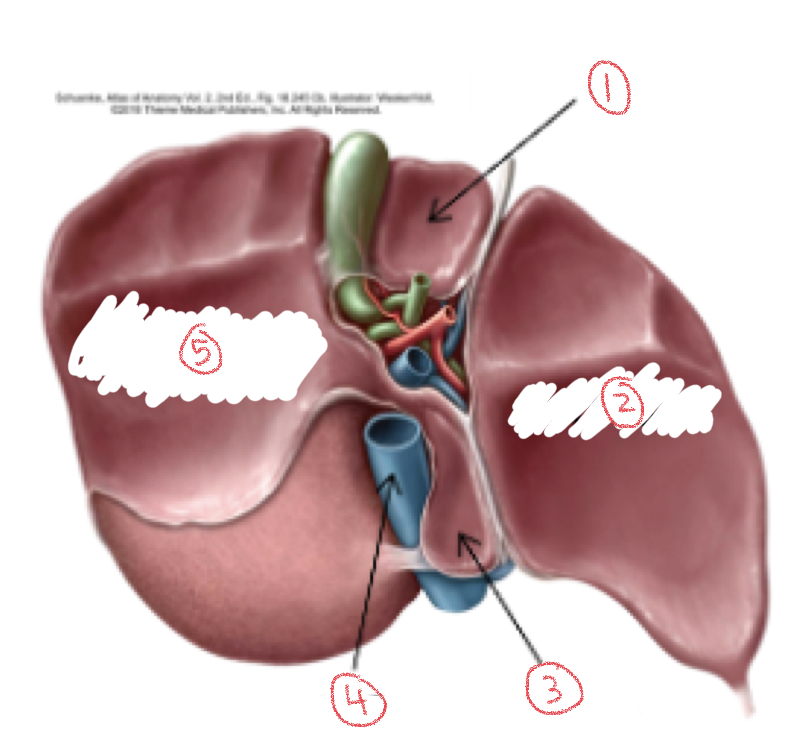
1. Quadrate lobe
2. Left lobe
3. Caudate lobe
4. Inferior vena cava
5. Right lobe
10
New cards
Ligaments of the liver
Attaches to liver to abdominal peritoneum and diaphragm
1. Coronary ligament
2. Falciform ligament
1. Coronary ligament
2. Falciform ligament
11
New cards
Abdominal peritoneum
Membrane between abdominal cavity and covers most of abdominal organs
12
New cards
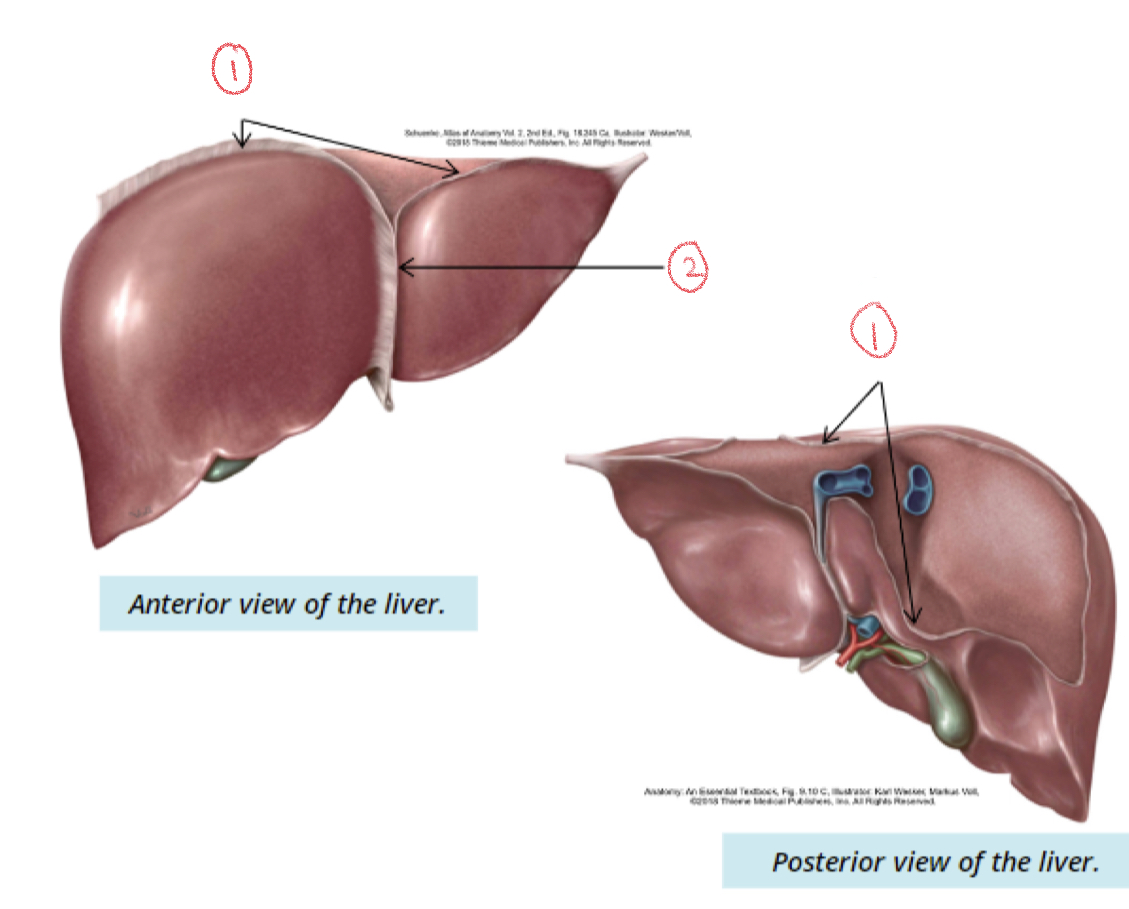
\
1. Coronary ligament
2. Falciform ligament
13
New cards
Coronary ligament
Suspends liver from inferior surface of diaphragm
14
New cards
Falciform
Separates right and left lobe
15
New cards
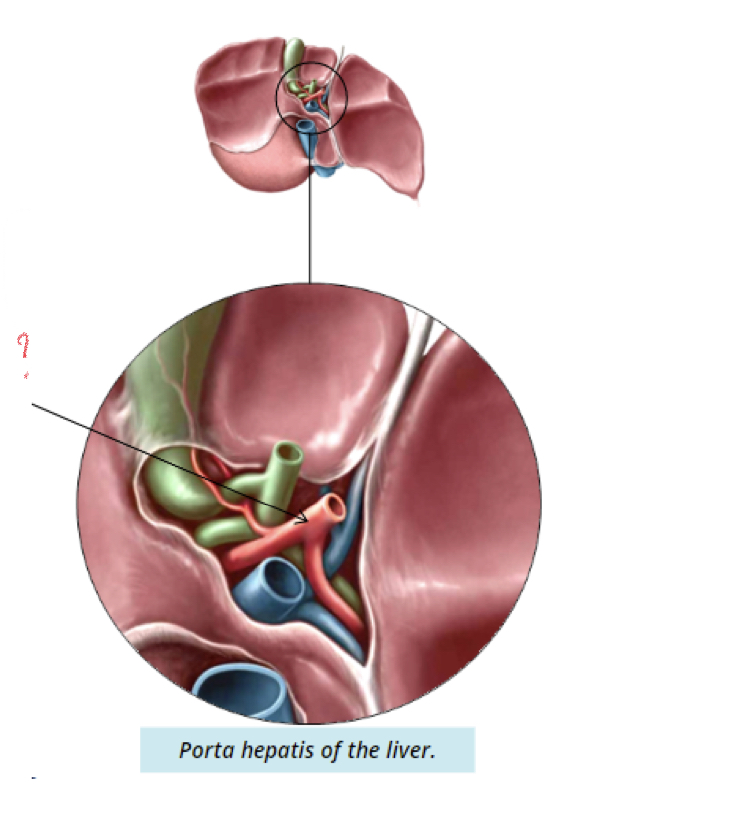
Porta hepatis (hilum)
* area where hepatic vessels and ducts enter and leave liver
* Hepatic vessels: common hepatic duct, portal vein, hepatic artery
* Hepatic vessels: common hepatic duct, portal vein, hepatic artery
16
New cards
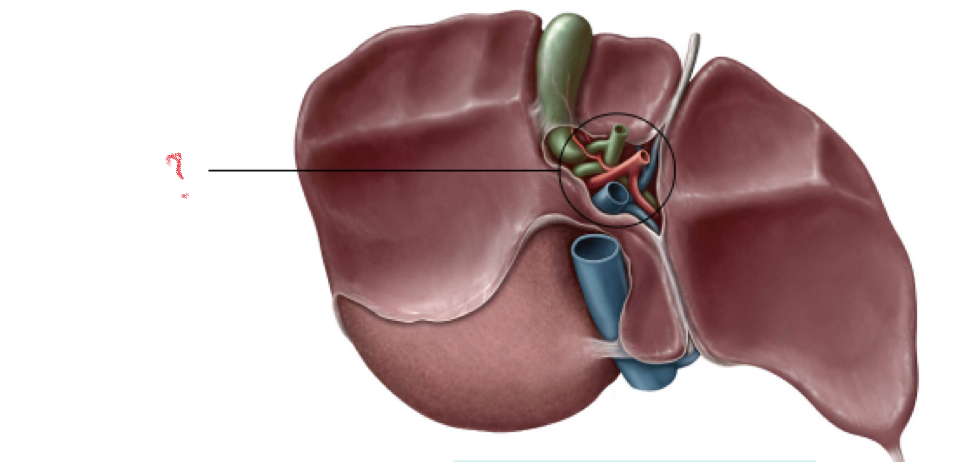
Porta hepatis
17
New cards
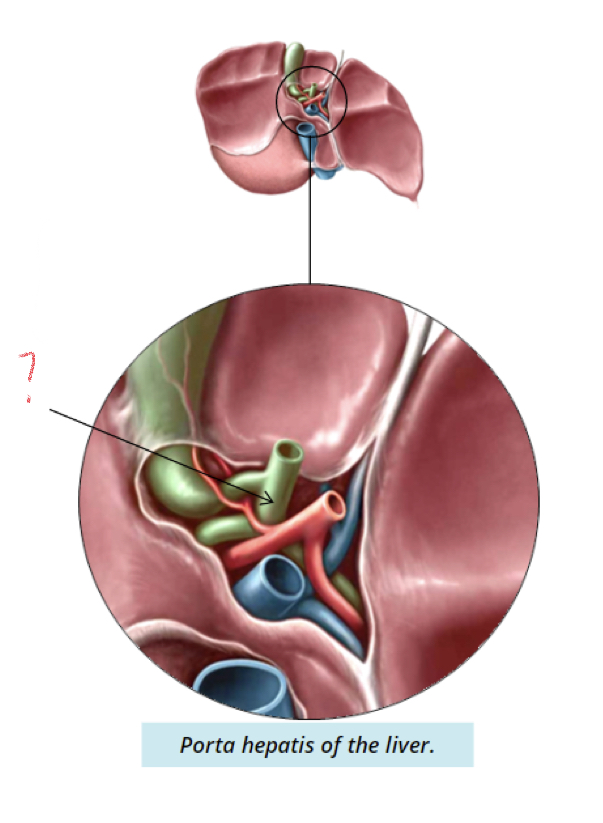
Common hepatic duct
18
New cards
Common hepatic duct
* drains bile produced in liver
* Combines with cystic duct of gallbladder to create common bile duct
* Combines with cystic duct of gallbladder to create common bile duct
19
New cards
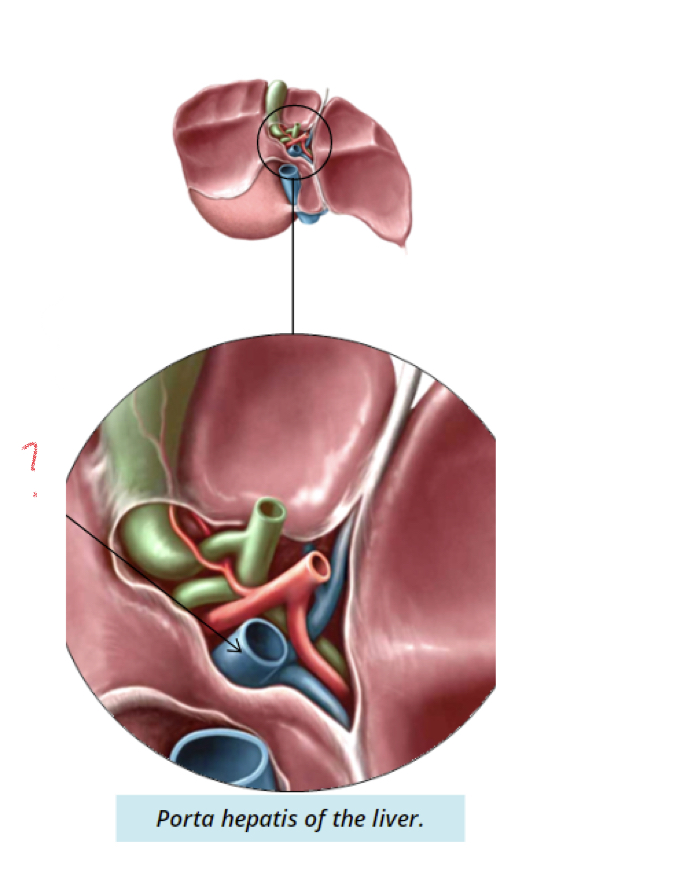
Portal vein
20
New cards
Portal vein
* carries nutrient rich blood from digestive system into liver
