mastering biology chapter 5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Last updated 3:48 AM on 12/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
fluid mosaic model
\-depicts the membrane as a mosaic of protein molecules suspended in a fluid phospholipid bilayer
\-kinks in the unsaturated fatty acid tails of phospholipids keeps the membrane fluid
\-kinks in the unsaturated fatty acid tails of phospholipids keeps the membrane fluid
2
New cards
selective permeability
\-allows membranes to regulate the passage of molecules across them
\-small nonpolar molecules (O2, CO2) can move freely across the membrane
\-small nonpolar molecules (O2, CO2) can move freely across the membrane
3
New cards
cholesterol
\-stabilizes the structure of the plasma membrane
\-prevents the close packing of phospholipids.
\-prevents the close packing of phospholipids.
4
New cards
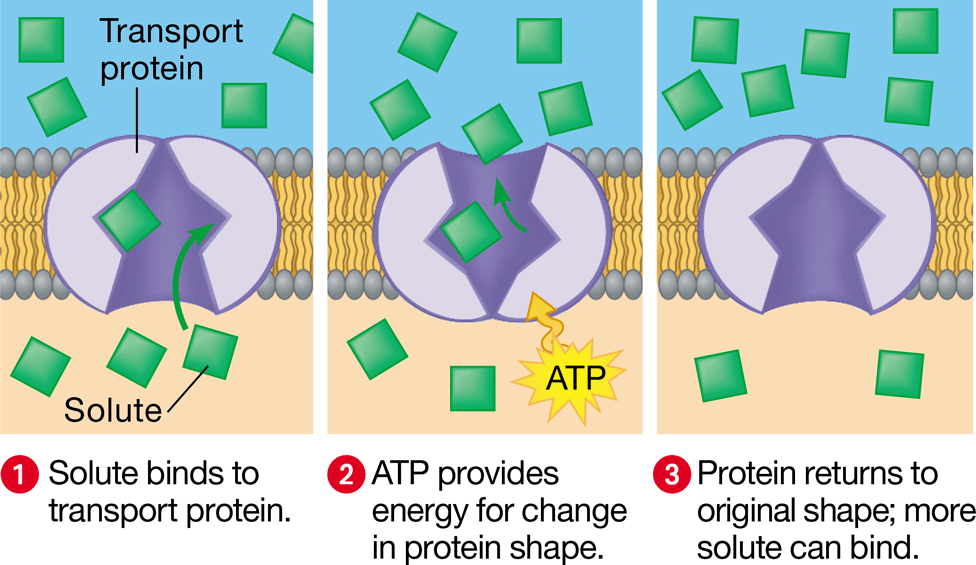
carrier protein
transport protein that releases molecules on the other side of the membrane by binding & changing shape
5
New cards
channel protein
transport protein that provides channels through which specific molecules/ions can diffuse
6
New cards
active transport protein
transport protein that uses ATP to pump molecules against their concentration gradient
7
New cards
receptor protein
\-binds to signaling molecules outside of a cell to transmit messages into the cell
\-activates other molecules within the cell
