Amino Acids (Polar, Nonpolar, Charged - basic/acidic)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Polar
When a side chain forms covalent bonds where the electron sharing is unequal, this gives the atoms within that bond partial charges (δ+ or δ-). Often, this involves bonds between the carbon backbone and nitrogen (N) or oxygen (O) because these are both more electronegative than carbon (or hydrogen).
Nonpolar
Any side chain that consists primarily of carbons (C) and hydrogens (H) is likely nonpolar because these have equal electronegativities. Thus the C-C or C-H bonds do not have partial charges, and would be considered nonpolar. Cysteine, the sulfhydryl-containing amino acid, can be classified as nonpolar or polar, depending on the environment it is found in!
Charged
Acidic side chains donate protons, and can usually be identified because they have a negative charge. Basic side chains (blue) accept protons, and can usually be identified because they have acquired the proton, and thus the positive charge.
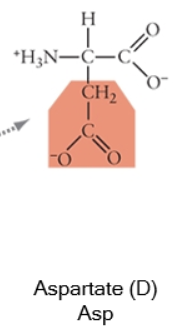
Charged (acidic)
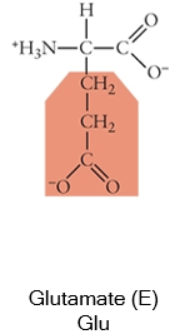
Charged (acidic)
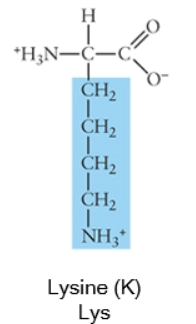
Charged (basic)
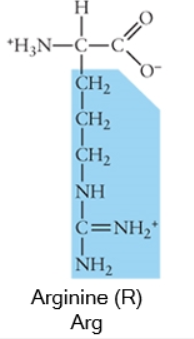
Charged (basic)
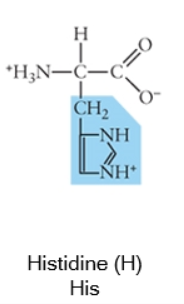
Charged (basic)
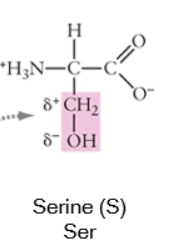
Polar
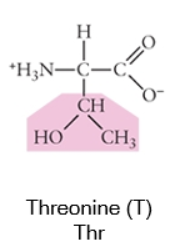
Polar
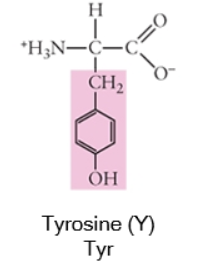
Polar
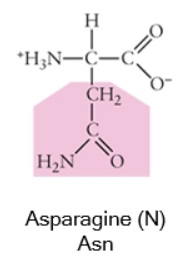
Polar
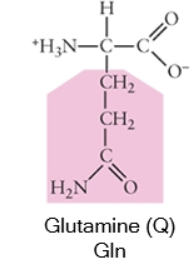
Polar
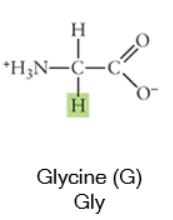
Nonpolar
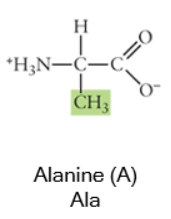
Nonpolar
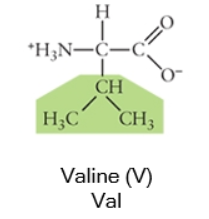
Nonpolar
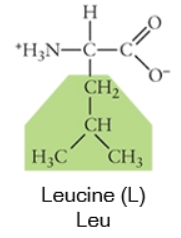
Nonpolar
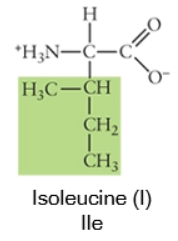
Nonpolar
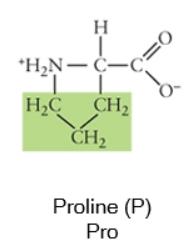
Nonpolar
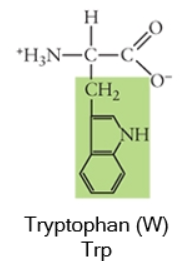
Nonpolar
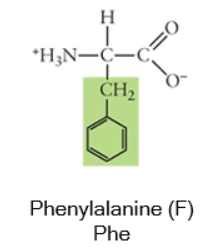
Nonpolar
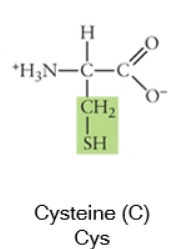
Nonpolar
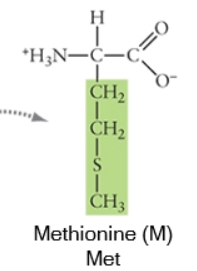
Nonpolar