FYP April Oral Exam
Section 4: the age of reason
- The intelectural and cultural movement of the 17th and 18th centuries
- enlightenments challeneges intelectural authouity (new begennings)
Descartes’ Meditations
- Turn to individual reason as a start of knowledge
- the start of modern philosphy
- about God and the soul
- doesnt want to offend the church
- Meditations are a Trojan Horse
- as they are read, readers have the foundations of their ideas brokmen down and have a realization of cartesian physics
- How do the mtaohysical and epistemilogical questions pave way for his physics?
- Describes his philosphical system as a tree
- the roots are metaphysics and the branches are the otehr sciences
- Written from first person POV
- explains what he felt and experienced over 6 days
- If you follow the mediator on the journed you would come to the same conclusion that the meditator does
- A way to democratize knowledge (like Luther with Faith)
- The power to judge soundly is in all men
- Purpose to achieve metaphysical knowldge
Meditation 1:
- Meditator will follow established practices and turn away from world especially through snese
- Main idea is doubt
- Rejection of all previour beliefs
- Method of doubt is to isolate the good apples from the bad apples (the good ideas from the bad ideas)
- The dream argument
- when we think were having a sensory experience but we are actually asleep
- dreams are imaginary
- How do we know that God isnt deceveing us?
- Idea of diffrent froms of doubt
- Calls into question our ablitity to reason
- Meditation ends with meditator being in etreme doubt
- What is Descartes’ purpose:
- Intrested in addressing the rise of skeptical philosophy
- The nature and limits of human knowledge
- Articulate the respomnce to the highest form of skepticism and then restablish it
- emphises on the posiblility we have to generate reliable knowledge from our sense experience
- to make way for the recounts of the physical world
Mediation 2:
- Meditator will clear the mind of sensory and find the idea of God in the mind
- suggest that one certain truth can produce great knowledge
- meditator reviews their doubts
- Descartes seeks to establish a foundation of knowledge that is certain and indubitable.
- He begins by doubting everything he has ever believed to be true, including his senses and even the existence of God.
- However, he realizes that even if he is being deceived by an evil demon, he must exist in order to be deceived.
- Therefore, he concludes that the only thing he can be certain of is his own existence, which he famously expresses "I think, therefore I am."
- From this foundation of certainty, Descartes goes on to argue for the existence of God and the distinction between mind and body.
- He argues that God must exist in order for him to have the idea of God, and that the mind and body are separate entities because the mind can exist without the body.
- Overall, Mediation 2 is a crucial step in Descartes' philosophical project of establishing a foundation of knowledge that is certain and indubitable.
- He can call in the existence of the doubt on the existence of the external world
- They cant doubt their own existance
- The meditator to exteend beyond the knowledge of the Cognitio, the must demonstrate the existence of God and that he is benevolent
Mediation 3:
- now looking for knowledge of other things they might hav not noticed- the contents of the mind
- Convinced they know they Cognito is true
- Knows that even though something seems true doesn’t mean it is true
- Concept of “I” has been established
- All ideas are equivalent - the idea of our mental image being on the same footing as truth
- The “Casual adequacy Principle”
- the degree of reality in the case must be as great in the reality of the effect
- Principle forms the basis for the existence of God
- There is more reality in an infinite substance than I finite one - the perception of the infinite is prior in someone than the finite - God is prior to perserptioon of the self
- The existence of any finite being only can be explained through the hesitance of the infinite creative power
- God is subject to no defects - he is perfect - being deceptive is a defect thus God can’t be deceptive
Meditation 4:
- There’s a problem
- IF God exists and doesn’t decide, how is there room for error and mistakes by people?
- The problem of error associated with idea of evil
- existence of error suggests that god is not benevolent nor omnipotent
- He comes to the realization of the initiations surrounding understanding God
- People are limited in nature
- To analyze judgement her relies on 2 faculties (both are imperfect)
- the intellect (knowing)
- The will (Choosing)
- God has given us these faculties and we make errors when we don’t use them properly
- humans are just the creators of error
- 2 forms of freedom
- Freedom of indifference - the will feels no inclination to affirm or deny propositions (Weak)
- Strong inclination to do good - freedom compatible with the determined will
Meditation 5:
- The meditator has discovered some truths about themself as a thinking being
- We should focus on determining the essence by considering our idea of things prior to knowledge of their existence
- The meditator examines their idea of material things - to find what is clear, distinct and what is confused
- He is placing the intuition in further philosophical foundations
- the essence of matter is “continuous quantity” or extensions
- this undercuts scholastics Aristotelianism
- The essence of matter has no motivations '
- iT reflects the propositions of the nature of material things
- Another proof of the existence of God
Meditation 6:
- Desire to regain a new world, different than the one we left behind
- Allows for the regain of the material world, the rehabilitation sense and sensory perception, and the distinction between mind and body
- Imagination vs Intellect
- imagination is the capacity to form mental images
- intellect doesn’t require the extra step of mental image
- The experience of other bodies as things with other qualitative properties
- Mind-body distinction
- If we can clearly and distinctly perceive 2 things to be different - it means they are different
- essence of body is extension - mind and body are different - they are distinct
- Properties of the mind - mental faculties are necessary for the existence
- Mind- body Dualism - 2 substances with defined exclusion from another
- For Descartes there’s a break between the human and natural world
- If the acts of sensations and imagination are non-essential to our nature as thinking things, why do they happen?
- Meditator thinks they have a passive faculty for receiving and knowing the idea of sensible things
- Our inclinations lead us to believe material things exist p God hasn’t given us aunty means to correct it - thus they must exist
- Descartes thinks pain and unpleasant sensations effect the mind body composite
- Sensory error
- To evaluate the trustworthiness of things we should compare recorded sensory experiences to one another
- What is most true is not learned through senses
- The meditation has discovered the essence of mind, proof of gods existence
- our knowledge of thought is more certain than our knowledge of corporeal things
- reason explains our sensory experiences
Elisabeth of Bohemia’s correspondence about the mind-body problems with Descartes:
- Descartes was opposed to Aristotelian explanations
- Elisabeth wanted to know about how our minds move our bodies
- 2 notions of mind and body, and a third of union
- Elisabeth says it would be easier to conceive matter in extension to the sound than the capacity of the soul to move the body
*Madame de LaFayette’s Princesse de Cleves
- book is an emblem for resistance
- the emergence of a modern novel
- The unrest is the source of the order - “orderly unrest”
- Hybridity
- The persistence of the medical romans and the formal characteristics of the genre portrait
- Complex structure of novel - many side stories which foreshadow the larger story
- Maxims of life
- 3 encounters with the princesse:
- 1st at the court
- madame is educating against worldly maxims - the only thing that can ensure happiness for a woman is to love her husband
- 2nd at the jewellers
- prince sees his wife at the jewellers matching stones (she is seeking her match)
- 3rd at the ball
- princesse and Duke of Nemours are a matching of Jews - not meriting like the prince and his wife
- Themes of good judgement and moral reflection
- The importance of last words - maxims for the use of the living
Baroque Art
- Protestants found imagery controversial
- Iconoclasm - rejection of images as heretical
- churches became bare for protestant places of contemplation
- Visual arts were replaces with places for contemplation on the world and not image of God
- Johannes Vermeer “Women Holding a Balance” - seen as a representation of Devine truth or justice or a balanced life
- Council of Trent invented by Pope Paul as the Catholic church’s response to the iconoclasm
- Church officials need to promote correct use of art to avoid idolatry
- art is a tool to teach the doctrine to the illiterate
- Mannerism art
- art that’s overly artificial and ambiguous
- pushes boundaries of imagination
- Bellori
- Artist should move away form extravagance to a more classist way
- Carracci
- Wanted to return to naturalism and renaissance style
- Michelangelo Caravaggio
- known for his naturalism
- Arremisis Gentileschi - “Judith Slaying Holofernes”
- Successful female artist
- Ecstasy of St Teresa
- combined architecture and theatre and structure
- sexual symbolism
- Height of counter-reformation art:
- Bernini counters this as he uses his imagery to illustrate a direct relationship to God
- about our union with the spiritual world
- breaks barriers between Devine and secular
Hobbes’ Leviathan
- thinks Decartes’ theory of incorporeal substance is nonsense
- Name “Leviathan” represents absolute sovereignty
- the state of nature:
- there is no government or social order, and individuals live in a state of constant war and conflict.