* Toxins travel through vessel into liver for metabolism
* Toxins travel through vessel into liver for metabolism
21
New cards
Hepatic artery
22
New cards
Hepatic artery
Carries oxygenated blood to liver and branches to supply each lobe
23
New cards
Liver lobule
Simple cuboidal liver cells → hepatocyte cords that radiate outward from central veins
24
New cards
Sinusoids
Between cell plates where venous blood flows
25
New cards
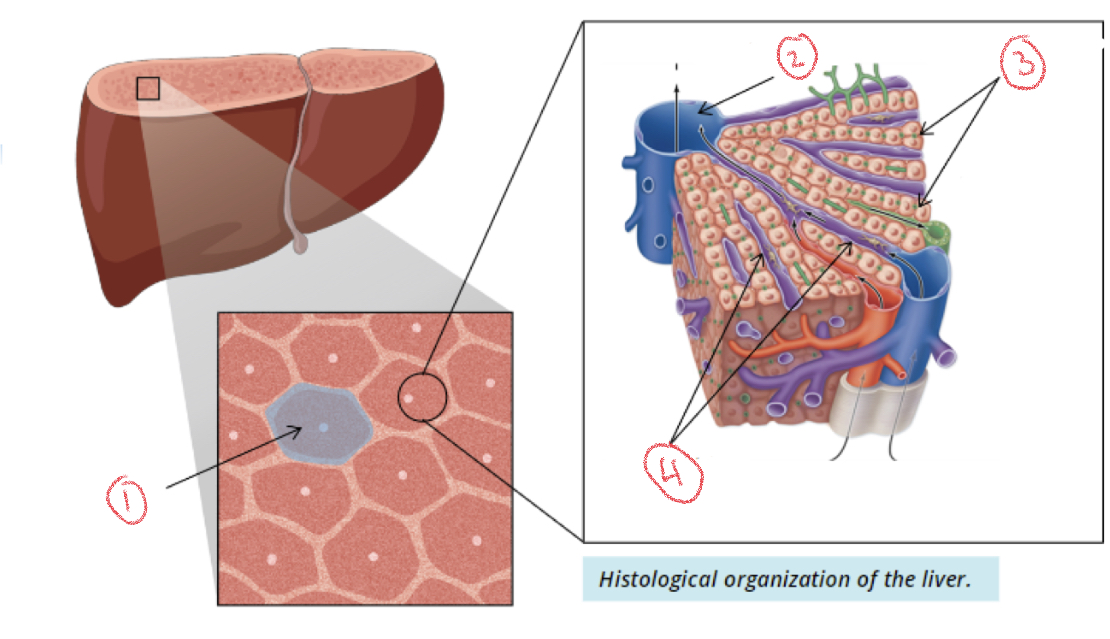
1. Liver lobule
2. Central vein
3. Hepatocytes
4. Sinusoids
26
New cards
Portal triads
Branches of hepatic artery, portal vein, hepatic duct (bile ductule) from porta hepatis
* each liver lobe surrounded by 6 triads
* each liver lobe surrounded by 6 triads
27
New cards
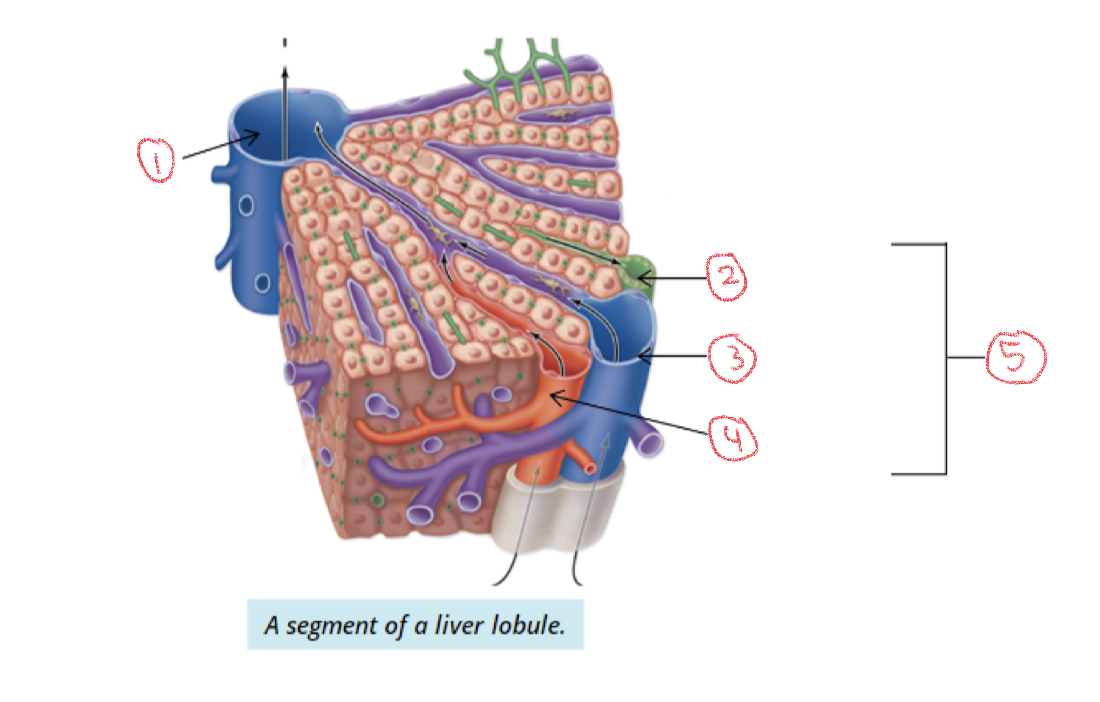
1. Central vein
2. Bile ductule
3. Portal vein
4. Hepatic artery
5. Portal triad
28
New cards
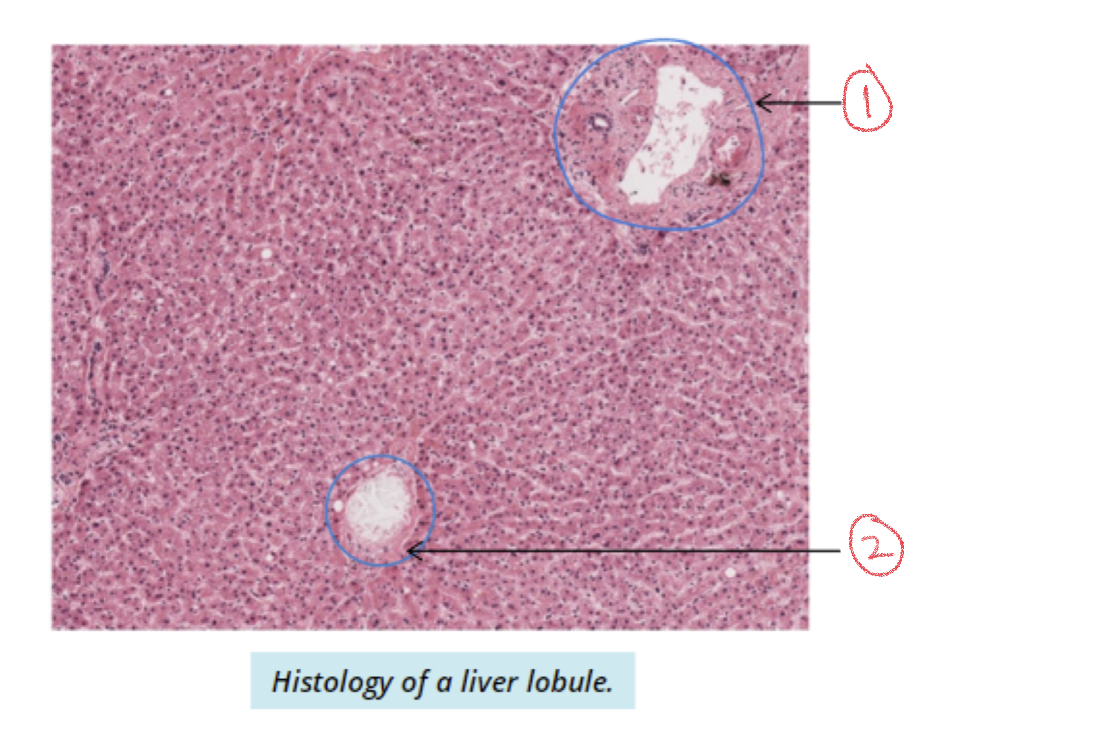
1. Portal triad
2. Central vein
29
New cards
Flow of venous blood
Portal vein → sinusoids → central veins → hepatic veins → inferior vena cava → heart
30
New cards
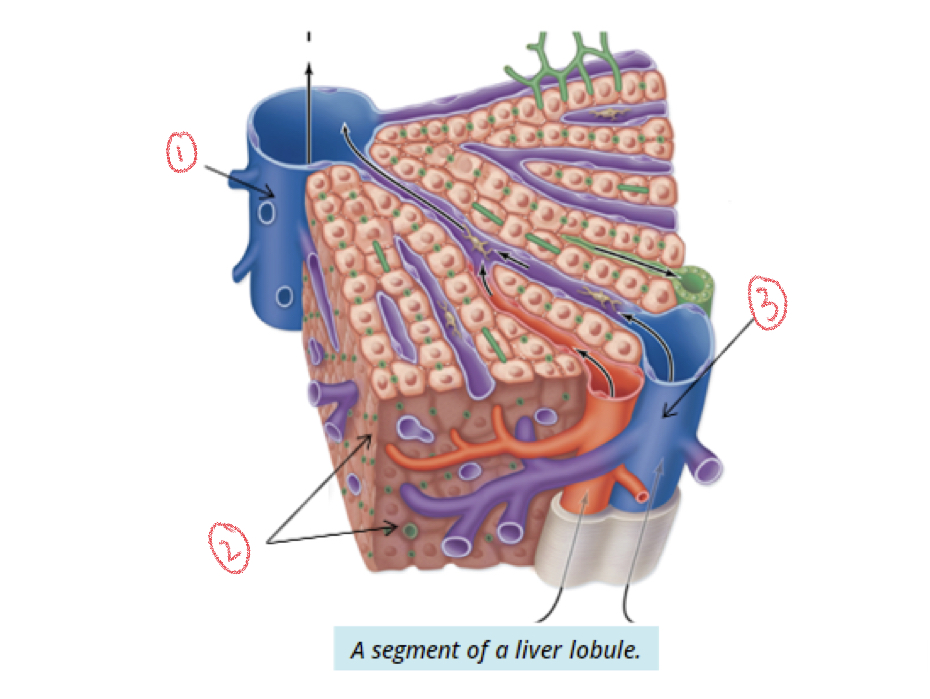
1. Central vein
2. hepatocytes
3. Portal vein
31
New cards
Where are bile fats produced?
Hepatocytes to aid in digestion
32
New cards
Flow of bile fats
Hepatocytes → canaliculi (small channels) → bile ductules → hepatic ducts
33
New cards
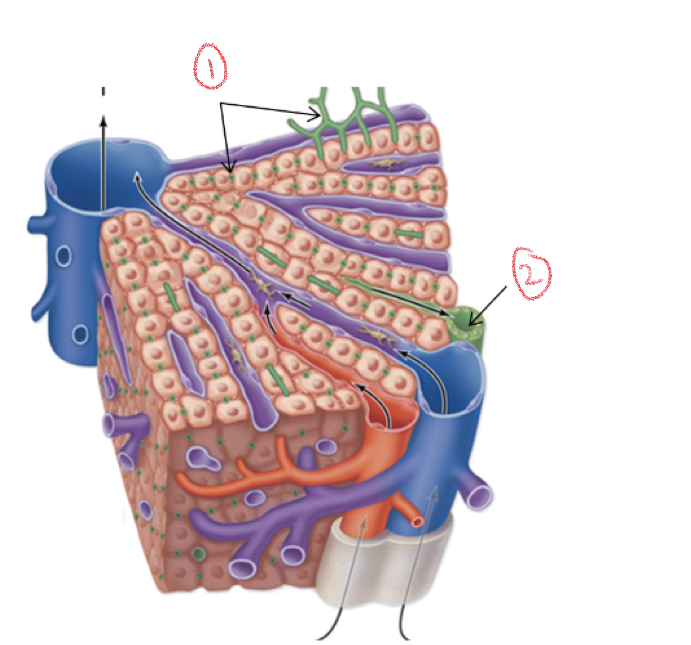