\-activates other molecules within the cell
8
New cards
attachment protein
\-provides support by connecting to the cytoskeleton & ECM
\-can relay information about internal & external conditions
\-can relay information about internal & external conditions
9
New cards
glycoprotein
\-allows other membrane proteins to recognize its attached sugars (ID tags)
\-composed of a carbohydrate & protein
\-composed of a carbohydrate & protein
10
New cards
junction protein
forms long-lasting connections between cells
11
New cards
aquaporin
transport protein that facilitates osmosis
12
New cards
enzyme
\-protein that carries out sequential reactions within the membrane
\-changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it
\-organic catalyst
\-changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it
\-organic catalyst
13
New cards
protein pore
passageway for facilitated diffusion
14
New cards
Na/K pump
\-Na+ binds to the transport protein so that it can be moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient
\-K+ binds to the transport protein so that it can be moved into the membrane against the concentration gradient
\-Phosphate group of ATP needs to be transferred to the protein so that it changes shape (active transport)
\-K+ binds to the transport protein so that it can be moved into the membrane against the concentration gradient
\-Phosphate group of ATP needs to be transferred to the protein so that it changes shape (active transport)
15
New cards
contractile vacuole
expels excess water from plant cells against the concentration gradient using ATP (active transport)
16
New cards
ligand
molecule that binds to a receptor protein
17
New cards
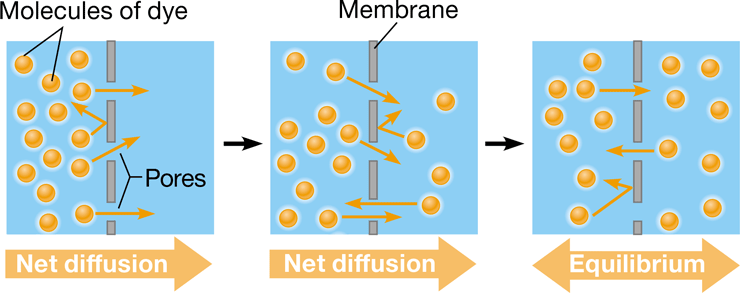
net movement
difference between the number of molecules moving in the direction of the force & the number of molecules moving in the opposite direction
18
New cards
concentration gradient
\-region along which the density of a substance increases or decreases
\-substances tend to move from higher concentration to lower concentration
\-substances tend to move from higher concentration to lower concentration
19
New cards
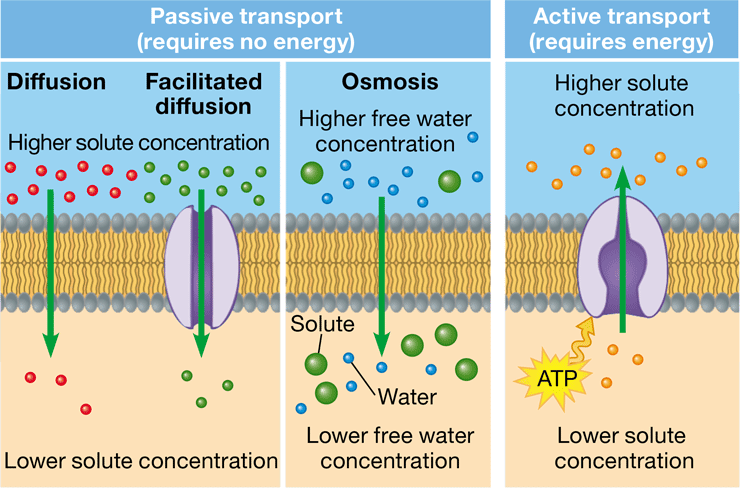
passive transport
diffusion of a substance across a membrane down a concentration gradient with no expenditure of energy
20
New cards
active transport
diffusion of a substance across a membrane against a concentration gradient that requires an input of energy
21
New cards
diffusion
\-movement of particles down a concentration gradient
\-tendency of particles to spread out in its available space
\-tendency of particles to spread out in its available space
22
New cards
facilitated diffusion
passage of a substance through a transport protein across a membrane down a concentration gradient
23
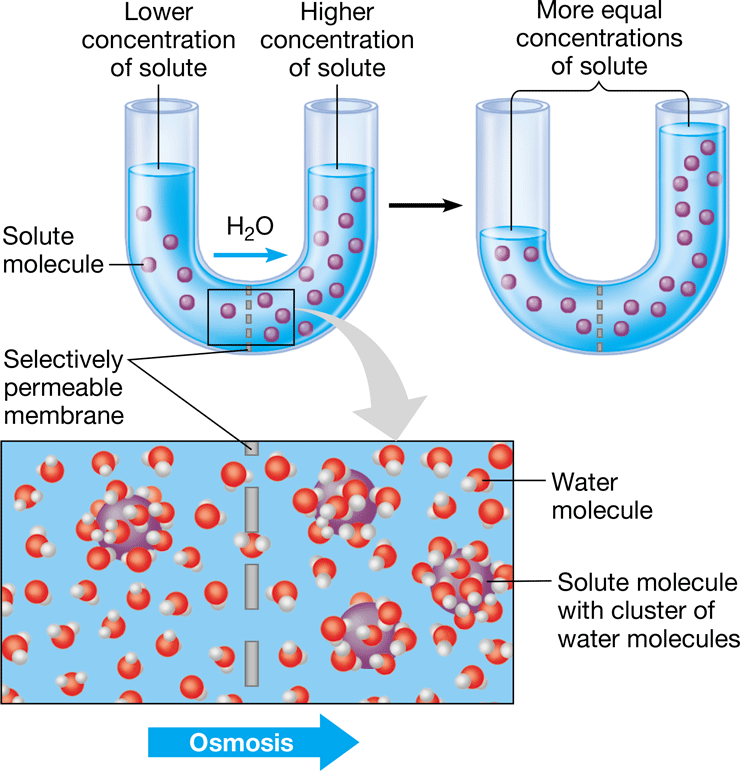
New cards
osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from high to low areas of concentration
24
New cards
osmoregulation
homeostatic maintenance of solute concentrations & water balance
25
New cards
exocytosis
movement of molecules out of a cell by the fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane
26
New cards
endocytosis
\-movement of molecules into a cell via formation of new vesicles from the plasma membrane
\-cell membrane pinches inward
\-cell membrane pinches inward
27
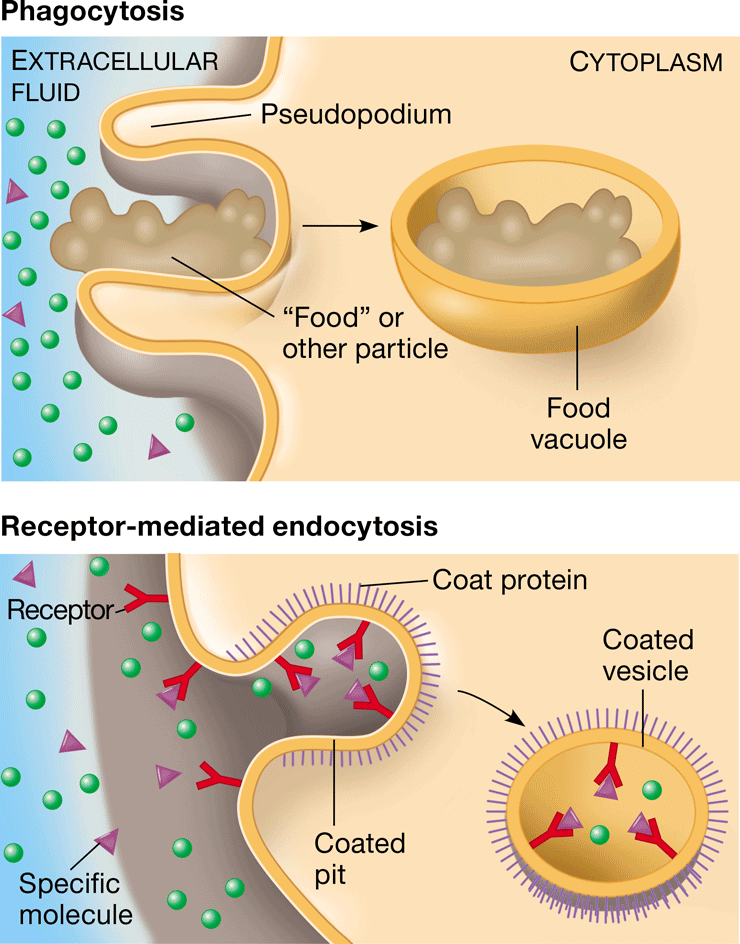
New cards
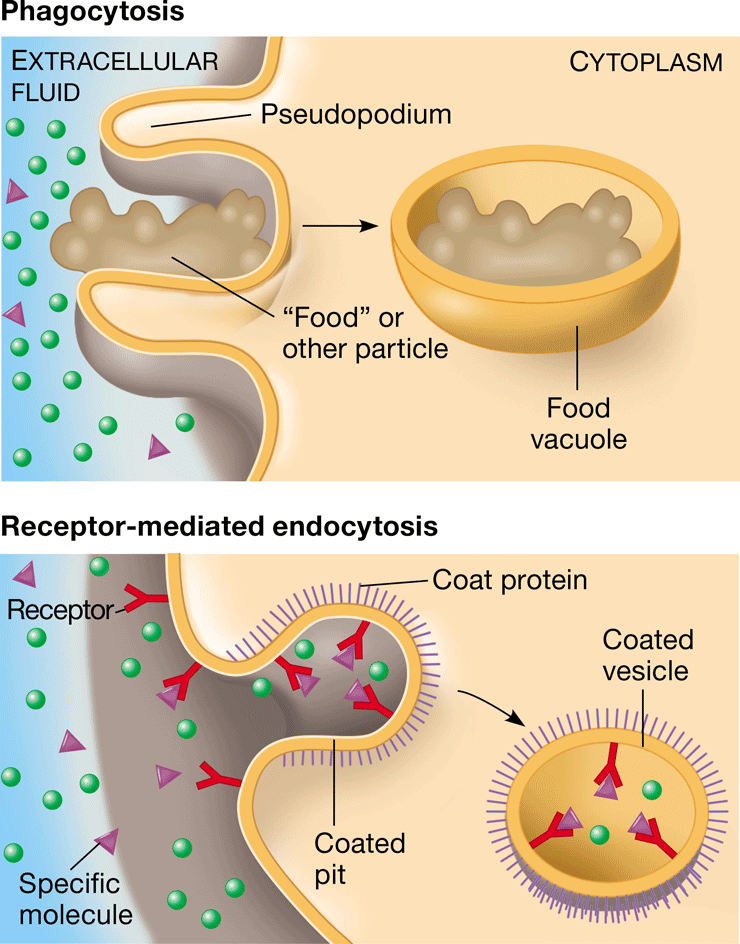
phagocytosis
\-endocytosis in which a cell engulfs macromolecules into its cytoplasm
\-”cell eating”
\-”cell eating”
28
New cards
pinocytosis
\-endocytosis in which the cell engulfs extracellular fluid
\-”cell drinking”
\-”cell drinking”
29
New cards
receptor-mediated endocytosis
movement of molecules into a cell by the infolding of protein-containing vesicles with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in
30
New cards
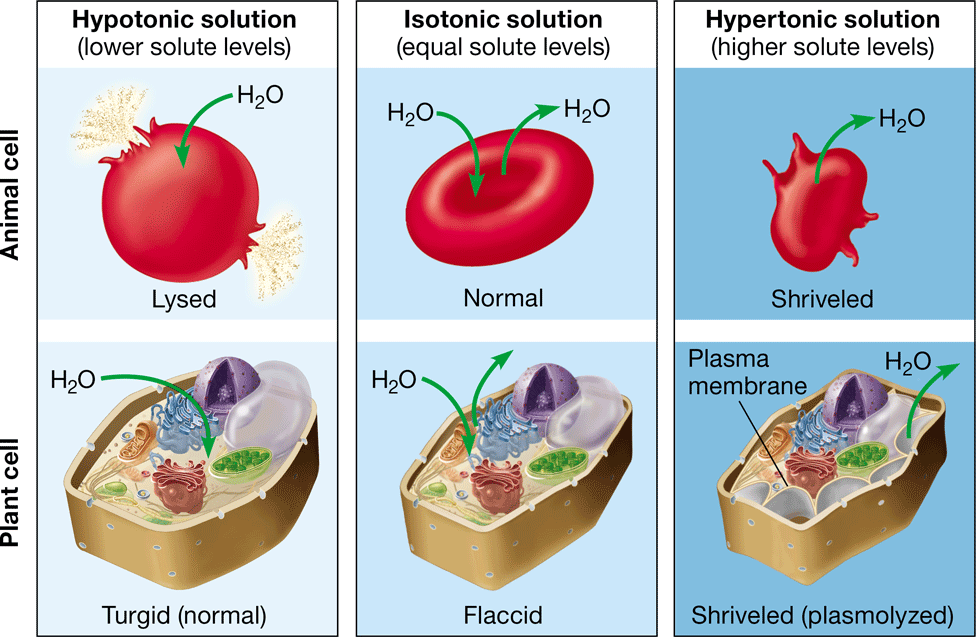
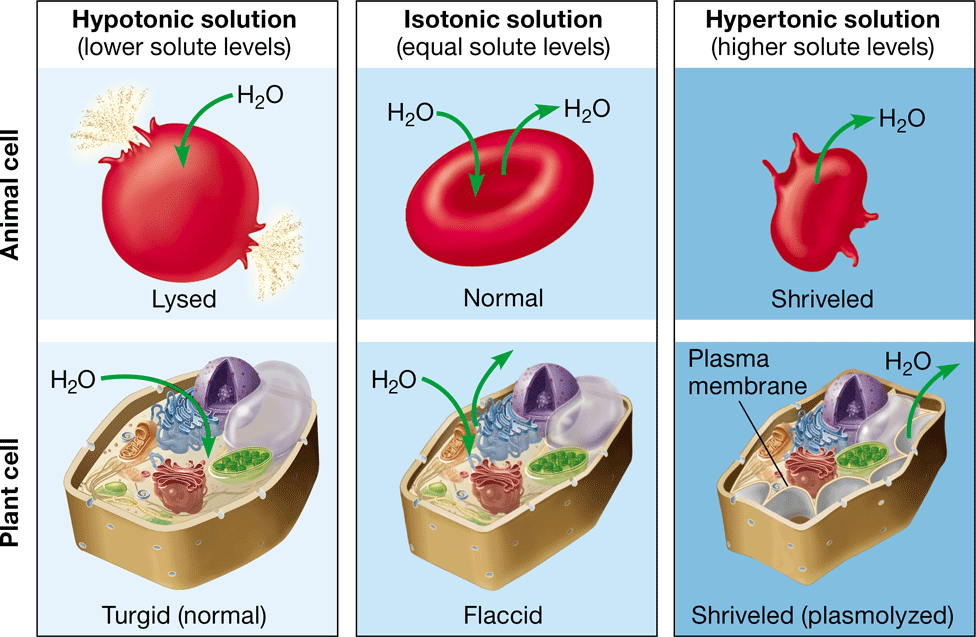
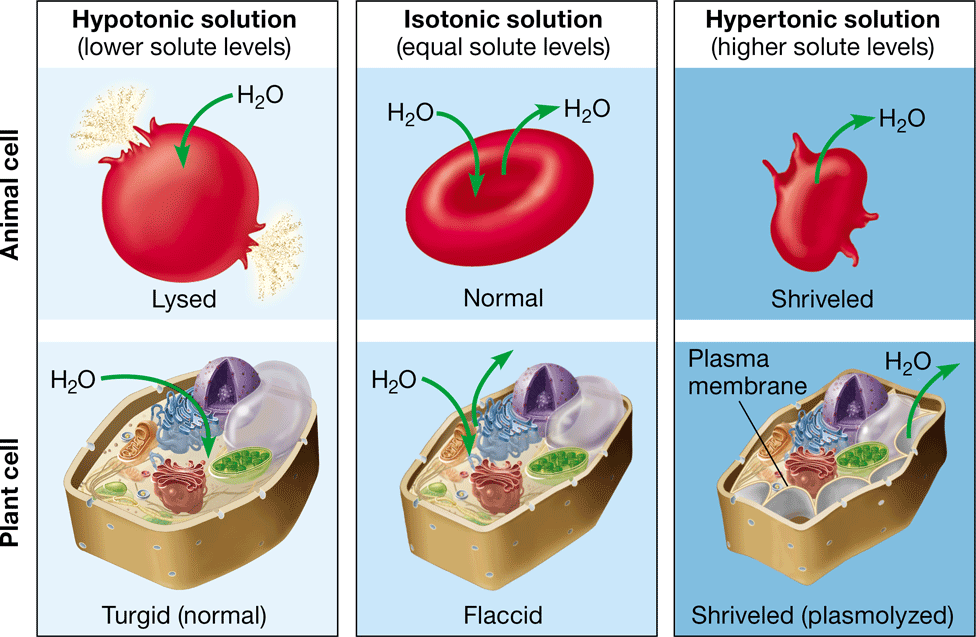
tonicity
the ability of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water
31
New cards
isotonic
\-no net movement of water
\-equal concentration of solvent and solute
\-equal concentration of solvent and solute
32
New cards
hypotonic
\-net movement of water into the cell
\-causes the cell to grow
