Spinal Cord Injury Overview and Management
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Injuries from MVAs, falls, GSWs, diving, sports.
Traumatic Causes
Vascular accidents, cord compression, spinal diseases.
Non-Traumatic Causes
Common unstable vertebral injury involving three columns.
Fracture-Dislocations
Fractures causing vertebrae to collapse.
Compression Fractures
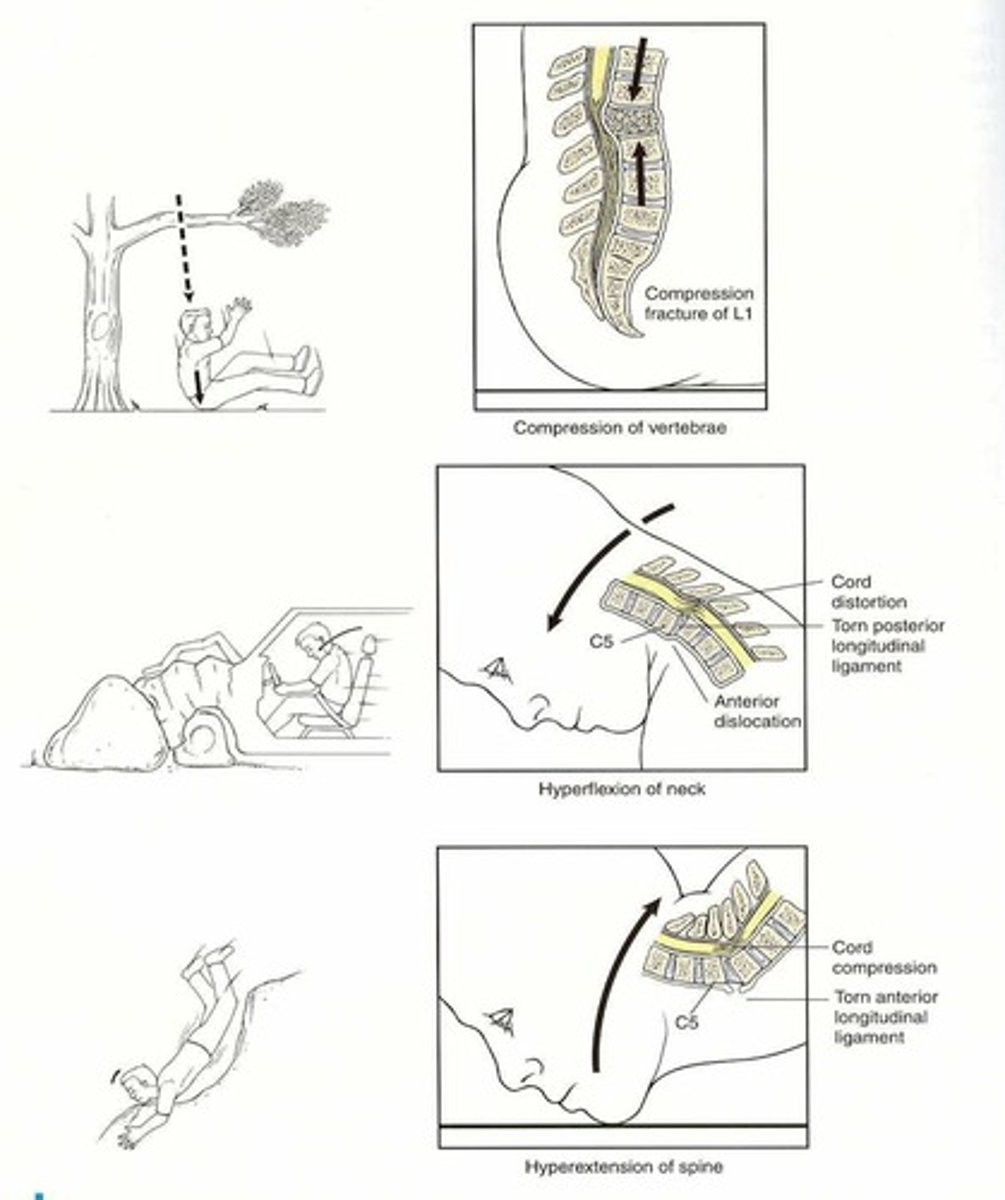
Injuries from excessive backward bending of the neck.
Hyper-Extension Injuries
Injuries from excessive forward bending of the neck.