- People are naturally self-interested and seek to satisfy their own desires and needs, even if it means harming others.
- Life in the state of nature is "solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short" due to the constant threat of violence and insecurity.
- Without a common authority to enforce rules and settle disputes, individuals are in a perpetual state of competition and struggle for survival.
- In the absence of laws and government, there can be no justice or property rights, and people are unable to make binding agreements or contracts.
- the state of nature is the main reason for the formation of society and government, as people seek security and protection from the violence and chaos of the natural world.
- The social contract:
- an agreement between individuals to surrender some of their natural rights and freedoms to a sovereign authority in exchange for protection and security.
- The social contract creates a commonwealth or Leviathan, a powerful entity with the authority to enforce laws and maintain social order.
- The sovereign authority is created by the consent of the people and derives its power from the social contract.
- The sovereign has absolute power and is not subject to the laws or authority of any other institution or individual.
- The social contract creates a hierarchy of power and authority, with the sovereign at the top and the people at the bottom.
- The social contract imposes obligations and duties on both the sovereign and the people, and failure to fulfill these obligations can result in the dissolution of the contract and the breakdown of social order.
- Hobbes believed that the social contract was necessary to prevent the chaos and violence of the state of nature and to create a stable and secure society.
- John Locke disagrees with Hobbes - thinks unchained power of the sovereign is dangerous
*Newtonian Cosmos
- Divided into celestial and terrestrial
- terrestrial is region of change
- celestial is unchanging and perfect
- Copernicus cosmos -sun is at centre
- Johnannes Keeper
- agreed with Copernicus
- Knew sun guided earths motion somehow
- uses math
- Decartes’ Vortice
- His explanation for the motion of planets
- isn’t mathematical
- Isaac Newton
- has mathematical proof for reason planets move around sun
- “The Principa”
- distinguish from the practical mechanics and the rational mechanics
- Turns outwards to understand external world
- descartes turnes inward
- Newton’s Law of laws of motion
- Law of inertia - continued state of rest
- a change in motions proportional to the motive force impressed and takes place along the straight line in which that force is impressed
- The General Scholium
- text which uses the principal - strengthen the idea of God
- God is the only explanation for the regular and stable system
Emilie Du Chatelet
- translates Newton’s philosophy which opens it up to the public
- “The foundations of Physics”
- includes commentary on nature of forces
- sense of how her approach differs form Newtonian and Cartesian thought
Leibniz, China, and The Kangxi Emperor
- Leibniz sought to deepen the connection between Chinese and European thinking
- Jesuits and Confucianism
- Kangxi Emperor
- sponsored western learning
- liked Leibniz
- The Jesuits in China
- saw Asia as an opportunity for conversion
- Leibniz sided with Chinese regarding Confucianism not being compatible with west
- Leibniz
- a universal genius
- completely the monadologie
- accepted challenge of Descartes that there’s only one substance
- new dynamic view of nature
- The Spirt and body don’t interact
- idea of the monad:
- monad is like an atom that constitutes everything
- Nothing can pass in or out of them
- Contrary to Descartes: Leibniz asserts that all living creatures have souls or monads
- God is sufficient reasoning for the universe
- Monads explain how the soul can affect the body
- God has pre established the harmony of the world - motion of people etc
- His conception of nature is dynamic
- changes come from an internal principal
- “Emperor of China - self portrait of Kangxi”
- open to christianity
- we draw our conclusions from experience not from study
- regarded western learning as useful in some ways
- did not westernize in the end
John Locke’s “On Property”
- Jurisdiction over territory - the right of sovereignty
- the creation of wealth through the conversion of nature into private property
- Acquisition of property is the rational for empire building
- Locke’s Political theory and foundations:
- 2 treatise
- 1 - absolute monarchy which Locke opposed
- 2 - Justice of European Imperialism and assertions of sovereignty inhibited by indigenous
- Importance of self-preservation (like Hobbes)
- Parliamentary democracy
Locke’s Larger Political theory:
- opposition to the monarchal rule - king’s are selfish
- Property is defined by the land and private property encompasses the lives, liberties and states of everyone
- God gave us this land
- move away form the state of nature - use the social contract instead
- Moral claim - anyone who creates something is entitled to it
- Empirical Claim - labour creates property by increasing its value to the general benefit of humanity
Ever de Vattel’s “The Law of Nations”
- authoritarian figure in European law of nations
- A nation can lawfully take possession of parts of a vast nation in which there are scant population
- justifies taking land form indigenous peoples
Royal Proclamation
- Locking background
- used to prevent way between American colonizers and French cononeis
- Treaty of Paris:
- Transferred French colonies to Britain
- prohibited colonial government from making declarations on land rights, and stopped the people from making claims without their proper licensing
- Treaty of Niagara:
- guaranteed the fundamental principle that both sides would respect their internal laws and governments
- reflected the European view that the empire was unoccupied before it was claimed
Proclamation in the US:
- Provoked by the American revolution
- Johnson and Macintosh
- Attempted to prevent conflicts between colonists and Native American tribes by establishing a boundary line that would separate them
- Macintosh won - removing indigenous peoples from their land would be lawful
Rousseau’s Discourses on the Origin and Basis of Inequality Among Men
- Society
- source of enslavement
- distorts our empathy
- We are unhappy in modern society because there is something in our unhappiness there’s remembering us before we fell int civilized life
- Need to be transformed - MOVE BACK TO NATURE
- Natural man (noble savage) - heightened man who likes in a naturalistic social category who is less corrupted by high society
- Attacks Locke and Hobbes
- Civilized vs Natural:
- secularization - the social becomes sacred
- conscience - morality comes to us in the voice of nature
- Authenticity - we yearn to overcome the 2 faced life of society
- External impact - very change in humanity is prompted by environment
- Two kinds of inequality - Natural and artificial
- Perfectibility - entirely human capacity and the source of all our unhappiness
- Private property is the orogen of all inequality among people
- Amour de soi -natural and innocent love of self which humans are bored with
- Amour Propre - self-love that is based on comparisons with others and the desire for recognition and approval from them
*Voltaire’s “Candide”
- rise of enlightenment and secularity
- Optimism theme
- 2 crucial thoughts:
- the monad - all of reality is composed on monads, spiritual or metaphysical atoms
- We live in the best of all possible worlds
- follows the adventures of Candide, a naive and optimistic young man, as he travels through Europe and South America.
