physics1 (chap11)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/21
Last updated 9:31 PM on 6/17/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
Mass-energy equivalence
E = mc²
2
New cards
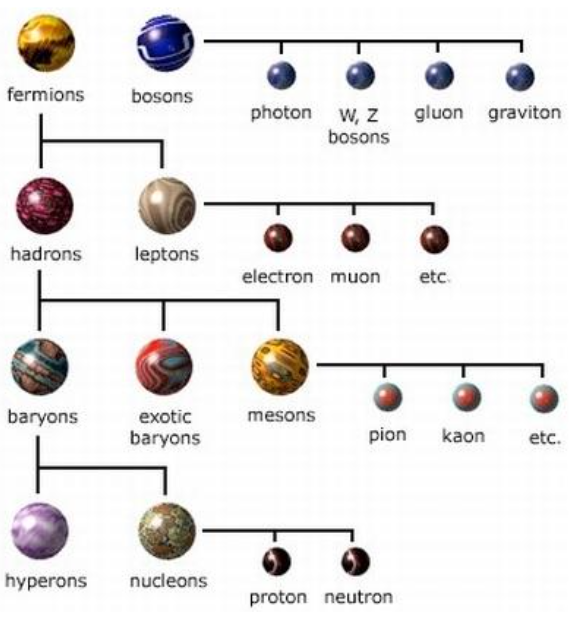
Two major categories of particles
- Bosons: photons, W/Z particles, gluons
and gravitons
- Fermions
and gravitons
- Fermions
3
New cards
Quarks
Fundamental particles condensed from energy released in the early universe

4
New cards
Charge
( + / - )

5
New cards
Two positive particles will...
( + ) ( + ) Repel
6
New cards
Two negative particles will...
( - ) ( - ) Repel
7
New cards
Two particles of opposite charge will...
( + ) ( - ) Attract
8
New cards
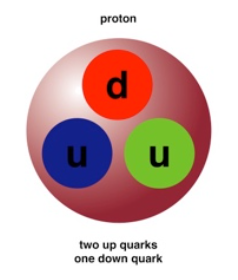
Protons
- Composed of two "up" quarks, one "down" quark
- Positive ( + ) charge
- Mass = 1.672 * 10^-27 kg
- Positive ( + ) charge
- Mass = 1.672 * 10^-27 kg
9
New cards
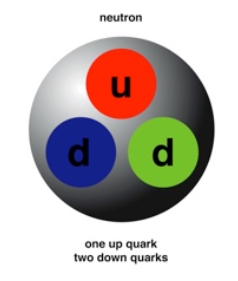
Neutrons
- Composed of two "down" quarks, one "up" quark
- Neutral ( 0 ) charge
- Mass = 1.674 * 10^-27 kg
- Neutral ( 0 ) charge
- Mass = 1.674 * 10^-27 kg
10
New cards
What are protons and neutrons collectively known as?
Nucleons, they are the particles that form the nuclei of atoms.
11
New cards
Electrons
- Leptons
- Negative ( - ) charge
- Mass = 9.109 * 10^-31 kg
- Negative ( - ) charge
- Mass = 9.109 * 10^-31 kg

12
New cards
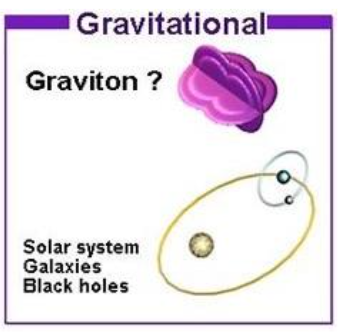
Gravitational force
- Weak attractive force
- Infinite range
- Acts within a field established by collections of baryonic matter
- Infinite range
- Acts within a field established by collections of baryonic matter
13
New cards
Electromagnetic force
- A strong attractive or repulsive force (dependent on charge)
- Infinite range
- Acts within a field established by stationary or moving charged particles
- Moving charged particles produce electromagnetic waves.
◊ The particle equivalent of electromagnetic wave energy is quantized as photons.
- Infinite range
- Acts within a field established by stationary or moving charged particles
- Moving charged particles produce electromagnetic waves.
◊ The particle equivalent of electromagnetic wave energy is quantized as photons.

14
New cards
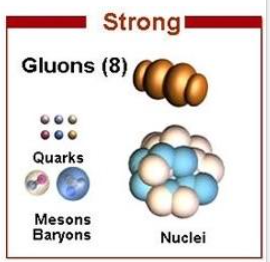
Strong nuclear force
- Within the nucleus of an atom, electrostatic repulsive forces exerted between protons destabilizes the cohesion of larger nuclei.
- Strong nuclear force is a very strong attractive force exerted between nucleons over extremely short range.
- Exerted by bosons called gluons
- Electrostatic repulsive forces between protons and strong nuclear force between nucleons act in equilibrium within atomic nuclei.
- Strong nuclear force is a very strong attractive force exerted between nucleons over extremely short range.
- Exerted by bosons called gluons
- Electrostatic repulsive forces between protons and strong nuclear force between nucleons act in equilibrium within atomic nuclei.
15
New cards
Weak nuclear force
- The process of radioactive decay of unstable atomic nuclei is mediated by the week nuclear force.
- Extremely short range
- Exerted by weak bosons.

