Antiarrhythmics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Sino-Atrial Node
Controls the heartbeat rate (60-100 bpm)
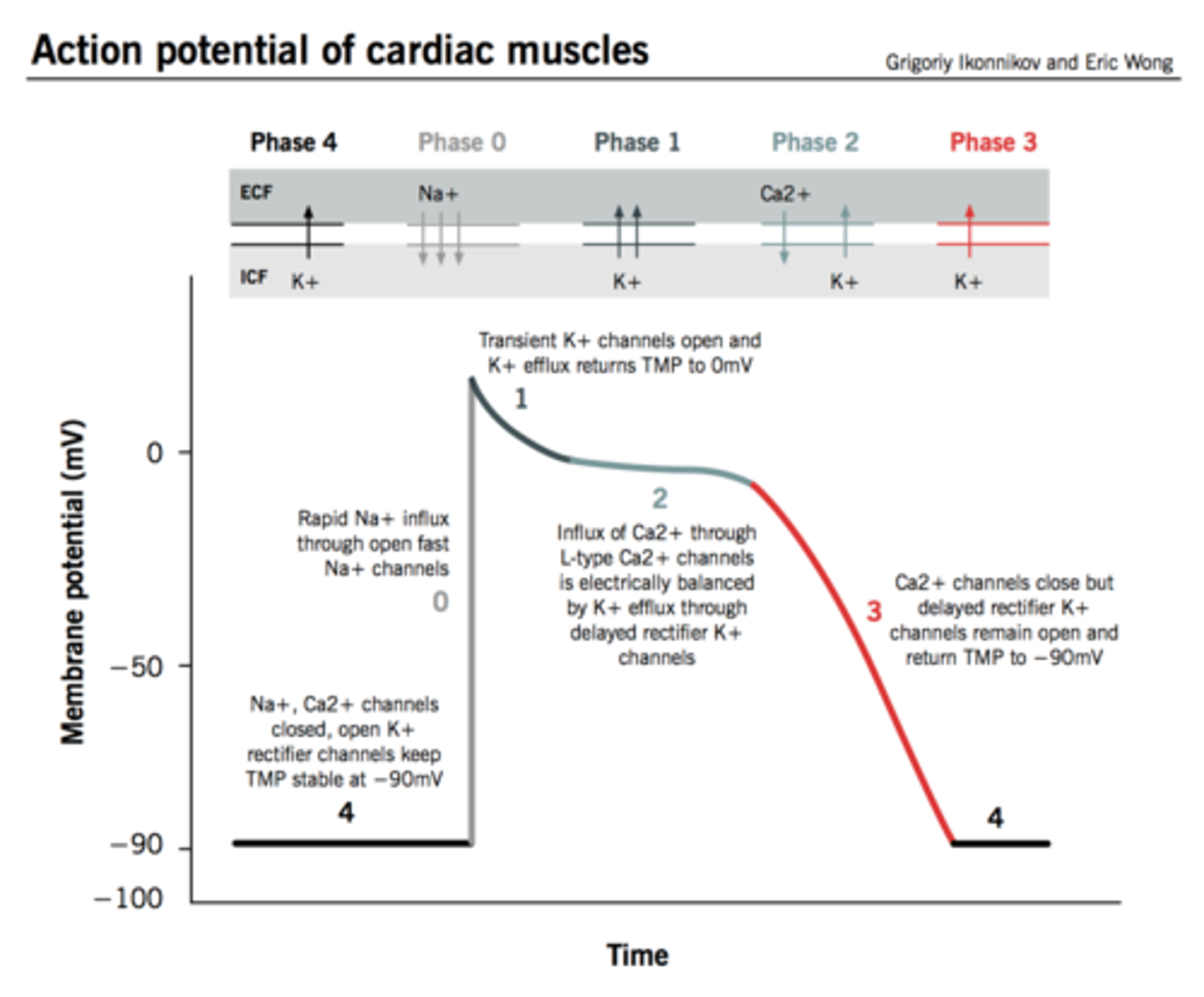
Cardiac Action Potential
Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Electrical conduction system malfunction
- Abnormal rhythms cause the heart to pump less effectively
- Result from disorders of impulse formation, conduction or both
Arrhythmias occur when:
- Heart's natural pacemaker develops an abnormal rate or rhythm
- Normal conduction path is interrupted
- Another part of the heart takes overas pacemaker
Causes of arrhythmias
- cardiac ischemia
- excessive discharge or sensitivity to autonomic transmitters
- exposure to toxins
- drugs, smoking, alcohol, caffeine
- unknown etiologies
Tachycardia
unusually fast heartbeat
Bradycardia
unusually slow heartbeart
Atrial fibrillation
- atria quiver instead of contract normally
- risk that blood pools in aria = clots
- supraventricular tachycardia
Ventricular fibrillation
- life threatening condition in which the heart ceases to beat regularly and instead"quivers" or fibrillates very rapidly
- 350bpm or more
- type of ventricular arrhythmia
Extra Beats Arrhythmias
- premature atrial contractions
- premature ventricular contractions
Supraventricular tachycardias
- atrial fibrillation
- atrial flutter
- paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Ventricular arrythmias
- ventricular fibrillation
- ventricular tachycardia
Goal of antiarrhythmic therapy
restore normal pacemaker activity and modify impaired conduction
Types of Antiarrhymtic Therapies
- Na+ or Ca2+ channel blockade
- Prolongation of effective refractory period
- Blockade of sympathetic effects on the heart
Class I Antiarrhythmics
- Sodium channel blockers
- slows depolarization in fast AP cells
- 1a: atrial and ventricular, PROCAINAMIDE & QUINIDINE
- 1b: acute tx of ventricular after MI, LIDOCAINE (IV)
- 1c: chronic supraventricular & vent., FLECAINIDE, PROPAFENONE
Fast AP cells =
atria, ventricles, His/Purkinje
Slow AP Cells =
sinus (SA) and AV nodes
PROCAINAMIDE & QUINIDINE
Class 1a antiarrythmic (sodium channel blockers); tx for atrial and ventricular arrhythmias (all purpose)
LIDOCAINE (solution injected IV)
Class 1b antiarrythmic (sodium channel blocker); For acute treatment of ventricular arrhythmias especially after MI
FLECAINIDE & PROPAFENONE
Class 1c antiarrythmic (sodium channel blocker); For chronic treatment of life-threatening supraventricular & vent. arrhythmias
