Chapter 10: Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, and Lightning
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Thunderstorms
Storm containing lightning and thunder
Convective storms
Storms that form with rising air
Severe thunderstorms
Characterized by large hail, wind gusts greater than or equal to 50 knots, or a tornado
Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms
When the wind speed and wind direction do not drastically alter with height
Ordinary cell thunderstorm stages
Cumulus, mature, and dissipating
Multicell Thunderstorms
Contain a number of cells, each in a different stage of development
The Gust Front
Leading edge of the cold out flowing air
Microbursts
Downburst with winds extending four km or less
Squall-Line Thunderstorms
Line of multicell thunderstorms that form ahead of fronts
Derecho
Windstorm associated with a squall line
Mesoscale Convective Complex
A big circular convective weather system formed when several small individual multicell thunderstorms develop in magnitude
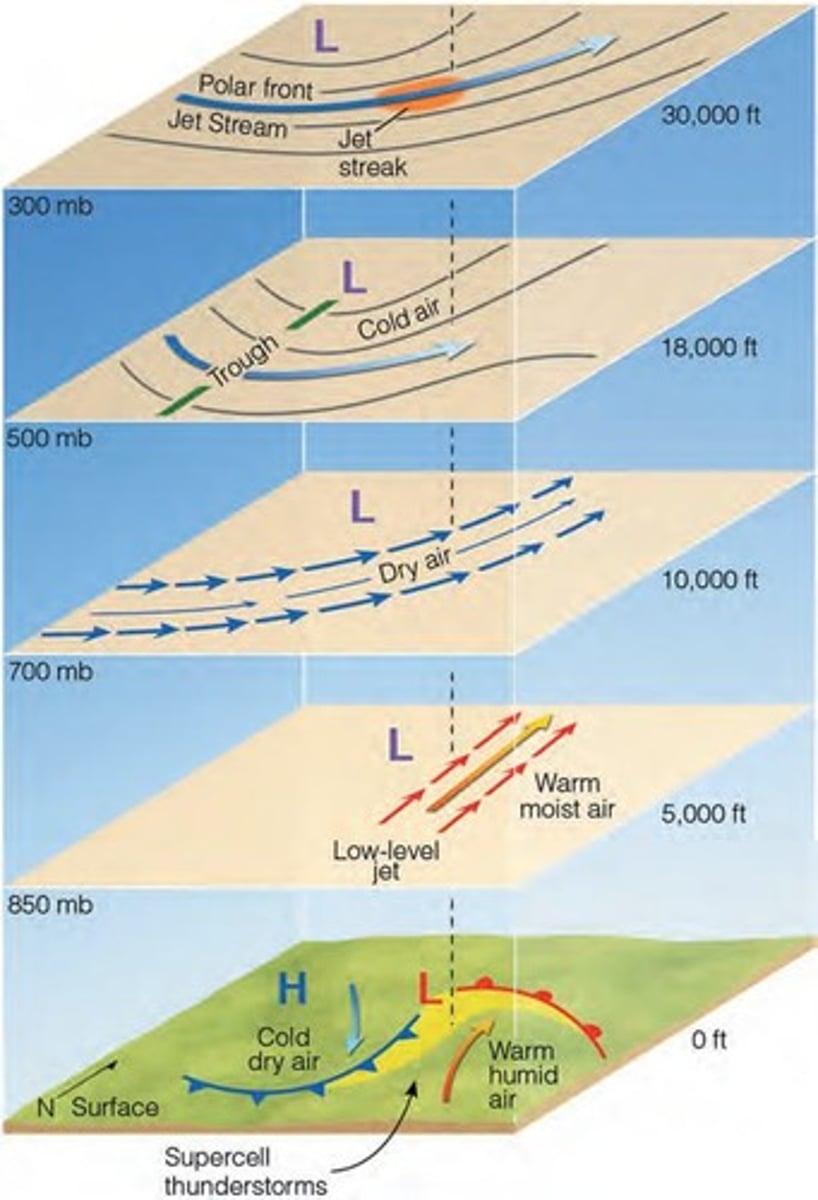
Supercell Thunderstorms
Strong vertical wind shear with a single violently rotating updraft
Pyrocumulus
Dense cumuliform cloud associated with fire
Outflow boundary
Occurs with a cold front with strong and gusty winds and where there are straight-line winds behind a gust front
Flash floods
Increase rapidly with little or no advance warning; often caused by stalled or slow thunderstorms
River flood
Occurs when a river overflows its banks or when its flow cannot be kept inside its channel
Distribution of Thunderstorms
More than 50,000 thunderstorms occur each day on Earth—over 18 million per year
Occurrence of thunderstorms
Over equatorial landmasses—about one every three days; prevalent over water along the intertropical convergence zone; less prevalent in polar and desert regions
Lightning
Discharge of electricity that occurs in mature cloud storms

Thunder
Booming sound wave caused by explosive expansion of air due to heat from lightning
Distance of Lightning