- Candide is taught by his mentor, Pangloss, that this is "the best of all possible worlds," despite experiencing various tragedies and injustices throughout the novel.
- Candide faces numerous challenges, including being forced into the army, witnessing an earthquake in Lisbon, being robbed and enslaved, and encountering a variety of absurd characters.
- criticizes various institutions and ideas of the time, including religion, philosophy, politics, and the concept of progress.
- concludes with Candide and his companions settling on a small farm and rejecting the idea of philosophical optimism in favor of a more pragmatic and realistic approach to life.
- uses humor and irony to critique the prevailing ideas of the Enlightenment era and to expose the flaws and hypocrisies of the society in which Voltaire lived.
Friedrich Schiller’s “The Robbers”
- unique way of expressing the revolt of the German Youth
- Strum and Drang:
- literary movement - storm and stress
- Enlightenment - man’s emergence from immaturity
- has internal and external dimension
- Strum(storm)
- External - external conditions of literal storm or upeahval
- internal - external pressure, oppression
- Drang (stress)
- external - externbal pressures
- Internal - individuals inner dirve
- seeks to consider previously unexplored topics or present familiar topics in a new light
- “The Robbers”:
- The play follows the story of Karl Moor, a young man who rebels against his father and becomes the leader of a band of robbers in the Black Forest.
- Karl's brother, Franz, conspires with their father to frame Karl and have him arrested.
- Karl's fiancée, Amalia, is caught in the middle of the conflict between Karl and Franz.
- The play explores themes of rebellion, justice, morality, and family conflict.
- The characters in the play often speak in dramatic, passionate language, reflecting the emotional intensity of the story.
- Frans vs Karl:
- Franz - Machiavellian and trickery and deceit
- Karl - embodyment of strum and drang and law and order
- Both ignore the nature of freedom
- many allusions to Jesus
- Despair major theme:
- Religious Despair
- despair -the loss of hope
- Franz cause his father, Karl, and Amalia despair
“Promentheus” by John Von Goethe
- from Greek Mythology - prometheus is one who has forethought
- depicts the radical subjectivity
Cugoano’s Thoughts and Sentiments on the Evil of Slavery
- pioneer of African thought
- gives us access to the culture he was born into
- Political philosophy
- natural rights theorist
- anticipates the modern philosophical discourse of the modern day
- Metaphysics of The Emblem theory:
- Emblem theory is how God communicates with us
- uses symbolic messages
- Cugoano denies the use of the bible as a valid reasn for slavery
- Original Sin - inherent even in everything contratr to that which is good
- Servitude:
- Puts slavery in larger context of sevitude
- Slavery is a form on unjustefied servitude
- also a non ideal but jusifyable servitude -punishment
- you have some rights as a slave
- Cugonano’s 3 point plan:
- National repentanmce
- abolish slavery
- prevention of slavery
John Locke’s On Slavery
- humans are inherently equal
- Locke and Cugoano both root our equality in our relationship with God and with each other as rational thinkers
- thinks complexion comes from climate
- uses bible as proof for arguments
- Africans and Europeans just as wise as each other
- age of reason occurring in text
- enlightenment values upheld
- state of nature justifies anyone being a slave owner
- law forced through punishment
- you dont have rights as a slave
Immanuel Kant’s “Groundwork for the Metaphysics of Morals”
- radical break in Kant’s work from what we’ve already encountered
- kant in the development of modern thought:
- Descartes is the background for his work
- 2 oppositions:
- Rationalism -law representing nature
- Empiricist - represented by Hobbes, all ideas are rooted in sense experience
- Enlightenment is experienced through subjective freedom
- Unprecedented skepticism
- freedom, duty and morality are the concerns of practical reason
- Enlightenment for Kant - not about acquiring something new but leavings something behind
- Kant’s solution to the rational Empiricist - in order to accept and trust cause and effect we would eb able to sensually perceive it
- Copernican revolution - turning ball to the human mind as the object of deliberation
- Give up the theoretical proofs for the existence of God
- use your reason for theoretical purpose
- in the direction of knowledge
- Text begins with the proclamation that we cannot conceive any thing food without qualification without a good will
- Free will:
- The faculty of the will is never directed deter emend by an external force
- for an object to become real for the will, an action must be take up into a rule
- maxims govern our actions - the practical policy which mediate the object for the will
- formulation of maxims:
- acts as mediator between natural inclination and the will to do it
- Formula for universal law - definitive stare if Kantian moral law
- categorical imperative:
- the concept of an object principle is a common of reason
- imperatives say that something would be good to do but the will doesn’t always follow it
- objective morals- laws we act in accordance to
- hypothetical imperatives - as if then statement
- categorical imperative - declared an action to be objectively necessary
*Mozart’s “The Magic Flute”
- conveys ideas verbally and musically through couples (pairs)
- Contrasts day vs night - statement on enlightenment
- challenges a binary reading of the story and the enlightenment from within
- The story revolves around Prince Tamino, who is tasked by the Queen of the Night to rescue her daughter Pamina from the clutches of the evil Sarastro.
- Tamino is accompanied by the bird-catcher Papageno, and both are given magical instruments: a flute for Tamino and bells for Papageno.
- Tamino and Pamina fall in love, but Sarastro tests their devotion through a series of trials.
- Papageno finds his own love interest in the form of Papagena.
- Ultimately, Tamino and Pamina prove themselves worthy and are united, while Sarastro and the Queen of the Night reconcile their differences.
- strong connection to masonic ritualism
- female connected with light and the male disconnected with night
- can be read as a unification of opposites or as a necessary polarization of it
Section 5: The Era of Revolutions
- Chant de Guerre pour L’Armée Du Rhin - “La MARSEILLAISE”
- inspired by the push to defend his homeland
- became the nation anthem of france
- image of unity and hope
- represents the age of revolution
- The French Revolution
- Napoleon named himself as emperor
- Bankruptcy
- French monarchy seen as represnter of God
- enlightenment thinks rejected Devine law and right of kings
- Riots
- assembly created new constitution
- inspired by the American declaration of independence
- Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
- replaced religious art in homes
- foundational document of the revolution
- represented the French people
- states that:
- everyone has right to own oppinions
- you can criticize the governemnt
- play should be equal
- everyone is equal - “man and citizen”
- active citizens - French men over 25, who payed taxes
- eliminated all women, children, servants
- reformation of the church
- Emergence of the wings of politics
- The French Terror:
- revolution raised questions globally
- France was at war with other countries
- idea of revolution under threat
- many people where ‘purged’
- punishment of traitors justice
- keeps aristocracy in its place
Haitian Revolution
- massive uprising of enslaved peoples
- not caused by French Revolution
- French government was reluctant to give them up
- torn relationship with France for many years to come
- First document - proclaimed their independence from France
Mary Wollstonecraft’s “A Vindication of the Rights of Woman”
- mother of Mary Shelley
- went to French Revolution
- first wave feminism
- wanted same rights as the French and American revolution
- What do we mean by equal?