1. Canaliculi
2. Bile ductule
34
New cards
What are the functions of the liver?
* produces bile → emulsification of fats and cholesterol
* Stores nutrients as glucose
* Stores nutrients as glucose
35
New cards
Liver cirrhosis
Slow progressive disease where healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue
* blocks flow of blood and bile through portal triads
* blocks flow of blood and bile through portal triads
36
New cards
Gallbladder
37
New cards
Gallbladder
Pear-shaped muscular sac inferior to right liver lobe
* stores and concentrates bile
* stores and concentrates bile
38
New cards
Areas of Gallbladder
1. Fundus
2. Body
3. Neck
39
New cards
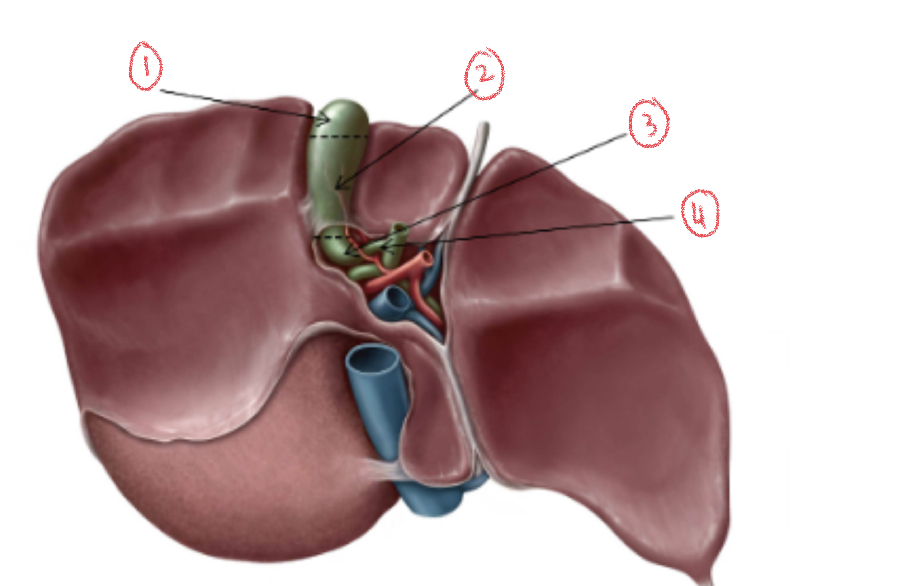
\
1. Fundus
2. Body
3. Neck
4. Cystic Duct
40
New cards
Billary system
Interconnected ducts that connect liver and gallbladder
* stores and drains bile into duodenum
* stores and drains bile into duodenum
41
New cards
Flow of bile
Cystic duct → common hepatic duct → common bile duct
42
New cards
Hepatic duct
Drain bile into common hepatic duct
43
New cards
Cystic duct
Attaches to common hepatic duct and transports bile to and from gallbladder
44
New cards
Common bile duct
Meets cystic duct to drain bile into commonbile duct which enters duodenum
45
New cards
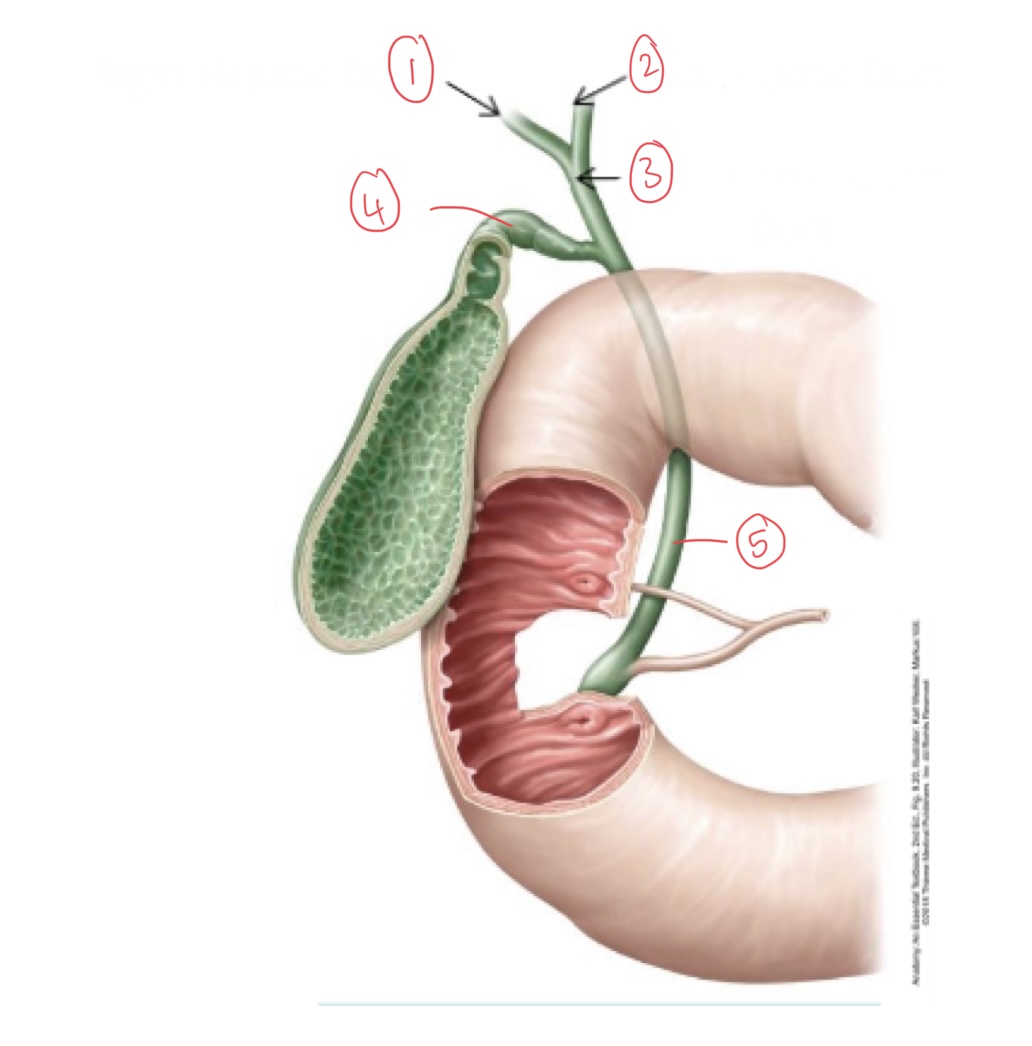
1. Right hepatic duct
2. Left hepatic duct
3. Common hepatic duct
4. Cystic duct
