Psych Unit 2 Test
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
cell body
houses the nucleus
dendrite
the neuron’s branching extensions that receives and integrates messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
axon
the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
myelin sheath
fatty tissue that surrounds and protects the axon and speeds up electrical impulses
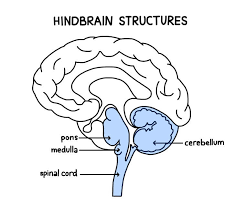
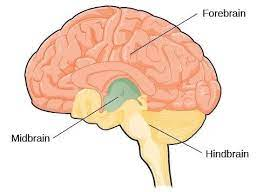
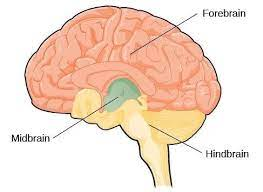
Hindbrain
-L: located on top of our spinal cord: cerebellum, pons, and medulla
-F: controls basic biological structures
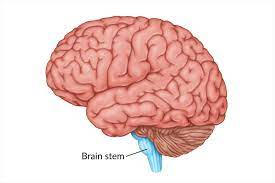
Brainstem
-L: base of the brain at the top of the spinal cord
-F: automatic, survival functions:
sends and receives info
severe damage to brainstem results in death
-oldest and innermost part
Spinal Cord
-L: starts at the base of brain and runs down the spine
-F: pathway for nerve fibers to carry info
connects brain to rest of body
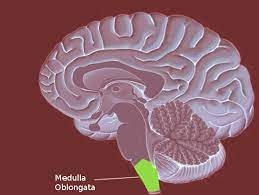
Medulla (oblongata)
-L: above spinal cord, below pons
-F: heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
reflexes (sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and swallowing)
pons
-L: above medulla on brainstem
-F: controls sleep, dreams, and facial expressions
connects multiple brain areas (medulla and cerebellum)
info processing
involved in control of breathing
coordinates movement
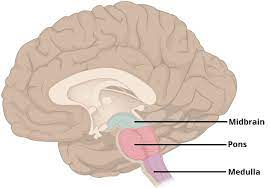
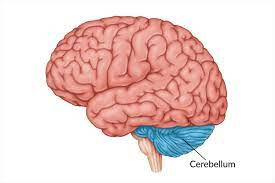
cerebellum
-”little brain”
-L: base of the brain, size of baseball
-F: balance of smooth and coordinated movements, fine motor movements
procedural (implicit) memory
judgements, emotions, discriminate, sounds/textures
Midbrain
-L: above the hindbrain, very small in humans
-F: coordinates simple movement with sensory info
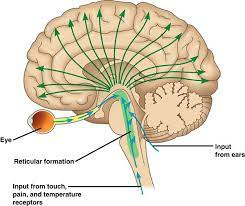
Midbrain- Reticular Formation
-L: finger-line shape through the brain stem
-F: arousal/consciousness to stimuli (awake-sleep cycle, not sexual)
-damage will put you in coma
-reflexes, breathing, and pain perception
Forebrain
-L: all brain parts except for brainstem and cerebellum
-largest part of the brain-most of it
-F: allows for the complex thoughts and behaviors unique to humans
-Tip: foremost of importance
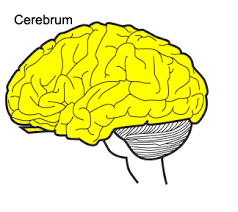
Cerebrum
-L: all brain parts except for brainstem and cerebellum (85% of the brain)
-F: all brain processes except for basic survival functions
the internal layer of the cerebrum is made up of the axons of neurons and glial cells
white matter
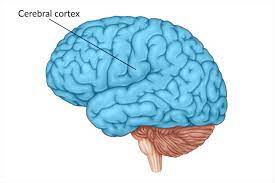
Cerebral Cortex
-L: ¼ inch wrinkled outer layer of the whole brain; 20-30 billion nerve cells are located here
-F: all higher mental functions (thought and planning)
ultimate control and info processing
-made up of the cell bodies of neurons called gray matter
-like a helmet
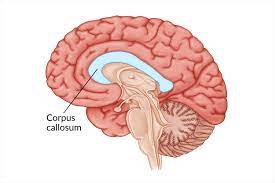
Corpus Callosum
-L: rainbow shape, like a bridge from back and front of brain
