Physiology Quiz 2 - Chem 3&4, Cell Structure & Function
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
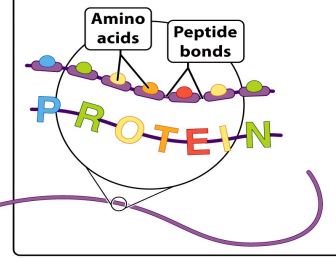
Primary Structure
The sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide chain
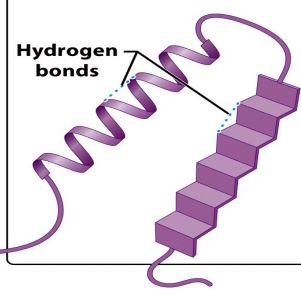
Secondary Structure
Protein structure achieved when alpha-helical or beta-pleated regions of the polypeptide chain fold upon one another to produce a compact ball-like /globular molecule.
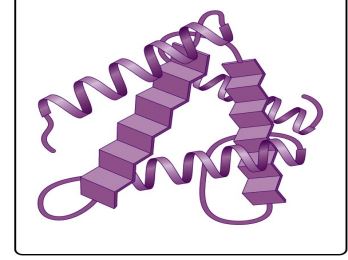
Tertiary Structure
Protein structure represented by alpha-helices and beta-sheets.
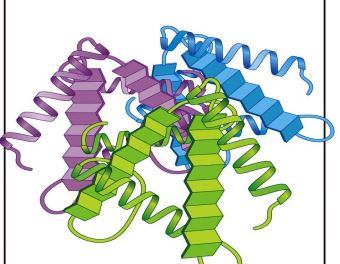
Quaternary Structure
Two or more polypeptide chains – each with its own tertiary structure.
How many amino acids are there?
20
Collagen
Structural protein found in hair, fingernails, feathers, horns, cartilage, tendons.
Antibodies
Protective protein that helps fight invading microorganisms and coagulates blood.
Insulin
Regulatory protein that controls cell activity and constitutes some hormones.
Actin & Myosin
Contractile protein that allows muscles to contract, the heart to pump, and sperm to swim.
Hemoglobin
Transport protein that carries molecules such as oxygen around your body.
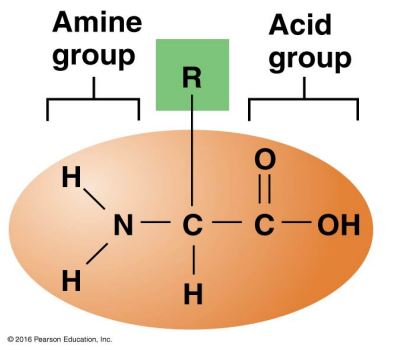
Amino Acid
Contains amine group, acid group, and R-group.
R-group is what differentiates amino acids.
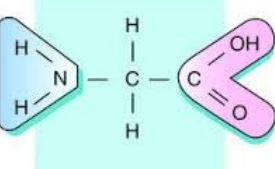
GlycineGlycine
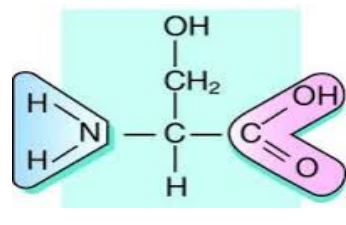
Serine
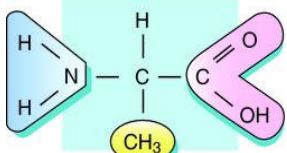
Alanine
Enzyme
Proteins that initiate and speed up chemical reactions.
EX: Lactase breaks down lactose for energy.
Substrate
Substance that enzymes act on.
Describe the structure and function of carbonic anhydrase.
A zinc-containing enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide: CO2+ H2O<-->HCO3(-)+H+
Dehydration Synthesis
The acid group of one amino acid is bonded to the amine acid group of the next, with loss of a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
Peptide bonds linking amino acids together are broken when water is added to the bond.
Transcription
DNA is converted to RNA; DNA is decoded into mRNA.
Steps of Protein Synthesis
DNA
Transcription
RNA Maturation
Translation
Isotonic
Cells retain their normal size and shape; concentration is same inside and outside cell; water moves in and out without net change.
Hypertonic
Solute concentration inside cell is less than outside; cells lose water by osmosis, shrink, and become crenated.
Hypotonic
Solute concentration inside cell is greater than outside; cells take on water, swell, and may burst (lyse).
Simple Diffusion
Does not require assisstance from membrane transporter or energy; passive transport.
Facilitated Diffusion
Requires assistance from membrane transporter, oftentimes a protein; always goes from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Active Transport
Cell uses energy to move solute across the membrane; requires transfer proteins that combine with transport substances; moves ions; active transport & vesicular transport.
Exocytosis
A process for moving large molecules out of the cell to the cell exterior
Endocytosis
Cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Fats
Long-term energy storage and insulation.
How many calories in 1 gram of fat?
9
How many calories in 1 gram of protein or CHO?
4
Saturated fats
Fats: solid at room temp
Unsaturated fats
Oils; liquid at room temp
Hydrophilic
Water-loving
Hydrophobic
Water-fearing
What is the purpose of cholesterol?
Cholesterol is the basis for all asteroids formed in the body and is essential to human life; synthesizes vitamin D.
Types of steriods
Estrogen, Testosterone, Cortisol,
Extracellular fluid
Found outside of cell.
Plasma
Interstitial fluid
Intracellular fluid
Found inside of cell.
Sterols
Regulate growth and development.
Phospholipids
Form the membranes that enclose cells.