BIO 152 Exam 2 Study Materials - Key Terms & Definitions
1/287
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
288 Terms
What does the signaling cell do?
Releases signaling molecules (ligands)
What does the responding cell do?
has receptor proteins that bind to the signaling molecule
What does the release of a signaling molecule affect?
Only certain cells in the body, some more than other
Clarifications about releasing a signal for intercellular communication
- There must be a receiving cell with functioning receptors for a signal to work
- Only cells with that receptor will respond
Clarifications about the signaling and receiving cell
- They can be the same cell (autocrine signaling)
- They can be far apart (endocrine signaling)
- They can be in different organisms (pheromone signaling)
Clarifications about the signaling switch for the responding cell
The amount of signal and type of receptor can cause different degrees of response in the responding cell
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining a stable internal environment
What does homeostasis involve?
Cells communicating and cooperating
What does a sensor do?
Determine stimulus value
What does the integrator do?
Compare the stimulus value to the setpoint
What does the effector do?
Change the conditions
Steps of homeostasis
1. Stimulus
2. Sensor/Receptor
3. Integrator/Controller
4. Effector
Clarifications about how variables are regulated by homeostasis
- Some variable are not regulated (conforming)
- Not all regulation is homeostasis
Clarifications about sensors, controllers, and effectors being unique organs/cells
- A cell, tissue, or organ can be both a sensor and a controller or a controller and effector
- A homeostatic system can have more than one type of sensor, controller, and effector
Clarifications about effectors releasing hormones
- Hormones are a type of signal
- Effectors are what produce a response that directly causes a change in the stimulus
Clarifications about a set point being a constant value
- Set points can be a range
- Set points can be changed by the body
Steps of a negative feedback loop
1. Sensor
2. Integrator
3. Effector
Negative feedback changes a variable to be?
Higher/lower
Clarifications about all feedback being negative feedback
Positive feedback is where feedback causes a stimulus to change in the same direction (higher to higher or lower to lower)
Clarifications about negative feedback always lowering a stimulus
- "Negative" refers to the direction of the response in relation to the stimulus
- If the stimulus is too low, the response is to make the stimulus higher
Clarifications about all negative feedback being homeostasis
Negative feedback can be a response to a stimulus that is not a regulated part of the internal environment
Endotherms
- Able to be active in cold temperatures
- Requires higher metabolic costs (more food)
Ectotherms
- Reliant on external environment
- Lower metabolic costs (less food)
Types of signals
- Small molecules (amino acids)
- Proteins & peptides (insulin)
- Steroids (lipids)
- Endogenous vs Exogenous ("normal" vs drug/toxin)
What do micelles look like?
Hydrophobic inside (heads on outside, tails on inside)
What do micelles do?
Store lipid signals
What do vesicles look like?
Hydrophilic inside (heads to tails, tails to heads)
What do vesicles do?
Store hydrophilic signals
What do signals release by exocytosis do?
- Vesicles/micelles fuse with plasma membrane
- Interior of vesicle is released into extracellular fluid
Types of signalling
- Endocrine
- Paracrine
- Autocrine
- Direct
What is autocrine signaling?
Signaling and responding cells are the same cell
What is direct signaling?
Gap junctions/plasmodesmata - passages between plasma membranes
What is endocrine signaling?
Through the bloodstream - requires bulk transport
What is paracrine signaling?
Nearby - about 20 micrometers or less (a few cells away)
What is the difference between endocrine and paracrine signaling?