-F: bundle of neurons (axons) connecting the two cerebral hemispheres for communication
Limbic system
a system of brain structures and neural networks involved in processing emotion and long term memory
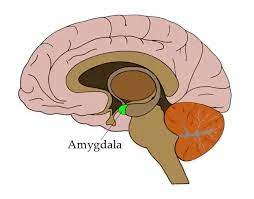
Amygdala
processes emotion especially fear and aggression
triggers flight or fight in response to danger
helps read other people’s emotions
helps store memories from emotional situations
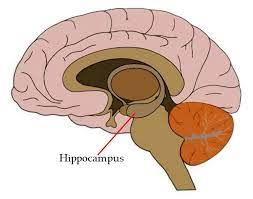
Hippocampus
stores information into long-term memory
stores spatial memory (navigation + location of objects)
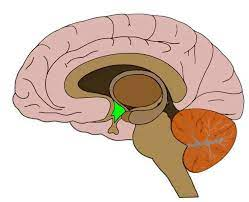
Hypothalamus
regulates autonomic nervous system
monitors + regulates body temp, hunger, thirst, and sexual responses
hormones alert hypothalamus of bodily states
directs other glands to release hormones in response
Lateral Hypothalamus
regulates feelings of hunger
-damage can cause you to never feel hungry
Ventromedial hypothalamus
regulates feelings of satiety (fulness)
-damage can cause you to never feel full
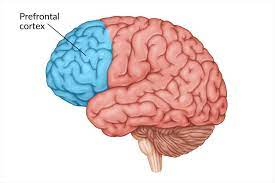
prefrontal cortex
judgement
planning
reasoning
problem solving
involved in personality
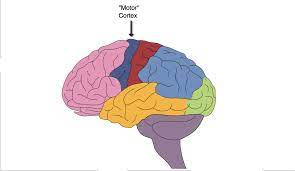
Motor cortex
L: in the rear of the frontal lobes
F: Controls voluntary movement
areas with more precise movement occupy more cortical space
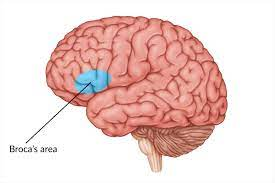
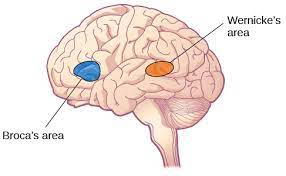
Broca’s area
-L: in the left frontal lobe next to motor cortex
-F: speech production
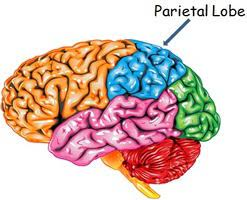
Parietal lobes
processes somatosensory input (touch, pressure, temp, and pain)
helps with spatial orientation (where you are and how you’re positioned)
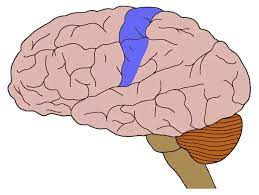
Somatosensory cortex
L: behind motor cortex
F: processes body movement and sensations
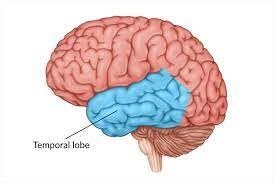
Temporal lobe
-L: behind ears
-F: involved in hearing, language processing, and storage of long-term memory
connects to the limbic system
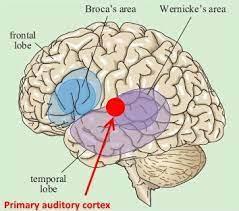
Primary Auditory Cortex
-L: in the frontal lobe
-F: main site of auditory perception and processing
Wernicke’s area
-L: in temporal lobe
-F: involved in comprehension of written and spoken language
Right Fusiform gyrus
-L: temporal lobe
-F: allows us to recognize human faces
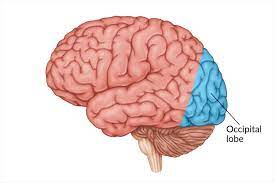
Occipital lobe
-L: back of brain
-F: processes visual info from eyes
norepinephrine
-Type: excitatory
-Function: helps control alertness and arousal, fight or flight
-Surplus: anxiety
-Deficit: depression
dopamine
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
-Surplus: schizophrenia
-Deficit: parkinson’s disease
endorphins
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: influences perceptions of pain and pleasure
-Surplus: artificial highs and inadequate responses to pain
-Deficit: depression, potential involvement in addiction
acetylcholine
-Type: Excitatory
-F: activates skeletal muscles and carries our voluntary movements
involved in memory formation and learning.