\-higher concentration of solvent
\-causes the cell to grow
\-higher concentration of solvent
33
New cards
hypertonic
\-net movement of water out of the cell
\-causes the cell to shrink
\-higher concentration of solute
\-causes the cell to shrink
\-higher concentration of solute
34
New cards
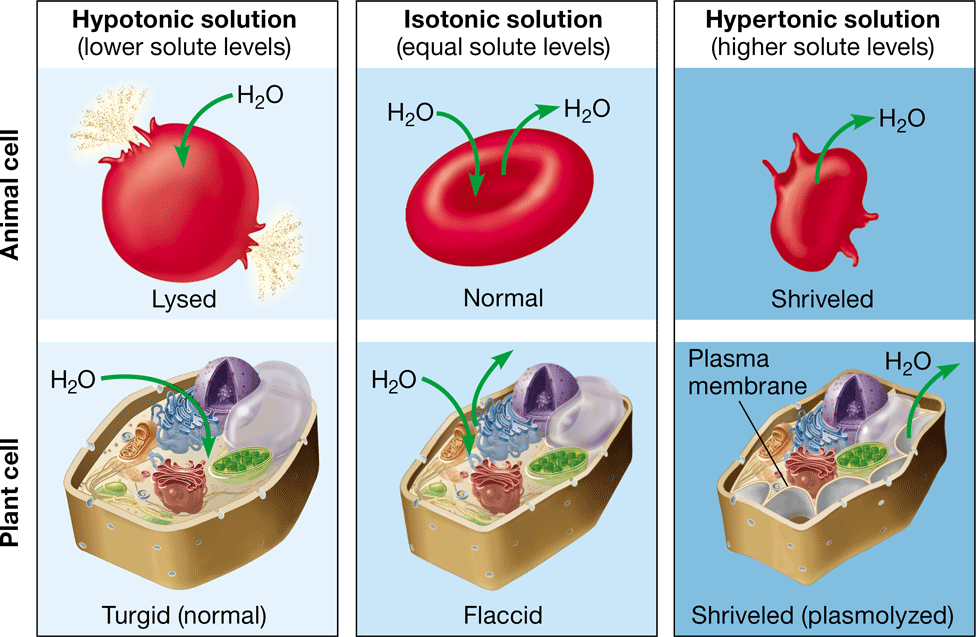
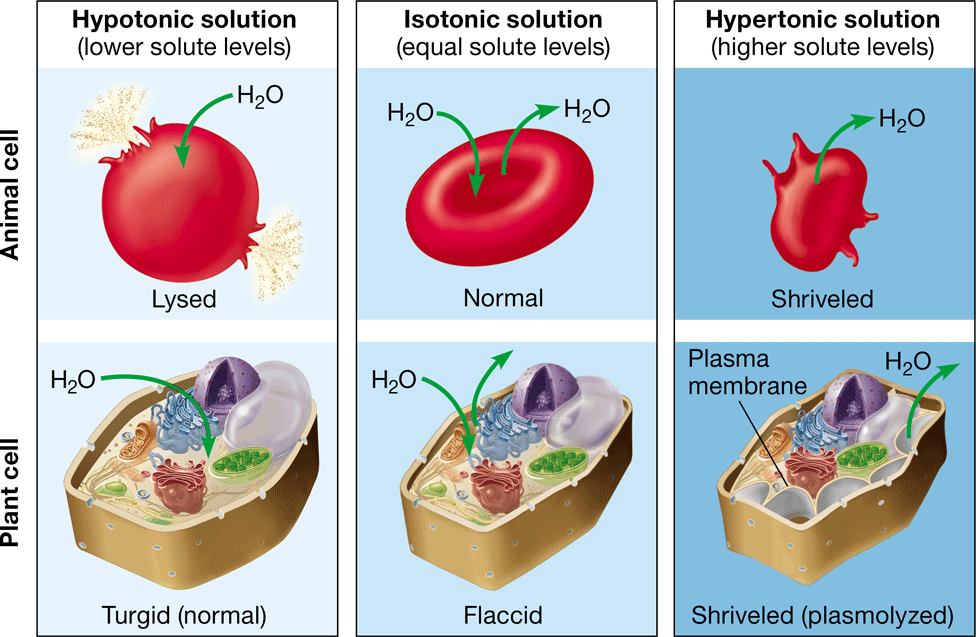
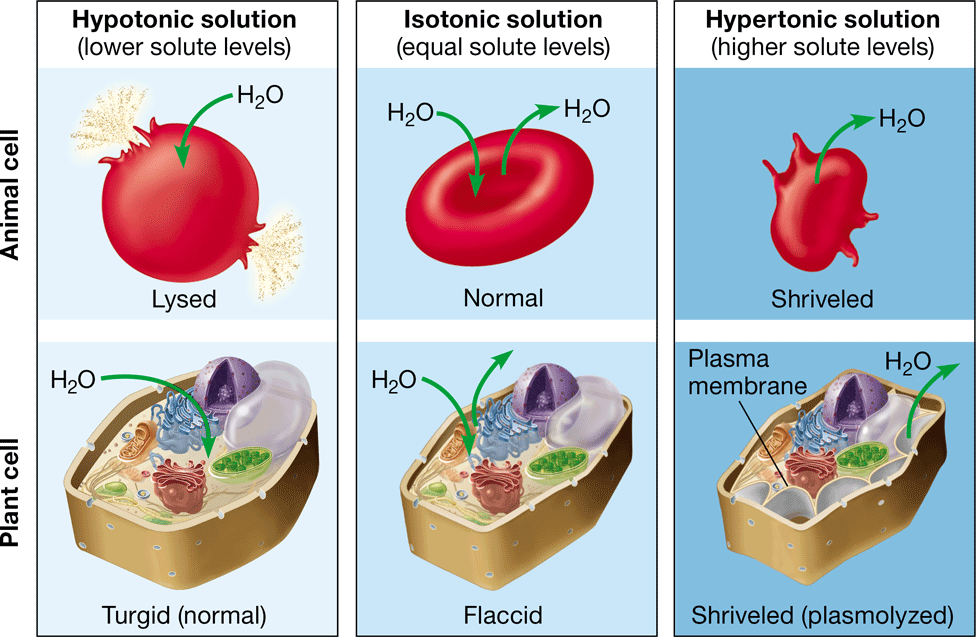
lysing
bursting of an animal cell caused by the net movement of water into the cell (hypotonic environment)
35
New cards
turgid
firm, healthy state of plant cells in a hypertonic environment
36
New cards
turgor pressure
prevents a plant cell from taking in too much water & lysing
37
New cards
flaccid
limp plant cell caused by the loss of water in an isotonic environment
38
New cards
plasmolysis
\-the pulling away of a plasma membrane from a cell wall
\-caused by the loss of water in a hypertonic environment
\-causes the plant to wilt
\-caused by the loss of water in a hypertonic environment
\-causes the plant to wilt
39
New cards
crenation
shrinking of an animal cell after exposure to a hypertonic environment
40
New cards
system
matter under study
41
New cards
surroundings
everything outside the system
42
New cards
thermodynamics
study of energy transformations that occurs in a collection of matter
43
New cards
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but not created nor destroyed.
