membrane structure
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what are the 2 components of the basic structure of a lipid
glycerol- hydrophilic head of lipid
fatty acid - hydrophobic tail of lipid
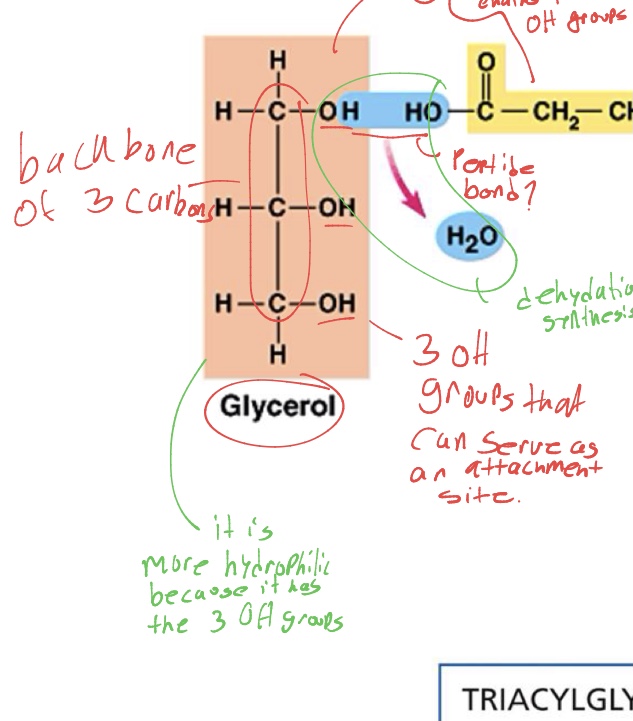
whats the chemical structure of the glycerol in a lipid
3 carbon chain backbone with 3 OH groups (make it hydrophilic) where the fatty acids attach

whats the chemical structure of the fatty acid tail of the lipid
lots of CH’s making it hydrophilic. and an OH that attaches to the OH of a glycerol through dehydration synthesis (lose H2O)
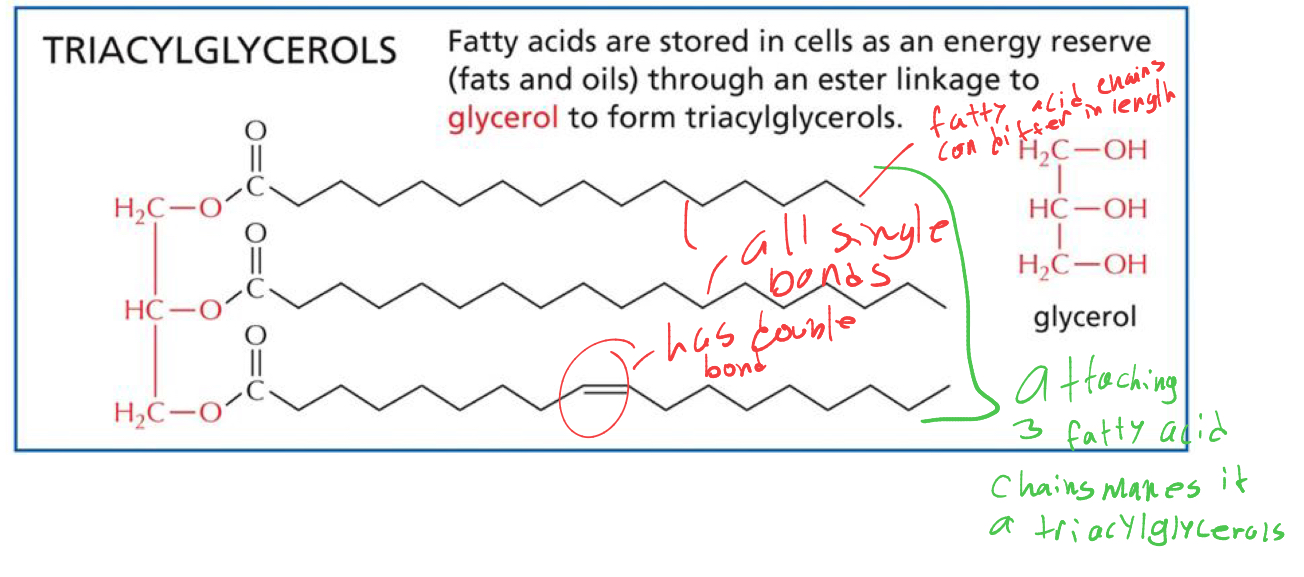
whats it called when we attach 3 fatty acid chains to the glycerol
triacylglycerols
whats the type of lipid we see in cell membranes
phospholipids- that have only 2 fatty acid chains.
