Biology Midterm Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Last updated 10:25 PM on 1/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
cells
smallest units of life
2
New cards
prokaryote
no nucleus; no membrane-bound organelles
3
New cards
eukaryote
has a nucleus; membrane-bound organelles
4
New cards
mitochondria
makes ATP
5
New cards
ribosomes
carry out protein synthesis
6
New cards
chloroplasts
absorb sunlight for photosynthesis
7
New cards
cell wall
found in plants and prokaryotes; surrounds the cell membrane
8
New cards
vacuole
stores water in plants; takes up most of the plant area
9
New cards
phospholipids
bilayer that forms the cell membrane
10
New cards
protein
transporters, enzymes, receptors
11
New cards
diffusion
passive transport; moves particles from high to low concentration
12
New cards
facilitated diffusion
passive transport; uses a protein carrier to move molecules from high to low concentration
13
New cards
osmosis
passive transport of water from a low to high solute concentration
14
New cards
active
transport that uses ATP to move molecules against their concentration gradient (low to high)
15
New cards
mitosis
shortest part of cell division
16
New cards
interphase
phase where the cell is growing and preparing for division
17
New cards
S (synthesis)
DNA is replicated during this phase
18
New cards
metaphase
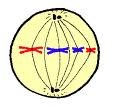
19
New cards
prophase

20
New cards
telophase
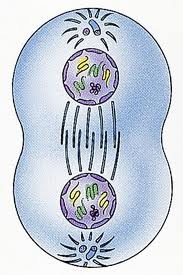
21
New cards
anaphase
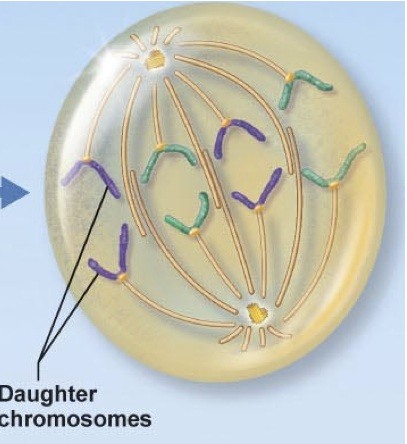
22
New cards
cytokinesis
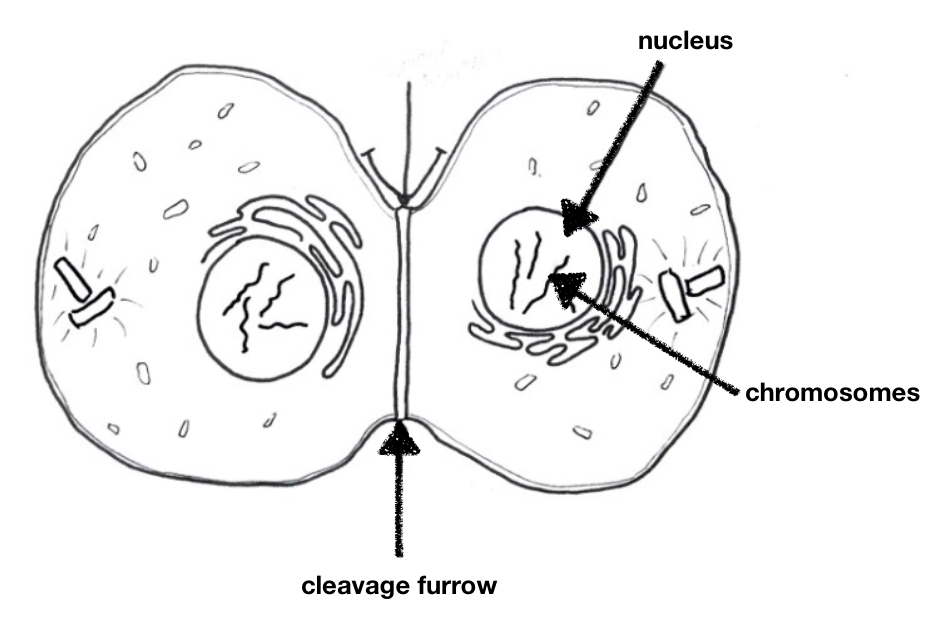
23
New cards
asexual reproduction
one parent cell/organism produces identical offspring
24
New cards
condensation
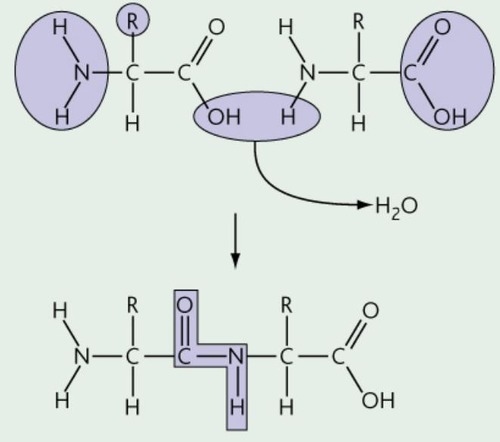
25
New cards
hydrolysis
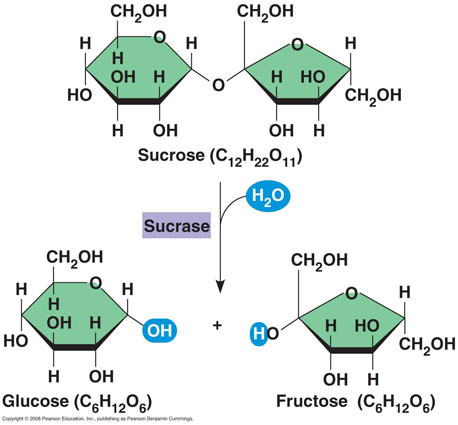
26
New cards
carbohydrates
sources of quick energy; contain the elements C, H, and O