5. Common bile duct
46
New cards
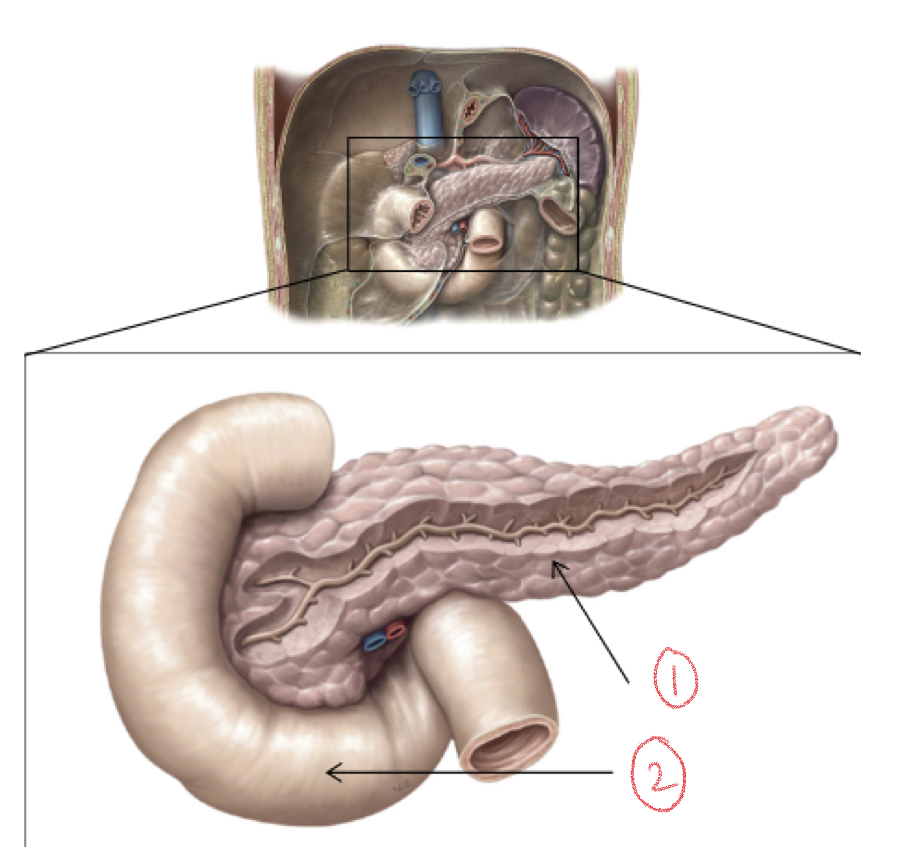
1. Pancreas
2. Duodenum
47
New cards
Pancreas
* lobular organ deep inside stomach
* Exocrine and endocrine functions
* Exocrine secretes enzymes that aid in digestion
* Exocrine and endocrine functions
* Exocrine secretes enzymes that aid in digestion
48
New cards
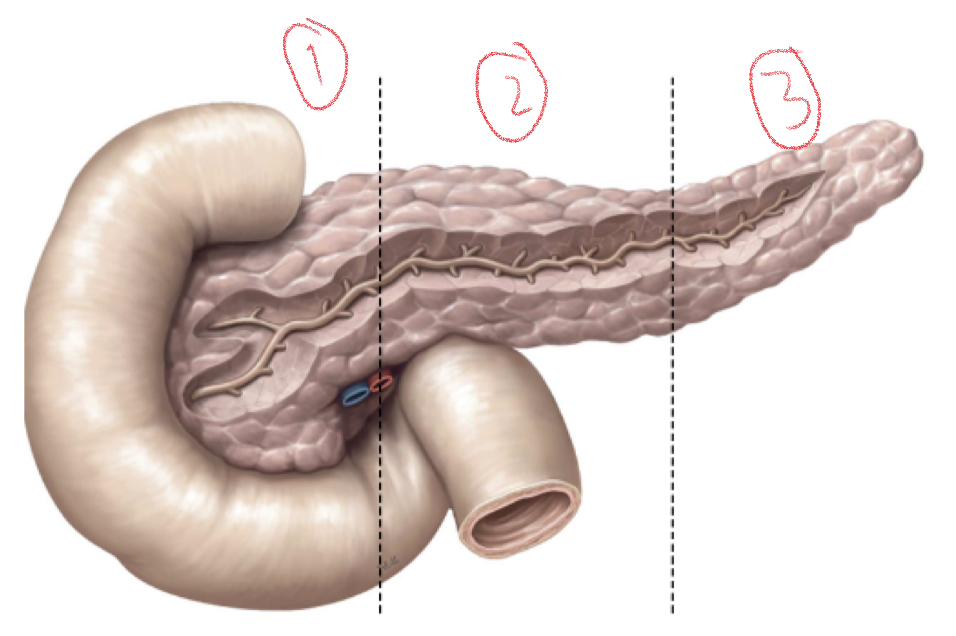
1. Head
2. Body
3. Tail
49
New cards
Pancreas head
Concavity of duodenum on right side of abdominal cavity
50
New cards
Pancreas body
Extends towards left, passing behind stomach and tapering to become tail
51
New cards
Pancreas tail
Medial side of spleen
52
New cards
Main pancreatic duct
* Collects exocrine products of pancreas
* Duct fuses with common bile duct to empty into duodenum through ampulla of vater
* Duct fuses with common bile duct to empty into duodenum through ampulla of vater
53
New cards
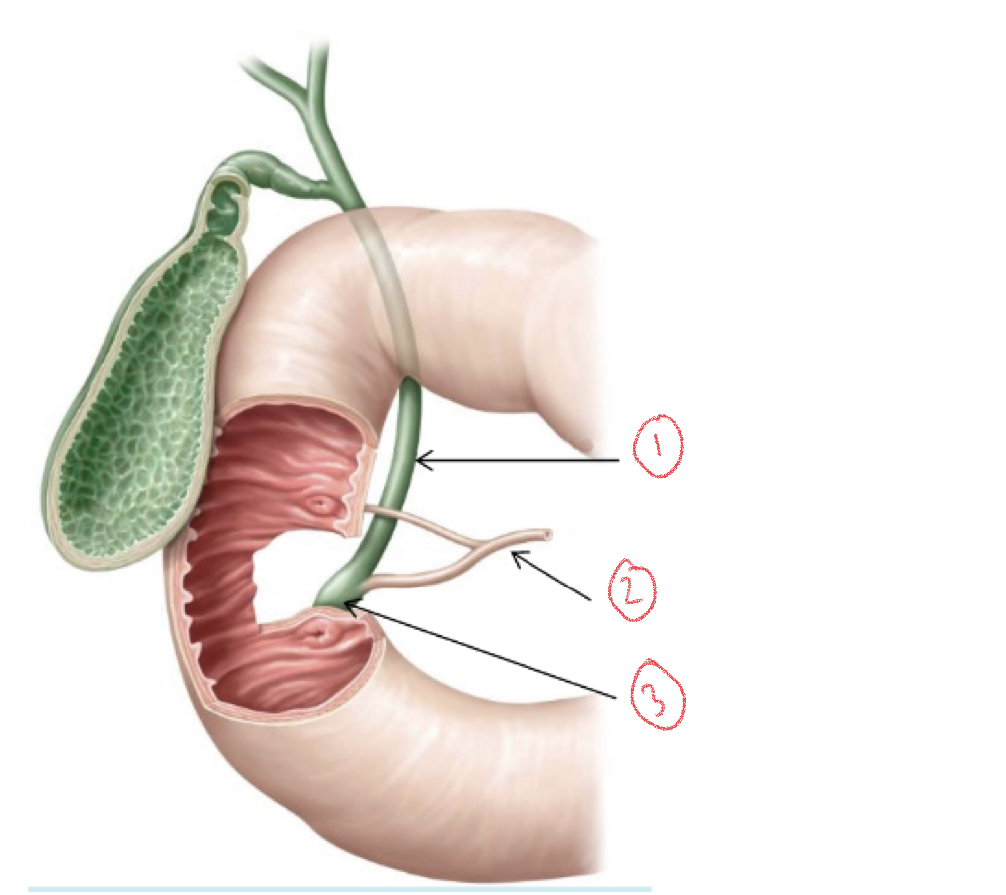
1. Common bile duct
2. Main pancreatic duct
3. Ampulla of vater
54
New cards
Histology of pancreas
1. 99% exocrine
2. 1% endocrine (islets of langerhans)
55
New cards
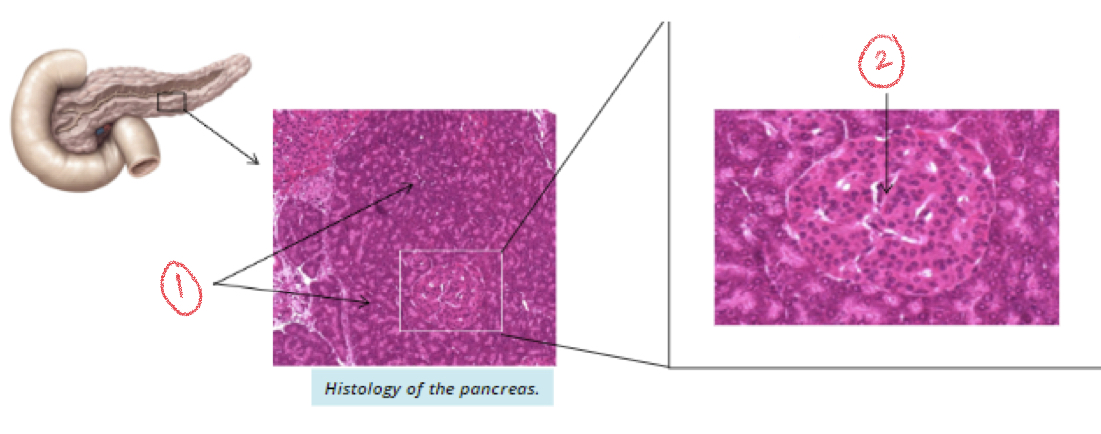
1. Exocrine pancreas
2. Endocrine pancreas (islets of langerhans)
56
New cards
Role of exocrine pancreas
Secretes pancreatic juices from pancreas acini into duodenum
57
New cards
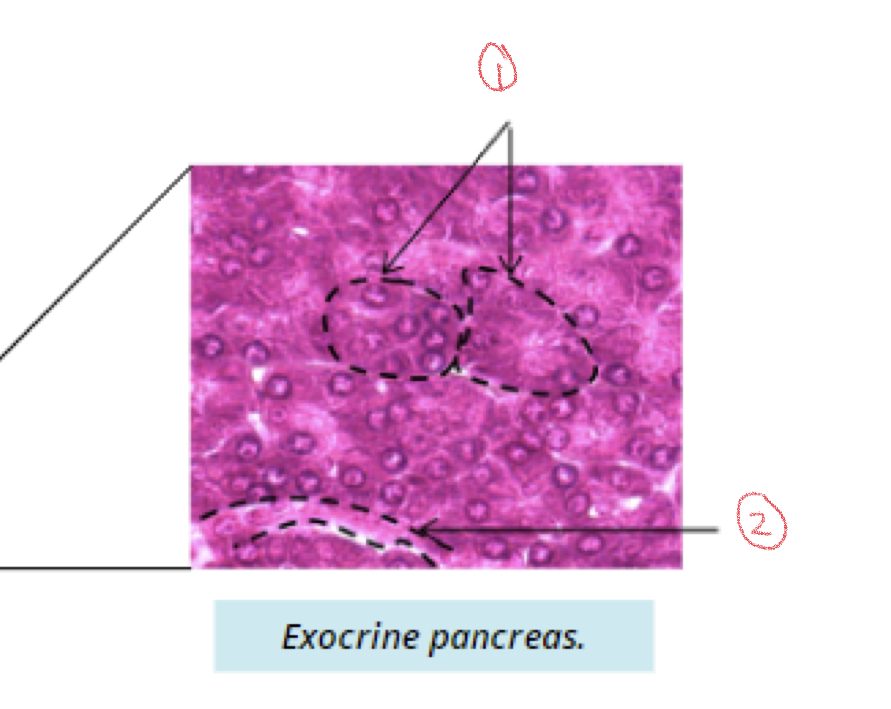
Components of exocrine pancreas
1. Pancreatic acini