44
New cards
second law of thermodynamics
Energy conversion reduces the order of the universe, increasing its entropy.
45
New cards
entropy
measure of disorder/randomness
46
New cards
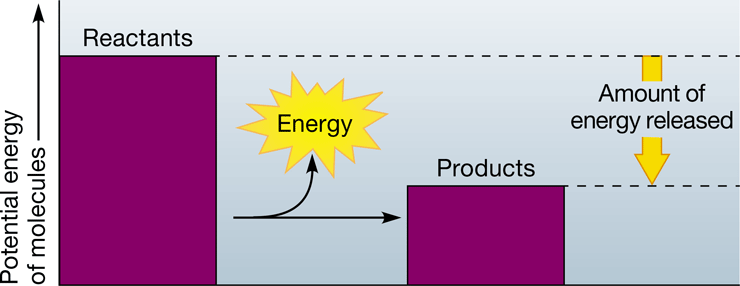
exergonic reaction
\-energy-releasing chemical reaction in which the reactants contain more potential energy than the products
\-i.e. cellular respiration
\-i.e. cellular respiration
47
New cards
endergonic reaction
\-energy-requiring chemical reaction in which products yield more potential energy than the reactants
\-i.e. photosynthesis
\-i.e. photosynthesis
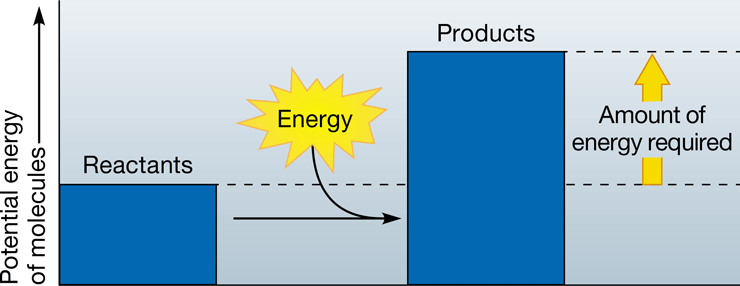
48
New cards
energy coupling
the use of energy released from an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction in cellular metabolism
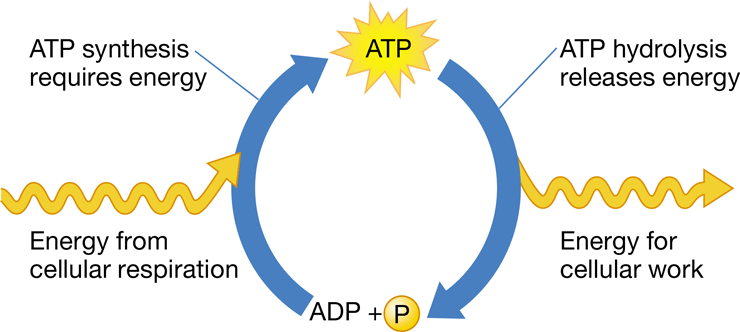
49
New cards
metabolic pathway
series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds
50
New cards
cellular respiration
\-aerobic harvesting of energy from food molecules
\-stores potential energy in a form that cells use to perform work (ATP)
\-stores potential energy in a form that cells use to perform work (ATP)
51