Hyper-Flexion Injuries
Blood collection compressing the spinal cord. Rupture of a blood vessel, bleeding causes ischemia or pressure on the cord
Hematoma
Blood supply cut off, causing ischemia.
Thrombosis
Vertebral fx can increase pressure on and possibly injure the spinal cord and its nerves
Spondylitis
Degenerative disorder that causes loss of normal spinal function
osteoarthritis/ Spondylosis
Fluid-filled cyst forms on the spinal cord.
Syringomyelia
Progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerve cells in teh brain and spinal cord
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
any paralysis of upper and lower extremities due to a cervical injury
Tetraplegia (quadriplegia)
partial of complete paralysis of the Legs and trunk due to thoracic, lumbar, or sacral injury
Paraplegia
complete motor and sensory loss below the level of injury, loss of cortical control of bowel and bladder
Complete Lesion
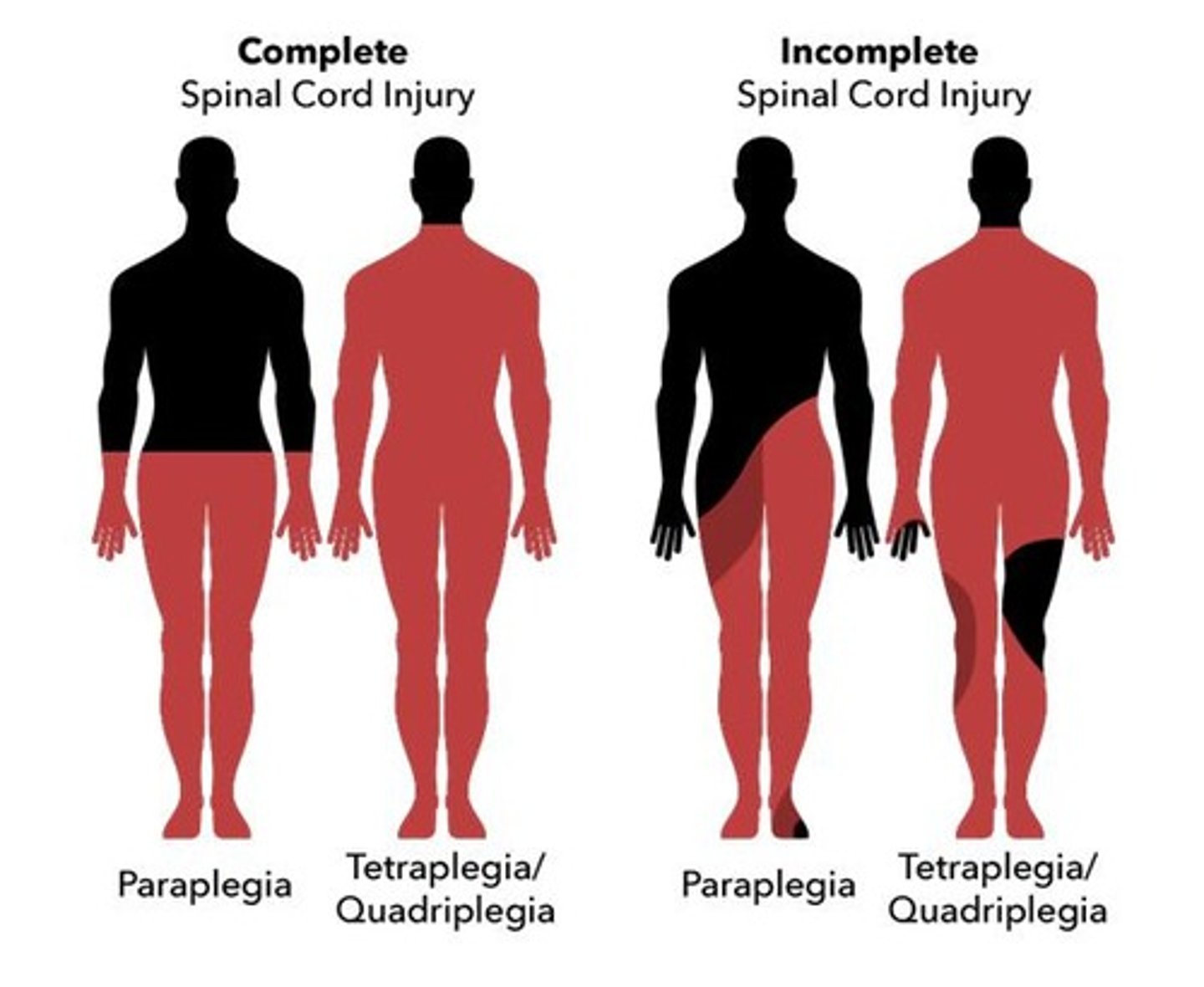
Partial disruption with some motor or sensory function intact.