2. Duct
58
New cards
Pancreatic juices
Rich in digestive enzymes
* contain bicarbonate ions to neutralize acid from stomach
* contain bicarbonate ions to neutralize acid from stomach
59
New cards
Why are digestive juices important?
Used to obtain nutrients from ingested food
60
New cards
Kidneys
Filters blood to produce urine
61
New cards
Location of kidneys
bean shaped organs in abdominal region on both sides of T12-L2 vertebrae
62
New cards
Size of kidney
* 12cm length
* 6.5cm width
* 2.5 cm thickness
* 6.5cm width
* 2.5 cm thickness
63
New cards
Why is the right kidney slightly lower in the abdominal cavity?
Liver is too large and sits superiorly and limits ascent of kidney
64
New cards
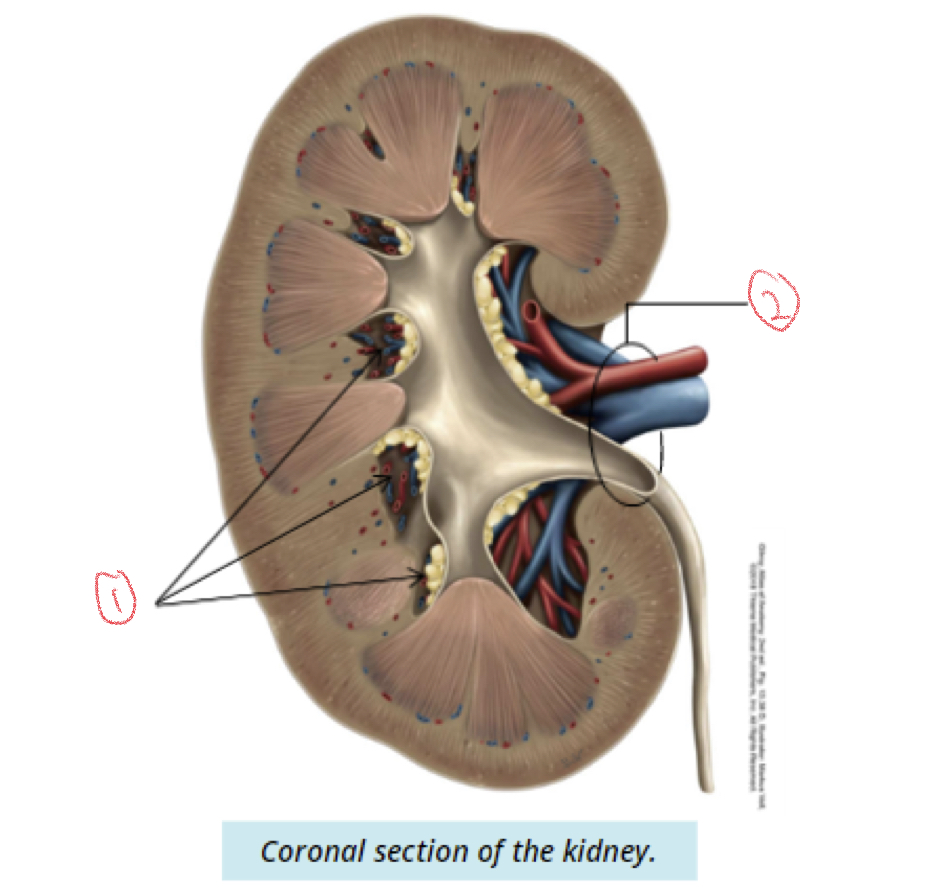
\
1. Renal sinuses
2. Hilum
65
New cards
Hilum of kidney
Medial surface
66
New cards
Renal sinus
Internal space in each kidney → fatty tissue
67
New cards
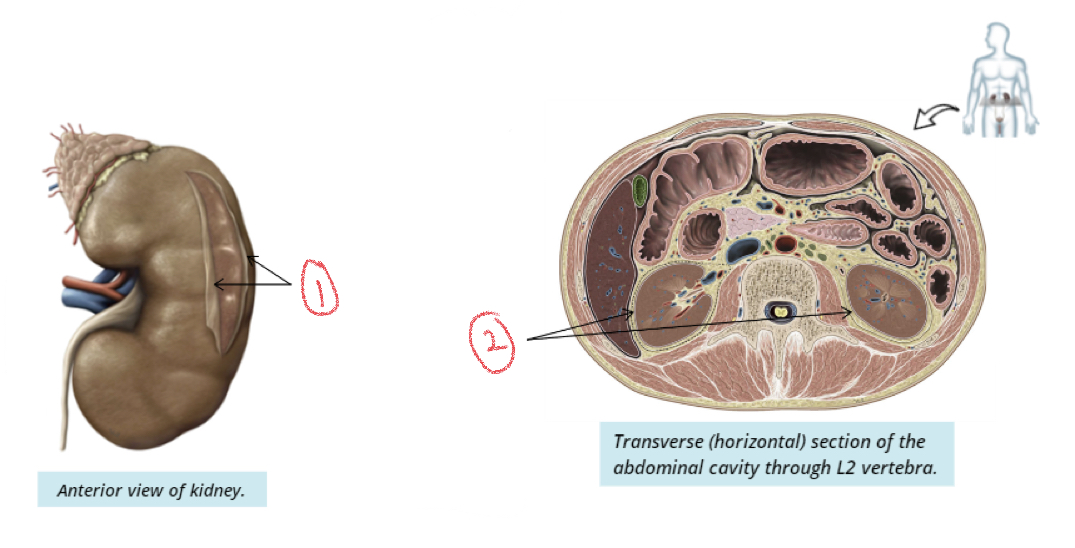
Supportive tissues of kidney
Protects and cushions kidneys
1. Renal capsule
2. Adipose capsule
1. Renal capsule
2. Adipose capsule
68
New cards
Renal capsule
Covers outer surface of kidney
* dense irregular tissue
* Protection from pathogens
* Maintains shape
* dense irregular tissue
* Protection from pathogens
* Maintains shape
69
New cards
Adipose capsule
Adipose tissue external to renal capsule
* cushion and protection
* cushion and protection
70
New cards
