APHUG all units
1/582
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
583 Terms
Urbanization
the process of developing towns and cities; highest in NICs and LDCs; NOT "urbanized" or "percent urban"; more a country is developing = more urbanization
percent urban
also called "urbanised"; an indicator of the proportion of the population that lives in cities and towns as compared to those who live in rural areas; higher in MDCs/HDCs
Factors affecting location of cities
site + situation; influence how cities function + grow (size, economic development, political+military history
Site
factor affecting location of cities; the physical characteristics of a place; includes water sources (rivers), climate, and natural features
Situation
factor affecting location of cities; location of a place relative to its surrounding; proximity to natural resources, proximity to other cities (trade routes, etc.), accessibility
population growth, improvement in transport + communication, migration, economic development, government policies
causes of city growth
urban area
a central city plus land developed for commercial, industrial, or residential purposes, and includes the surrounding suburbs
metropolitan (metro) area
a collection of adjacent cities economically connected, across which a population density is high and continuous
Metro population
population of a city; city + suburbs + exurbs + boomburbs etc.
Borchert's transportation model
model describing the form of cities based on the transportation technology existing at their time of creation; eg. 1700-1800s cities on water because boats were main form of transports, 1900s cities spread out because of cars and aeroplanes
urban sprawl/suburban sprawl
the unrestricted growth of urban area
Suburbanization
the process of people moving to residential areas on the outskirts of cities; centre is the most crowded; major trend of '60s - '70s
edge cities
large concentrations of businesses, shopping, and entertainment on the outskirts of a city; like another "downtown"
Exurbs
communities beyond traditional suburbs; usually has infrastructure that connects it to downtown; occurs when suburbs fill up
Boomburbs
suburb or exurb that is growing so rapidly that it begins to approach the population of the core city itself (25-30%)
Megacities
metro area with a population over 10 million; includes Tokyo, Jakarta, Delhi, Manila, Seoul; most common in NICs in Asia
Metacities
metro area with population over 20 million; same trend as megacities (most common in NICs in Asia)
Megalopolis
descries a chain of connected cities
world city (global city)
city that exerts influence and significance far beyond its boundaries; drivers of globalisation; eg. London, New York, Shanghai
primate city
a city in a country that is at least twice the population of the country's next largest city; eg. Mexico City, Mexico, Jakarta, Indonesia; likely in NICs, physically small countries, or constrained by geography
rank-size rule
the concept that the nth largest city is 1/n the size of the country's largest city (population wise); as a country develops, more people are attracted the cities; usually more common in HDCs with federal level of government; eg. 3rd largest city's population = ⅓ size of largest city
gravity model
based of principle of distance decay; 2 factors: population size, absolute distance; cities with higher population + lower absolute distance interact more
Christaller's central place theory
theory behind layout of cities/ urban landscapes
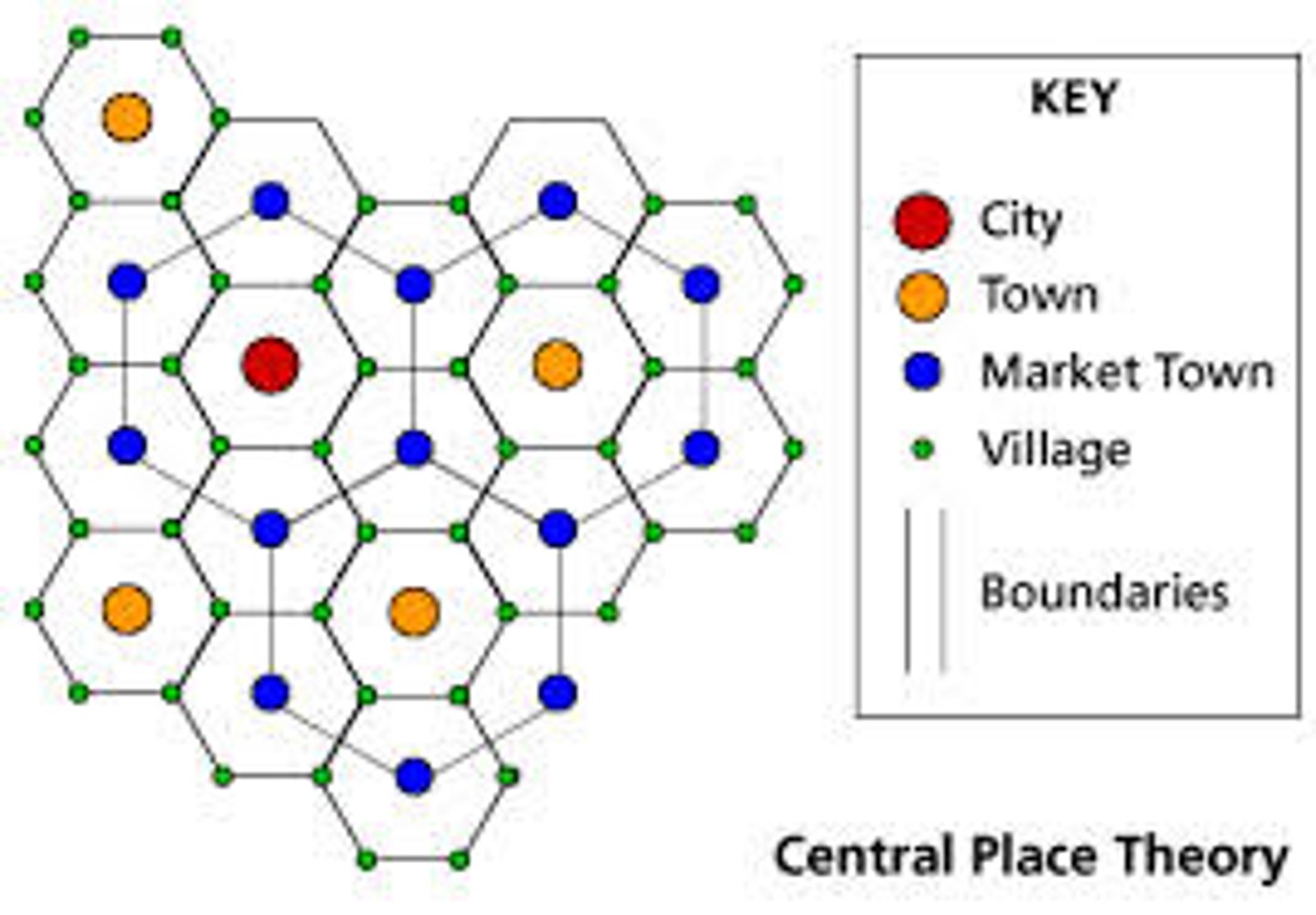
central place
the city/town/village where people go to receive goods + services; can specialize in specific good service
market area
Area around the central place where people travel from the market area to get the goods and services from the central place; goods + services can be delivered or transferred to people from central place to market area
Threshold
concept defining central place theory; the size of population necessary for any particular service to exist + remain profitable; goods + services only exist in area that can support them; higher threshold = closer to city centre
Range
concept defining central place theory; the distance people will go to obtain + services; willing to travel long distance = fewer goods/ services exist
functional zonation
the idea that portions of an urban area, regions or zones within the city, have specific and distinct purposes