Incomplete Lesion
perianal sensation or toe flexion may be intact
Sacral Sparing
Lowest spinal segment with normal function (most caudal)
Neurological Level
Skin areas innervated by sensory nerve roots.
Dermatomes
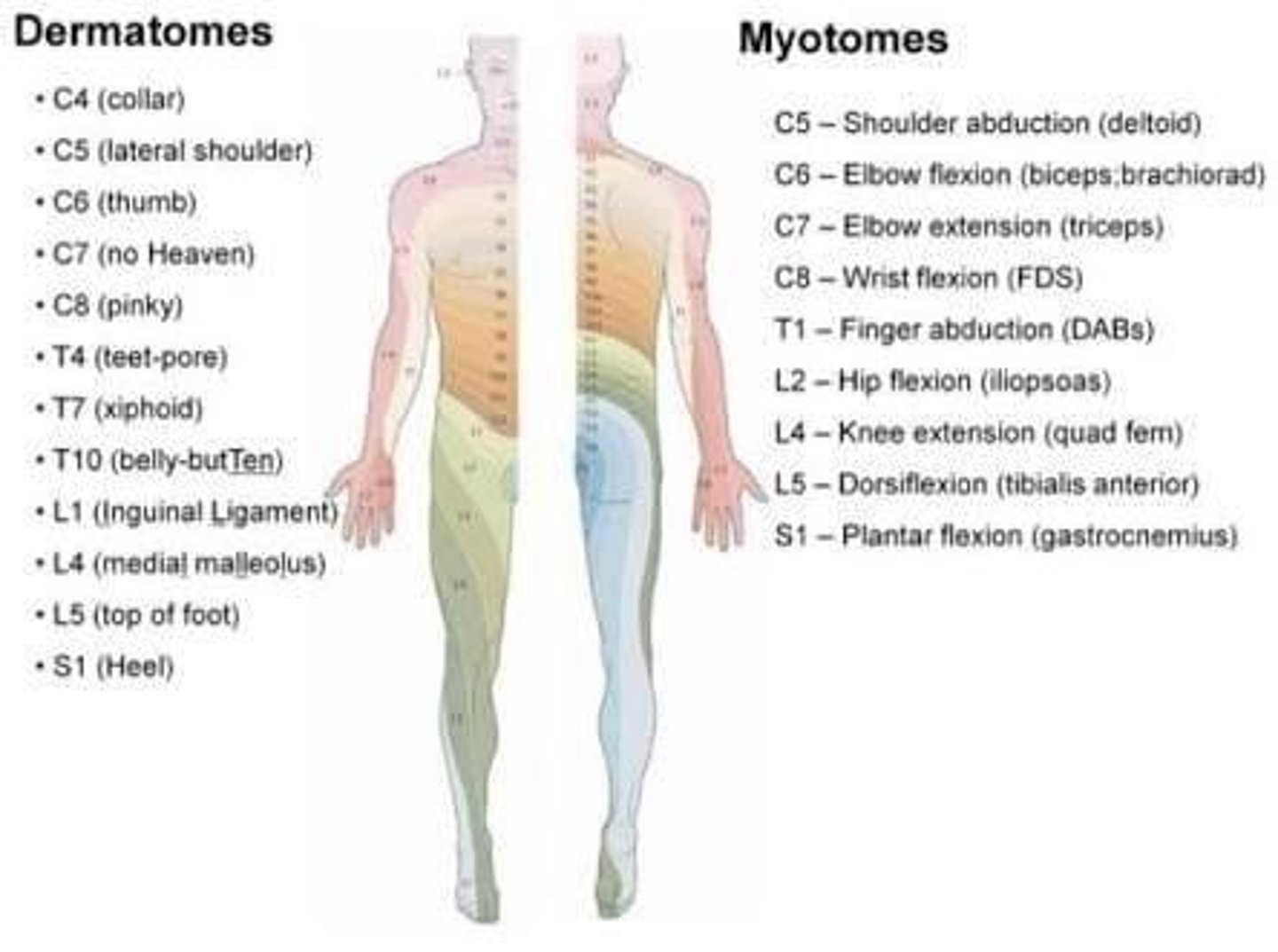
Muscle fibers innervated by motor nerve roots.