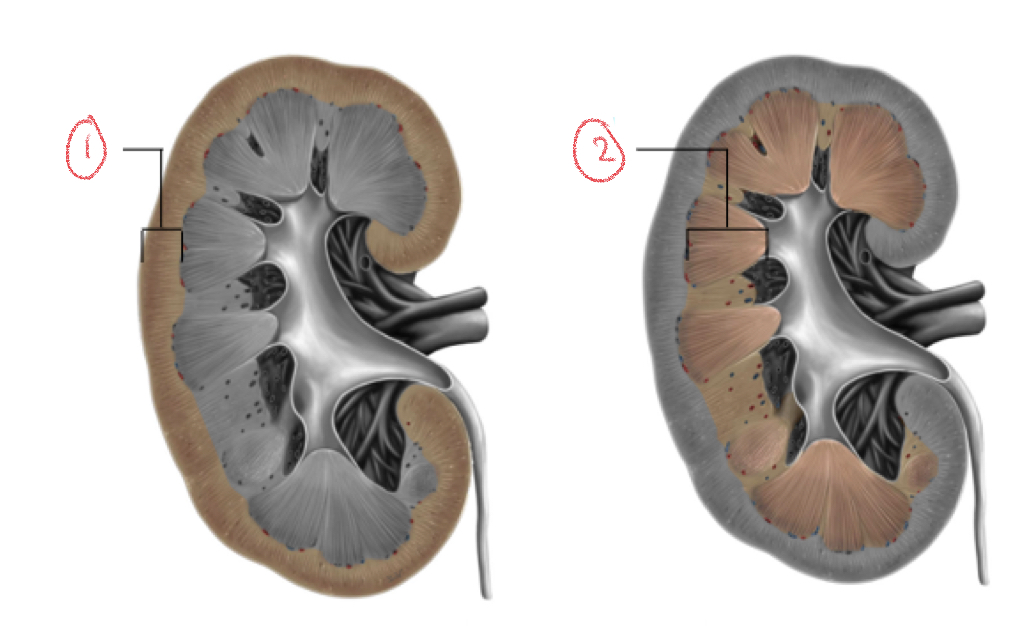
Internal anatomy of kidney
Both filter blood to produce urine
1. Renal cortex
2. Renal medulla
1. Renal cortex
2. Renal medulla
71
New cards
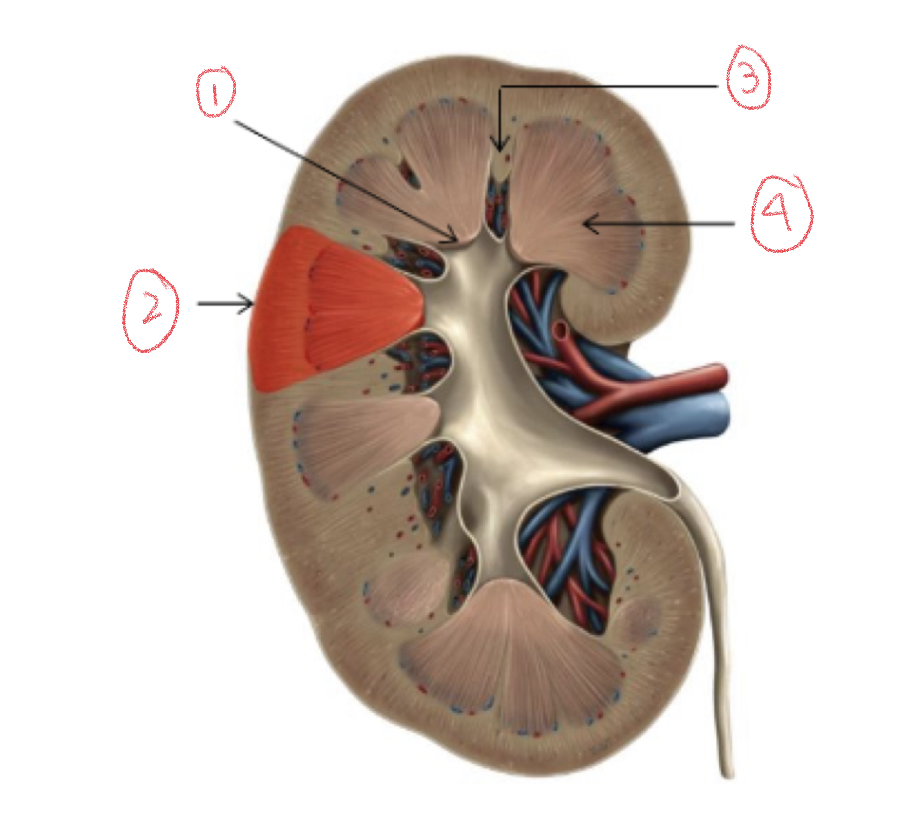
\
1. Renal papilla
2. Renal lobe
3. Renal column
4. Renal pyramid
72
New cards
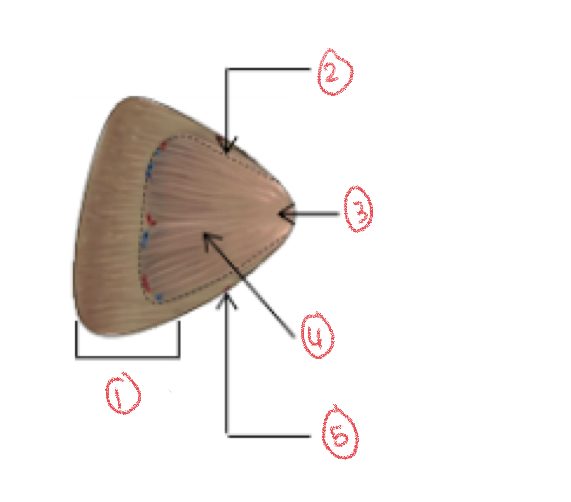
Renal lobe diagram
1. Renal Cortex
2. Renal column
3. Renal papilla
4. Renal pyramid
5. Renal column
73
New cards
Renal lobes
Each lobe has renal pyramid, cortex, and surrounding renal column
74
New cards
Renal columns
Extension of cortex → separates medullary into renal pyramids
75
New cards
Renal papilla
Apex of pyramid
76
New cards
Renal pelvis
Urine → minor calyces → major calyx → renal pelvis → uterus
77
New cards
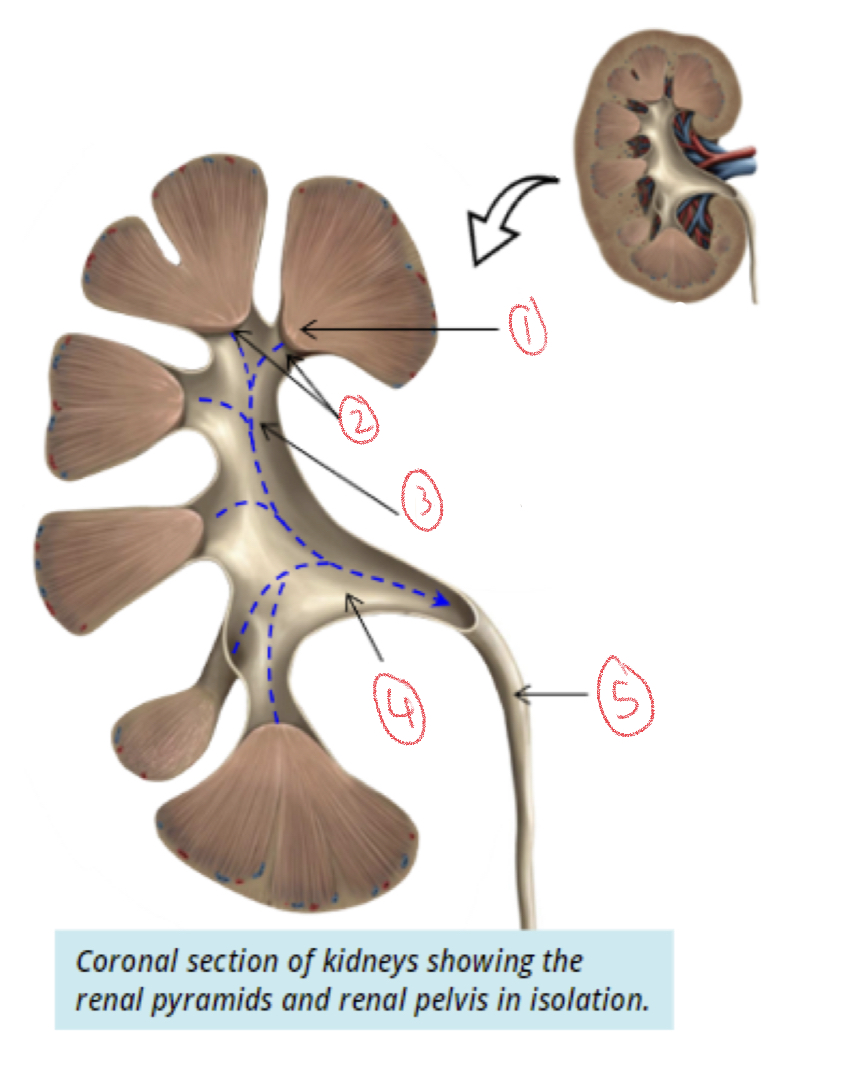
1. Renal papilla
2. Minor calyces
3. Major calyx
4. Renal pelvis
5. Ureter
78
New cards
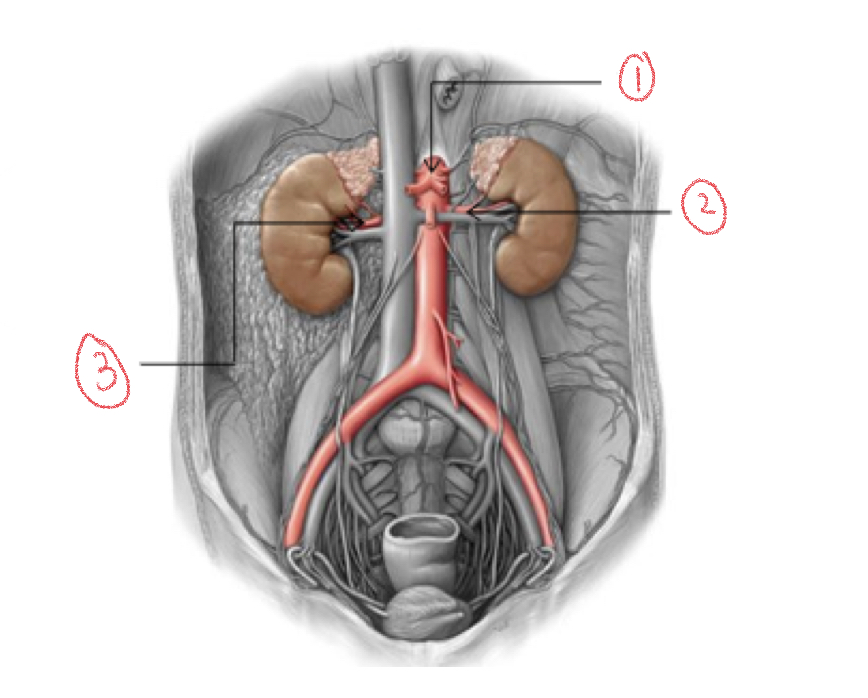
1. Abdominal aorta
2. Left renal artery
3. Right renal artery
79
New cards
Blood supply
Kidneys receive blood from paired renal artery
* renal artery = branches of abdominal aorta
* renal artery = branches of abdominal aorta
80
New cards
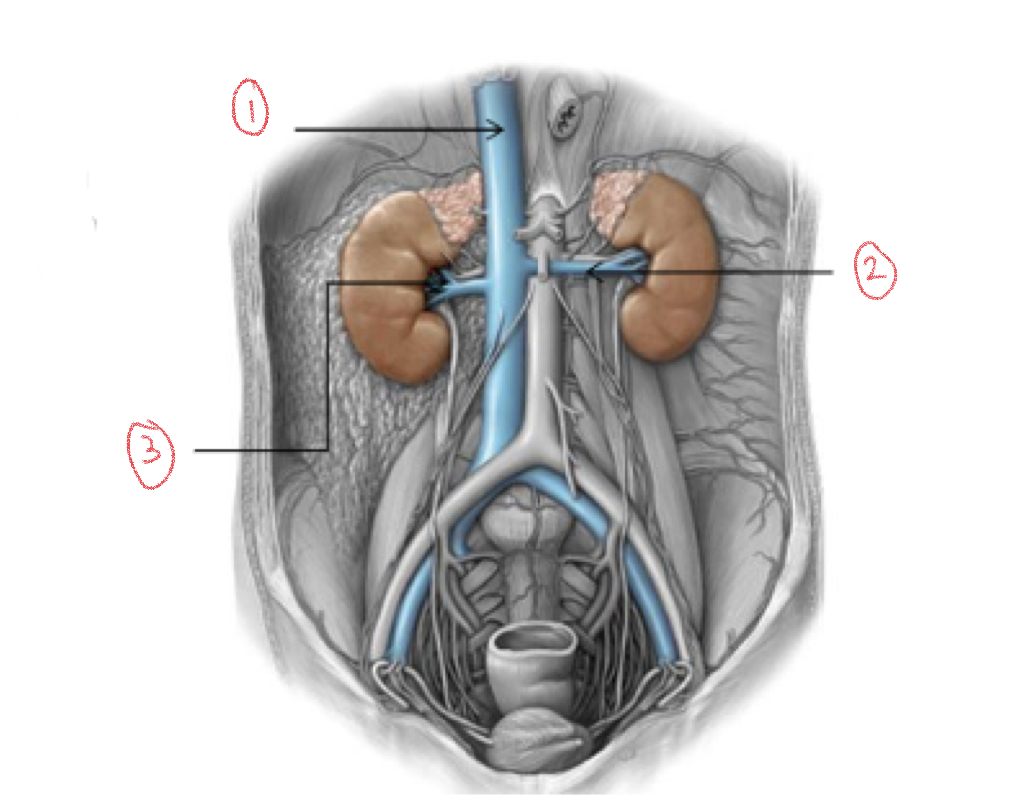
1. Inferior vena cava
2. Left renal vein
3. Right renal vein
81
New cards
Blood drainage
Kidneys drain by renal veins into inferior vena cava
82
New cards