- fighting for virtue - men and women having equal opportunities
- influenced by Rousseau and Robbespierre
- political propagandist
- critiques arbitrary power
- secular in her arguments
- weak women and children = weak state
- they should be educated and involved
Hegel’s “Philosophy of History”
- The Aristotle of modern philosophy
- Eurocentric thinker
- Culture
- what is fundamental isn’t just culture - its which can be realized through culture
- freedom is the fundamental principle
- Specificities - particular forms of life (people, institutions, events)
- universality - all of that particularity is the way that something universal and fundamentally human or Devine is at work
- Freedom:
- needs to be universal in character
- sense of self
- not in the natural state
- state is subjective
- secularity
- moments of freedom
- negative freedom (Hobbes, Locke, voltaire) - limiting the givovernment
- positive freedom ( Rousseau and Kant) - creates slavery
- Absolute or total freedom - desired sense of freedom speaks to our deepest aspirations when made absolute = against itself and produces terror
- result is death
- romantic freedom - desire to recognize that freedom is connected not only to external political forms but also to th human life
- freedom is not subjective
- spirt:
- subjective
- objective
- abstract light
- morality
- ethical life
- family
- civil society
- the state
- absolute
- art
- religion
- philosophy
- knows itself as itself
- History:
- hot just human evernbts
- eurocentric
- pre-history
- world history
- end of history
- written history
- original history (primary texts)
- reflective history (moral evaluation)
- philosophical history (relationship go the OG events)
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein
- context
- written during cold and rainy summer in Geneva - volcano euruption
- Title:
- near a castle called Franenstein where a famous alchemist lived (like victor)
- subtitle:
- the modern prometheus - remains us to ancient world
- stole fier to give to humans - manipulates nature
- connected to victor - both push past the natural limits of death, lack foresight, and chained
- fire imagery - to warm, distruct, comfort, danger
- gothic literature -context
- sub-genre of romantic lit.
- Volume 1:
- wrote as a series of letters between Walton and sister
- vol 1 -walton and victor
- vol 2 - walton to creature
- vol 3- creature to walton
- Main themes
- isolation
- the sublime (creature)
- you are what you read
- walton introduces us to the problematic nature of the Martin -connects to the story of Victor
- egotistic indivodulaism
- Waltons ambition '
- the cooperative ideal is part and parcel of victors childhood in Geneva
- the cooperative ideal is part and parcel of visors childhood inGenerva
- Generosity
- carolines childhood
- Elizabeth is taken up into the family
- The catalyst for victors ambition is his reading of Agryppa
- he leaves home to study at the university
- the appearance of the creature repels actor
- nature is described as a women - science as a source
- Volume 2:
- devoted to the creature’s story
- offers education in compassion - to sympathize with others
- Volume 3:
- disastrous conclusion of the relationship between creature and maker
- most significant
- John Milton’s Paradise lost:
- Adam and Eve fall from paradice
- read in conjunction with the notes from Victor about his creation
- converges and difference with Creature and Adam
- Various readings
- Monster rad as an image of the working-class poor
- liberated slave is like a liberated create - would cause destruction to its maker
- Analogy for america - monster created by the elite
- commentary on the technological domination of our loves
- anticipates the future
- ambitions of the labor moubements and civil rights activist
Marx’s And Engel’s “Communist Manifesto”
- most influential text of 19th centurey
- predicted how would world would be transformed
- republicanism - the ancient ethos of self-sacrifice for the good of the state
- admired Hegel’s idea of the state
- Asians of the morderns is more modest- enjoyment of secularity and private pleasure
- individual independence demands endless sacrifices - disastrous consequences
- Marx and Engelstasked with determining the true nature of communism
- the new system of the division of labour = repetitive motions and injury
- Bourgeoisie:
- the burgess of the towns arose form the rising class
- infusion of the new forms of wealth that leads to a drastic scaling up of the means of productions in Europe
- system of production dense only include the machinery but individual labour
- Demand is rising and manufacturers can’t cope
- money and capital are transformed
- capital :
- like a process
- money doesn’t equal capital
- Purpose of consumption is to satisfy needs
- Heat and soul of labour (social labour) is the life force for the bourgeoisie
- the work of the proletariat only produces capital for the bourgeoisie - their only purpose
- gothic language
- criticizes the structure of the world
- want a new social and political structure of emerge
- proletariat revolution wa not actualized
- bourgeoisie didn’t live up to its revolutionary potential
*Mill’s “On Liberty”
- wife Harriet was the co-auther
- Sovereign
- core elements of his writing
- concerned about society as a whole
- interfering with someones freedom is only justified when its for the protection of others
- barbarians doens’t deserve rights
- liberalism may not just be bout freedom but about a specific vision rooted in western culturee
- ch.3 - emphasizes how its only the exceptional individual that can save society from being mediocre
- utalitarianism - a view according to which we should evaluate our actions through their consequences
- maximize the good and happiness and truth
- cha.2 - defence of freedom and expression
- we should be able to speak our mind
- mill limits speach
- hold other accountable for harming others without condemning them of harm themeslebes
Emily DIckinson Poetry
- works are fragmented like Sappho but its intentional
- illuminates the complexity of one subjectivity
- radical individuality
- disire to organize poems and present them -to herself
- plunged into her own mental world
- emphasis on love and loss
- death
- meaning in how her poems sound aloud
- painful and ironic cry
- personal loss
- God although she didn’t attend church
- short poems with large subject matter
- sexual delight and joy
- blurs lines between nature and sexuality
- joy and bliss
- fact of morality
- loosing ourselves and others
- both ecstatic and horrifying at once
- consciousness, inspiration and the process of making her poetry
- caught between old order of faith and a new one of science and evendence
Wagner’s “Tristan Und Isolde”
- prelude:
- ominous feeling
- lament, sinking feeling
- Total artwork - gives the fullest expression of community
- The myth of Desire:
- desire can never be fulfilled
- will manifests itself in desire - generative
- we can only find relief in art or death
- how do we resolve the opposition of day and nigh, duty and will/ desire, illusion and reality
- Music, desire and deliverance
- difference - challenged by the night of love
- reason and society rules
- there’s a struggle until they get to the dissolution of the difference
- Tristan chord - uneasy, dark
- chord doesn’t resolve
- light motif
- romanticism
- core opposition of day and ugh, life and death
- suggest tha the highest peak of pre can bring freedom or relief form desire, time and pain
- music as pornogrpahy
- Wagner makes himself the opera
- immoral
- connection to Terror - desire for an end, relief in death
*Darwin’s “The Descent of Man”
- demographic law dictates that any population is leading towards overpopulation
- solutions:
- preventing surpulus
- famin
- connection to Tristan und Isold - pessimism, love death
- most interested in natural selection
- connection of law of over population to non-human animals
- perpetual scarcity of resources there must be a struggle for existence
- Natural selection :
- Core argument is an analogy that breeds of pigeons vary but they all have one common ancestor
- selection of charitable characteristics
- Components of artificial selection :
- variation
- inheritance
- differential rate of reproduction
- Natural selection founts predestine direction of the divergence of a pollution from the ancestors
- means natural forms depart naturaly form their ancestors
- Eugenics
- advocates championed the ideas of stringent having kids bit also having sterilization
- Duty and Morality:
- quotes kant on duty
- agrees with kant that we have a sense of duty because we are rational beings
- duty is innate
- morally is due to social instinct and developed intellectual power