If you see lightning and hear the thunder 15 seconds later, the lightning stroke is about three miles away
Electrification of Clouds
Occurs when graupel and hailstones fall through supercooled liquid droplets and ice crystals, freezing and releasing latent heat
The Lightning Stroke
Involves a negative charge at the bottom of the cloud and a positive charge on the ground beneath it
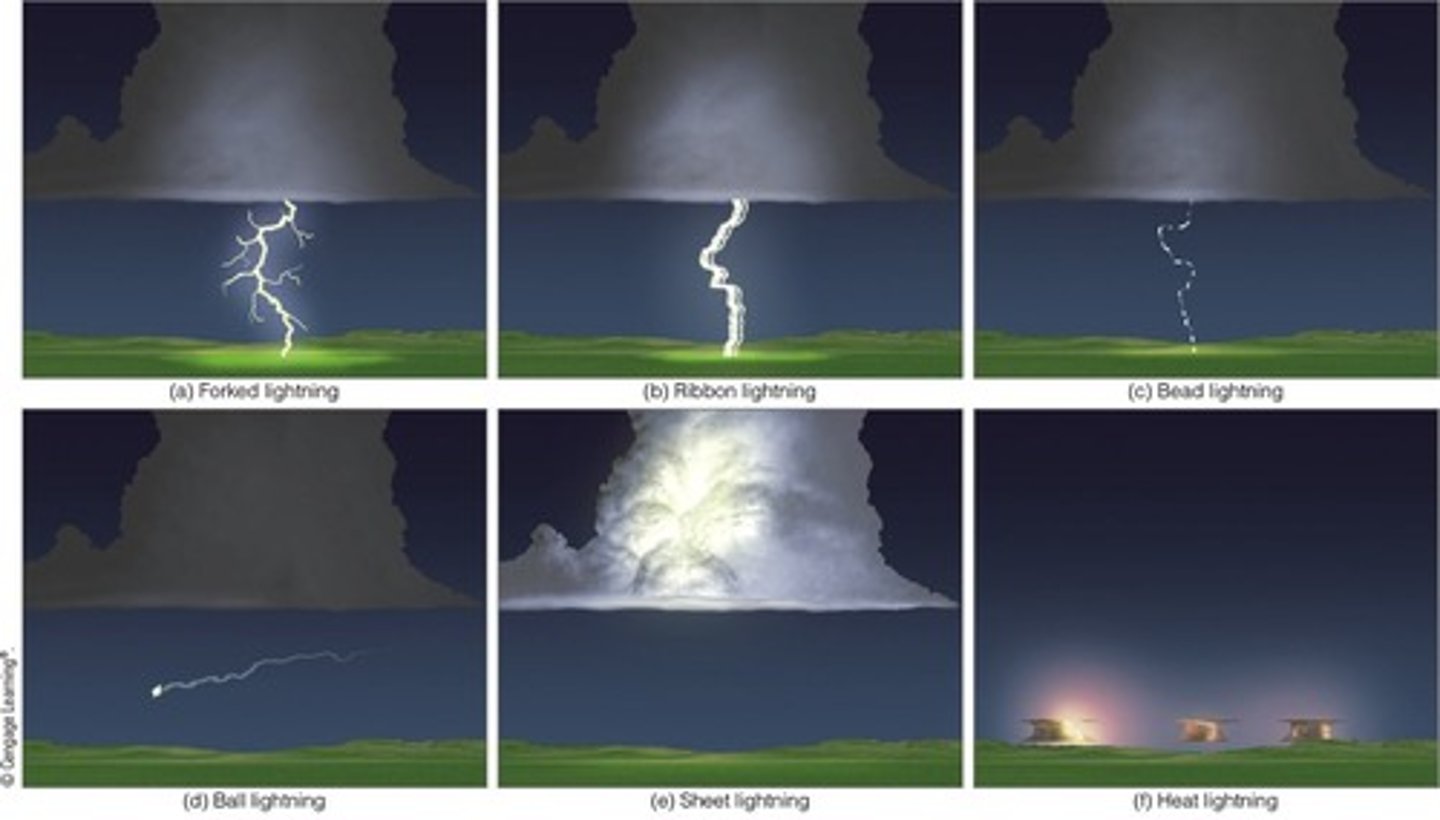
Types of Lightning
Can take a variety of shapes and forms including forked, ribbon, bead, ball, sheet, and heat

Lightning Detection and Suppression
Lightning direction-finders detect radio waves produced by lightning; networks of magnetic devices are used to pinpoint locations
Lightning Distance Calculation
Count the seconds from the moment you see lightning until you hear thunder. Sounds take 5 seconds to travel a mile.
Tornado
Rapidly rotating column of air that blows around an intense area of low pressure.
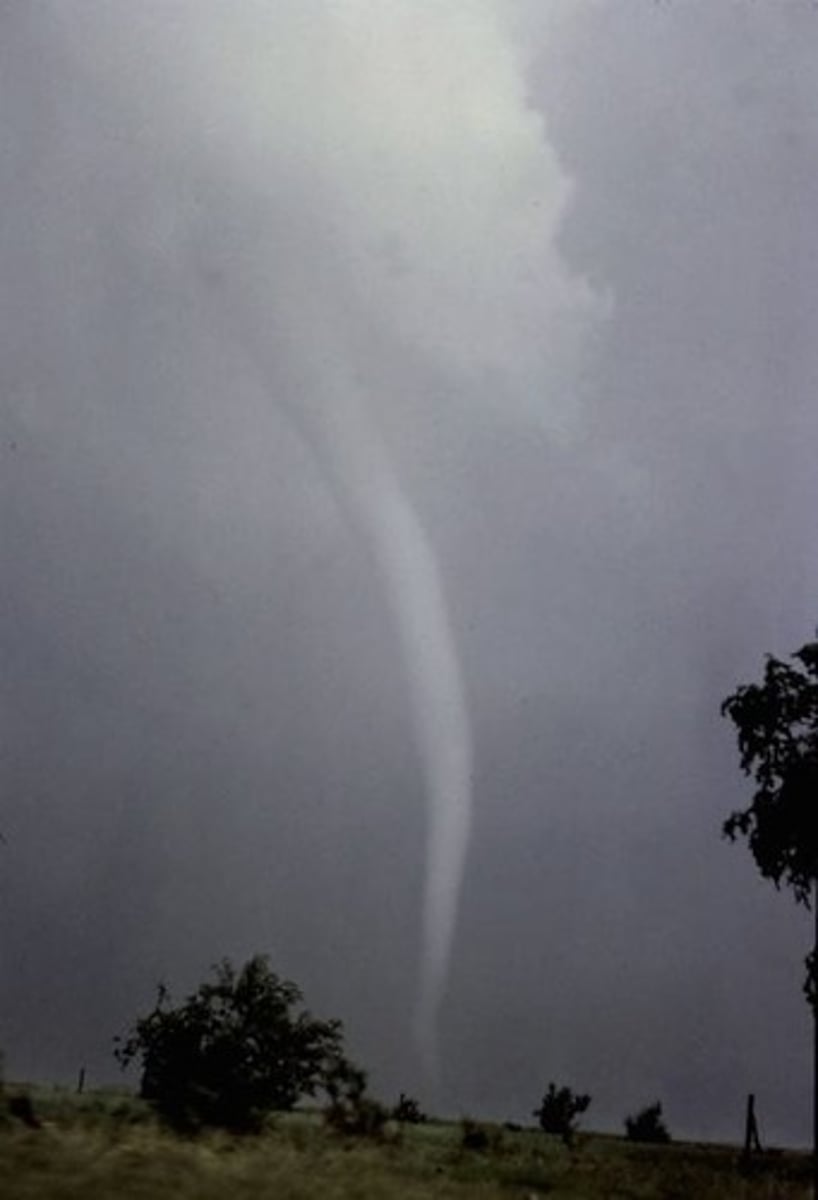

Tornado Life Cycle
Stages include Dust-whirl, Mature, and Decay.