Difference between renal artery supplying right kidney compared to real artery supplying left kidney
* right artery longer than left
* Right vein shorter than left
* Right vein shorter than left
83
New cards
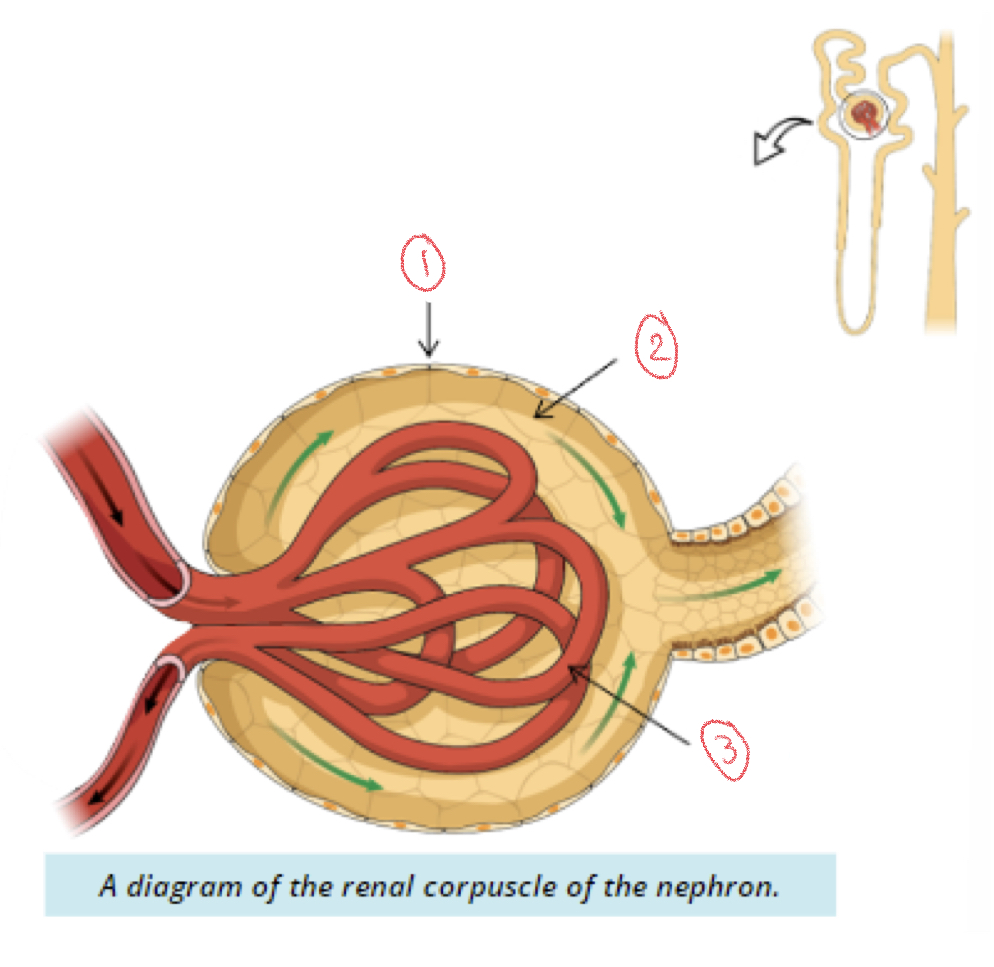
Renal Corpuscle
1. Bowman’s capsule
2. Bowman’s space
3. Glomerulus
84
New cards
Glomerulus
Bundle of capillaries within glomerular capsule
85
New cards
Bowman’s space
Space between walls and glomerular capillaries
86
New cards
Fenustrations
Capillaries of glomerulus with holes
* allows ions, water, and molecules to move through membranes
* allows ions, water, and molecules to move through membranes
87
New cards
Podocytes
Surrounds glomerular capillaries
* creates filtration slits that allow water and salts to pass
* creates filtration slits that allow water and salts to pass
88
New cards
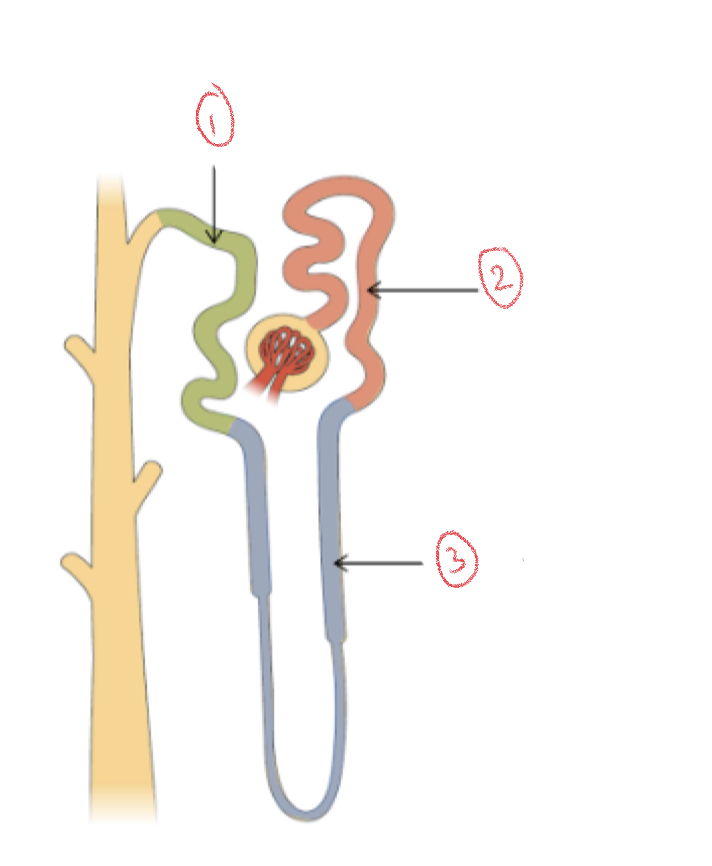
1. Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
2. Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
3. Loop of henle
89
New cards
Renal Tubule
Extends throughout cortex and medulla of kidney
* 3 sections: proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle, distal convoluted tubule
* 3 sections: proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle, distal convoluted tubule
90
New cards
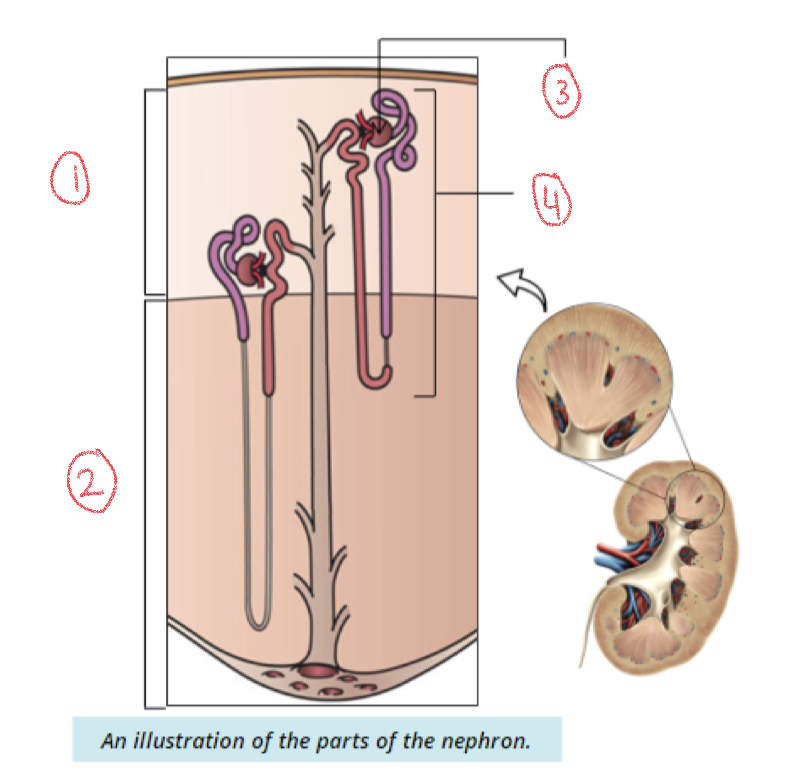
1. Renal cortex
2. Renal medulla
3. Renal corpuscle
4. Renal tubule
91
New cards
Collecting system