- man is a social animal
- moral instincts and intelligence is what makes hims unique
- we have aggressive instincts - sex with lust, self preservations etc
- evolution by natural selection is not something morality provides an exception but something our morality is evident of
- ch 5 most famous
- argument that if human intellect and morality have evolved, it occurred throiugh natural selection
- humans struggle for existence has taken place in constant war (HOBBES)
- race:
- monogenesis (cugonano)
- updated to polygenesis
- abolitionist
- convergence to transmutationism connected to his abloiistionsit views
- origins or race - claims there are difference between racial differences and mental differences
- sexual selection
- mechanism that explains why certain characteristics dominate certain groups
- exists from sexual characteristics
- applied to humans and non-humans
WEB Du Bois’ “The Souls of Black Folk”
- Notion of Double Consciousness
- main question - how does it feel to be the problem - “negro problem’
- from whit male perspective
- metaphor of the veil
- thin
- the experience of rejection
- between white and black world
- connection to Hegel - bases of history, describes the 6 people described by DuBOis
- Hegel thinks Africa was outside history
- rejects despsisle of black people - suggests they are emerging as a world of historical people as significant as others
- alienated consciousness
- second sight - ability to see from another perspective
- results from alienation of double counscousnes.
- goal is to be African American - whole
- Higher education
- elitist
- individual indication of the value of higher learning
- admission the current conditions of racism to dictate the risk of ragout
- the black church
- descriptions of the southern black revival
- detachment and unfamiliarity helps with the equalization of European and African heritage he desires
- questions leadership that black people have
- religious tendency thats hypocritical
- cblack church was politically ineffective (up until the 1960’s)
- On the sorrow Song:
- black music is a new American creation
E. Pauline Johnson’s “A Red Girl’s Reasoning” and “A Strong Race Opinion”
- writer who’s outside of the western tradition we have studies so far
- drama of identification and misidentification
- Definition of Setteler colonialism
- vanishing indian
- Indian princess
- diffrent socia roles that that of western women - lead to fantacy of women as an object of desire
- Nobel savage
- Stereotypes
- domination of an indigenous popiipation by a minority population of settlers
- Her poetry:
- not a new style
- sentimental
- victorian style
- speaks to growing fascination with the indigenous
- few today remain - vanishing Indian trope
- “A request”
- reflects aftermath of northwest resistance
- invokes patriotic enthusiasm of settler canada’
- “A Strong race opinion”
- about indegfenout material
- costume changes capitalized on her mixed race and white passing - culture socks to the audience
- symbol of her pre-euepean like - not historical authentic
- capitalized on racism of her audience
- essay disputes that white people can’t write real indigenous characters
- women are tragic characters
- victorian dress and buckskin dress both are costumes
- “A red girls reasoning “
- new women cultivation of feminist mouvement (Wollstonecraft too)
- resisted many western genre roles (autonomy )
- uses pre indirect discourse (3rd person - no ones perspective)
- Christine reflects Johnstone
- Charlie embodies new state of organized colonialism dominating after Canadian independence
- deosn’t need anyones permission to get a divorce - feminism
- drama of identification and misidentification with her audience
- speaks in idiom of the colonize to say that she is still her and surviving
*Colonial Deformations in Modern Chinese and Japanese lIterature
Lu Xun - “A mad man’s Diary”
- china’s 1st short story
translates modernity - western ideas came to Japan
lu xun encountered stereotypical books that he referenced in his dirareos
idea of nice Chinese character
national character and individualism formed basis of claims to modernity
connection to Johnson - taking colonial attitudes and stereotypes as means to counter
Chinese modernists appropriates western modernists
linear, progressing forward moving time
“A madman’s Diary”:
- hes not really mad - speaking truth to power - out of sink with reality since he’s ahead of his time
- read as a literary perspectivism
- perspective and knowledge are linked to the perspective of those experiencing it - Nietzsche
- testament to the mans past
- time and chronology - reliable and sympathy
- presents as a true and unfiltered account of the sick mind
- exploitative - voyeruistic pleseure
- man is anticipating our presence so he can critique society
- self-rgocnition of this madness in the title
- controversial relationship between metaphoric and literal is a little blurred
- mad man confuses referent with the sign - confusing the metaphorical meaning
- view through Freudian lens - pschoanalys
- movement back and forth - confusion tradition
- doctor misdiagnoses the man - dismissal of his paranoia and his ability to see the truth
- self-realization = recovery
Netsuke Soseki “Bicycle Diary”:
- describes experience of being an object of gaze and orientalization
- strong support of westernization and westernization to avoid that fate of china
- sees himself an an other
- what does it mean to be Japanese?
- Bysicle has a gendered aspect
- for bourgeoisie
- escapism
- emancipation of woven
“travels in Manchuria and Korea”
- emphasize japans modernity can’t be separated from coloiamsn
- describes Chinese through stereotypes - they are filthy
- Japanese modernity is colonial - alabour of Colonia subjects
- complicity - relates to the canon
Nietzsche’s “beyond Good and Evil” and “On truth and extra-moral sense”
influential and disturbing critiques of the foundations of morality
- can’t understand his work as break of western tradition
Nihilism - to live and suffer meaninglessly
- isn’t advocating for nihilism - saying that we need to find meaning in our suffering
Rift between Wagner and Nietzsche
“On truth and Lie”
- major claim - that truths are illusions wee have forgotten are illusons
- can’t understand lie as opposite of truth
- lie is primary
- no moral understanding of a lie
- fiction comes before truth
- truth claims are build on shifting sand
- drive toward the formatting of metaphor is fundamental human drive
- rejects idea of finding a philosophy grounded in first principles
- aphoristic tone as the development of the theory of truth
“The Gay Science” - death of God
- god - symbolic for any value we regard as eternally / self-evendely true
- symbol for truth its self
- aphorism made of madman’s declaration of the death of god and the question
- we are nihilism - lack of value in life
- death of god - death of eternal truth
- god is the antidote for nihilism
- victor is death of god - FRANKENSTEIN
“Beyond Good and EVIL”
- moral and fundamental categories
- dent start with anything we recognize as morality
- Structure
- epistemological - theological -polictical - ethical
- what we can know about what it means to have knowledge (Descartes)
“ON the prejudices of Philosphers”
- assigning value to truth - Will
- we are separated from our knowing - it just grasps us
- the mediator doubts in order to know
- truth is posited - its the opposite of life
Section 3 part 1:
- no contraction between action being instinctual and unconscious
- philosophical throught is the expression of the drive or the preservation fro a certain species
Section 4 part 1
- He’s offering a less of a philosophy of truth and more of a psychology of philosophers
- philosophy makes the vision of the world that it claims to merely interpret of inscribe
- Will to power = self preservation
- attacks the foundations of western philosophy - rejects Descartes
- thinks “I” is a falsification - a condition of thinking
- Theory of the Will :
- willing involves a plurality of sensations that we reduce to a fictional unity
- involves a command not just a thought
Part 3: Theological and part 9: what is noble
- distinguishing modern christianity from the ancient
- Good and evil have historical genesis
- master morality
- only between those which fulfill the aims of life and those that impede them
- slave morality
- emerges from negation of every quality associated with the Nobel
- indifference to suffering
- organizes itself as the antithesis
- cultivates an inwardness
- self restraint and mercy
- every value associated with master morality is evil
- creativity
- binary of good vs bad
- requires invention of a rich moral live
- What is beyond good and evil??