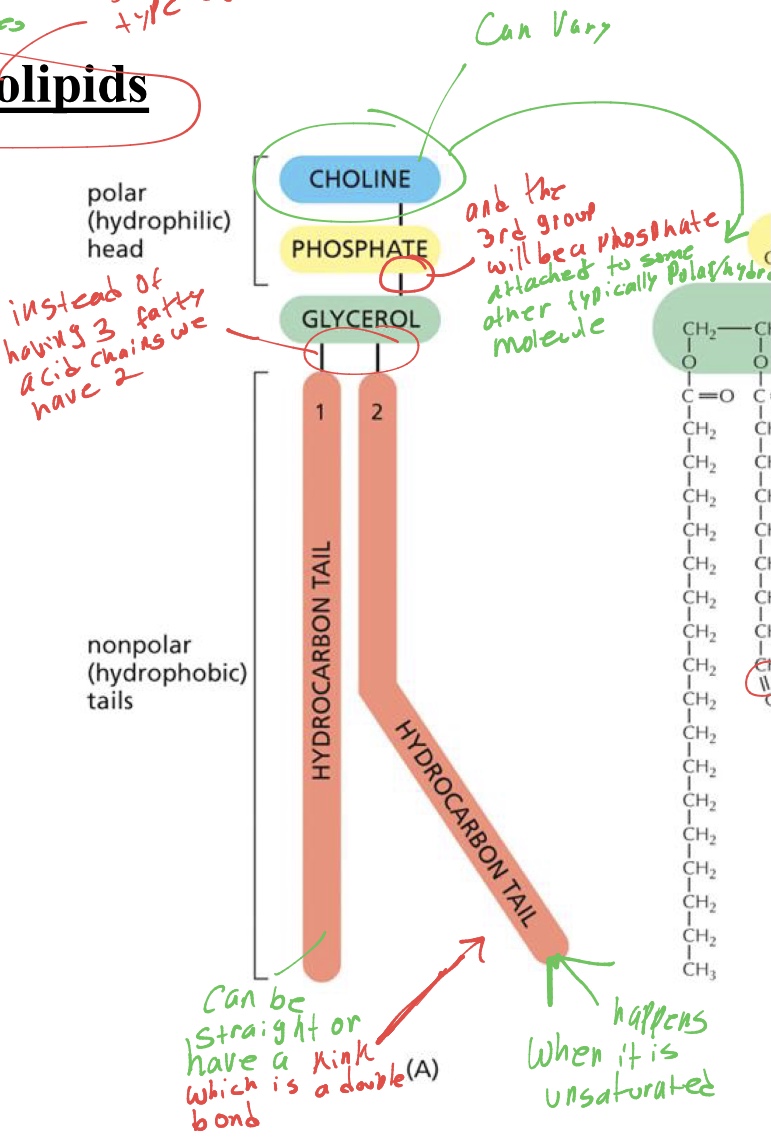
whats the structure of the phospholipid
only 2 fatty acid tails- non polar
glycerol+ phosphate+ polar molecule in head - polar
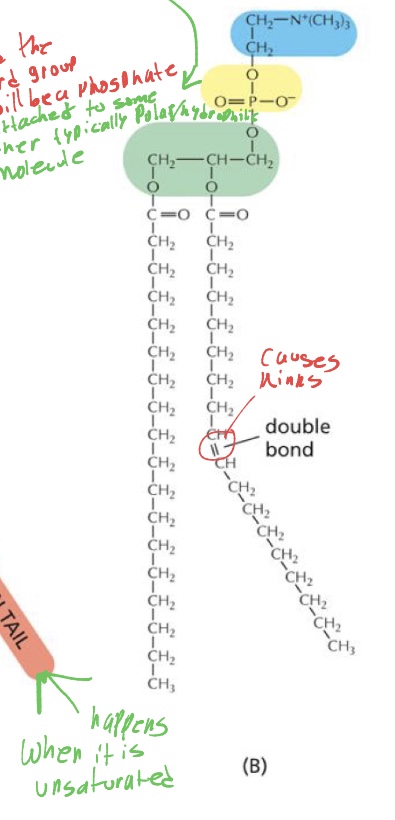
how do kinks form in the fatty acid chains in the lipids, when we have a lot of kinks what does that do to the cell membrane
a double bond in the chain, that’s caused by it being unsaturated
lots of kinks makes It more fluid, bc more double bonds don’t allow fatty acid tails to stack on top of one another tightly.
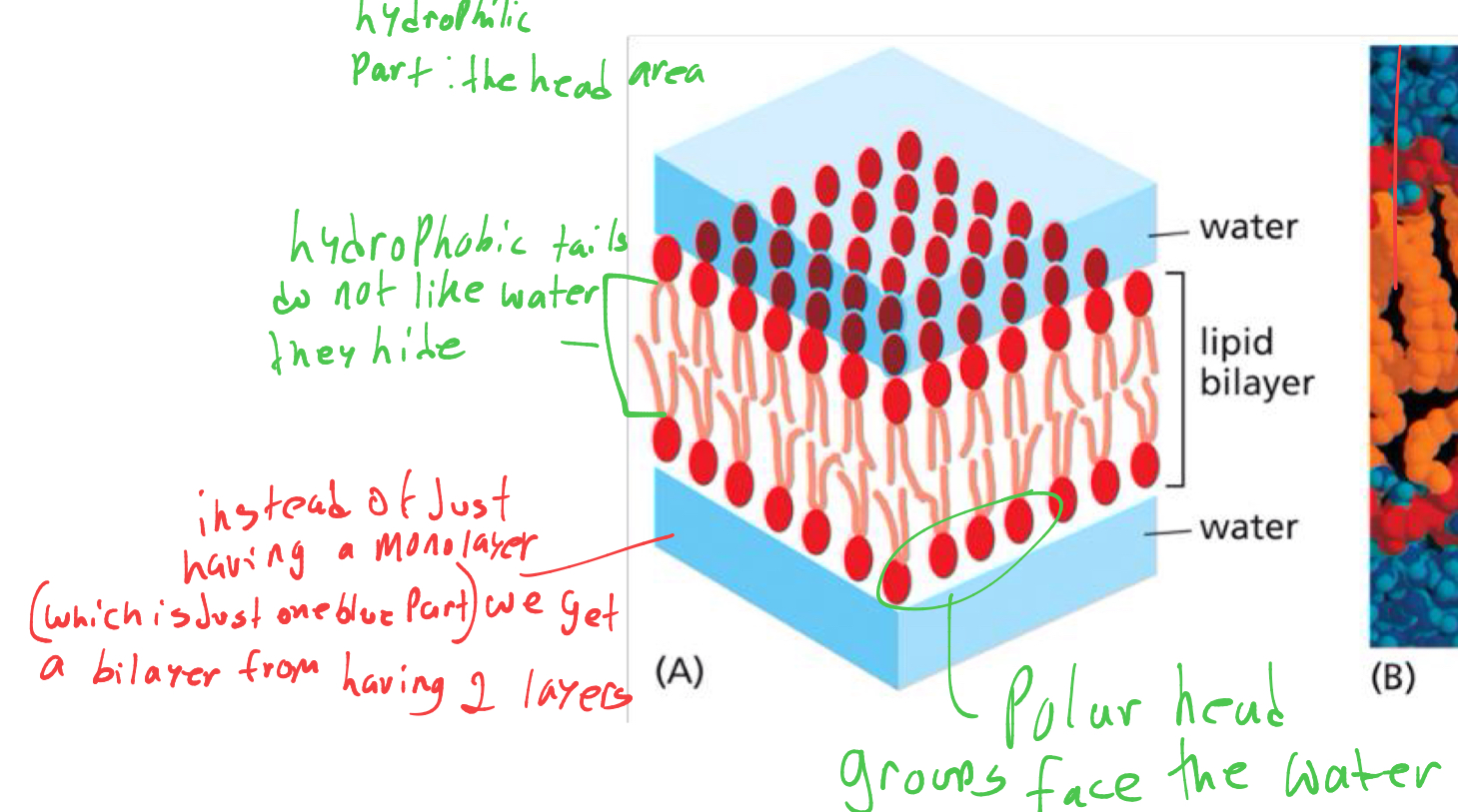
in the membranes lipid bilayer what direction to the phospholipids face
the heads of the lipids are polar so they will always face the outside while the tails are inside the membrane. with 2 layers so no water gets in middle.