Renal tubules → collecting tubules → collecting ducts (inside renal medulla)
* final filter: collecting duct → renal papilla → urine
* final filter: collecting duct → renal papilla → urine
92
New cards
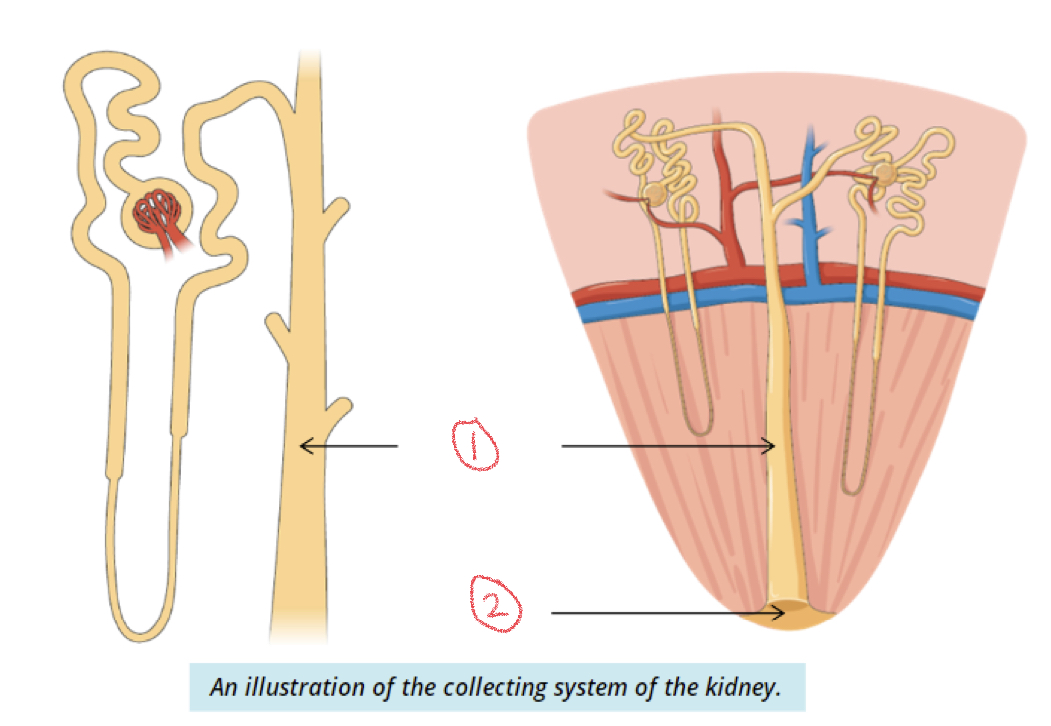
1. Collecting duct
2. Renal papilla
93
New cards
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
Strict unit that regulates blood pressure by monitoring ion concentration in filtrate
94
New cards
Juxtaglomerular cells
Modified smooth muscle cells of afferent arteriole
* smaller artery brings blood into glomerulus
* smaller artery brings blood into glomerulus
95
New cards
Macula densa
Modified cuboidal cells of distal convoluted tubule
96
New cards
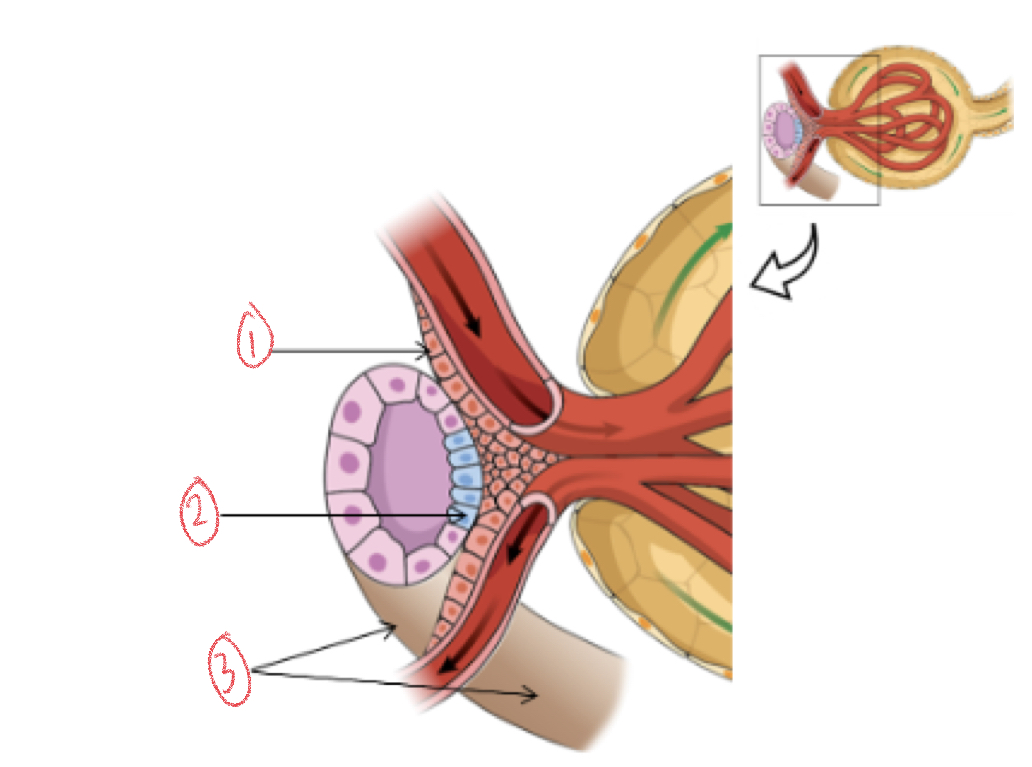
1. Juxtaglomerular cells
2. Macula densa
3. Distal convoluted tubule
97
New cards
Kidneys summary
* Kidneys: filter blood to get rid of waste, balance ion concentrations, produce RBC
* Produce urine through nephrons
* Pass filtrate on minor and major calyces into renal pelvis (drains ureters)
* Produce urine through nephrons
* Pass filtrate on minor and major calyces into renal pelvis (drains ureters)
98
New cards
Urinary tract
Transfers and stores urine produced by kidneys until ready for excretion
99
New cards
3 parts of urinary tract
1. Ureters
2. Bladder
3. Urethra
100
New cards
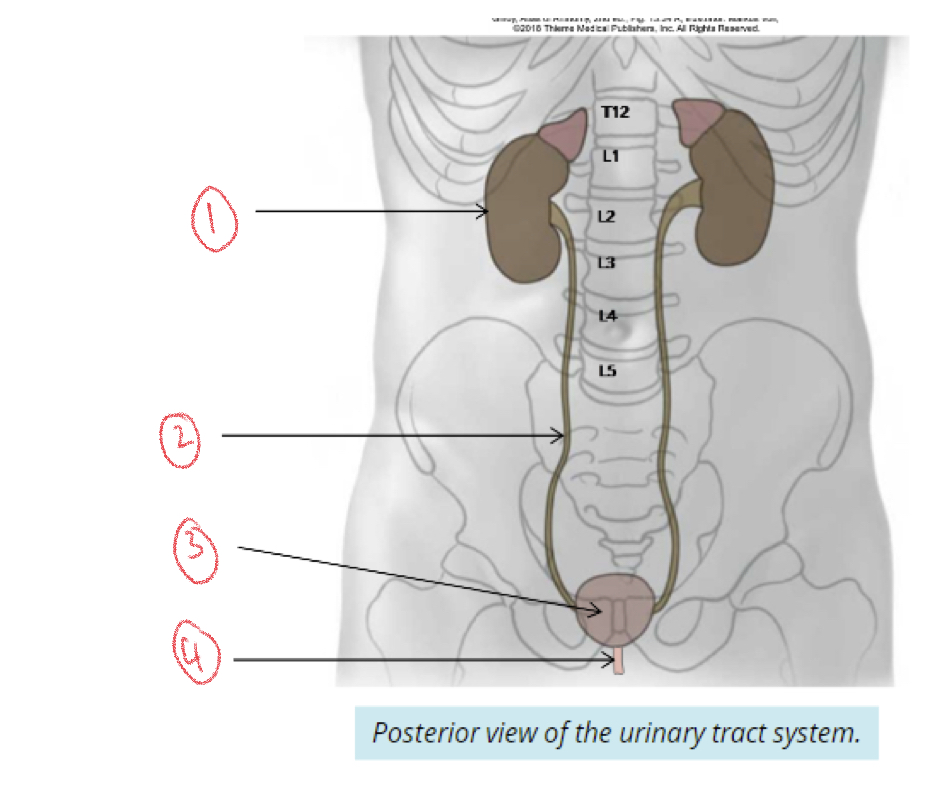
1. Kidney
2. Ureter
3. Bladder
4. Urethra