27
New cards
lipids
sources of long term energy; insulators; make up the cell membrane
28
New cards
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
29
New cards
glucose
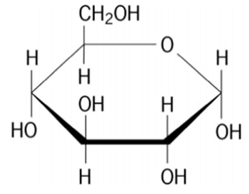
30
New cards
amino acid
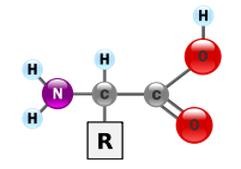
31
New cards
nucleotide
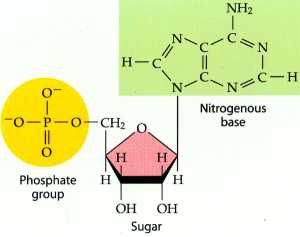
32
New cards
triglyceride
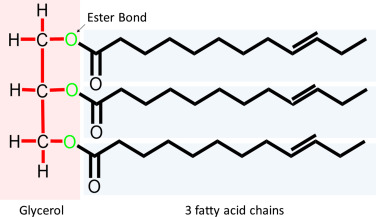
33
New cards
saturated fatty acid
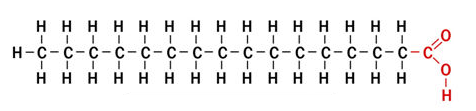
34
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
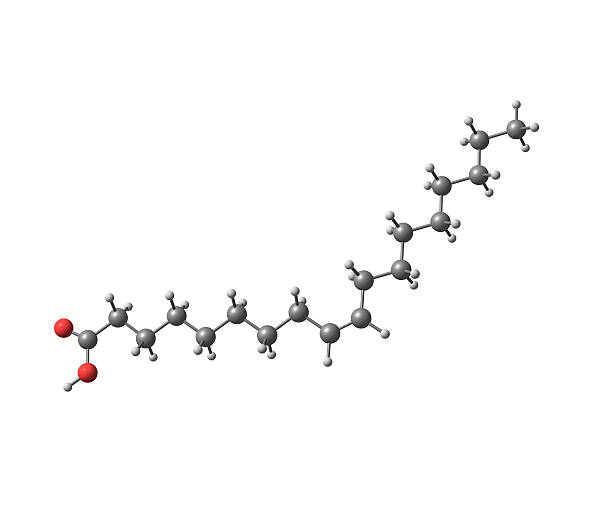
35
New cards
cohesion
water molecules stick together
36
New cards
adhesion
water molecules stick to other things
37
New cards
monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose
38
New cards
disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
39
New cards
polysaccharides
cellulose, glycogen, starch
40
New cards
enzyme
a catalyst and a protein
41
New cards
denature
when an enzyme's active site is changed
42
New cards
hydrogen
bond that holds DNA bases together
43
New cards
covalent
bond that connects sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA
44
New cards
peptide
bond that connects amino acids
45
New cards
transcription
DNA --\> mRNA in the nucleus
46
New cards
translation
mRNA --\> amino acid --\> protein at the ribosome
47
New cards
replication
DNA --\> DNA during interphase
48
New cards
cell theory
1. all living things are made of cells
2. cells are the smallest unit of life
3. cells come from preexisting cells
49
New cards
membrane protein functions
Transport (protein channel), Receptors (for hormones), Anchorage (cytoskeleton attachments), Cell recognition (antigens), Intercellular joinings (tight junctions), Enzymes
50
New cards
evidence against davson-danielli model
freeze fracturing, fluorescent antibody tagging, biochemical techniques
51
New cards
