lab practical 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:46 PM on 2/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
**Eyelid/palpebrae**
covers eye
2
New cards
**Medial/lateral commissure (canthus)**
medial and lateral junctions of upper and lower eyelids
3
New cards
lacrimal carnucle
located on the medial commissure – produces oily secretion
4
New cards
conjuntiva
inner surface of eyelid; secretes mucus
5
New cards
Lacrimal Apparatus
ecretes tears (contains lysozyme – an antibacterial enzyme). Apparatus consists of:
1. Lacrimal gland – located superior and lateral to each eye
2. Lacrimal canaliculus – tears enter thru lacrimal punctum
3. Lacrimal sac
4. Nasolacrimal duct
1. Lacrimal gland – located superior and lateral to each eye
2. Lacrimal canaliculus – tears enter thru lacrimal punctum
3. Lacrimal sac
4. Nasolacrimal duct
6
New cards
Ciliary glands
modified sweat glands found between eyelashes; lubricates eye
7
New cards
Tarsal glands
sebaceous glands posterior to eyelashes; produces oily secretion, lubricates eye
8
New cards
six extrinsic eye muscles
* **Lateral/External rectus**
* **Medial/Internal rectus**
* **Superior rectus**
* **Inferior rectus**
* **Inferior oblique**
* **Superior oblique**
* **Medial/Internal rectus**
* **Superior rectus**
* **Inferior rectus**
* **Inferior oblique**
* **Superior oblique**
9
New cards
Fibrous layer
outer connective tissue layer.
Consists of:
1. Sclera: “white of the eye”
2. Cornea: transparent anterior structure for light entry
Consists of:
1. Sclera: “white of the eye”
2. Cornea: transparent anterior structure for light entry
10
New cards
Vascular layer (Uvea)
middle layer; iris - most anterior part.
Consists of:
1. Ciliary body: found anteriorly; composed of ciliary muscle (controls lens shape) & ciliary processes (secretes aqueous humor).
2. Choroid: found posteriorly; blood-rich nutritive layer containing dark pigments preventing light scattering
Consists of:
1. Ciliary body: found anteriorly; composed of ciliary muscle (controls lens shape) & ciliary processes (secretes aqueous humor).
2. Choroid: found posteriorly; blood-rich nutritive layer containing dark pigments preventing light scattering
11
New cards
Sensory layer
innermost layer, contains the two-layered retina. The retina consists of:
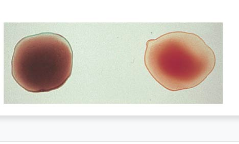
1. Pigmented epithelial layer: layer closest to choroid layer; covers ciliary body & posterior side of iris
2. Neural (nervous) layer: transparent layer containing photoreceptors (rods & cones); extends up to ciliary body
Rods: for black and white vision; used in dim light
Cones: for color vision; used in bright light; concentrated at the macula lutea (its center is the fovea centralis)
Blind spot located at optic disc where optic nerves leave the eye
1. Pigmented epithelial layer: layer closest to choroid layer; covers ciliary body & posterior side of iris
2. Neural (nervous) layer: transparent layer containing photoreceptors (rods & cones); extends up to ciliary body
Rods: for black and white vision; used in dim light
Cones: for color vision; used in bright light; concentrated at the macula lutea (its center is the fovea centralis)
Blind spot located at optic disc where optic nerves leave the eye
12
New cards
Ciliary Zonule
AKA: **Suspensory ligament.** Holds lens vertical; ciliary muscle contraction changes lens thickness to focus light onto retina
13
New cards
Lens
found anteriorly; focuses light onto retina.
Divides eye into two segments:
1. **Anterior segment/cavity**: contain watery aqueous humor (formed by ciliary body; reabsorbed by scleral venous sinus). Has 2 chambers:
Anterior chamber (before iris); Posterior chamber (after iris)
2. **Posterior segment/cavity**: contain gel-like vitreous humor
Divides eye into two segments:
1. **Anterior segment/cavity**: contain watery aqueous humor (formed by ciliary body; reabsorbed by scleral venous sinus). Has 2 chambers:
Anterior chamber (before iris); Posterior chamber (after iris)
2. **Posterior segment/cavity**: contain gel-like vitreous humor
14
New cards
Cones
photoreceptor in retinal layer that perceives color light; bright light; found mostly in **fovea centralis**
15
New cards
Rods
photoreceptor in retinal layer that perceives black/white; dim light; found mostly in periphery
16
New cards
bipolar cells
connects and modulates input from photoreceptors to ganglion cells. In the retinal layer.