Endocrine signaling uses bulk transport (such as blood) while paracrine signaling uses diffusion
Example of paracrine signaling
Neurons cause muscles to contract at the neuromuscular junction
Example of autocrine signaling
Interferon release by viral-infected cells induces the same cell to undergo apoptosis
Example of endocrine signaling
In the medaka fish digestive tract, islet of the pancreas release insulin into the bloodstream. The insulin travels to liver cells that respond to insulin
Example of direct signaling
Multiple cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) are connected by a gap junction
What are receptors
Proteins on/in a cell
Examples of receptors
- Cell surface proteins
- Intracellular receptors
What does the ligand (signal) bind to
The shape of the active site
Steps of receptor activation
1. Receptor inactive (no ligand bound)
2. Ligand binds to receptor (temporarily)
3. Conformational change (change in shape of receptor)
4. Singla transduction: Receptor activation leads to activity in cell
Types of receptors
- Intracellular receptor
- G-protein coupled receptor
- Ligand-gated ion channel
- Enzyme-linked receptor (receptor Kinase)
What type of signaling molecule is non-polar
Steroid
Steps of an intracellular receptor
1. Hormone goes through plasma membrane, binds to receptor, receptor changes shape
2. Receptor migrates to nucleus
3. Gene expressed
Where are cell surface receptors located
plasma membrane
What do cell surface receptors receive
hydrophilic signals
What is the extracellular domain
binding site for ligand
What is the transmembrane domain and what does it do
hydrophobic amino acids, transduces signal to inside
What does the intracellular domain do
causes a cellular effect
What are ion-channel linked receptors dependent on
Ca++ for muscle contraction
What are the types of ion channels
- Ligand gated
- Mechanically gated
- Always open
- Voltage-gated
When a protein changes shape, it
must be destroyed because it no longer works
What does activated adenylyl do in G-protein activation
converts ATP into the second messenger cAMP, which in turn activates protein kinase A
What does activated protein kinase A do in G-protein activation
phosphorylates proteins in the heart muscle, causing the heart rate to increase
What does cAMP act as
second messenger, binds to enzymes to activate/inactivate them
Steps of going from ATP to cyclic AMP
ATP - Adenylyl cyclase - cAMP
What does each member of the receptor pair do in enzyme linked receptors
each member of the receptor pair attaches phosphate groups to the other member
What does the phosphate group do in enzyme linked receptors
provide binding sites for intracellular signaling proteins
Steps to activating a receptor
1. Receptor is inactive
2. Receptor dimerizes
3. Receptor autophosphorylates
4. Signal transduction leads to activation of second messengers
What is a kinase?
Enzyme that transfers phosphate to a protein (phosphorylates)
What is a phosphatase
Enzyme that removes phosphate from protein (dephosphorylates)
What does phosphorylation cascade allow
allows for integration of signals from different sources
Which organisms have cellular communication?
All complex multicellular organisms
What are nervous systems found in?
Only animal, not protists, plants, fungi
What do all eukaryotic cells have
electrical difference across membrane
What does a negative charge inside a cell help do
helps move cations into the cell against a concentration gradient (Na/K/ATPase pump)
What is the first even in nervous system evolution
Neurons in a nervous system - use changes in electrical charge to transmit signal within a cell, then use paracrine signaling/gap junctions between cells
In what organisms is a nerve net found?
sea anemones, jellyfish, comb jellies
What do jellyfish, comb jellies, and sea anemones not have
central nervous system
What is the structure of a nerve net
- Sensory neurons: detect stimuli, output to motor neurons
- Motor neurons: input from sensory neurons, output to muscles
What do pacemaker neurons do in jellyfish
create rhythmic electrical signals that do not require input
What are ganglion
group of neurons in communication with each other
What are internuerons
neurons between sensory and motor neurons
What do ganglia allow for
allows for processing of information
Steps of information processing
1. sensory neuron
2. interneurons
3. motor neurons
What are ganglia, centralization & cephalization in
bilateral animals
What is centralization
localization of ganglia in central part of the body
Types of nerve cords with ganglia
- Ventral nerve cord: most invertebrates
- Dorsal nerve cord (spinal cord): vertebrates
What do pacemaker neurons help with in centralization
movement
What is cephalization
large ganglion in the head
What organisms have more/less cephalization
- More: mammals
- Less: insects
The adult starfish has ganglia in each arm connected by a ring, but no brain. This shows...
Centralization
What does a sea anemone have
nerve net
What does a flatworm have
eyespots, paired ganglia, ventral nerve cord
What does an earthworm have
brain, ventral nerve cord, segmental ganglion
What does an insect have
brain, eye, ventral nerve cord
What does a squid have
brain, giant axon
What does a frog have
eye, brain, dorsal spinal cord, nerves
What are the functions of the neuron?
- Convert chemical signals (neurotransmitters) into electrical signals (postsynaptic potentials/graded potentials)
- Merging (convergence) of multiple signals
- Creation of a regenerating electrical signal (action potential)
- Transmission (propagation) of electrical signals
- Convert electrical signals into chemical signals
What does the axon do
Conducts action potential
What does the axon hillock do?
- Initiates action potential
- Convergence of multiple signals
What does the axon terminal do?
Converts electrical signal to chemical signal
What does the cell body (soma) do?
Basic cellular functions
What do the dendrites do?