whats the term that describes a molecule that has hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts to it
amphipathic
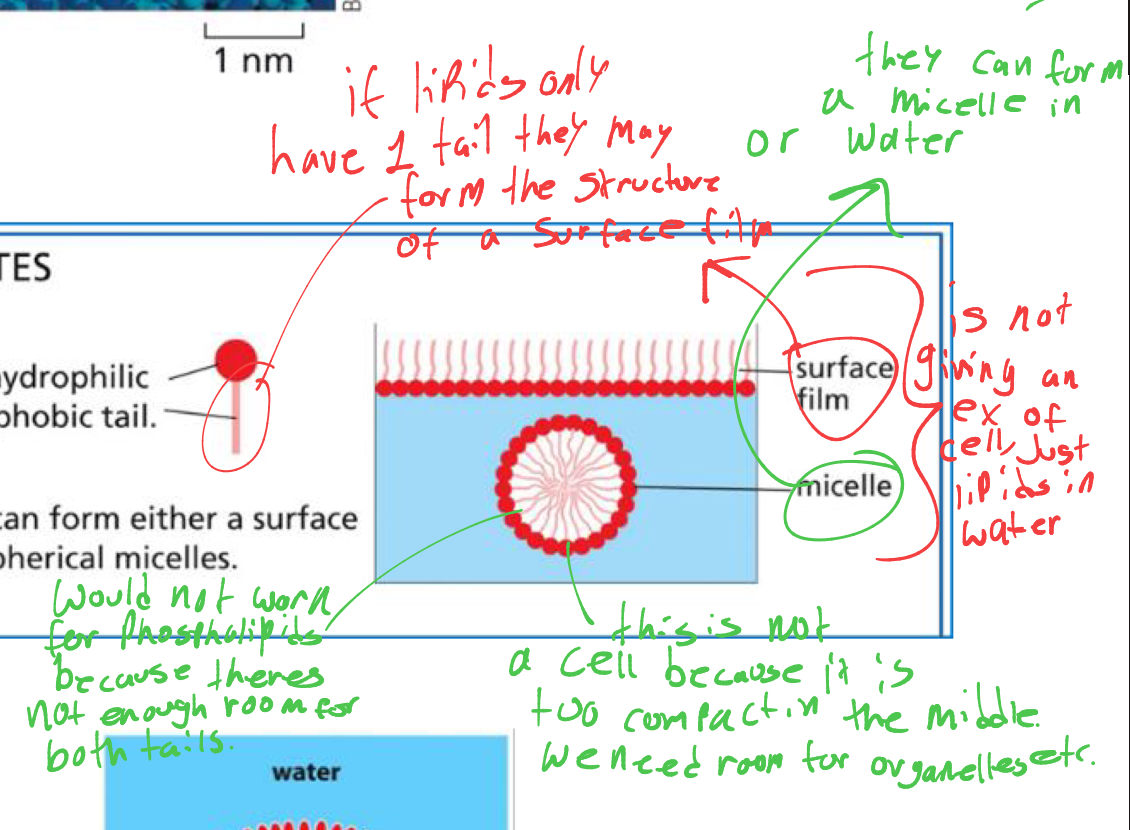
what 2 structures can form if the lipid only has 1 fatty acid tail
surface film, - float at top of water
micelle - cannot from phospholipids bc no room for other layer (to form bilayer)
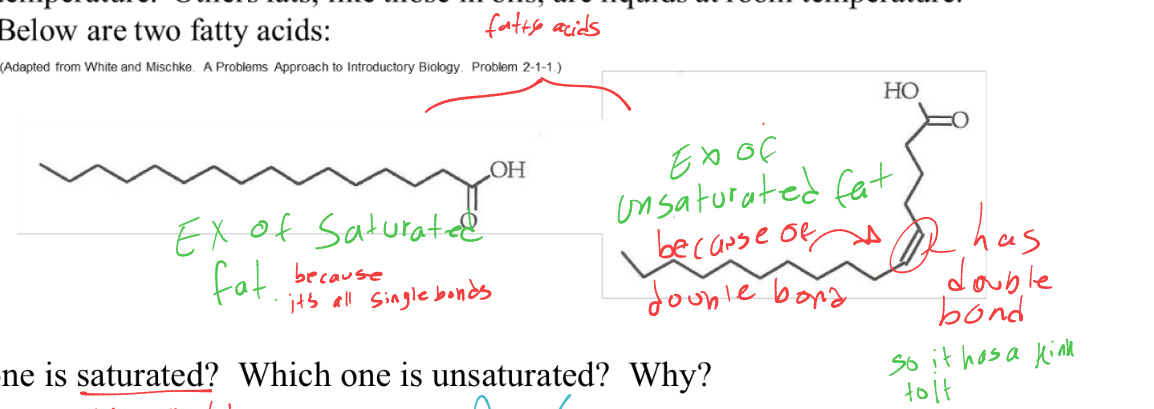
fats be saturated or unsaturated, how do you tell the diff
unsaturated- has kinks in chain with double bonds- making it more fluid
saturated- all single bonds so its straight and stackable,- making it less fluid
which fatty acid would be solid at room temp
saturated- bc its straight and stackable/compact so it becomes solid. ex. butter
unsaturated- has kinks making it loose so it’ll be liquid. ex. oil
whats the 3 types of fatty acids
saturated fat
unsaturated fat
trans fat- scientifically made.