Myotomes
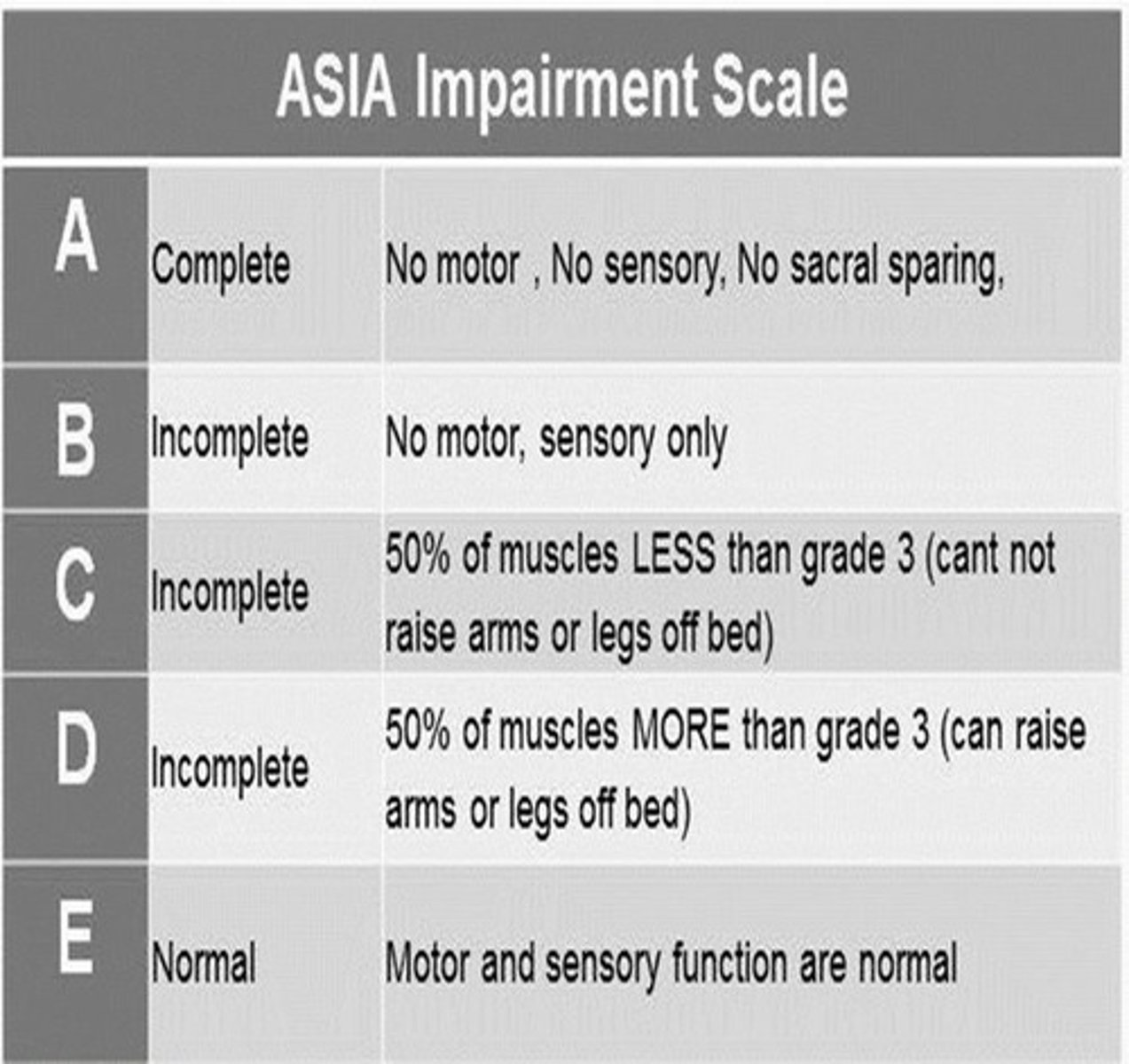
Classifies spinal injuries by preserved function.