Converts chemical signal to electrical signal
Anatomy of the neuron
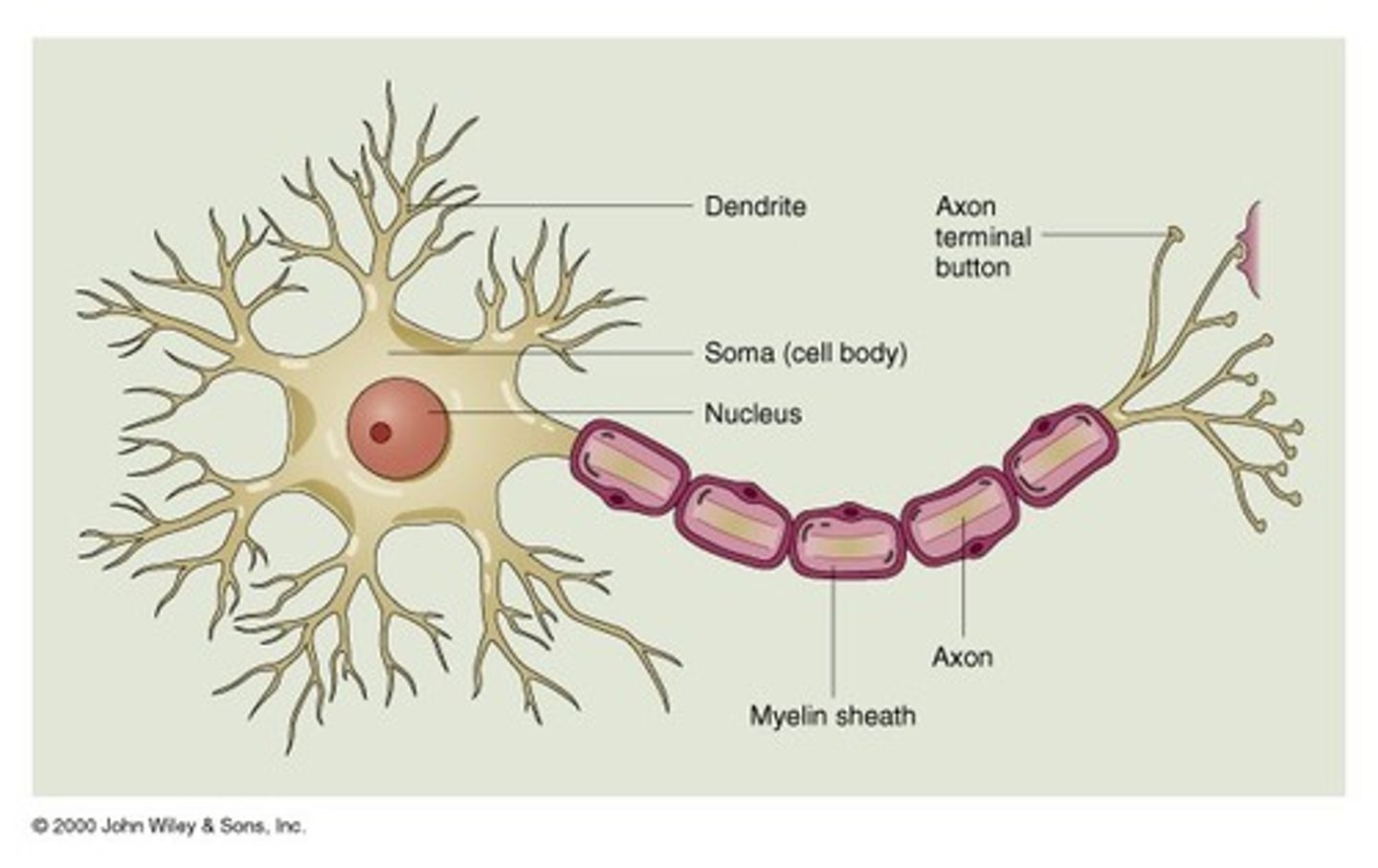
Specific flow of information through neurons
1. Neurotransmitters cross synapse to receptors on dendrites
2. Ligand-gated ion channels open on dendrites, starting electrical signal
3. Electrical signal spreads passively down dendrites to converge at the axon hillock
4. Axon hillock- multiple electrical signals from different dendrites converge, add up
5. If high enough electrical signal at hillock, action potential starts
6. Action potential travels down axon in one direction to the axon terminal
7. At axon terminal, action potential causes neurotransmitters to be released
What do sensory neurons have and what do they do?
Specialized endings, receive sensory input
What do motor neurons have?
Many branching dendrites, axon muscle/gland