-deficit: lead to alzheimer’s disease or paralysis- limited mobility
-surplus- violent muscle spasms and contractions
serotonin
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: regulates mood, sleep, digestion
-Surplus: seizures and hallucination
-deficit: depression, mood disorders
Glutamate
-Type: excitatory
-Function: main excitatory neurotransmitter and involved in memory
-Surplus: overstimulate the brain, migraines, or seizures
-Deficit: none
GABA
-Type: inhibitory
-Function: major inhibitory neurotransmitter, regulates sleep-wake cycle
-surplus: sleep and eating disorder
-Deficit: seizures, tremors, insomnia, and huntington’s disease
Endocrine system
-system of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream to help control body functioning
-slow
Hypothalamus
-controls the pituitary gland
-connects NS to endocrine system
Pituitary gland
-master gland
-regulates growth, breast milk production, childbirth and bonding, communicates to other glands to release hormones
-prolactin and oxytocin
-dysregulation=extremes in height
Pineal gland
-in brain above pituitary
-melatonin
-regulates seasonal and sleep cycles
-dysregulation=seasonal affective disorder
thyroid/parathyroid
-in throat
-thyroxine and calcitonin
-regulates metabolism or the rate at which glucose is converted into energy
-regulates calcium levels in blood
-dysregulation=hypothyroidism (underactive) and hyperthyroidism (overactive)
Adrenal gland
-located above kidneys
-cortisone, cortisol, epinephrine (adrenaline), and norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
-controlled by ANS, increases heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels
-fight or flight
-dysregulation= excessive activity can compromise immune system
Pancreas
-located by stomach
-insulin and glucagon
-regulates sugar metabolism
-dysregulation= diabetes, low blood pressure
Gonads
-the testes and ovaries
-androgens (testosterone), estrogen, and progesterone
-allows sexual reproduction
-dysregulation= reproductive difficulties, higher levels of testosterone are correlated with increased aggression
Nervous system
body’s primary info system for voluntary and involuntary actions/thoughts
Fast
split into several major divisions (6 of them), neural cells, and the brain
Central vs peripheral, autonomic vs. somatic, parasympathetic vs. sympathetic
Sensory (afferent) Neurons
runs from sensory receptors (eyes, ears, nose, tongue, skin) TO the spinal cord and brain
afferent=to go toward
Keeps us constantly informed of events going on inside and outside of body
cell bodies always found in a ganglion outside of CNS
tells brain ouch
Motor (efferent) neurons
runs from brain and spinal cord TO the muscles and glands of the body
effects motor response
carries impulses to effector organs; the muscles and glands
cell body always located in CNS
tells body to move
Interneurons (Association Neurons) google translate
processes messages between sensory and motor neurons in neural pathways
cell bodies always located in CNS (brain and spinal cord)
Central nervous system (CNS)
neurons located in the brain and spinal cord
interpret incoming sensory info and issue instructions based on past experiences and current conditions
processing center, command center
Peripheral nervous system
All outside of the brain and spinal cord
All nerves that extend from brain (cranial nerves) and spinal cord (spinal nerves)
serves as communication lines
motor and sensory
Somatic NS
branch of PNS
voluntarily control skeletal muscles and our 5 senses
sensory and motor neurons
Autonomic NS
branch of PNS
controls body activities that are automatic and involuntary
heart, skin, blood vessels, eye, stomach, intestines, bladder
homeostasis
Sympathetic
a branch of autonomic NS
arousing (flight or fight)
provides best conditions to respond to a threat
tends to use norepinephrine (accelerate)
rapid heart beat, deep breathing, cold, sweaty skin, dilated eyes
digestion slows!