ASIA Impairment Scale
most common incomplete SCI, more damage to central cord than periphery, falls, hyperextension injuries, older adults w/ arthritic changes
Central Cord Syndrome
one side of the cord is damaged, stabbing or a gun shot wound, motor and proprioception loss on ipsilateral side, loss of pain, temperature and touch on contralateral side
Brown Sequard Syndrome
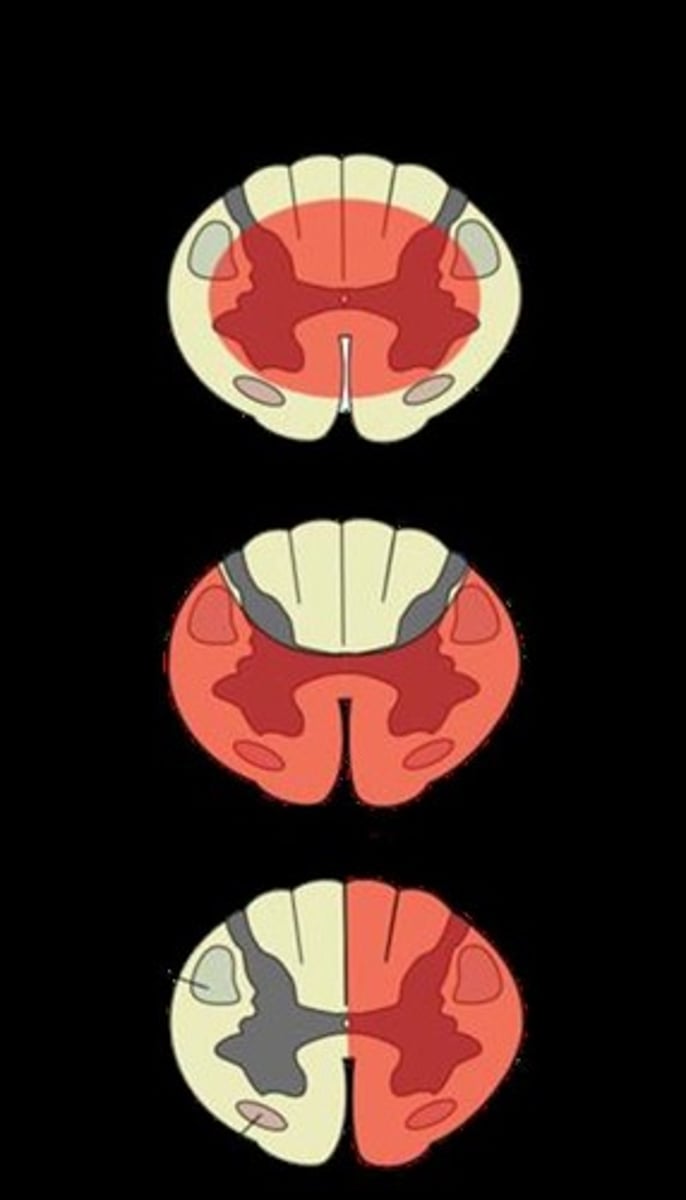
Loss of pain and temperature sensation.