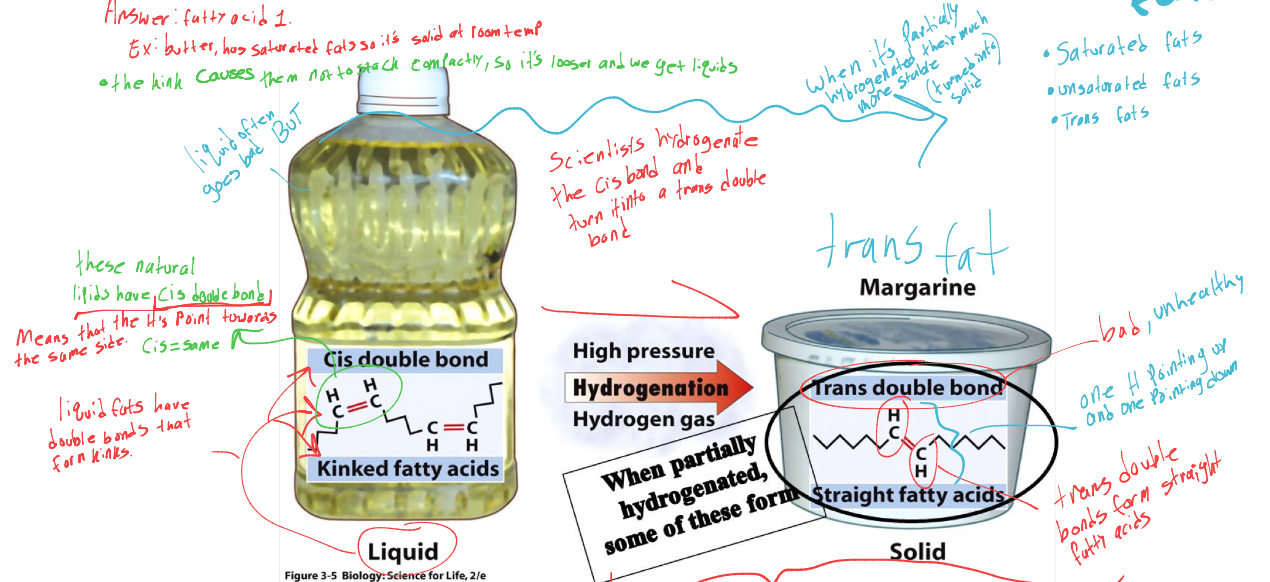
what happens when the kinked fatty acid (liquid) is hydrogenated (by scientists )
it turns into solid, bc the “cis double bond” turns into trans double bond= straight fatty acid chains.
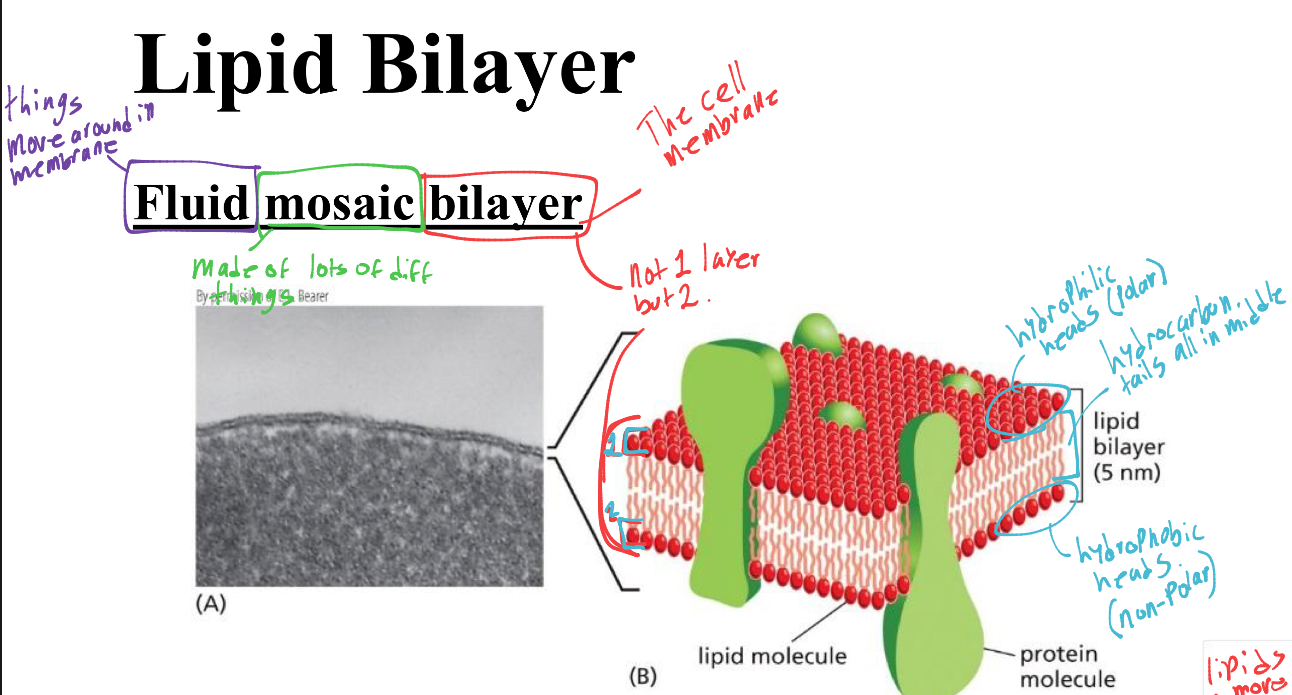
whats the lipid bilayer officialy called
fluid mosaic bilayer