davson-danielli model
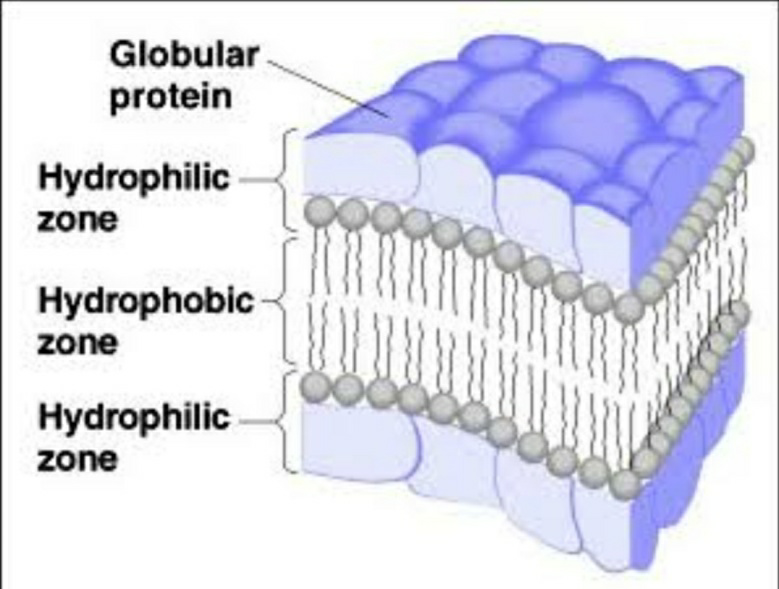
52
New cards
singer-nicolson fluid mosaic model
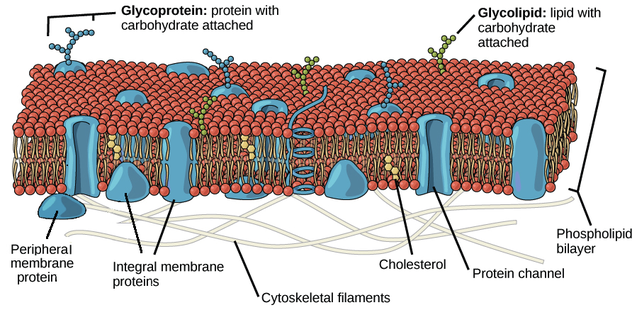
53
New cards
properties of water
thermal: high specific heat capacity, high heat of vaporization, & high heat of fusion
cohesive: water sticks to water molecules. adhesive: water sticks to other molecules
solvent: water can dissolve many substances with charges/polar regions
cohesive: water sticks to water molecules. adhesive: water sticks to other molecules
solvent: water can dissolve many substances with charges/polar regions
54
New cards
autotroph
an organism that makes its own food
55
New cards
heterotroph/consumer
an organism that gets its energy from another living organism
56
New cards
saprotroph
secretes digestive enzymes and absorbs non-living organic matter to get energy
57
New cards
detritivore
ingests non-living organic matter
58
New cards
mesocosm
a biological system that contains biotic and abiotic features of an ecosystem but is restricted in size and/or are under controlled conditions
59
New cards
food chain
shows the flow of energy through the trophic levels of a feeding relationship
60
New cards
primary consumer
an organism that eats producers
61
New cards
secondary consumer
an organism that eats primary consumers
62
New cards
community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in the same area
63
New cards
species
a group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
64
New cards
ecosystem
a community and its abiotic environment
65
New cards
greenhouse effect
the natural warming of the earth’s surface
66
New cards
global warming
a gradual increase in average global temperature
67
New cards
peat
partially decayed plant matter found in bogs
68
New cards
trophic level
each step in a food chain/web
69
New cards
saprotroph examples
bacteria; fungi
70
New cards
detrivore examples
earthworm; pillbug