New cards
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
\-main energy source for cells
\-releases energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed
\-2 phosphoanhydride bonds
\-releases energy when its phosphate bonds are hydrolyzed
\-2 phosphoanhydride bonds
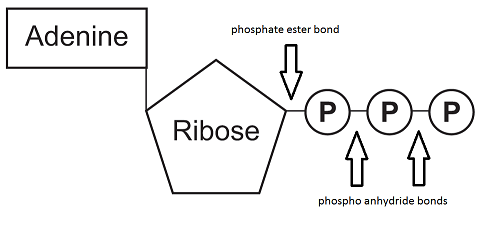
52
New cards
ADP
\-1 phosphoanhydride bond
53
New cards
AMP
\-0 phosphoanhydride bonds
54
New cards
phosphoanhydride bond
high-energy bonds that link phosphate groups to one another in ATP, ADP, AMP
55
New cards
phosphorylation
\-transfer of a phosphate group to a molecule
\-ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is phosphorylated to form ATP
\-ADP (adenosine diphosphate) is phosphorylated to form ATP
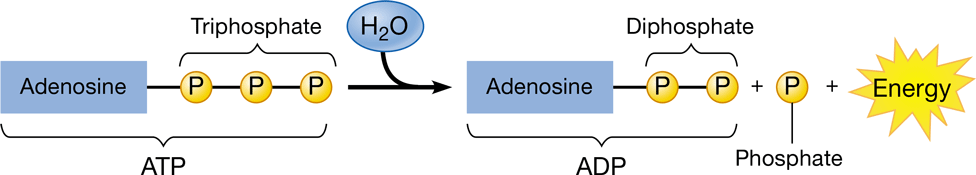
56
New cards
activation energy
amount of energy that reactants must absorb before a chemical reaction will start
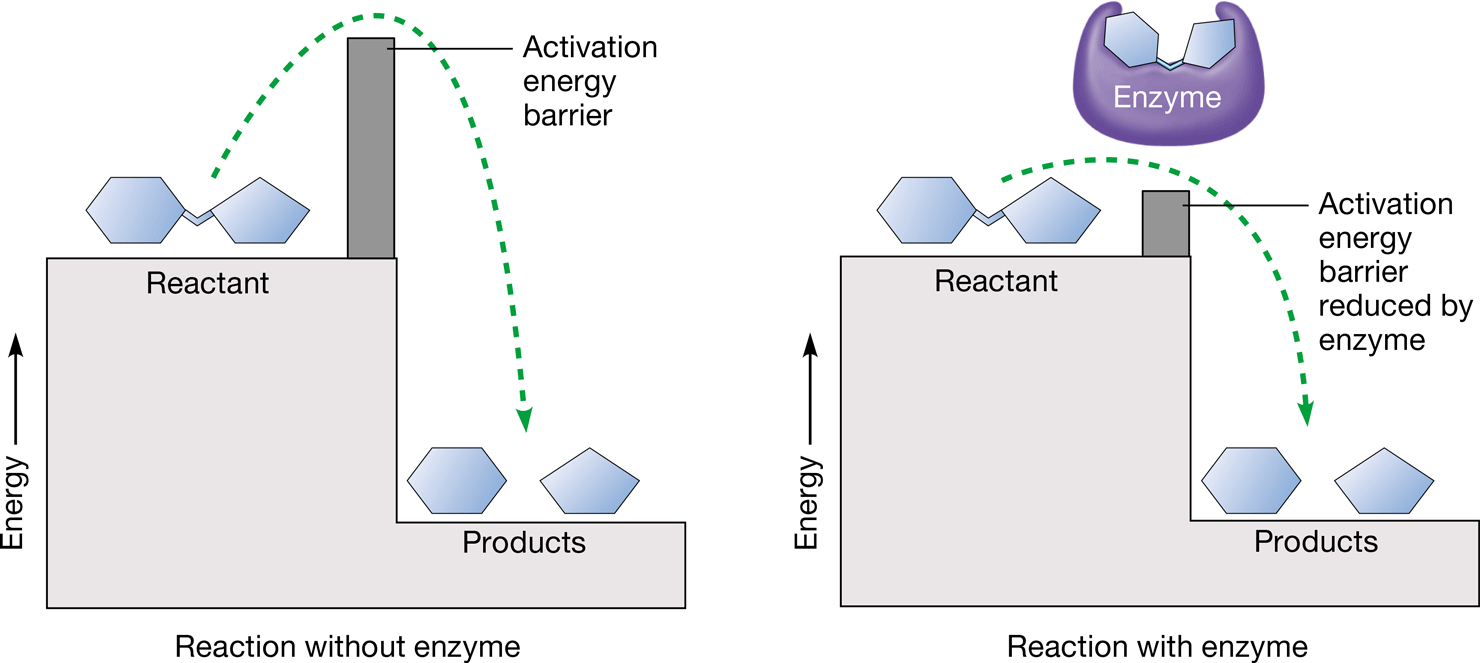
57
New cards
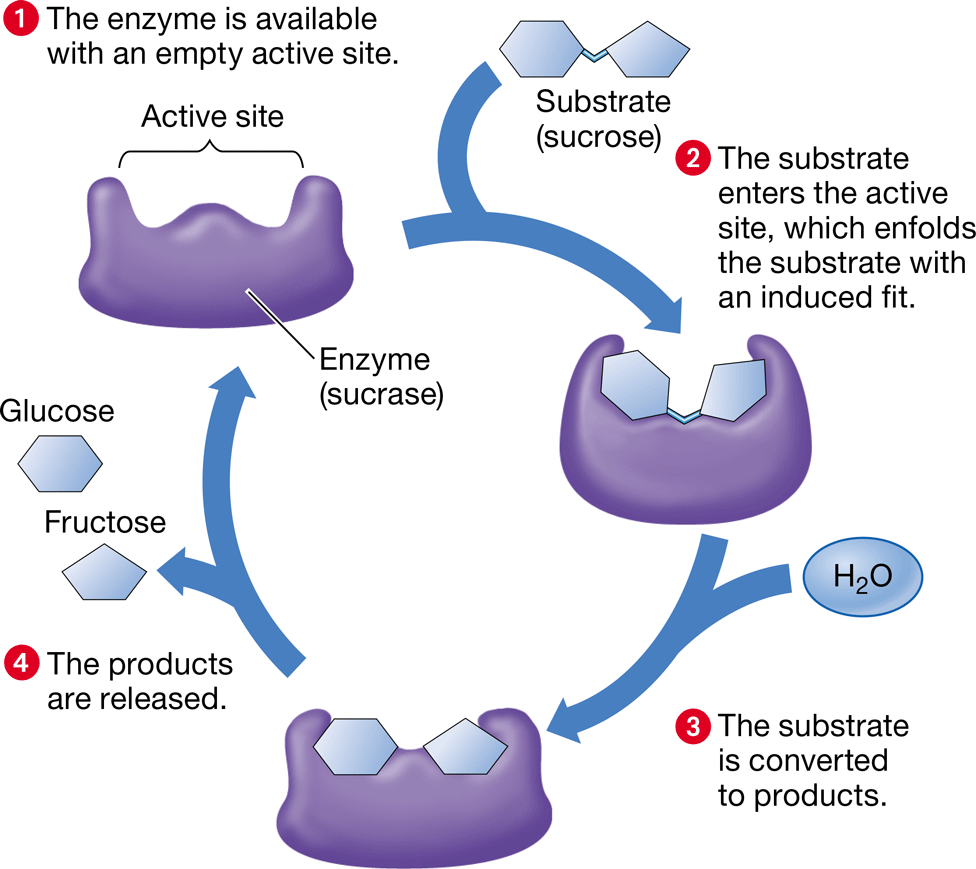
induced fit
\-changes in the shape of an active site caused by the entry of the substrate so that it binds the substrate snugly