Tornado Occurrence and Distribution
The U.S. experiences most tornadoes.
Tornado Winds
Measured by Doppler radar.
Multi-vortex Tornadoes
Violent tornadoes that contain smaller whirls that rotate within them.
Seeking Shelter
Recommended locations include basement, storm shelter, or 'safe room.'
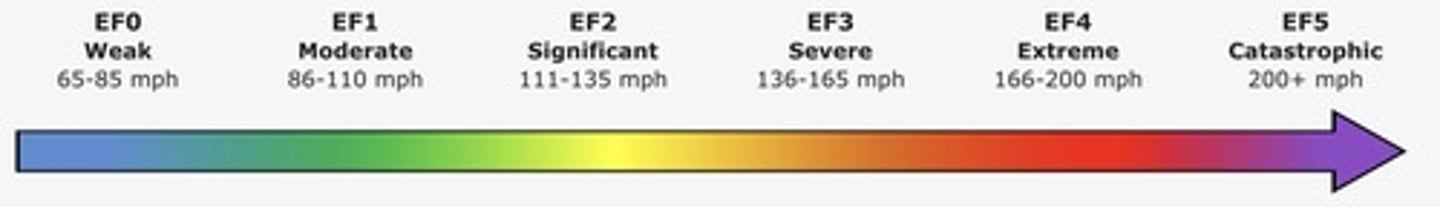
Enhanced Fujita Scale
Attempts to provide a wide range of criteria in estimating a tornado's winds by using a set of 28 damage indicators.
Tornado Outbreaks
Group or series of tornadoes spawned by the same thunderstorm, typically six or more.
Tornado Damage Classification Scale
Includes categories such as EF0, EF1 for weak tornadoes; EF2, EF3 for strong tornadoes; EF4, EF5 for violent tornadoes.
Destructive Potential of Wind
The pressure of the wind increases with the square of the wind speed, meaning if you double the wind speed, you get four times as much destructive potential.
Tornado Strength Variation
Tornadoes can strengthen or weaken dramatically, and shrink or enlarge, in just a few seconds.
Supercell Tornadoes
Form with supercell thunderstorms and are associated with hook echoes.
Nonsupercell Tornadoes
Tornadoes that do not occur in association with a pre-existing wall cloud of a supercell.
Waterspouts
A rotating column of air connected to a cumuliform cloud over a large body of water.
Tornadic Waterspout
A waterspout that formed over land and then traveled over water.
Doppler Radar Principle
The frequency of the returned radar pulse fluctuates as precipitation travels closer or away from the antenna.
Storm Chasing
Can be done informally or in organized tour groups.
VORTEX
Verification of the Origin of Rotational Tornadoes Experiment.
VORTEX2
A follow-up to the original VORTEX experiment conducted by the National Severe Storms Laboratory/NOAA.