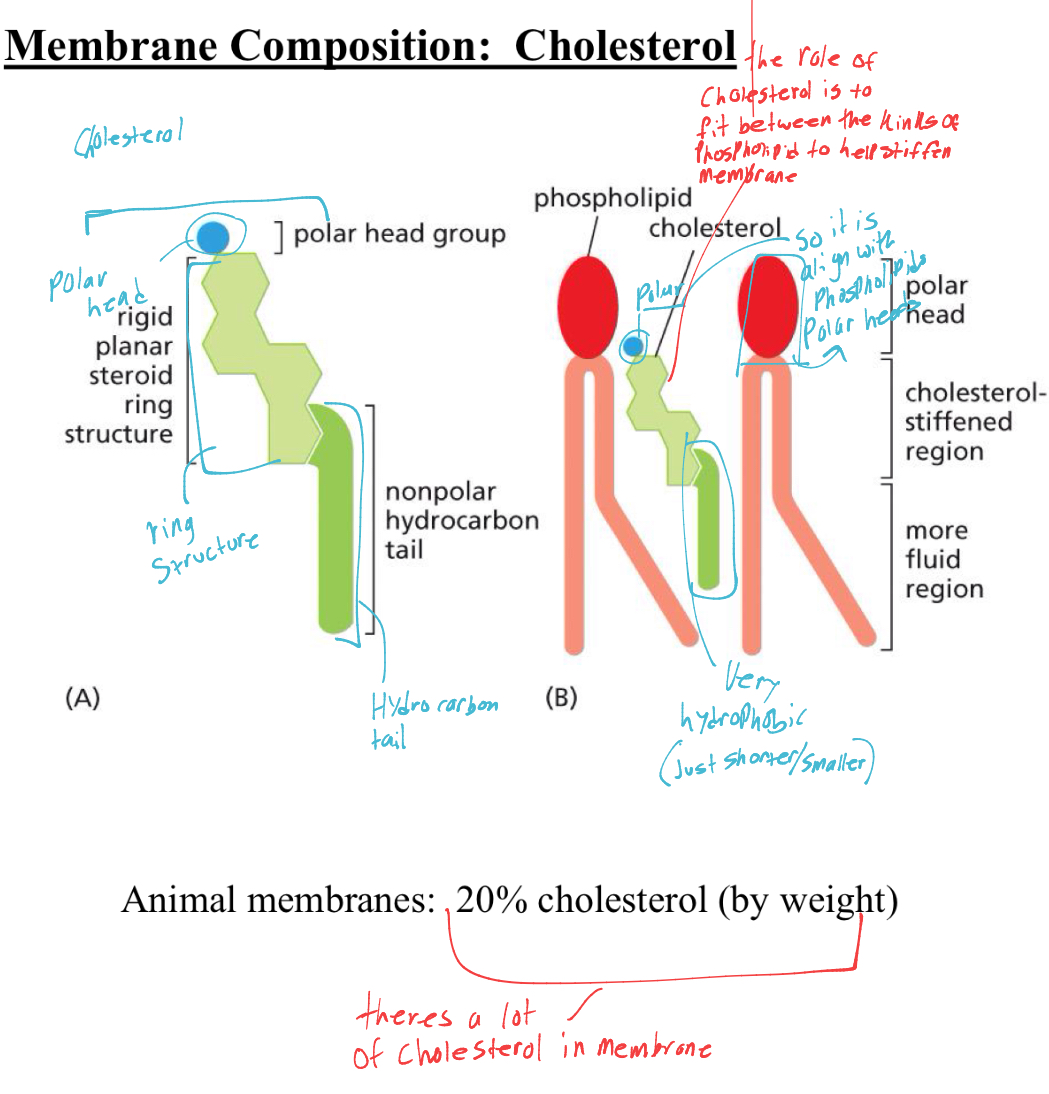
Membrane composition: whats the structure of cholesterol in cell membrane
lil polar head
ring structure attached to head
then its non polar tail
It goes inbwtween the phospholipids and helps straighten the structure by going in-between the kinks of the tails. making the membrane less fluid.