Anterior Cord Syndrome
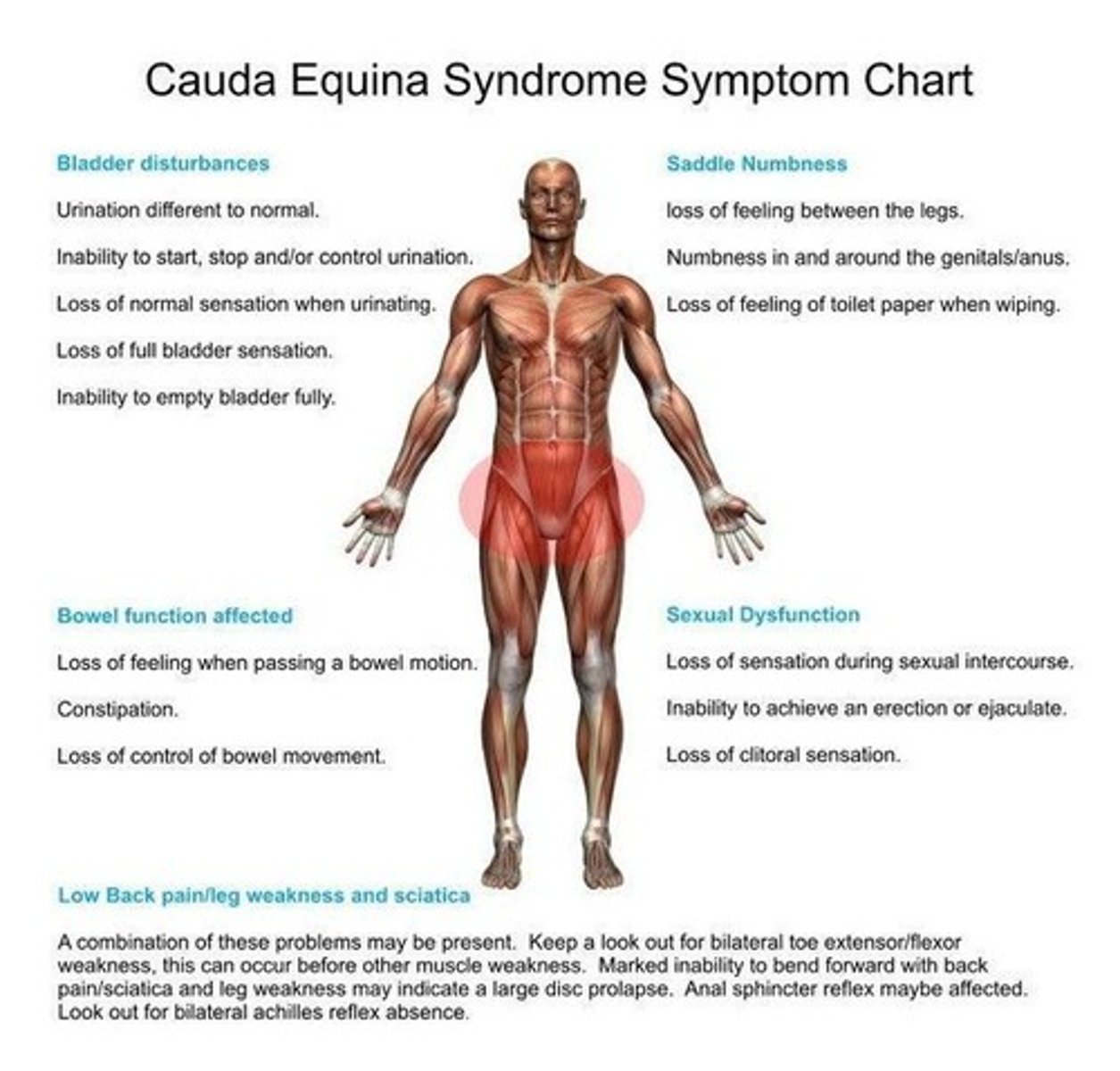
Injury below L2 causing flaccid paralysis.
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Temporary loss of reflexes post-injury.
Spinal Shock
-Bladder dysfunction requiring catheterization
-high risk of UTI
-spastic bladders allow for reflex emptying
-(T12 and above has no control over when the bladder empties)
-(T12-L1 is unable to detect when the bladder is full)
Neurogenic Bladder
Reflex response to a noxious stimulus below level of injury.
Autonomic Dysreflexia
Abnormal bone growth in SCI patients.