17
New cards
ganglion cells
project axons to the brain via optic nerve and tract. Ganglion cell axons leave the eye thru the **optic disc**. In the retinal layer.
18
New cards
Visual pathway to the brain
Light stimulus causes impulses to travel from the: Optic nerves ⇒ optic chiasma (some optic nerves cross to opposite side) ⇒ optic tracts ⇒ superior colliculus & lateral geniculate body of the thalamus ⇒ occipital lobe (visual cortex)
19
New cards
emmetropic eye
normal eye; focuses properly.All images are inverted by the lens when focused onto the retina
20
New cards
myopia
near-sightedness; image focused in front of retina
21
New cards
hyperopia
far-sightedness; image focused behind of retina; **presbyopia** – far-sightedness caused by age-related decrease in lens elasticity
22
New cards
Astigmatism
irregular corneal curvatures that distort image
23
New cards
Auricle/pinna
composed of skin covered cartilage
24
New cards
external acoustic meatus
external auditory canal lined with ceruminous glands (secretes wax)
25
New cards
Tympanic Membrane
eardrum that vibrates with same frequency as sound waves that enter canal
26
New cards
middle ear
consists of a tympanic cavity containing auditory ossicles
27
New cards
auditory ossicle
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
Amplify and transmit tympanic membrane vibrations to **oval window** (on **cochlea)**
Amplify and transmit tympanic membrane vibrations to **oval window** (on **cochlea)**
28
New cards
Pharyngotympanic/auditory tube
Connects the tympanic cavity to nasopharynx. Equalizes middle ear pressure with outside air
29
New cards
Inner ear
\-consists of a system of bony (osseous) labyrinth filled with the aqueous fluid perilymph; bony labyrinth subdivided into:
1. Cochlea: involved in hearing
2. Vestibule: involved in equilibrium
3. Semicircular canals: involved in equilibrium
\-Suspended inside the perilymph of the bony labyrinth is the membranous labyrinth which consists of the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals (the inside of the membranous labyrinth is filled with the more viscous endolymph)
1. Cochlea: involved in hearing
2. Vestibule: involved in equilibrium
3. Semicircular canals: involved in equilibrium
\-Suspended inside the perilymph of the bony labyrinth is the membranous labyrinth which consists of the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals (the inside of the membranous labyrinth is filled with the more viscous endolymph)
30
New cards
Cochlear duct (scala media)
filled with endolymph; separates cochlear cavity into upper chamber (**scala vestibuli**) & lower chamber (**scala tympani**).
31
New cards
scala vestibuli
terminates at **oval window** with stapes, filled with perilymph
32
New cards
scala tympani
terminates at **round window**; filled with perilymph
33
New cards
spiral organ
found within cochlear duct; contains the sensory receptors (hair cells that project to **cochlear nerve**, part of **vestibulocochlear nerve C.N. VIII**).
34
New cards
Membrane of Spiral Organ: Basilar membrane
forms the floor of cochlear duct where hair cells rest
35
New cards
Membrane of Spiral Organ: Tectorial membrane
contains a gelatinous membrane that **stereocilia** from hair cells project into
36
New cards
Membrane of Spinal Organ: Vestibular membrane
roof of cochlear duct
37
New cards
Sound Transduction – how sound is converted to nerve impulses
The stapes sends vibrations through perilymph of the scala vestibuli and scala tympani. These vibrations cause the basilar membrane to move and thus stimulate the hair cells there (sensitivity to specific sound frequencies depends on hair cell location):
* __High frequency__ sounds detected primarily by hair cells at the __base__ of cochlear duct
* __Low frequency__ sounds detected primarily by hair cells at the __apex__ of cochlear duct
* __High frequency__ sounds detected primarily by hair cells at the __base__ of cochlear duct
* __Low frequency__ sounds detected primarily by hair cells at the __apex__ of cochlear duct
38
New cards
weber test
determines if sound conduction is equally loud for both ears. If not, may indicate sensorineural deafness from side with less sound.
39
New cards
Rinne test
compares conduction between bone and air. If air conduction sounds lower, can be caused by compared earwax, a perforated eardrum, inflammation of the middle ear (**otitis media**), or damage to the ossicles.
40
New cards
Vestibular apparatus
suspended in perilymph Vestibule (monitors static equilibrium): composed of:
1. Utricle: detects horizontal acceleration
2. Saccule: detects vertical acceleration
1. Utricle: detects horizontal acceleration
2. Saccule: detects vertical acceleration
41
New cards
Semicircular Canals
* contains the membranous **semicircular ducts**; monitors angular acceleration (dynamic equilibrium)
* Three ducts: anterior, posterior, and lateral.
* filled with endolymph
* Three ducts: anterior, posterior, and lateral.
* filled with endolymph
42
New cards
Vestibule
the utricle and saccule contain hair cells that project **stereocilia** and **kinocilium** into the **otolithic membrane** – gelatinous material containing **calcium carbonate** crystals called **otolith**. Movement of the head causes the otolithic membrane to move and stimulate or inhibit the hair cells to alter electrical signals sent along the **vestibular nerve** to the brain.
43
New cards
semicircular canals
contain hair cells in the **crista ampullaris** (sensory area) of the **ampulla**. The stereocilia of the hair cells in the crista ampullaris are covered by a gelatinous cap (the **ampullary cupula**) that moves when you move (when you move, the endolymph ‘pushes’ against the cupula). As the cupula moves, the hair cells send movement information to the brain as electrical impulses through the **vestibular nerve**.
44
New cards
neurons
nerve cells that function to transmit electrical impulses
45
New cards
neuroglia
cells that support the neurons
46
New cards
Soma
the neuron’s cell body (a cluster of cell bodies in the PNS is known as a __ganglion__ while in the CNS it is a __nucleus__)
47
New cards
Axon Hillock
tapered structure between soma and axon (important for producing the action potential)
48
New cards
Dendrites
processes that conduct electrical impulses towards the soma (usually receives a signal from another cell)
49
New cards
Axon
process that conduct electrical impulses away from the soma (in the CNS, a bundle of these processes form __tracts__, in the PNS, these axon bundles form __nerves__)
50
New cards
Axon/synaptic terminal
found at the end of axon.
51
New cards
Synaptic cleft
gap found between the axon terminal of one neuron and the target cell
52
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
* produce myelin
* located in the CNS
* located in the CNS
53
New cards
Schawwn Cells
* produce myelin
* Located in the PNS
* Located in the PNS
54
New cards
Neuroglia
* are important to neuron function.
* They can:
* Produce myelin to insulate a neuron’s axon
* Form __nodes of Ranvier__ found between myelinated sections of the axon. These nodes help propagate and increase action potential velocity
* They can:
* Produce myelin to insulate a neuron’s axon
* Form __nodes of Ranvier__ found between myelinated sections of the axon. These nodes help propagate and increase action potential velocity
55
New cards
How does an electrical impulse (action potential) travel down the neuron?
* An action potential is formed at the axon hillock when:
* An excitatory stimulus reaches axon hillock. This causes
* Influx of Na+ ions into the neuron which depolarizes the membrane at that area (makes that area more positive)
* When the depolarization reaches a **threshold** level, more Na+ ions enter the cell at that area
* Further membrane depolarization (influx of more Na+) occurs so the charge inside the cell actually becomes positive (normally at rest, the inside of a neuron is negatively charged)
* Na+ influx stops when the cell becomes positively charged (at \~ +30 mV) at that area. K+ ions then start leaving the cell. This repolarizes the cell at that area (starts turning the inside charge back to negative state).
* Once the cell is repolarized at that area, K+ ions stop leaving and the resting potential (the cell’s negative membrane potential) is restored.
* An excitatory stimulus reaches axon hillock. This causes
* Influx of Na+ ions into the neuron which depolarizes the membrane at that area (makes that area more positive)
* When the depolarization reaches a **threshold** level, more Na+ ions enter the cell at that area
* Further membrane depolarization (influx of more Na+) occurs so the charge inside the cell actually becomes positive (normally at rest, the inside of a neuron is negatively charged)
* Na+ influx stops when the cell becomes positively charged (at \~ +30 mV) at that area. K+ ions then start leaving the cell. This repolarizes the cell at that area (starts turning the inside charge back to negative state).
* Once the cell is repolarized at that area, K+ ions stop leaving and the resting potential (the cell’s negative membrane potential) is restored.
56
New cards
absolute refractory period
* immediately follows an action potential – further stimulation cannot generate another AP
57
New cards
relative refractory period
* follows absolute refractory period – a strong stimulation can cause the generation of another AP
58
New cards
olfactory sensory receptors
bipolar neurons; extend cilia out from epithelium into mucus layer to detect odors, axons extend thru cribriform plate, form nerves, & synapse at olfactory bulb. From there, impulses bypass the thalamus and go directly to the olfactory area of cortex.
59
New cards
tongue
covered by 3 types of papillae containing taste buds
1. __Foliate__ – located on the side walls of posterior tongue
2. __Fungiform__ – mushroom-shaped papillae located on the superior surface
3. __Vallate__ – arranged in a V formation on posterior surface
1. __Foliate__ – located on the side walls of posterior tongue
2. __Fungiform__ – mushroom-shaped papillae located on the superior surface
3. __Vallate__ – arranged in a V formation on posterior surface
60
New cards
Taste buds
composed of a globular arrangement of:
* __Gustatory epithelial cells__ – the receptor cell responsible for taste sensation, developed from support cells
* __Basal epithelial cells__ – stem cells that develop into support cells
Impulses carried to sensory cortex by facial VII (anterior 2/3 of tongue), glossopharyngeal IX (posterior 1/3 of tongue), & vagus X (pharyngeal area)
* __Gustatory epithelial cells__ – the receptor cell responsible for taste sensation, developed from support cells
* __Basal epithelial cells__ – stem cells that develop into support cells
Impulses carried to sensory cortex by facial VII (anterior 2/3 of tongue), glossopharyngeal IX (posterior 1/3 of tongue), & vagus X (pharyngeal area)
61
New cards
taste receptors
opening that exposes taste cell microvilli (gustatory hairs) to oral cavity
62
New cards
gustatory cell
(from the gustatory epithelial cell) contact with certain chemicals causing the gustatory receptor cell to depolarize
63
New cards
Endocrine System
helps nervous system coordinate/integrate body activity by releasing hormones (steroids, peptides, & amino acids) into the circulation system
* A specific hormone affects only its target organs (organs that have receptors for that hormone)
* A specific hormone affects only its target organs (organs that have receptors for that hormone)
64
New cards
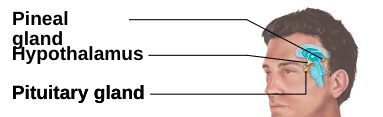
Pituitary gland
attached to hypothalamus through the __infundibulum__ (stalk); has two functional lobes
65
New cards
Anterior Pituitary
* (adenohypophysis) releases hormones to the body through the __hypophyseal portal system__ (primary and secondary capillary beds and the __hypophyseal portal veins__); **6 hormones secreted**:
* __Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)__: gonadotropin regulating gonad gamete production/hormone activity
* __Luteinizing hormone (LH)__: gonadotropin regulating gonad gamete production/hormone activity
* __Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)__: regulates adrenal cortex activity
* Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): regulates activity of thyroid gland
* Growth hormone (GH): regulates body/muscle/bone growth \*\*(too little GH causes dwarfism; too much GH causes gigantism)
* Prolactin (PRL): regulates breast development/lactation in females
* __Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)__: gonadotropin regulating gonad gamete production/hormone activity
* __Luteinizing hormone (LH)__: gonadotropin regulating gonad gamete production/hormone activity
* __Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)__: regulates adrenal cortex activity
* Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): regulates activity of thyroid gland
* Growth hormone (GH): regulates body/muscle/bone growth \*\*(too little GH causes dwarfism; too much GH causes gigantism)
* Prolactin (PRL): regulates breast development/lactation in females
66
New cards
posterior pituitary
(neurohypophysis) releases:
* Oxytocin: stimulates uterine contractions (birth & coitus) & milk ejection in lactation
* Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): stimulates kidney collecting tubules to reabsorb water from urinary filtrate & increase blood pressure via vaso-constriction of arterioles \*\*(too little ADH causes diabetes insipidus)
* Oxytocin: stimulates uterine contractions (birth & coitus) & milk ejection in lactation
* Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): stimulates kidney collecting tubules to reabsorb water from urinary filtrate & increase blood pressure via vaso-constriction of arterioles \*\*(too little ADH causes diabetes insipidus)
67
New cards
Pineal Gland
located on roof of 3rd ventricle in brain, produces:
* Melatonin: involved in biological rhythms. May have an inhibitory effect on reproductive system (prevents precocious sexual maturation)
* Melatonin: involved in biological rhythms. May have an inhibitory effect on reproductive system (prevents precocious sexual maturation)
68
New cards
Thyroid gland
located in throat, secretes:
* Thyroid hormone (TH): controls body metabolism & cellular oxidation; two active hormones:
* T4 (thyroxine)
* T3 (triiodothyronine)
* Calcitonin: increases calcium deposit in bones; decreases blood calcium levels
* Thyroid hormone (TH): controls body metabolism & cellular oxidation; two active hormones:
* T4 (thyroxine)
* T3 (triiodothyronine)
* Calcitonin: increases calcium deposit in bones; decreases blood calcium levels
69
New cards
Parathyroid gland
located on posterior surface of thyroid, secretes:
* Parathyroid hormone (PTH): releases calcium from bones to increase blood calcium, stimulates kidneys to activate vitamin D and reabsorb more calcium from filtrate \*\*(too little PTH causes __tetany__ – prolonged muscle spasms)
* Parathyroid hormone (PTH): releases calcium from bones to increase blood calcium, stimulates kidneys to activate vitamin D and reabsorb more calcium from filtrate \*\*(too little PTH causes __tetany__ – prolonged muscle spasms)
70
New cards
Thymus
located behind the sternum & above the heart, produces:
* Thymulin, thymosins, and thymopoietins: responsible for maturation/specialization of T lymphocytes used in the immune response
* Thymulin, thymosins, and thymopoietins: responsible for maturation/specialization of T lymphocytes used in the immune response
71
New cards
Adenal glands
located on kidneys
* Adrenal medulla controlled by sympathetic system to release:
* Epinephrine (80%)
* Norepinephrine (20%)
* Adrenal medulla controlled by sympathetic system to release:
* Epinephrine (80%)
* Norepinephrine (20%)
72
New cards
adrenal cortex
releases corticosteroids:
* Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone): regulate sodium reabsorption in kidney tubule
* Glucocorticoids (cortisone, hydrocortisone, corticosterone): increase blood glucose to resist stress
* Gonadocorticoids (androgens, estrogens): sex hormones \*\*(too much gonadocorticoids cause hirsutism & masculinization)
* Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone): regulate sodium reabsorption in kidney tubule
* Glucocorticoids (cortisone, hydrocortisone, corticosterone): increase blood glucose to resist stress
* Gonadocorticoids (androgens, estrogens): sex hormones \*\*(too much gonadocorticoids cause hirsutism & masculinization)
73
New cards
Pancreas
located behind stomach, produces digestive enzymes & both insulin and glucagon
* Insulin: decreases blood glucose levels \*\*(too little insulin causes __diabetes mellitus__; too much insulin causes __hypoglycemia__)
* Glucagon: increases blood glucose levels
* Insulin: decreases blood glucose levels \*\*(too little insulin causes __diabetes mellitus__; too much insulin causes __hypoglycemia__)
* Glucagon: increases blood glucose levels
74
New cards
Gonads
reproductive organs (ovaries and testes)
* Ovaries: located in pelvic cavity, produces:
* Estrogens: stimulates development of secondary sex characteristics, regulates menstrual cycle (uterine lining) & mammary glands for lactation
* Progesterone: regulates menstrual cycle, uterine musculature in pregnancy & mammary glands for lactation
* Testes: located in scrotum, produces:
* Testosterone: stimulates development of secondary sex characteristics, maturation of reproductive organs, & responsible for sex drive
* Ovaries: located in pelvic cavity, produces:
* Estrogens: stimulates development of secondary sex characteristics, regulates menstrual cycle (uterine lining) & mammary glands for lactation
* Progesterone: regulates menstrual cycle, uterine musculature in pregnancy & mammary glands for lactation
* Testes: located in scrotum, produces:
* Testosterone: stimulates development of secondary sex characteristics, maturation of reproductive organs, & responsible for sex drive
75
New cards
Blood
connective tissue that has non-living fluid matrix (plasma) that suspends living cells (formed elements)
76
New cards
Formed elements
* 45% of whole blood
* __Erythrocytes__: red blood cells (RBC) – most; transports oxygen
* __Leukocytes__: white blood cells (WBC) – immune system
* Platelets: blood clotting
* __Erythrocytes__: red blood cells (RBC) – most; transports oxygen
* __Leukocytes__: white blood cells (WBC) – immune system
* Platelets: blood clotting
77
New cards
Plasma
* 55% of blood
* Over 90% water
* Contains nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes, metabolites, proteins, electrolytes
* Over 90% water
* Contains nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes, metabolites, proteins, electrolytes
78
New cards
Erythrocytes
anucleated (lacks a nucleus) red blood cells (RBC’s); concave shape; unable to replicate/repair themselves; lasts 100-120 days
79
New cards
Leukocytes
white blood cells (WBC’s); nucleated cells produced from hemocytoblast stem cells in bone marrow; can move into/out of blood vessels (this process is known as __diapedesis__); has amoeboid motion; two main groups:
* __Granulocytes__: cytoplasmic granules stain differentially with Wright’s stain
* __Neutrophil__: most abundant of WBCs – active phagocyte (engulfs foreign particles), number increases with infection
* __Eosinophil__: attacks parasitic worms, lessens allergic reactions
* __Basophil__: contain granules with histamine, causes the inflammatory response
* __Agranulocytes/agranular leukocytes__: no visible cytoplasmic granules; found more in lymphatic system
* __Lymphocyte__: smallest leukocyte; functions in immunological response; two types:
* __B lymphocytes__: produces blood antibodies
* __T lymphocytes__: has ‘antibodies’ on cell surface to detect and destroys grafts, tumors, & virus-infected cells
* __Monocyte__: largest leukocyte, converts to macrophages when inside tissues; act as macrophages (engulfs foreign particles)
* __Granulocytes__: cytoplasmic granules stain differentially with Wright’s stain
* __Neutrophil__: most abundant of WBCs – active phagocyte (engulfs foreign particles), number increases with infection
* __Eosinophil__: attacks parasitic worms, lessens allergic reactions
* __Basophil__: contain granules with histamine, causes the inflammatory response
* __Agranulocytes/agranular leukocytes__: no visible cytoplasmic granules; found more in lymphatic system
* __Lymphocyte__: smallest leukocyte; functions in immunological response; two types:
* __B lymphocytes__: produces blood antibodies
* __T lymphocytes__: has ‘antibodies’ on cell surface to detect and destroys grafts, tumors, & virus-infected cells
* __Monocyte__: largest leukocyte, converts to macrophages when inside tissues; act as macrophages (engulfs foreign particles)
80
New cards
Platelets
cell fragments of megakaryocytes in bone marrow; vital role in blood clotting
81
New cards
Coagulation
injured tissues release tissue factor TF while platelets release platelet factor PF3 ⇒
they combine to form __prothrombin activator__ ⇒
converts __prothrombin__ (in blood plasma) to __thrombin__ ⇒
polymerizes soluble __fibrinogen__ (in plasma) to insoluble
__fibrin__ which forms the clot
they combine to form __prothrombin activator__ ⇒
converts __prothrombin__ (in blood plasma) to __thrombin__ ⇒
polymerizes soluble __fibrinogen__ (in plasma) to insoluble
__fibrin__ which forms the clot
82
New cards
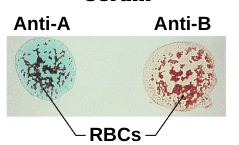
Blood typing
* RBC contain surface __antigens/agglutinogens__ which are determined by genetics (inherited). Blood contains antibodies/agglutinins that reacts with RBC that contain other antigens on their cell surface (your blood should not contain antibodies to the antigen on your red blood cell)
* Blood types: A, B, AB, O
* Rh: also known as the D antigen. (+ indicates the presence of the antigen, - indicates its absence)
* Blood types: A, B, AB, O
* Rh: also known as the D antigen. (+ indicates the presence of the antigen, - indicates its absence)
83
New cards
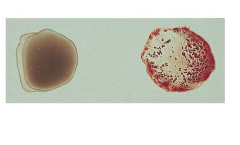
Type AB
contains antigens A and B
84
New cards
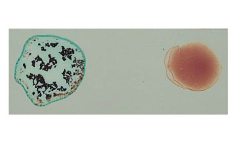
Type B
contains B antigens
85
New cards
Type A
contains A antigens
86
New cards
Type O
contains no antigen
87
New cards
Leukocytosis
Abnormally high WBC count indicates bacterial/viral infection
88
New cards
Leukopenia
Decreased WBC count indicates typhoid fever, measles, infectious hepatitis, cirrhosis, TB, excessive antibiotic/X-ray therapy
89
New cards
Leukemia
uncontrolled proliferation of WBC & reduction of RBC & platelets
90
New cards
Polycythemia
Increased RBC count from living in high altitudes or bone marrow cancer (tumors causing growth of RBCs)
91
New cards
Anemia
Decreased RBC count. Types of anemia:
* __Iron deficiency__ – caused by lack of iron
* __Sickle cell__ – RBC have abnormal shape causing decreased O2 carrying ability
* __Aplastic__ – bone marrow produces too few RBC’s
* __Pernicious__ – reduced RBC production due to lack of vitamin B12
* __Iron deficiency__ – caused by lack of iron
* __Sickle cell__ – RBC have abnormal shape causing decreased O2 carrying ability
* __Aplastic__ – bone marrow produces too few RBC’s
* __Pernicious__ – reduced RBC production due to lack of vitamin B12
92
New cards
Hematocrit
the percentage of blood volume occupied by RBC’s; PCV (packed cell volume) – used to detect anemia – high PCV to hemoglobin ratio indicates anemia
93
New cards
erythropoietin
hormone from kidneys that stimulate RBC production in bone marrow
94
New cards
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
measures RBC settling.
* Low sedimentation: normal person
* Increase sedimentation: person with increased production of fibrinogen & immunoglobulins
* Low sedimentation: normal person
* Increase sedimentation: person with increased production of fibrinogen & immunoglobulins
95
New cards
Hemoglobin determination
measures Hb concentration in RBCs.
* Normal person: 12-18 grams/100ml of blood
* Anemic person: lower value than normal
* Polycythemia: higher value than normal
* Normal person: 12-18 grams/100ml of blood
* Anemic person: lower value than normal
* Polycythemia: higher value than normal
96
New cards
blood typing
RBCs have antigens on cell surface. Antibodies against these antigens can be used to determine blood type.
* For example: if a RBC has the A antigen on its cell surface, then exposing the blood to A antibodies will cause the blood to coagulate (the antibody will attach to its antigen).
* For example: if a RBC has the A antigen on its cell surface, then exposing the blood to A antibodies will cause the blood to coagulate (the antibody will attach to its antigen).
97
New cards
heart
part of the cardiovascular system; the myocardium is composed of cardiac muscle; reinforced by dense fibrous connective tissue network; base of the heart is found beneath 2nd rib, apex at the left on top of the diaphragm
98
New cards
Pericardium
* (doubled walled fibroserous sac), serous fluid lubricates heart, prevents friction
* __Visceral pericardium/epicardium__: inner layer - closest to muscle; from the base of the heart to the apex. At the apex, it forms the __parietal pericardium__ which attaches heart to diaphragm
* __Fibrous pericardium__: outer layer; formed from dense connective tissue; lined by parietal pericardium. \*\*__Pericarditis__: pericardial inflammation due to serous pericardial layers adhesion
* __Visceral pericardium/epicardium__: inner layer - closest to muscle; from the base of the heart to the apex. At the apex, it forms the __parietal pericardium__ which attaches heart to diaphragm
* __Fibrous pericardium__: outer layer; formed from dense connective tissue; lined by parietal pericardium. \*\*__Pericarditis__: pericardial inflammation due to serous pericardial layers adhesion
99
New cards
cardiac muscle cells
line the myocardium
* Are striated muscle cells that have only one nucleus
* Have branched endings. The ends of the cardiac muscle cells are attached to other cardiac muscle cells by **intercalated discs**:
* Contains **gap junctions** that link the cytoplasm of one cardiac muscle cell to the adjacent cardiac muscle cell. Allows ions and small molecules to flow from one cell to another – allows for action potential to travel through the myocardium
* Are striated muscle cells that have only one nucleus
* Have branched endings. The ends of the cardiac muscle cells are attached to other cardiac muscle cells by **intercalated discs**:
* Contains **gap junctions** that link the cytoplasm of one cardiac muscle cell to the adjacent cardiac muscle cell. Allows ions and small molecules to flow from one cell to another – allows for action potential to travel through the myocardium
100
New cards
Interventricular septum
separates left & right atria and ventricles, respectively.