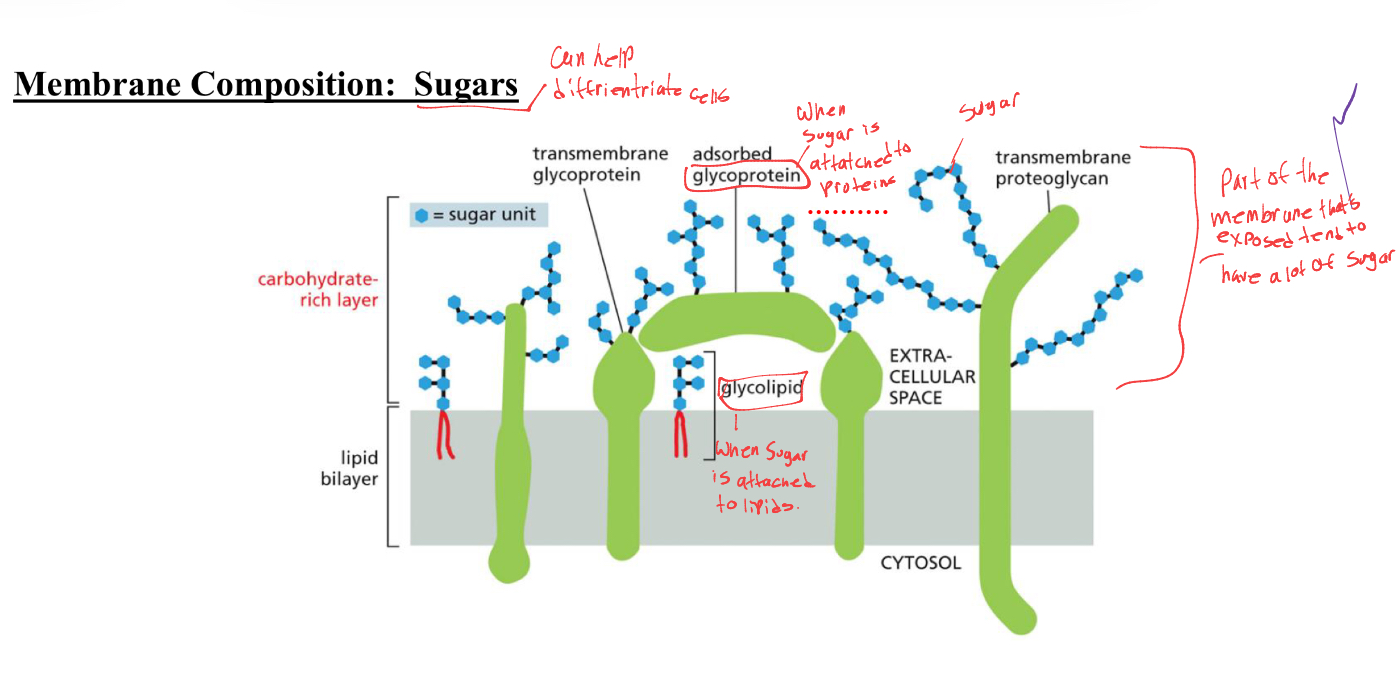
Membrane compositon: sugars can help differentiate cells
glycoprotein- when sugar is attached to protein
glycolipid- when sugar is attached to lipid
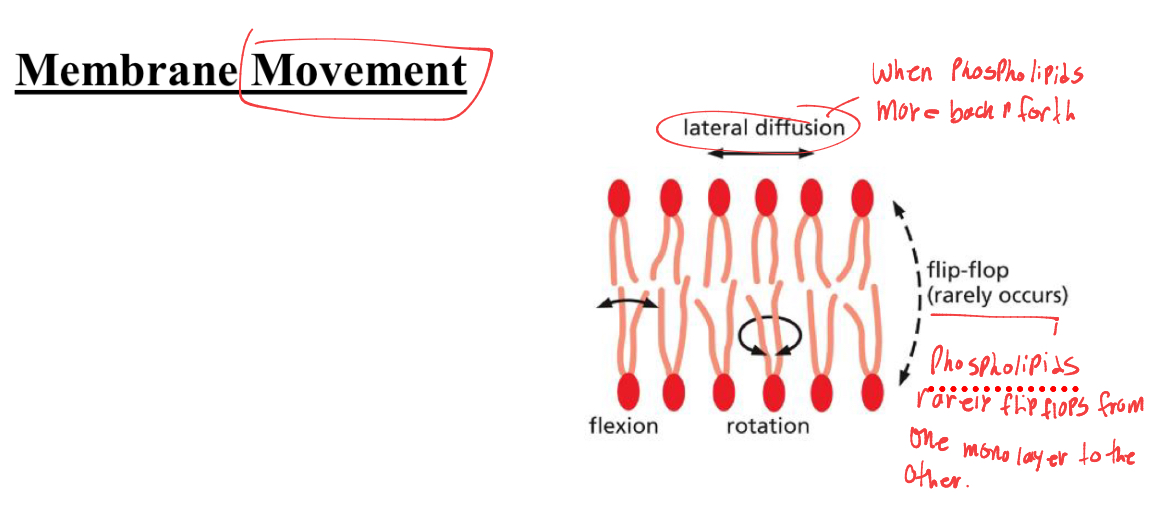
Membrane Movement: whats the term for when phospholipids are moving back and forth
lateral diffusion
phospholipids rarely flip flop from one monolayer to the other
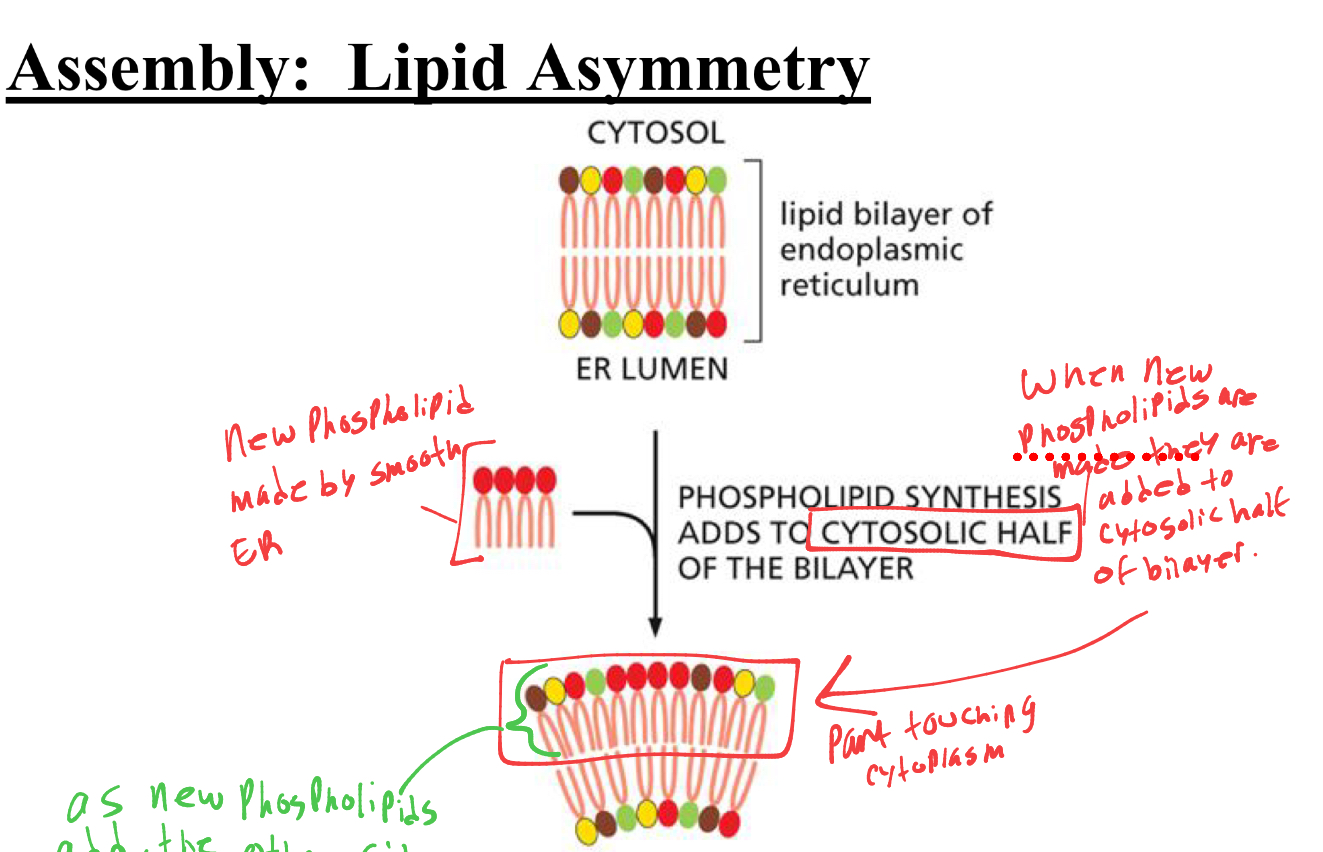
when new phospholipids are made from smooth er, where do they attach in membrane bilayer
to the “cytosolic half” (monolayer touching cytoplasm)
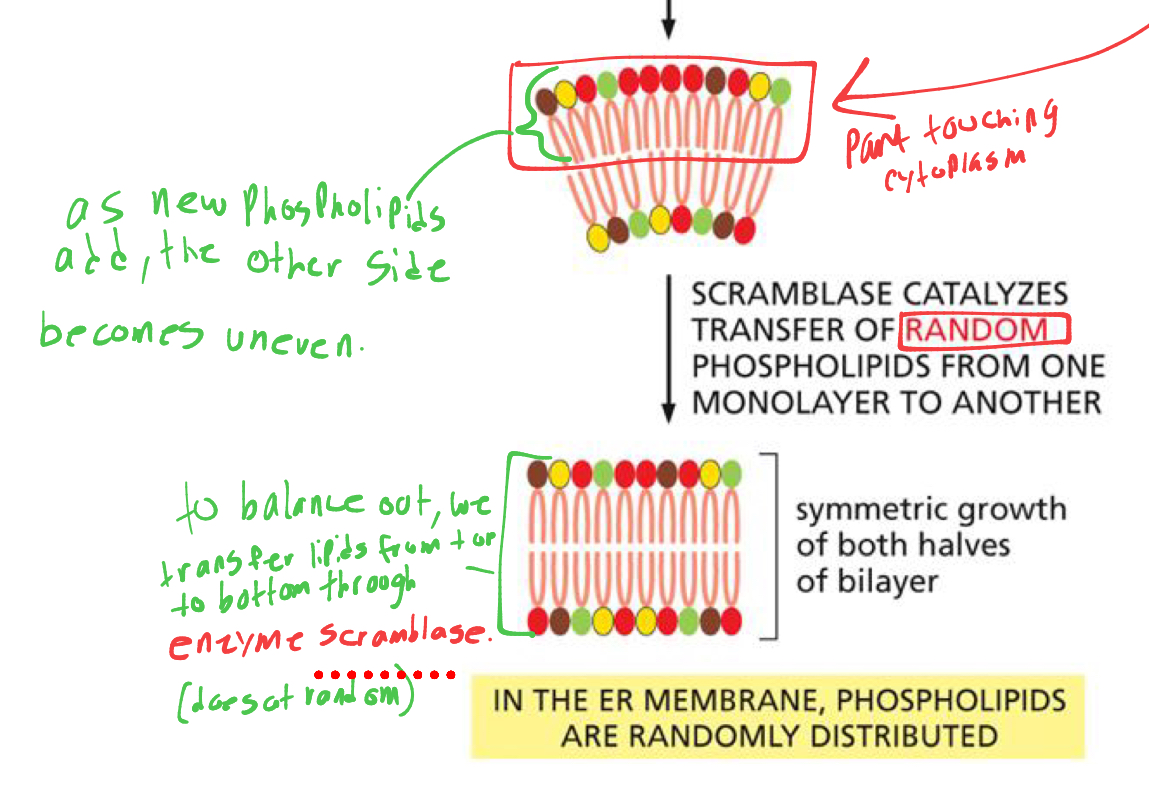