Heterotopic Ossification
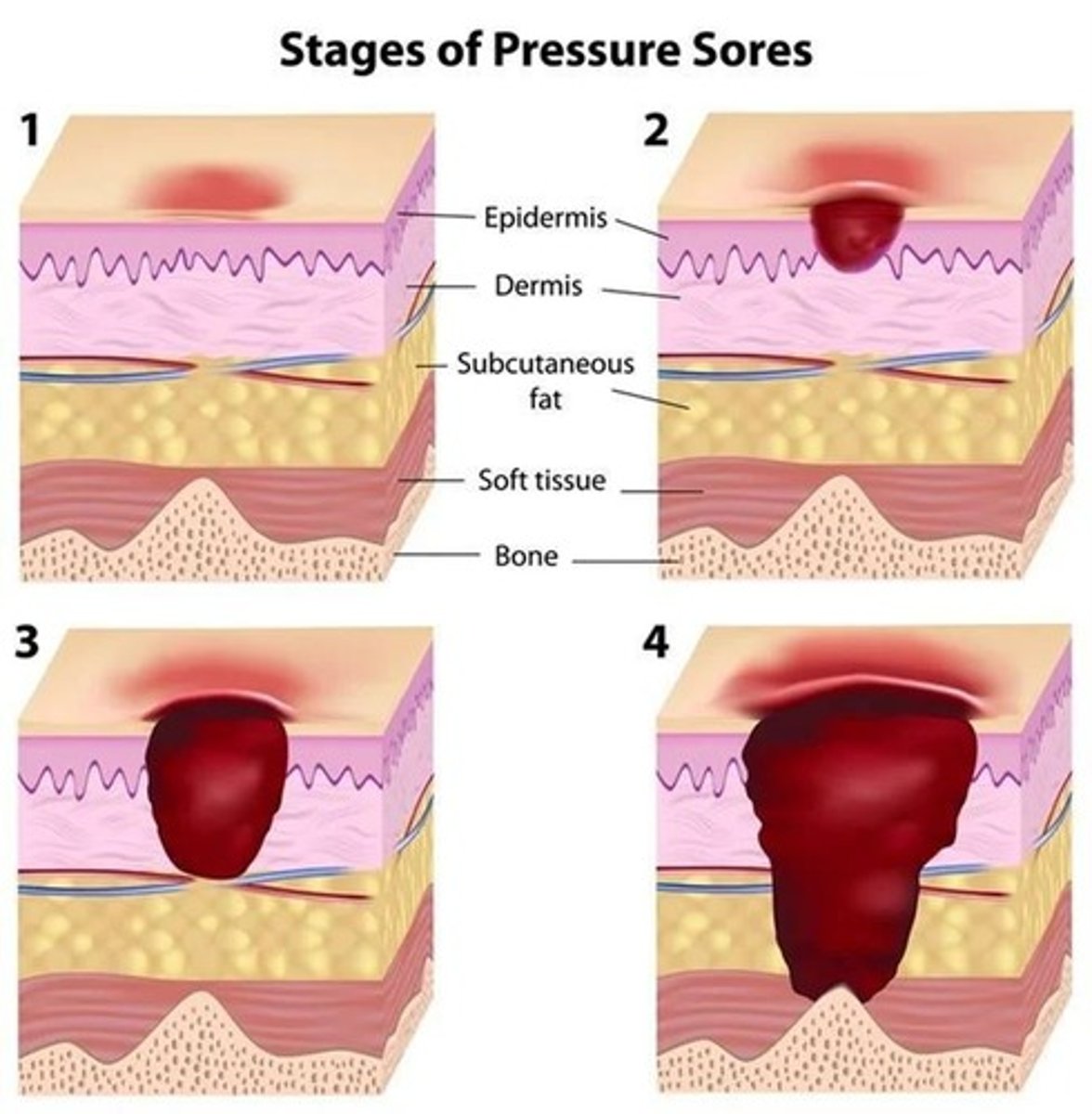
Skin ulcers due to loss of blood supply.
Pressure Sores
lead to pain, paralysis and neruological disfunctions
tumors
inflammation of the arachnoid mater
arachnoiditis
what is another name for spinal tuberculosis
potts disease
what are two associated injuries that can occur with spinal cord injuries
TBI and Brachial plexus injury
in complete injuries, this refers to partially innervated myotomes or dermatomes below the neurological level
zone of partial preservation (ZPP)
what kind of stabilization and immobilization device is a cervical traction or halo brace
closed methods
what kind of stabilization and immobilization device is a bone graft or the use of wiring
open methods
what are some medical complications that go along with spinal cord injuries
spinal shock, insensitive skin, bowel and bladder dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, pain, spasticity, respiratory, orthostatic hypotension, autonomic dysreflexia, osteoporosis, heterotopic ossification, pressure injuries
how long does spinal shock last
1-6 weeks
why do people with spinal cord injuries often have problems with respiration
due to their "butter bean" posture
what area of the cervical spine requires tracheostomies or respirators
c4-c6
when moving supine to sitting, BP drops, causing dizziness or black-out. PT must be tilted back and legs elevated
orthostatic hypotension
what are some causes of autonomic dysreflexia
distended bladder or UTI, bowel impaction, winkled clothing, pressure sores or pain
due to lack of weight-bearing, may be a cause of pathological fractures
osteoporosis
what percentage of patients who have spinal cord injuries have heterotopic ossification
16-53%
what are the common sites of heterotopic ossification
hips, knees, shoulders, and elbows