adverse effect of class 1b antiarrhythmics
blurred vision, dizziness
Class II Antiarrhythmics
- Beta blockers = block sympathetic
- Decrease heart rate, contractility, and conduction velocity
- slows depolarization in slow AP cells
- Increase AP duration and effective refractory period
- Used for tachyarrhythmias, esp from inc SNS
- Ex) PROPANOLOL (INDERAL)
- Adverse effects: hypotension, bradycardia
PROPRANOLOL (Inderal)
- Class II Beta blocker
- Can block arrhythmias induced by exercise or apprehension
- Decrease heart rate, contractility, and conduction velocity
- Increase AP duration and effective refractory period
Class III Antiarrythmics
- Potassium Channel Blockers
- Prolongs repolarization phase by blocking outward K+ flux (prolongs AP)
- For treatment of ventricular tachycardia and Afib
- Ex) AMIODARONE (Cordarone)
AMIODARONE (Cordarone)
- Class III antiarrhythmic (K+ channel blocker)
- SE: corneal deposits, pulmonary fibrosis & pneumonitis, and can affect thyroid fxn
- tx ventricular tachy and Afib
Class IV Antiarrythmics
- Calcium Channel Blockers
- Prolong repolarization phase by blocking inward calcium current in slow AP cells
- Predominantly for treatment of atrial arrhythmias
- Ex) VERAPAMIL (ISOPTIN) & DILTIAZEM (CARDIAZEM CD)
VERAPAMIL (ISOPTIN) & DILTIAZEM (CARDIAZEM CD)
- Class IV antiarrythmic (Calcium Channel Blockers)
- prolonds repolarization phase in slow AP cells by blocking inward calcium current
- tx for atrial arrythmias
ADENOSINE
- DOC for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
- IV only, extremely short half-life (seconds)
- Inc. K+ conductance and dec Ca2+ activity => hyperpolarization
- Reduces release of NE from nerve terminals
- Net effect = reduce automaticity
DIGOXIN (LANOXIN)
- Direct suppression of AV node, increase refractory period
- for atrial fibrillation
Magnesium
dec Ca2+ influx
ATROPINE
- increases rate & conduction velocity
- Tx for bradyarrythmias
- SE: dry mouth, mydriasis
ISOPROTERENOL
- Increases heart rate & contractility
- tx for bradyarrhythmias
- Used to maintain adequate heart rate & CO in patients with AV block
- SE: tachycardia, flushing
Antiarrhythmics Adverse Effects
- affect normal cardiac function, have the potential to be pro-arrhythmic
- Tachycardia, not necessarily life-threatening, may initiate a life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia when treated