central business district (CBD)
the commercial heart of a city, usually at the physical centre of the city; place of business/ commerce; models can have one or multiple
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
model describing the structure of older cities in the US; same shape as von Thunen's model (5 rings); further from CBD = better housing; eg. Chicago
Burgess Concentric Zone Model ring 1
1 main CBD in centre
Burgess Concentric Zone Model ring 2
where factories used to be; poorest people live; worst quality of housing
Burgess Concentric Zone Model ring 3
working class housing
Burgess Concentric Zone Model ring 4
middle class housing
Burgess Concentric Zone Model ring 5
suburbs
Hoyt Sector Model
similar to Burgess Concentric Zone Model but with sectors NOT rings; one side of city = low income housing, industry, transport; other side = middle + high class housing; 1 CBD; any older US cities that don't follow Burgess concentric zone model; eg. Detroit;
Harris and Ullman Multiple-Nuclei Model
only occurs while city is developing; multiple nuclei (each has specific activity) = jobs everywhere; cars invented = can move throughout cities; common in some modern north american cities; 1 CBD, multiple centres
Galactic City Model
can be developed from Multiple-Nuclei Model; edge cities created from nuclei with features of CBDs BUT still 1 CBD; common in more modern NA. cities; eg. Houston, LA
Latin American City Model (Griffin-Ford Model)
CBD has 2 parts (traditional market centre + modern high-rise centre w/ commercial "spine" attached); quality of housing decreases further away from CBD (outer ring often has disamenity zones)
disamenity zones
when a neighbourhood is not connected to city services/ amenities, including infrastructure + police; often controlled/ run by "drug lords"/ gangs who provide services to residents
African City Model
common in sub-saharan africa; 3 parts to CBD = market zone (informal economic activities), traditional CBD (formal economy w/ small, clustered shops + narrow streets), colonial CBD (large homes + broad streets); residential zones based on ethnicity
Parts of African City Model
CBD (3 parts), mining + manufacturing zones, informal settlements (periphery), disamenity zones + squatter settlements
squatter settlements
homes and buildings built where people have no legal right to the land; owned by government / agricultural landowners = conflicts; cut deals w/ politicians to bribe/ promise votes
land tenure
the legal right to own land
Southeast Asian City Model (McGee Model)
does not have a single CBD = usually centred around a port; CBDs are basedon income/ ethnicity; low income people live between CBDs
zoning ordinances
rules + regulations determining how property in cities can be used; residential (housing), commercial (buying/selling goods + services), industrial (manufacturing)
Filtering
process in which houses pass from one social group to another
Infilling
process of "filling in" empty spaces in cities; strategy to increase density, popular in US cities; decreases green areas
public transportation
buses, subways, light rail, trains, etc., that are operated by a government agency
Brownfields
areas in which factories or manufacturing buildings used to be; crumbling buildings + polluted soil
zones of abandonment
an area where crime + economic factors (unemployment, etc.) get so bad no one wants to live in the neigbourhood; people struggle to sell houses
Segregation
the separation of people on the basis of ethnicity, race, gender, or sexual orientation (things they can't change); can be legal or "defacto" (due to the economic gap of ethnicities/race)
Redlining
the systematic denial of home mortgage and insurance applications to certain candidates; method of segregation; keeps certanin people out of certain neighbourhoods; common in multinational states
Blockbusting
the practice of real estate agents manipulating property owners (usually white) to sell their homes at low prices because of racial minorities (usually african american) moving to the neigbourhood; common in North of US during great migration
Great Migration
when African americans moved from south to north of the US to escape the Jim Crow laws
Ghetto
areas of poverty occupied by a specific minority group as a result of discrimination
Gentrification
the process of changing the character of a neighbourhood throught the influx of more affluent residents and businesses; in US + Europe: wealthier people moving back to CBD
urban canyons
streets line with tall buildings, that can channel and intensify wind and precent natural sunlight from reaching the ground
urban heat island
an area of a city that is warmer that surrounding areas because of the concentration of buildings + concrete
environmental justice
fair treatment of all people with respect to development and enforcement of envrionmental laws
ecological footprint
impact of a person/ community on the environment
New Urbanism
the trend in recent decades; rethinks of the design + layout of cities; smart growth + slow growth;
Features of New Urbanism
mixed land use, inclusionary zoning, gentrification + urban renewal, greenbelts, brownfield remediation + redevelopment, urban growth boundary (UGB), farmland protection
smart growth
idea that growth should remain compact
slow growth
contreversial idea that urban sprawl should be limited and green areas should be protected
mixed land use
Feature of New Urbanism; using land for a variety of purposes including housing/ accommodation, businesses, recreation; eg. shophouses
inclusionary zoning
Feature of New Urbanism; zoning ordinance that requires share of new construction to be affordable by low income people
Greenbelts
undeveloped natural land surrounding or near urban areas
urban growth boundaries (UGBs)
Feature of New Urbanism; a boundary beyond which land must be preserved in its natural state or to be used for agriculture
transit-oriented development (TOD)
locates mixed use residential and business communities near mass transit stops, resulting in a series of more compact communities with a decreased need for automobiles
benefits of mixed land use
Less need for infrastructure between places, Stronger sense of community, Lower ecological footprint
benefits of inclusionary zoning
Decreases segregation
benefits of gentrification + urban renewal
Increase property values, improvement in schools, lower ecological footprint
benefits of greenbelts
Enhanced air quality and reduction of climate change, limits flooding, Areas for recreation
benefits of brownfield remediation + redevelopment
enhanced water quality, Land for housing, commercial opportunities, infrastructure, or green space
benefits of urban growth boundaries (UGBs)
Simplest way to reduce sprawl , Limits chances of disamenity zones to form
benefits of farmland protection
Limits urban sprawl , Protects rural jobs/employment, Recreational opportunities , Keeps culture/tradition
drawbacks of mixed land use
Increase in housing costs, could lead to segregation if housing prices rise too much
drawbacks of inclusionary zoning
Builders might not build, Can be administratively complex
Loss of historical character and cultural identity, Pushes out low income people
drawbacks of gentrification + urban renewal
drawbacks of greenbelts
Increased housing costs
drawbacks of brownfield remediation + redevelopment
Can be extremely costly
drawbacks of urban growth boundaries (UGBs)
Biggest factor : increased housing prices (limits potential supply and forces construction on costly land)
drawbacks of farmland protection
Wasteful if farmland is not profitable , Increase housing costs in urban areas
Number of member states of WTO
160
Number of member states of EU
27
Number of member states of Mercosur
4
Number of member states of NAFTA
3
eg member states of WTO
New Zealand, France, Canada, Australia, US, UK
eg member states of EU
France, Italy, Germany, Denmark
member states of Mercosur
Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, Paraguay
member states of NAFTA
United States, Canada, Mexico
Key Policies and Issues of WTO
Regulates trade between countries, Solves trade disputes between countries, Encourages free trade
Key Policies and Issues of EU
Free trade between countries, Common currency: most EU members use the Euro, Aid economies of struggling countries
Key Policies and Issues of Mercosur
Free trade between member countries, Ability to work in any other member country
Key Policies and Issues of NAFTA
Free trade between member countries, Concern over manufacturing/secondary sector jobs leaving US for Mexico
WTO stands for
World Trade Organisation
EU stands for
European Union
NAFTA stands for
North American Free Trade Agreement
Industrial Revolution
set of changes in technology that dramatically increased manufacturing productivity