16
New cards
Contact forces
- Macroscopic object interactions are the result of microscopic electromagnetic force field interactions.
- The interaction electromagnetic force field range between macroscopic objects can be as small as an angstrom (10⁻¹⁰m), so objects appear to touch or come into “contact”.
- The interaction electromagnetic force field range between macroscopic objects can be as small as an angstrom (10⁻¹⁰m), so objects appear to touch or come into “contact”.
17
New cards
Field forces
- Gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear and weak nuclear forces all occur at range or within a “field”.
- Some models relate interacting field density to an exchange of virtual particles, but that will not be addressed in the scope of this course.
- Some models relate interacting field density to an exchange of virtual particles, but that will not be addressed in the scope of this course.
18
New cards
Forces resulting in a change in velocity
- Velocity changes can be the result of a change in the magnitude of a velocity.
- Velocity changes can be the result of a change in the direction of a velocity.
- A net force is required to alter magnitude and or direction of a particle.
- Velocity changes can be the result of a change in the direction of a velocity.
- A net force is required to alter magnitude and or direction of a particle.
19
New cards
Forces resulting in deformation
- Materials are composed of arrays of atoms linked together by electromagnetic forces.
- External electromagnetic forces may displace the relative position of individual atoms, while the material remains intact.
- This alteration of composite atom position is defined as deformation.
- Some materials have the capacity to return to initial configurations after an external force is discontinued, while others experience permanent deformation.
- External electromagnetic forces may displace the relative position of individual atoms, while the material remains intact.
- This alteration of composite atom position is defined as deformation.
- Some materials have the capacity to return to initial configurations after an external force is discontinued, while others experience permanent deformation.
20
New cards
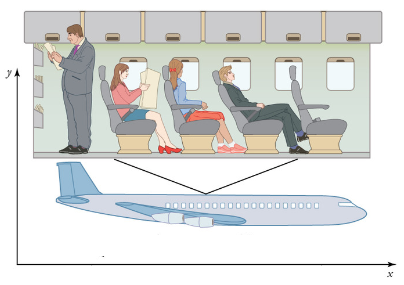
Inertial frame of reference
- A particle that is “stationary” within the context of its surroundings, or moving with a uniform velocity is defined to be in an inertial frame of reference.
- A particle within an inertial frame of reference is defined to have no net force exerted upon it.
- Consider a particle within closed container. If the container particle system is moving with a uniform velocity, from the point of view of the particle – the particle is stationary, with no reference points or net force evidence to indicate that it is within a moving system.
- Inertial reference frames are usually hypothetical constructs for simplification of problem solving and conceptual interpretation.
- The net force exerted on a particle in an inertial frame of reference is defined to be zero.
- A particle within an inertial frame of reference is defined to have no net force exerted upon it.
- Consider a particle within closed container. If the container particle system is moving with a uniform velocity, from the point of view of the particle – the particle is stationary, with no reference points or net force evidence to indicate that it is within a moving system.
- Inertial reference frames are usually hypothetical constructs for simplification of problem solving and conceptual interpretation.
- The net force exerted on a particle in an inertial frame of reference is defined to be zero.
21
New cards
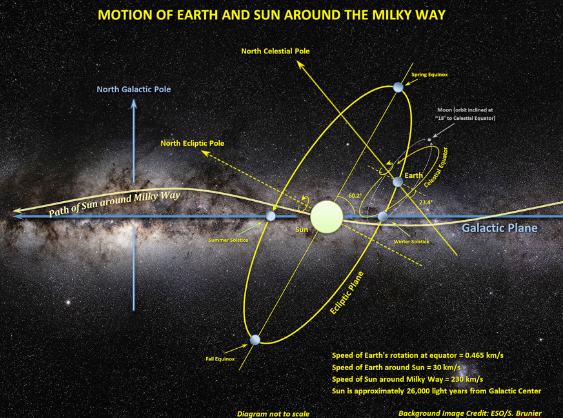
Non-inertial frame of reference
- Any particle that is experiencing a change in velocity (a≠0) is in a non-inertial frame of reference.
- A particle within a non-inertial frame of reference is defined to be experiencing a net force.
- All particles on the surface of the earth are in a non-inertial frame of reference because the Earth is revolving on its axis(1/day), translating on an elliptical path around the sun (1/365.25day), translating on an elliptical path around the Milky Way galaxy(1/250my), and accelerating through the universe.
- A particle within a non-inertial frame of reference is defined to be experiencing a net force.
- All particles on the surface of the earth are in a non-inertial frame of reference because the Earth is revolving on its axis(1/day), translating on an elliptical path around the sun (1/365.25day), translating on an elliptical path around the Milky Way galaxy(1/250my), and accelerating through the universe.
22
New cards
Force relevance and frame of reference
- Gravitational forces are exerted at all scales and dominate at the largest distances and mass scales.
- Electromagnetic forces are exerted at all scales, and for our purposes are most relevant at contact force scales.
- Strong and weak nuclear forces are exerted at very small scales and are not considered in great depth in this course.
- Electromagnetic forces are exerted at all scales, and for our purposes are most relevant at contact force scales.
- Strong and weak nuclear forces are exerted at very small scales and are not considered in great depth in this course.