as we add new phospholipids to one monolayer, it becomes uneven compared to the other monolayer, what enzyme solves this
Scrambles enzyme- it transfers random phospholipids from one monolayer to the other to balance it out
in some cells they want a certain type of phospholipid on each monolayer. so what enzyme causes this
flippase- as chunk of membrane comes it flips certain lipids to match
whats the n- termini and c- termini
n-termini: outside monolayer
c-termini- inside monolayer
what are integral membrane proteins 3 types
proteins imbedded in membrane
transmembrane protein
monolayer associated
lipid linked
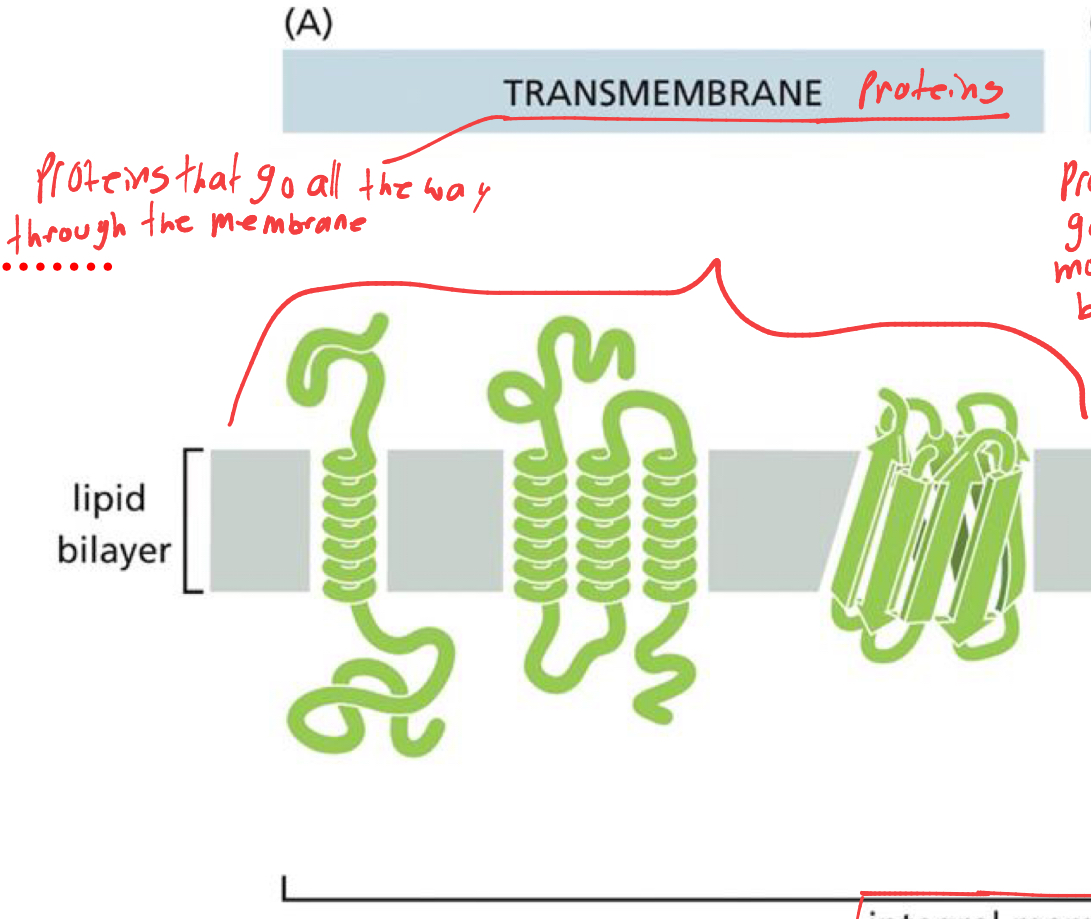
what are transmembrane proteins