\-may contort substrate bonds/place amino acids in position to catalyze the reaction
\-may contort substrate bonds/place amino acids in position to catalyze the reaction
58
New cards
cofactor
nonprotein molecule/ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme
59
New cards
coenzyme
organic molecule serving as a cofactor
60
New cards
competitive inhibitor
\-substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate
\-structure mimics that of the enzyme’s substrate
\-structure mimics that of the enzyme’s substrate
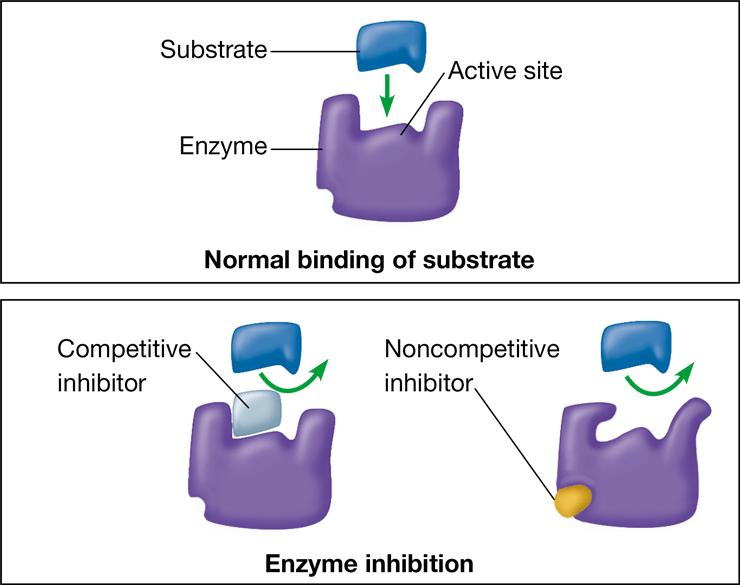
61
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitor
\-substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding elsewhere on the enzyme
\-changes that shape of the enzyme so that the active site no long catalyzes the conversion of substrate to product
\-changes that shape of the enzyme so that the active site no long catalyzes the conversion of substrate to product
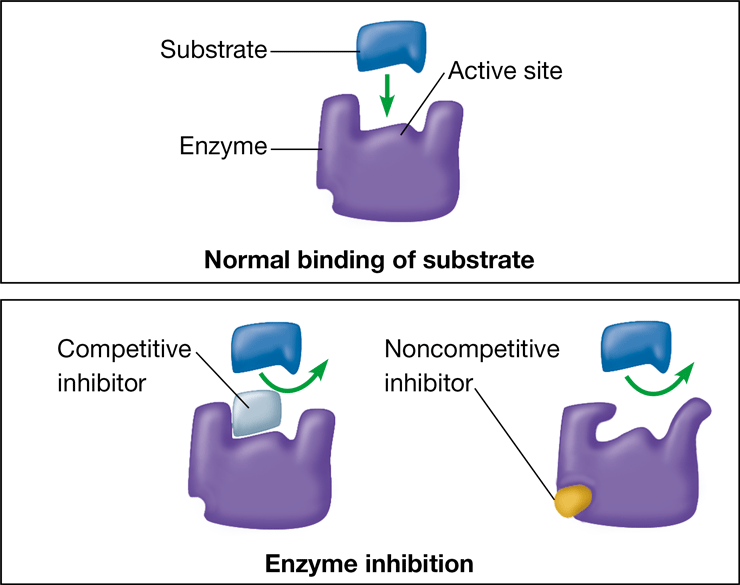
62
New cards
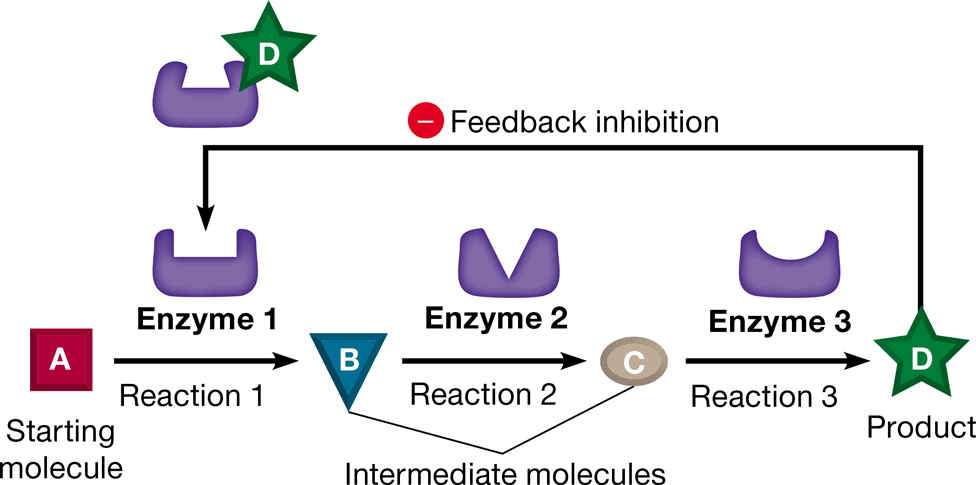
feedback inhibition
metabolic control in which a product of the metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway