Module 2 - Behavior and situation oriented leadership styles
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
What is the difference between leadership style and leadership behavior?
Leadership style is independent from the situation
Leadership behavior depends on the situation
Leadership behavior depends on the situation
2
New cards
Difference between person-oriented and behavior oriented leadership approaches
person-oriented: ^^personality traits are difficult to observe,^^ cannot be trained
^^behavior oriented:^^ ^^easy^^ to observe, therefore ^^easy to assess^^ for employees, it can be trained, it gives valuable easy to ^^implement practical implications^^ for the development of leaders
^^behavior oriented:^^ ^^easy^^ to observe, therefore ^^easy to assess^^ for employees, it can be trained, it gives valuable easy to ^^implement practical implications^^ for the development of leaders
3
New cards
Two approaches of behavior oriented leadership?
Ohio state leadership approach
GRID leadership model
GRID leadership model
4
New cards
What is the contribution of behavior oriented leadership approaches?
to identify leadership styles that aim for success
5
New cards
Main idea of Ohio state leadership approach
^^Typical behavioral patterns^^ are identified, called management leadership styles, which ^^relate to the way^^ a ^^leader deals with his employees.^^
6
New cards
Which are the two dimensions of Ohio state leadership approach?
Performance orientation
Employee orientation
Employee orientation
7
New cards
Based on the 2 dimensions of leadership behavior from the Ohio state, which are the 4 types of leadership styles
1\.- authoritarian: leader sets goals alone, employees interests are least concern
2\.-bureaucratic: impersonal climate, strong regulation of behavior
3\.-cooperative: leader and follower define goals together, hard to balance,
4\.-relationship oriented: positive climate, leader gives more importante to interpersonal relationships than performance
2\.-bureaucratic: impersonal climate, strong regulation of behavior
3\.-cooperative: leader and follower define goals together, hard to balance,
4\.-relationship oriented: positive climate, leader gives more importante to interpersonal relationships than performance
8
New cards
Examples of leadership styles in Ohio state
1.- Authoritarian: Military, police
2.-Bureaucratic: government, big organisations
3.-cooperative: start ups
4.-relationship oriented: family businesses, small business
2.-Bureaucratic: government, big organisations
3.-cooperative: start ups
4.-relationship oriented: family businesses, small business
9
New cards
What is customer-oriented leadership
Addition to the performance and employee orientation dimensions from ohio state leadership, ^^means exemplification, alignment, recognition, permanent emphasis^^
10
New cards
What are the five different styles of leadership that emerge from the customer, performance and employee oriented dimensions?
1.- authoritarian (high performance and customer orientation but low employee)
2.- softy (high customer and employee orientation but low performance)
3.-kicker (high performance orientation only)
4.-internal optimizer ( zero customer orientation)
5.-manager (balance of the 3)
2.- softy (high customer and employee orientation but low performance)
3.-kicker (high performance orientation only)
4.-internal optimizer ( zero customer orientation)
5.-manager (balance of the 3)
11
New cards
Main idea of GRID leadership model
based on conceptual conceptions of Ohio state leadership, it has two dimensions:
1.- Socio-emotional orientation
2.-Objective & rational orientation
Best mix between objective and socio-emotional orientation is key
1.- Socio-emotional orientation
2.-Objective & rational orientation
Best mix between objective and socio-emotional orientation is key
12
New cards
Another name for GRID leadership model
Managerial grid
13
New cards
Which are the 5 styles of leadership from the GRID dimensions?
1.- Country club (1,9)
2.- Team (9,9)
3.- Middle of the road (5,5)
4.- Impoverished (1,1)
5.- Produce or Perish (9,1)
2.- Team (9,9)
3.- Middle of the road (5,5)
4.- Impoverished (1,1)
5.- Produce or Perish (9,1)
14
New cards
Critique of GRID model
-Neglect employees characteristics
-Neglect leadership situation
-Neglect leadership situation
15
New cards
Which are the 3 most important situation-oriented leadership approaches?
1.- Contigency theory
2.- Path goal theory
3.- Maturity model
2.- Path goal theory
3.- Maturity model
16
New cards
What is the assumption of the situation-oriented leadership approaches?
^^Situation affects the behavior^^. The ^^effectiveness^^ of ^^personality traits and behaviors^^ of leaders ^^depends^^ on the ^^**situations**^^ in which the ^^leadership takes place^^
17
New cards
Main idea of contingency theory
^^**leadership success depends on the interaction of leader behavior and situation**^^. leader ^^should adapt leadership style^^ ^^depending on the situation,^^ leader need to identify critical and favorable leadership situations
18
New cards
What are the situational factors from the contingency theory?