Parasympathetic
branch of autonomic NS
calming (rest and digest)
allows body to save and store energy
tends to use acetylcholine (slow down)
heart slows
you digest, eliminate feces and urine, blood pressure and respiratory rates are low, skin is warm
Lesion
tissue destruction; brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue
electroencephalogram (EEG)
-records brain’s electrical activity
-brain waves are measured by electrodes placed on scalp
-helps identify seizures and abnormalities in brain activity
PET scan
-examines brain functioning by observing the amount of metabolic activity in different brain regions
-measures glucose absorption after injection with radioactive isotope
-shows which brain regions are active at the time
CT scan
-examines brain structure by using X-rays
-shows exact shape + position of brain structures
-can diagnose tumors
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
-shows healthy tissue, tumors, tissue degeneration, and blood clots or leaks that signal strokes
-shows images of brain from exposure to magnetic fields and radio-waves
FMRI
-examines brain function by measuring blood flow and oxygen in the brain
-more precise than PET scans
-magnetic fields
plasticity
the brain’s ability to change and build new pathways as it adjusts to new experiences and damage
-makes human brain unique
-strongest during childhood
Psychoactive drugs
chemicals that change perception and mood through their actions at neural synapses
Depressants
-physical effect- slows down activity in CNS, increases GABA
-examples- alcohol, sleeping pills, tranquilizers
-psychological effects- mild euphoria, talkativeness, memory disruption, reduces self control, impairs judgements.
stimulants
-physical effect- speeds up activity of CNS, increases release of norepinephrine + dopamine
-examples- amphetamines, cocaine, caffeine, nicotine, and ecstasy
-psychological effects- increases mental alertness, reduce fatigue, produce stimulant induced psychosis, schizophrenia, and hallucinations
Opiate
-physical effect- sleepiness, relieves pain, agonist for endorphins
-examples- opium, morphine, and heroin
-psychological effects- intense rush of euphoria, contentment, and withdrawal symptoms
Hallucinogens
-physical effect- similar to serotonin, regulates mood and perceptions
-examples- LSD, ketamine, mescaline, marijuana
-psychological effect- loss of contact from reality, alters emotion, perception, and thought, produces hallucinations
Biological influences of drug use
-genetic predispositions
-variations in neurotransmitter systems
psychological influences
-lacking sense of purpose
-significant stress
-psychological disorders, like depression
socio-cultural influences
-urban environment
-cultural attitude toward drug use
-peer influences
Circadian rhythms
A 24-26 hr biological clock related to the sleep + wake cycle involving changes in hormones, blood pressure, and internal temperature
sleep functions
-protection: safety and energy conservation
-recovery: repair cells and strengthen immune system
-memory consolidation: key role in learning especially REM
-Growth: pituitary releases growth hormone during deep sleep
Sleep cycle
approximately 90 min and repeats pattern of REM and NREM stages
REM
-sleep stage characterized by rapid eye movements where dreams take place
-awake-like brain activity
NREM
-non-rapid eye movement and dreaming is less common
-stages 1, 2, and 3 of sleep.
during stage 2: sleep spindles- bursts of rapid rhythmic brain-wave activity
heritability
-the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
-heritability of a trait varies depending on the range of populations and environments studied
epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are involved in mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
hypnagogic sensations
bizarre experiences, such as the feeling of falling or floating weightlessly while transitioning to sleep
melatonin
sleep inducing hormone
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
-a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm
-causes pineal gland to adjust melatonin production based on light (no light-melatonin, light-no melatonin)
how lack of sleep effects physical health
suppresses immune cells that battle viral infections and cancer
insomnia
ongoing difficulty falling or staying alseep
narcolepsy
sudden attacks of overwhelming sleepiness
sleep apnea
breathing stops repeatedly while sleeping
dreams
sequence of images, emotions and thoughts
manifest content
according to freud, the symbolic, remembered storyline of a dream
latent content
according to freud, the underlying meaning of a dream
information-processing dream theory
dreams help sort out our day’s events and consolidate our memories
physiological function dream theory
regular brain stimulation from REM sleep may help develop and preserve neural pathways
activation-synthesis dream theory
REM sleep triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories, which our sleeping brain turns into stories
glial cells
-work to support, nourish, and protect neurons
-plays a role in learning, thinking, and memory
action potential
a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Beta waves
awake and alert
Alpha waves
awake and relaxed
Theta waves
slow regular waves of light sleep
Delta waves
deep stage 3 sleep