Section 6: The Contemporary World
Franz Kafka’s short stories
- period marked by the “crisis of orientation”
- incomparable to others
- contemporary - deeper. essential sense
- “god is dead” - not just christian got - general loss of faith
- catacgorail atheist doesn’t know what it means to speak of the death of got
- enlightened secularists critical of Christianity like Nietzche - dont understand christianity belongs to metaphysics
- not a philospher
- law summons and situates man within his fame
- law not represented in his stories but is enacted in them
- comes in form of a message
- announces its authority in form of song
- subject to the law means you are its subject
- “a report to the Academy”
- title describes what happens
- a report
- Ape reports what begins after his capture
- chooses stage over zoo
- socializes by day on stage at night
- only making a report - sharing knowledge
- actually rooted in his desire rather than effort to impart lmpwledge
- death of god - plunging backwards
- freedom - not available to Peter
- the way out isn’t freedom - wanted liberation from his cage
- suicide reference
- stopries resist the simple meaning
- “On the cares of the Family man”
- Odradek -being unwilling to dies
- questions if its a person or a thing
- similarities to Adam
- marxist interpretation - represents materialist world
- return of family man
- no definitive interpretation
- “before the law”
- parable told by pries to subject of a trial
- explains nature of trial
- door is law
- what are we to make of the door being opened the whole time
- form of authority to the law that remains in force
- must be read with the provocations of Odradek
T.S. Elliot’s “the Wasteland”
- opens with description of the season
- poetry is a medium - practice of escaping emotions
- thought to be inner counterpart of the devestation of Europe from the war
- can be read a social statement
- “Part 1: Burial of the Dead”
- instruction for funeral
- vegetative states - moral example
- summer. - casting mind back to happier times
- Wagner nostalgia
- part 2 “a game of chess”
- doesn’t take direct allusions - he turns them into nihalitsc black human references
- allusions to Cleopatra
- monarch and irresistible saucer
- destruction of an empire
- modern Cleopatra
- latin words
- part 3: “the Fire sermon”
- theme of grim and joylessness
- sexual encounters
- story of Tiresias
- both female and male
- most importat character
- what he says is the substance of the poem
- Magnus harder - church in ruins
- part 4: “Death by water”
- phelbas - internal part of perm
- repeated motifs
- death by water
- meaning of east Europe - famine
- Part 5: “what the thunder said”
- refers to hallucinations of explorers and christ
- vision of apocalypse
- god = control
- human = give
- demins = compassion
- end of prom - doesn’t describe heroic collaps of control
- love is terror- demans loss of self control
- reference to theatrics
*Freud
- father of psychoanalysis
- 2 theories:
- existence of the unconscious (unconscious motivation) - rejecting the claim that you know what you’re doing and why you react
- reminding of father
- process in the domain of the mind
- unconscious dynamics - dreams and mental illness
- process that go in you down head without you knowing
- in conflict with one another
- “The Ego and the Id”
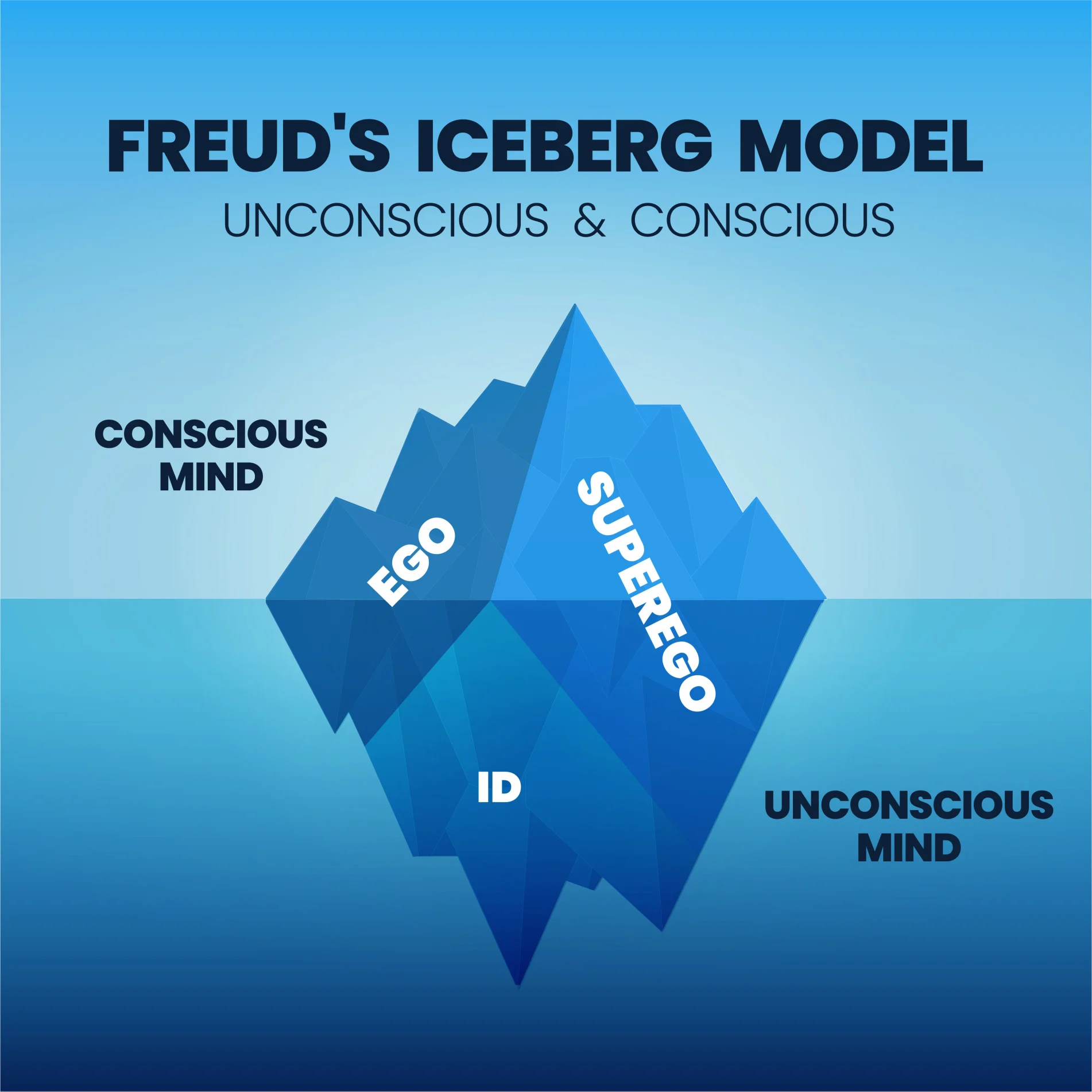
- model of the mind
- id, ego, super-ego
- psychic conflict is a matter of unconscious ideas emanative from the “unconscious system”
- ego ideal - super ego
- ego develops from ID and super ego is exertion of the ego
- Id - compels individual to engage in satisfying needs, activities reducing tension (pleasure)
- relations self preservation - ego masters internal stimuli
- Ego develipemt (understanding yourself as “I”
- super-ego first represented through parents
- oedipal complex - one of the many explanations for the development of a chidl’s character
- ego incoperates ideal and value
- super-ego idea seeking perfection
- akin to conscious of reality
- “Mourning and melancholia”
- rational awareness
- understanding these feelings
- critical ambiguity and gendered ambiguity
- libido - recevoir of driv/ energy
- object libido is what draws us out of ourselves
- hallucinatory which psychosis - when we impose of psychic reality during morning peeriod onto reality
- conception of melancholia - characterized by same thing as mourning - except for self-loathing
- demonstrate that our close familial relationships bear repressed hostitlies
- ego forms identification with lost object and itself structurally altered
Woolf “To the Lighthouse”
- memory of one is transported into another
- her mom died at same age a mrs Ramseys death
- modernist cacophony - breaking, crashing, rebuilding
- about search to compose itself
- thought swell and break apart - nothing behind them
- self is a kind of canvas
- lily’s painting desire for self apprehension
- self isn’t a concete thing
Part 1:
- brings out inner life
- eternity between 2 thoughts
- contrasting mr and mrs Ramsey
- internal battlefield
- mr Ramsay juxtaposes with Tansley
- self esteem connected to academics
- work is about influence of someone on something
- youth
- protector
Part 2:
- fate of civilization - gender
- women communicate telepathically
- Lilly - knowledge of many perspectives
- perceives the role of women is what sustains life
- shortcut that doesn’t get you anywhere
- zoning out from dinner table to outer world - flow of time
- darkness of time
- war novel
- occurs without readers witnessing it
- gives us what’s left after the war
- feminine pov
- mrs Ramseys shawl
- her memory
- maternal protection
- time vs duration
- time has 2 faces
- scientific, objective, constant
- reaction of the night and illumination
- protagonist of book contrasts with nature in to
Part 3:
- lily moves tree in painting
- freedom
- creativity
- standing up to mrs Ramsey
- tells stories of lives endlessly connected
Heidegger’s “What is Metaphysics?”
- seen as something have and revived from lived experienced
- articulation with Nazis
- problem of the philosopher
- simple value judgements.- philosopher can only affirm himself through meta physicists