1\.- Task structure
2\.- Leader’s position of power
3\.- Leader-member relationship
2\.- Leader’s position of power
3\.- Leader-member relationship
19
New cards
How to measure leadership on the contingency theory?
LPC (least preferred worker)
20
New cards
Which are two dimensions of contingency theory?
y\= Performance / satisfaction of employees
x\= favorability of situation
*Situational factors
x\= favorability of situation
*Situational factors
21
New cards
According to contingency theory, which style of leadership is best in favorable or unfavorable conditions
When majority of situational factors are high (favorable conditions): performance orientation
When majority of situational factors are low (unfavorable conditions): performance orientation leadership style
When majority of situational factors are low (unfavorable conditions): performance orientation leadership style
22
New cards
According to contingency theory, which style of leadership is best in medium degree of favourable conditions
When majority of situational factors are medium favorable: employee orientation leadership style is best
23
New cards
Weaknesses of contingency theory
-It doesnt have empirical confirmation in real environments
-selective selection of situational factors
-limited implications for business practice
-Medium LPC correlates with success more than high or low LPC scores
-selective selection of situational factors
-limited implications for business practice
-Medium LPC correlates with success more than high or low LPC scores
24
New cards
Main idea of path goal theory
Based on two assumptions:
1\.- person is ^^willing to accept a task^^ only when he is convinced that the commitment will lead to a certain result
2\.- ^^goals should bring personal benefits or inner satisfaction^^
1\.- person is ^^willing to accept a task^^ only when he is convinced that the commitment will lead to a certain result
2\.- ^^goals should bring personal benefits or inner satisfaction^^
25
New cards
Which leadership styles derive from the path goal theory?
1.- Supportive
2.- Directive
3.- Participative
4.- Result-oriented
2.- Directive
3.- Participative
4.- Result-oriented
26
New cards
Describe supportive leadership from path goal theory
Leader shows ^^concern^^ for employees ^^psychological wellbeing^^, is good on situations psycological or physically stressing
27
New cards
Describe directive leadership from path goal theory
Leader plans ,controls and tells employees, how to perform activities. its good when tasks are vague
28
New cards
Describe participative leadership from path goal theory
Leader involves employee on decision making processes.
29
New cards
Describe result-oriented leadership from path goal theory
Leader has high performance expectations, can be seen with scientists and engineers.
30
New cards
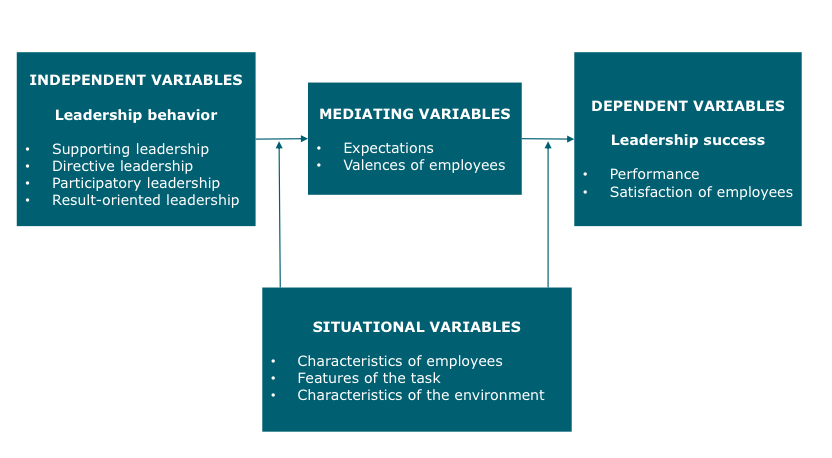
What is the relationship between the leadership behaviors and the leadership success in the path goal theory?
