Cyber Security :<
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is an ethical hacker?
An ethical hacker is a cybersecurity professional trained to identify and fix vulnerabilities in systems before malicious hackers can exploit them. They simulate real-world cyberattacks to assess risk and strengthen security posture.
Penetration Testing
A penetration test is a simulated cyber attack against a device to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. It is commonly used to augment a web application firewall.
Difference between Ethical Hackers and Unethical Hackers
The main difference lies in permission and intent. Ethical hackers identify and fix vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them, strengthening an organisation’s cyber security. Unethical hacker exploit vulnerabilities for personal gain, steal data, disrupt operation and/or hold data hostage.
What was the role of the Privacy Act 1988?
Introduced to promote and protect the privacy of individuals and regulate how the Australian Government and other organisations handle personal information. It establishes rules for collecting, storing and disclosing by agencies and private sector organisations with an annual turnover of $3 million or more.
Example: A federal law that gives the server to be in another state.
What are the Australian Privacy Principles?
They are the cornerstone of the privacy protection framework in the Privacy Act 1988. There are 13 Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) that govern standards, rights and obligations around:
the collection, use and disclosure of personal information
an organisations or agency’s governance and accountability
integrity and correction of personal information
the right of individuals to access their personal information
What is Network Authentication?
A process that verifies and confirms the identity of a use, device or system trying to access a network. This is often achieved through the use of login credentials such as usernames and passwords.
What are the characteristics of a strong password?
Strong passwords are characterized by their length, complexity (mixing uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols), randomness (avoiding personal information and common words), and uniqueness (not reusing the same password across multiple accounts).
What are some organisations approaches to password policies?
An organisation should focus on creating an effective password policy which prioritises strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular employee training.
What are passwords policies impact on data security?
They are crucial for data security because they directly impact the strength and management of passwords which tend to help minimize the risk of data breaches, unauthorised access and account take overs.
What is two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication is an network security method that requires users to provide two different factors to verify their identity when accessing an account or system. This is generally done through hardware tokens, push notifications, SMS verification and voice-based authentication.
Some other advantages of 2FA include:
There’s no need to use a hardware token generator. These types of 2FA methods are often lost or misplaced. However, with advanced technology, 2FA methods are more convenient than ever.
Passcode generators are more efficient than traditional passwords. Generators are the safer option because no two passcodes are the same.
Max passcode entry prevents cybercriminals from hacking and accessing sensitive data.
The process is manageable and user-friendly.
What are biometrics in network security?
Biometrics use unique biological or behavioral characteristics to verify a person’s identity for authentication and access control. This includes fingerprints, facial features or voice patterns.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of protecting information or data by using mathematical models to scramble it in such a way that only the parties who have the key to unscramble it can access it. Data encryption is important because it helps protect people’s privacy, and secures data from attackers and other cybersecurity threats.
Encryption performs four important functions:
Confidentiality: keeps the contents of the data secret
Integrity: verifies the origin of the message or data
Authentication: validates that the content of the message or data has not been altered since it was sent
Nonrepudiation: prevents the sender of the data or message from denying they were the origin
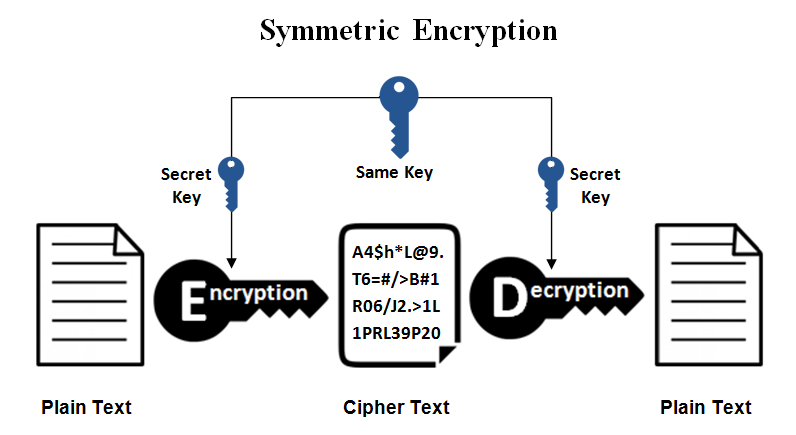
What is symmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption, also known as a shared key or private key algorithm, uses the same key for encryption and decryption. Symmetric key ciphers are considered less expensive to produce and do not take as much computing power to encrypt and decrypt, meaning there is less of delay in decoding the data.
The drawback is that if an unauthorized person gets their hands on the key, they will be able to decrypt any messages and data sent between the parties. As such, the transfer of the shared key needs to be encrypted with a different cryptographic key, leading to a cycle of dependency.
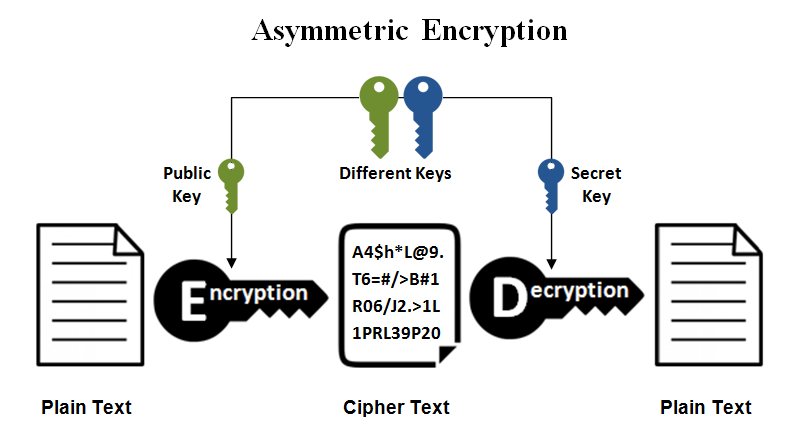
What is asymmetric encryption?
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, uses two separate keys to encrypt and decrypt data. One is a public key shared among all parties for encryption. Anyone with the public key can then send an encrypted message, but only the holders of the second, private key can decrypt the message.
Asymmetric encryption is considered more expensive to produce and takes more computing power to decrypt as the public encryption key is often large, between 1,024 and 2,048 bits. As such, asymmetric encryption is often not suited for large packets of data.
Example: Emails.
What are some disadvantages to encryption?
Ransomware: While encryption is generally used to protect data, malicious actors can sometimes use it to hold data hostage.
Quantum computing: Quantum computing poses an existential threat to modern encryption techniques. When it is ready, quantum computing will be able to process massive amounts of data in a fraction of the time of normal computers. As such, quantum computing has the potential to break existing encryption.
What is social engineering (phishing?)
Phishing is a form of social engineering and a scam where attackers deceive people into revealing sensitive information or installing malware such as viruses, worms, adware, or ransomware, generally by pretending to be legitimate companies or agencies.
zero day vunelerivility
what cna be done to avoid a vero day vunelrability
ip spoofing
deautheticate