Unit 3 - Sonoran Desert
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
annuals
plants that die every year and must be replanted.
perennials
plants that come back every year
desertification
land degradation where the fertile landscape turns arid, with soil quality, vegetation, water, and wildlife all decreasing
cellulose
molecule that makes up most of a plant’s biomass. made of long chains of glucose
roots
obtain H2O for plant
leaf
part of the plant where sunlight hits to initiate photosynthesis
stem
aids in transport and provides structure to grow upwards`
flower
responsible for sexual reproduction/pollination
fruit
responsible for seed dispersal
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
photosynthesis equation
cell wall
provides protection, structure, and shape for cell. made of cellulose
chloroplast
organelle that performs photosynthesis and contains chlorophyll
vacuole
stores water in cell and creates turgor pressure
turgid
rigid plant, vacuoles full of water
flaccid
wilted plant, vacuoles lack water
passive transport
transport that does not require any ATP/energy input. dependent on potential energy differences
diffusion
movement of molecules from high to low concentrations in order to reach equilibrium
osmosis
movement of water from less concentrated → more concentrated across a semipermeable membrane
Moves from higher WATER CONCENTRATION to lower water concentration
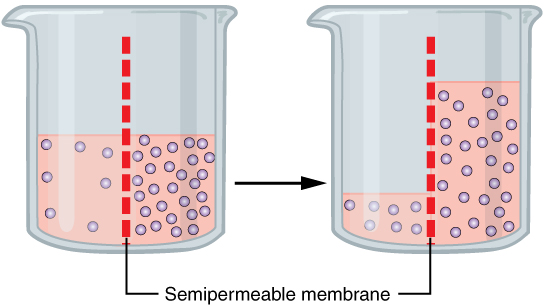
dilute
solvent high, solute low
concentrated
solute high, solvent low
turgor pressure
exerted by water in a plant cell against the cell wall
phloem
carries nutrients around plant, controlled via osmosis
xylem
carries water through dead cells from roots to leaves
cohesion
water sticks to each other via hydrogen bonds
adhesion
water sticks to other molecules
capillary action
cohesion + adhesion, movement of liquid through narrow space
stomata
gaps in leaf that open and close via guard cells
open stomata
water leaves, guards cells are turgid, H2O is abundant in the environment
closed stomata
water conserved, guard cells flaccid, and H2O scarce in environment
rate of water loss
how fast water transpired increases with an increase in the gradient
transpiration
evaporation from plants
water use efficiency
how much water a plant keeps to itself (carbon gain / H2O lost)
relative growth rate
how fast a plant grows (biomass gained / time)
photosynthesis
process where plants create glucose from CO2 and solar energy
respiration
process where organisms convert glucose to ATP
gradient
a difference in 2 things
potential energy
energy of position or charge
kinetic energy
energy of motion
ground state
state where electrons are in a stable form. electrons are close to the nucleus.
excited state
electron is in a higher energy state or orbital. electrons are further away from the nucleus and have more potential energy, making them more unstable.
C-O bond
the most stable carbon bond, with the lowest potential energy. it can be reduced to more unstable forms.
C-C bond
the middle-stable carbon bond. it can be either oxidized or reduced.
C-H bond
the most unstable carbon bond, with the highest potential energy. it can be oxidized to become more stable.
reduction
H is added, more unstable
gaining electrons/energy
oxidation
oxygen is added, more stable
Losing electrons/energy
redox
a paired reaction where one molecule is reduced (gains an electron) and another is oxidized (loses an electron)
reducing agent
causes reduction, gets oxidized
oxidizing agent
causes oxidation, gets reduced
cuticle
waxy secretion (fats, waxes) at the top of a leaf
palisade cells
located under cuticle in a column-shaped organization, tissues full of chloroplasts where photosynthesis takes place
spongy mesophyll
located under palisade cells, this is where gas exchange takes place. products of photosynthesis and water gather here.
thylakoid
located inside chloroplast, this is where light-dependent reactions take place.
Disk-like sacs suspended in the stroma
calvin cycle
light-independent reactions: a series of reactions that occur in the stroma, where CO2 and chemical energy is converted into sugar.
nucleus
where we find the DNA in eukaryotes in the form of linear chromosomes
mitochondria
the site of cellular respiration (ATP production!)
photosystem 2
light excites electron, chlorophyll → chlorophyll+, electron bounces around and travels to the ETC
water splitting
process where water is broken down into O2, H+, and electrons. this is necessary to replenish the lost electron from chlorophyll+
electron transport chain
electron moves through membrane, loses energy as it is used to power the H+ pump, where there is the active transport of H+ ions from the stroma into the lumen
photosystem 1
chlorophyll+ → chlorophyll, re-excited by light, electron from chlorophyll lands on NADP+, which creates NADPH
ATP synthase
enzyme that facilitates the creation of ATP from ADP and Pi, lets H+ ions flow from the lumen into the stroma via passive transport
fixation
CO2 is added to RuBP, which is broken down by Rubisco to create PGA
reduction
PGA, along with ATP and NADPH as energy, is converted into G3P, ADP, and NADP+
regeneration
G3P, along with ATP as energy, is converted into RuBP and ADP
6 turns
how many turns for 1 glucose?
3 turns
how many turns to fully regenerate RuBP?
photorespiration
Rubisco can bind to O2 instead of CO2 when it is hot or when there is not enough intercellular CO2
C4 photosynthesis
photosynthesis that modifies the first step of the Calvin Cycle. Fixation and the rest of the cycle occur in different cells, separating Rubisco from O2 entirely.
bundle sheath cells
cells that contain modified chloroplasts that contain no grana. this is where malate is converted back to CO2
CAM photosynthesis
photosynthesis where plants only open their stomata at night, fixing CO2 to malate during the day only and storing malate in vacuoles.
succulents
What types of plants perform CAM photosynthesis?
grasses
What type of plants perform C4 photosynthesis?
niche
a set of environmental conditions and resources that are necessary for a species survival and reproduction
competitive exclusion
the better competitor survives, and the worse competitor goes extinct. there is one winner and one loser.
niche partitioning
species with overlapping resources compromise and thus, they can both persist. the weaker species cedes some of the resource.
temporal
type of partitioning where two species use the same resource but at different times
spatial
type of niche partitioning where two species use a similar resource but in different areas
functional
type of niche partitioning where two species use a similar resource but in different ways
fundamental niche
space an organism could occupy
realized niche
space an organism actually occupies, this accounts for competition with other species
specialists
species that have a narrow niche and need certain requirements to survive. more vulnerable to changes.
generalists
species that can survive with a broad niche/broad range of resources
exponential growth
no limit on resources, population always growing
logistic growth
limited resources constrict population growth, hits carrying capacity and hovers around there
r-selected species
high growth rate, but also high death rate
K-selected species
maintain carrying capacity over time
type 1
survivorship where most survive infancy and live to old age
type 2
survivorship where there is no age-related mortality
type 3
survivorship where most die young, and those who do survive will live a full life to adulthood