proteins that go all the way through the membrane
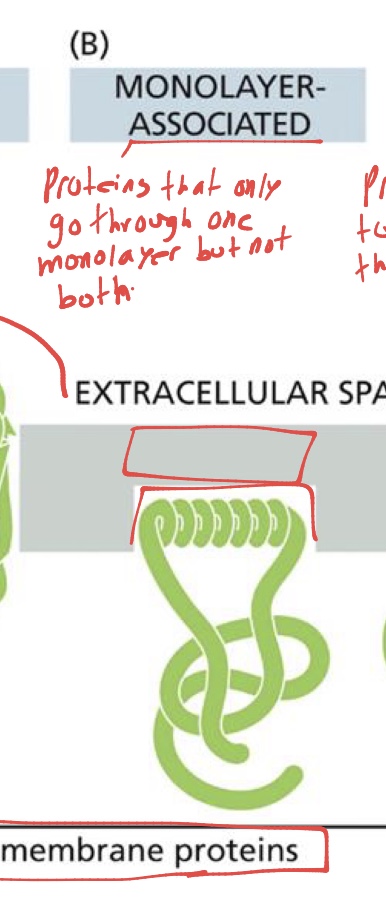
monolayer associated
proteins that only go through one monolayer but not both
lipid linked
proteins chemically bonded to certain lipids in membrane
whats peripheral membrane proteins
proteins not imbedded in membrane but are associated
If 2 cells fuse what would it looks like
they would be Half n half at first but then would mix bc the cell is fluid.
how would temp affect cell fluidity
cold= less movement and fluidity- stiff
warm=more movement and fluidity
what can restrict cell movement
tight junctions, they hold together cell membrane proteins