1\.- **Leadership behavior** (independent variables):
^^\*supportive \*directive \*participative \*result-oriented^^
2\.- **Leadership success** (dependent variables)
^^\*Performance of employees \*Satisfaction of employees^^
3\.-**Mediating variables**( this transmit the relationship of leadership behavior to success)
^^\*Expectations from employee
\*Valences from employee^^
4\.- **Moderating variables** (situational factors):
^^\*task structure
\*characteristics of employee
\*characteristics of environment^^
^^\*supportive \*directive \*participative \*result-oriented^^
2\.- **Leadership success** (dependent variables)
^^\*Performance of employees \*Satisfaction of employees^^
3\.-**Mediating variables**( this transmit the relationship of leadership behavior to success)
^^\*Expectations from employee
\*Valences from employee^^
4\.- **Moderating variables** (situational factors):
^^\*task structure
\*characteristics of employee
\*characteristics of environment^^
31
New cards
What are managerial implications of path goal theory
Path goal theory can be used:
1.-lack of work related self confidence in employees: supportive
2.- Lack of task clarity: directive
3.-Unfair rewards: Participative
4.-Low challenging tasks Result-oriented
1.-lack of work related self confidence in employees: supportive
2.- Lack of task clarity: directive
3.-Unfair rewards: Participative
4.-Low challenging tasks Result-oriented
32
New cards
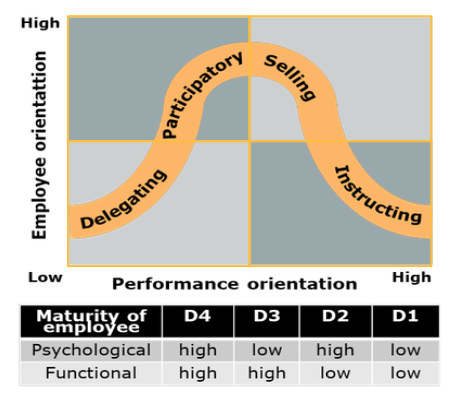
Main idea of maturity model
Based on Ohio state leadership, ^^employee and performance^^ orientation ^^can be extended by the situation. It has two dimensions (employee and performance orientation) and two components ( psychological maturity, functional maturity )^^
33
New cards
Which are the two components of maturity model?
^^Psychological maturity^^: motivation of employee to perform
^^Functional maturity:^^ skills, knowledge expertise from employee
^^Functional maturity:^^ skills, knowledge expertise from employee
34
New cards
Which are two dimensions of maturity model?
y\=Employee orientation
x\=performance orientation
x\=performance orientation
35
New cards
Which are the leadership styles that result from the maturity model?
1.- Delegating
2.-Participatory
3.-Selling
4.-Instructing
2.-Participatory
3.-Selling
4.-Instructing
36
New cards
Describe the delegating leadership style from the maturity model
Leader has minimal influence on employees performance of tasks, leader controls selectively
Works when employees have high psychological and functional maturity levels
Low employee and performance orientation
Works when employees have high psychological and functional maturity levels
Low employee and performance orientation
37
New cards
Describe the participatory leadership style from the maturity model
Leader gives problems and employee solutions
Works when employee is high in functional maturity level but low in psychological
High on employee orientation, low on performance
Works when employee is high in functional maturity level but low in psychological
High on employee orientation, low on performance
38
New cards
Describe the selling leadership style from the maturity model
Leader focuses on developing the skills of employee
Works when psychological is high but functional maturity is low.
Employee orientation is moderated
Works when psychological is high but functional maturity is low.
Employee orientation is moderated
39
New cards
Describe the instructing leadership style from the maturity model
It is like authoritarian style in Ohio
Works when both psychological and functional maturity levels are low
High in performance and low employee orientation
Works when both psychological and functional maturity levels are low
High in performance and low employee orientation
40
New cards
How to measure maturity in employees?
To increase psychological maturity:
*Explain importance of services for company
*Explain importance of services for employees
*Offer attractive career opportunities
To increase functional maturity:
*Offer trainings and workshops
*Regular evaluation of performance
*Implement forums of knowledge exchange
*Explain importance of services for company
*Explain importance of services for employees
*Offer attractive career opportunities
To increase functional maturity:
*Offer trainings and workshops
*Regular evaluation of performance
*Implement forums of knowledge exchange
41
New cards
Critique of maturity model
\*==No empirical evidence==
\*no ==confirmation of validity==
\*==high demands== on leader to ==correctly asses== the leadership style
\*leader needs ==high analytical capability==
\*no ==confirmation of validity==
\*==high demands== on leader to ==correctly asses== the leadership style
\*leader needs ==high analytical capability==
42
New cards
What is biostructural analysis?
Self analysis of 3 areas of the brain
1.- Brain stem (green)
2.- Interbrain (red)
3.-Cerebrum (blue)
1.- Brain stem (green)
2.- Interbrain (red)
3.-Cerebrum (blue)
43
New cards
Characteristics of the biostructural analysis on the 3 brain areas
%%1.- Brain stem (green): creativity, act based on past experiences, feeling people, closeness, way to work is their intuition%%
==2.- Interbrain (red): natural authority, acts in the present, no risks, impulsive actions, way to work is practical==
^^3.- Cerebrum (blue): need for safety, future oriented, thinks of consequences, planned action, way to work is systematic^^
==2.- Interbrain (red): natural authority, acts in the present, no risks, impulsive actions, way to work is practical==
^^3.- Cerebrum (blue): need for safety, future oriented, thinks of consequences, planned action, way to work is systematic^^
44
New cards
What is the goal biostructural analysis?
^^Self analysis to detect structures of individual data^^ / and typical behaviors on individuals and visualize it in a structured chart