- follows Nietzsche’s lead challenging conception of truth
- anxiety is a psychological phenomena
- distorted and dismissed
- “Being and Time” / term origins
- inquiry into meaning of being
- What is man?
- regents the idea that man is a rational animal
- man is animal
- doesn’t address uniqueness of man
- brings out critical potential by connecting them to the cartesian understanding of subjectivity
- to theorize about the world is falling away from the original mode of being
- we dont start atop the world - we are within it already
- we exist alongside other beings
- no choice
- you relate to the world by living in it
- we encounter things though function not appearance
- break with Nietzsche
- N - anxiety originates in man
- H - man originates in anxiety
- anxiety teaches is
- “What is Metaphysics”
- doesn’t situate experience of anxiety in contest of world - now in context of metaphysics
- each of the positive sciences concern itself with its own delineative set of beings
- nothing is not same as negation
- negation is specific act of intelects
- To acknowledge myself as a thing in the world is to acknowledge myself as the very opening in which beings can exist
- groundlessness of humans originates in the privelegd experience
- metaphysics is born in experience of being gripped by being in its withdrawal
- exists as long as man exists
- unity binds knowledge - share origin sustaining this knowledge
*Hannah Arendt’s “Origins of Totalitarianism”
- political thinker
- critiques human rights
- camp meant to be treatable outside of totalitarianism
- centreal establisment
- exists only for the cam
- forgiving is hard
- understanding isn’t easy
- Totalitarian Politics:
- implies impossibility of political action
- nazisim and stalinism is the same
- breaks down left and right barriers
- no cause and effect
- Antisemitism - central element
- decay of nation state
- racism
- new and unsettling alliance between capital and mob
- totalitarianism isn’t logical
- designed to presser shock factor
- signalling out terror ( it doesn’t use it)
- totalianterian terror - not means for consolidation of power but is its essence
- tests limits of human power
- ideology - instruments and systems of total explanation
- makes the claim to explain everything tags happened and anything that will happen
- Terry and the concept of law
- characterized by randomness -lawless
- randomness actives of violence
- claim they had a higher reason for lawlessness
- transformationmation of he law transforms mankind into active character of the law
- The concentration camps:
- concerns persevayoj of most partite parts of live and indiscrimination of total terror
- requires obliteration of obstacles
- overzealous administrator and resistant prisoner = problematic
- terror transcends traditional sense as a means for suppression
- features of titliatrian terror
- total terror sets in when it has no more enemies
- traditional terror ends when its object has been destroyed
- terror in the camps isn’t understandable in strategics terms
- rule by terror is characterized by unprecedented lawfulness
- how is the degredation of humans accomplished :
- destruction of the political person
- destruction of the moral person
- make it impossible to escape
- destruction of the individual
- stopped inviduaality
Marie Clements “Burning Vision”
- engaging with the play - engaging in the ethics and epistemology
- generalizes indigenous people
- general narrivite of western culture is linear
- factual narratives
- linear narratives at begening, expanse at the end
- indigenous culture uses non-linear story telling
- cultural references
- desire to hep people - radium helps and destroys
- canada central to development of nuclear weapon
- Fat man represents mr america - dummies in teat house
- miners lied to about radium use
- Act 1:
- degree and non-linearity
- enlightenment thinking
- light and vision
- flashlights, dials, tv
- mystical connection
- dene seer
- prophecies
- use of prophecies often seen as steroteypicsw
- difficult in placing them in literary world
- difficulty in placing them in literary worlds
- claim to intellectual and moral authority
- eros
- eroticiosm, sexx love and connection
- source of hope
- seal imagery and war
- Tokyo rose
- widow and Dene
- communities and ancestors
Simone De Beauvoir’s “The Second Sex”
- Elovution of sociological and historical conditions of women:
- her experienced conditioned by fact that she was a women
- THE SECOND SEX:
- first writer to politicize sexuality
- women need to take their sexuality into their own hands - women liberation movement
- Phenomenology - way of seeing rather than set of docterines
- existentialism - characterized revolts against traditional philosophy
- Hegel - influential role
- considers female oppression through master- slave dialected
- there is consciousness -verything else is negation
- she has a position of strength
- The Book:
- begins with pronoun I
- transition from I am me to I am a women
- situation - structural rationship between our project (freedom ) and the world
- lived experericnece - the way n individual makes sense of actions and the world
- articulates différente between immanence and trancsendane
- externalized eternal feminine is a myth created by men
- Embodiment - the body is theviechicle of being in the world
- she thinks because its true focuses on freedom - begins using WE
- the birth of the female child is not the same as the birth of her womanhood
- never uses term gender
Audre Lorde
- black lesbian feminist mother lover poet warrior
- founder of coloration that helped women in domestic violence in South Africa
- complex identity
- Intersectionality: Kinberele Crenshaw
- motivated voices
- critical race theorist - coined term
- means that social categorizations must be regarded as constituting an overlapping system of discrimination
- lorde doesn’t use this word but its relayed
- “The masters tools will never dismantle the master’s house”
- reformist attitude towards white feminism
- move away for binary - must embrace and class the difference between women
- master - many forms of domination
- masters tool - concrete tools of prodcution
- masters house - product
- “Poetry is not a luxury”
- feeling comes first for Lorde
- growing admits the darkness
- white father - “I think therefore I am”
- black mother - “I feel therefore I can be free”
- poetry can be misssured
- THe cancer journals:
- deep value of the expressive work -make sense of the overwhelming
- comforts dark parts of her expereicen
- shares range of experence
- 3 dimensions:
- confronting death
- refashion of a prosthetic breast
- love of women which health her
- read as providing a journey into the underworld and back
- pain is motivation
- story of warrior women
- refused prosthetics -syumbol of solidarity
- critizesd by other women
- fake subsute
- not real feel or look
- covers marks of her expereicen
- support from women was erotic
- “The use of the exotic: the erotic as power”
- draws people together
- new identity
Modern and Contemporary Art
- Art as politics
- shocks people
- not understood
- Nazi propeganda
- plays -Wganber
- concentration camps -Kids art
- Art History
- Impressionism -
- doent express any particular aesthetic
- visual perception
- renoir, monet etc
- new trade with Japan
- Fin - de -ciècle Vienna
- turn of century
- Gustav Klimt - female body as subject
- nudes
- Egon Schiele - male nudes
- Expressionism -dread after death of god
- representational
- Cubism
- visual representation of fragmented world
- multiple perspectives
- Dada and Surrealism
- resolve conditions of dream and reality
- Frida Kahlo -gender, identity etc
- No more isms:
- pop art - Andy Warhol
- artistic expression and advertising
- multiple mediums
- “rejecting the White Cube”
- Jean-Michel Basquiat
- graffiti
- political and social commentary
- concurrent with hiphop
- la hará - slang for police (commentary on police brutality)
- El Anatsui - tapestryy
- Guillermo Kuitica
- place private spaces in most public spaces
- Cai Gio-Qiang
- gunpowder to create instead of destroy
- Chirtavao Canhavto
- tree of life
Cronon’s “The Trouble with Wilderness”
- wilderness - on e of the tenets of environmental groups
- call tp rethink wilderness is call to rethink on of the founding ideas of envrionementalism
- Environmentalism:
- anti war mouvement and civil rights mouvement connected
- to preserve forests
- social program
- to cherish habitats and prevent their decline
- bene with the pioneers and the prophecy
- 1st wave - initial response to industrialization
- 2nd wave - wide spread social movement
- 3rd wave - comes with era of refelection, self-consciousness, Cronon is the 3rd wave
- coincides with feminism waves:
- nature and women share similar path of oppression and liberation
- 3 responses:
- 1st - moral and cultural critique for the Industrial Revolution
- 2nd - scientific concervation
- 3rd - combines previous elements→ the wilderness ideal
- wilderness ideal accuse ofd being racist, imperialist, western
- place with no culture
- used to have connotations of terror
- then became the new eden
- This reversal has 2 origins:
- the romantic sublime (kant and Burkw)
- sensory
- The dynamically sublime
- feeling of rason to nature
- The myth of the vanishing frontier
- radical enevrionmentalissts unconsciously plan out the frontier myth
- wilderness is problematic for the environmentalism mount
- environmentalism rejects idea that humans are separate from nature
- cultural view - wilderness doens’t exist without culture or gains its values through culture
Fanon’s “The Wretched of the Earth”
- The subject - the political uses of violence, is heavy
- Our reflexive position seems to be "why cant we all just get along?"
- says that our political feelings can be sorted through recognition
- conflict of interest that are not theoritcal
- I have no rational thinking
- thriving comes at a cost
- silence can be mistaken as peace
- dissaray - project of decolonization
- Influences on his thinking:
- aime Césaire - figue in the self determination mouvement
- goal to achieve black solidarity
- hegel - master slave dialectiec
- Valence and political Violence:
- common internal identity must be forgetd by anti-colonial violence
- Ribespierere
- “On Violence”
- patchwork text - composition of old works
- Hannah ärendet - he indulges a glorification of violence
- glorifying violence means he’s pressing it as praise-worthy
- not a philosopher
- militant
- “Third worldism”
- 3rd world - not aligned with 1st or second world
- foregroumndimh the colonial dimensions of the context
- Axism of struggle
- north - imperial powers
- south -terriotires ecolioted
- 3rd world emerges out of colonialism
- colonialism is always violent
- compartmentalized the world
- colonial society is fundamentally violence
- decolonization unifies the world
- connection to Neitzche - the will to truth is the disguise of the will to power
- bourgeois is aversion to violence
- complications of post -colonial period
- doest grand dignity to those emerging nations
- theyre vassals now
- Violence is the absolute praxis of the colonies
- Hegel lacks the sense of praxis
Coetzee’s “The Lives of Animals”
- prose and poetry
- the life - life of an animal with everything to loose
- makes sure Elizabeth sees herself as an animal
- she can’t come to terms with life
- horrified by what we do to animals
- loss of sanity
- animals compared to humans in holocaust
- we are human animals - were loosing humanity
- fall into state of sin
- deflection
- cortical factor in deciding what is accessible is if we share something we being in question
- her response : important to the lives of animals, but also to the question of liberal arts education
- its a disembowmnety of our own immorality
- a daily to acknowledge something about ourselves
- project of radical skepticism
- Elizabeth divides people top image themselves like she does - though being of a corps
- Beauvoir - being comes into existance thgough words and deeds
- continuity of all mortal beings
- syymapthectic imaginatiuon:
- character gains our sympathy since they unsettle the preconceived experience
- descartes - if we could achieve certainty rearing other people
- knowledge relies on action and response