WVU Chem 115 Final Exam
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Chlorate
ClO₃⁻
Chlorite
ClO₂⁻
Phosphate
PO₄³⁻
Phosphite
PO₃³⁻
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
Nitrite
NO₂⁻
Permanganate
MnO₄⁻
Perchlorate
ClO₄⁻
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
Ammonia
NH₃
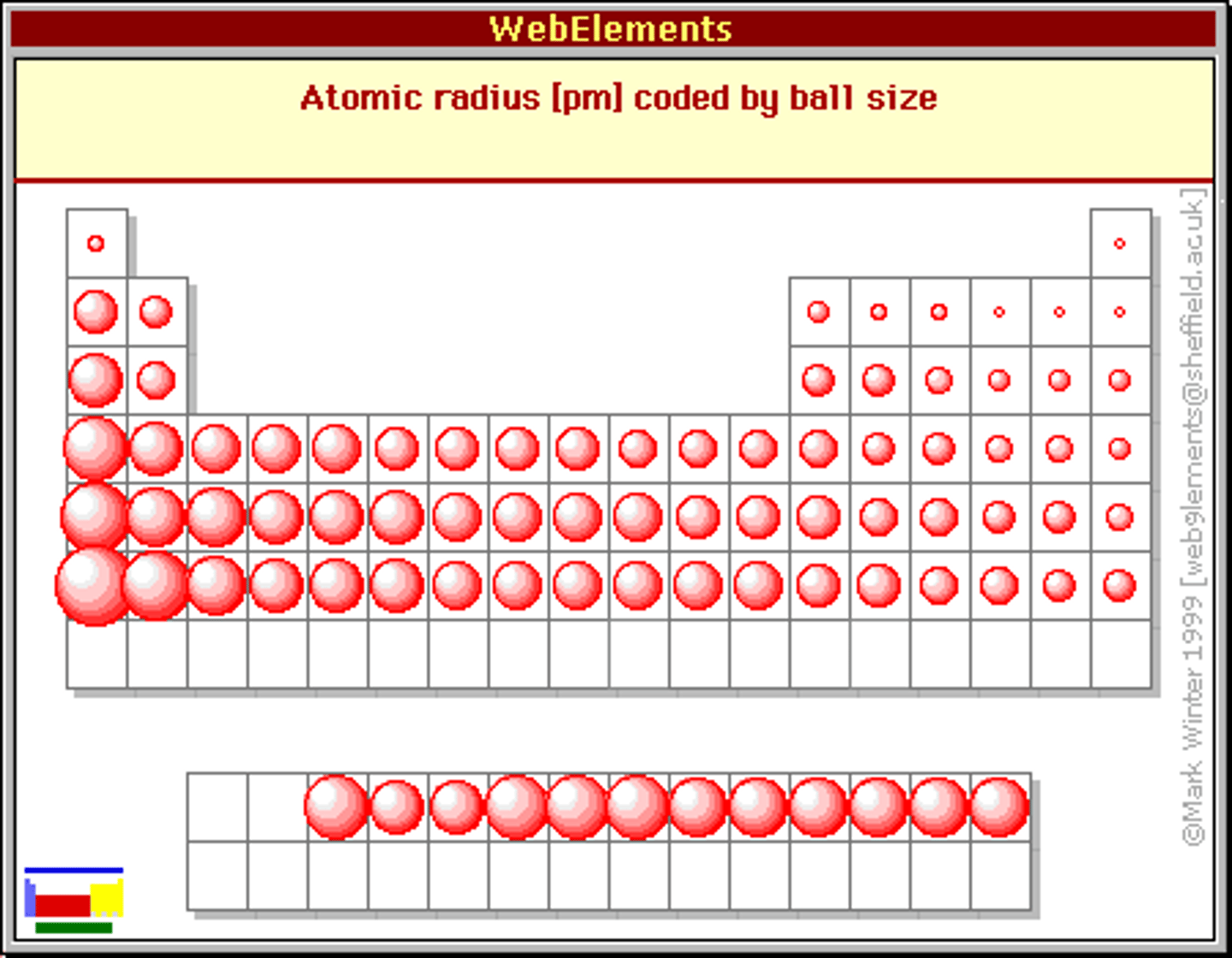
Periodic Trends: Atomic Radii
Remember:
Zeff = Zactual-Electron Shielding
Greater Zeff --> Smaller Atomic Radii
Gets bigger as you go down and to the left
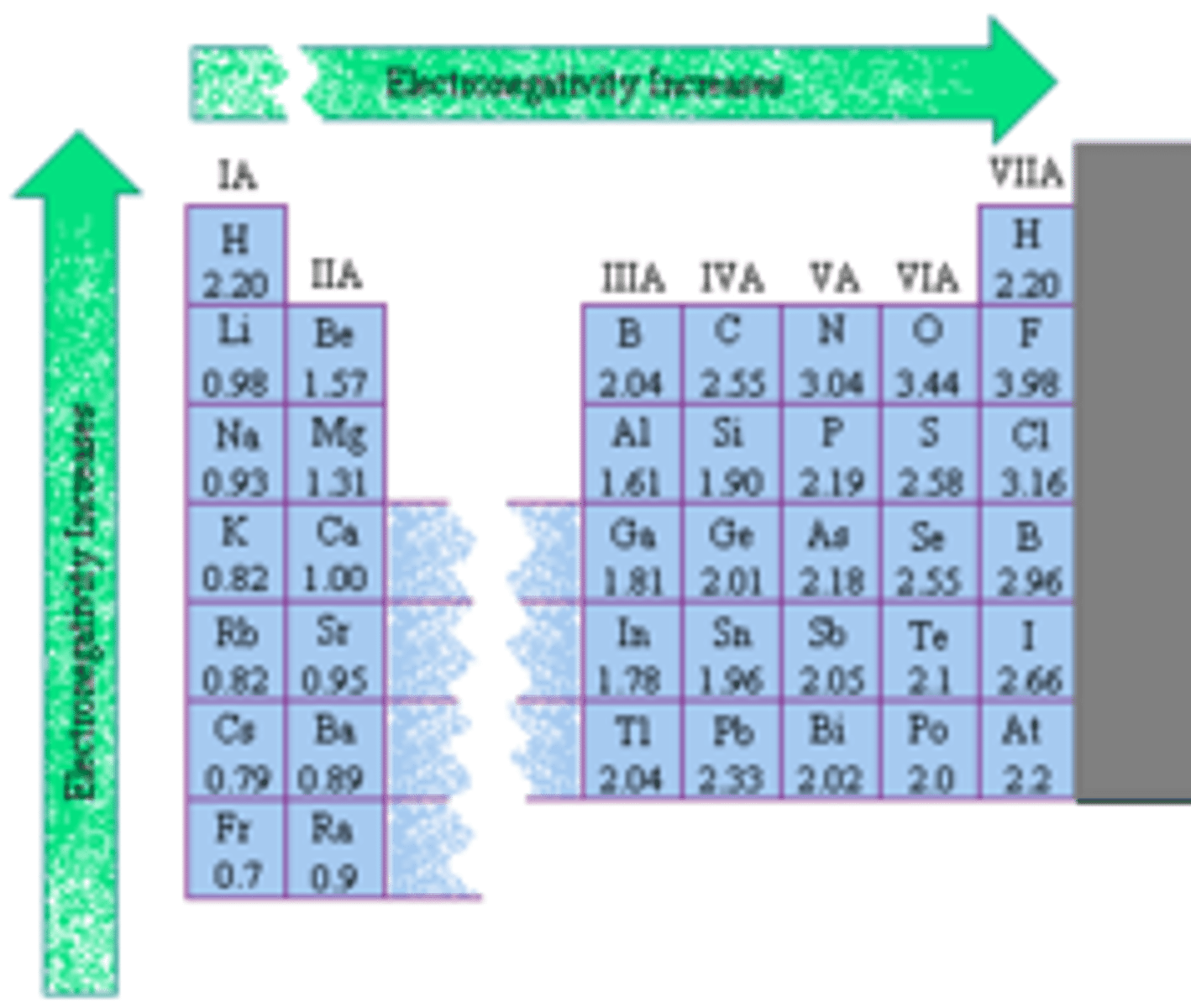
Periodic Trends: Electronegativity
Exception to trend --> Noble Gases (EN=0)
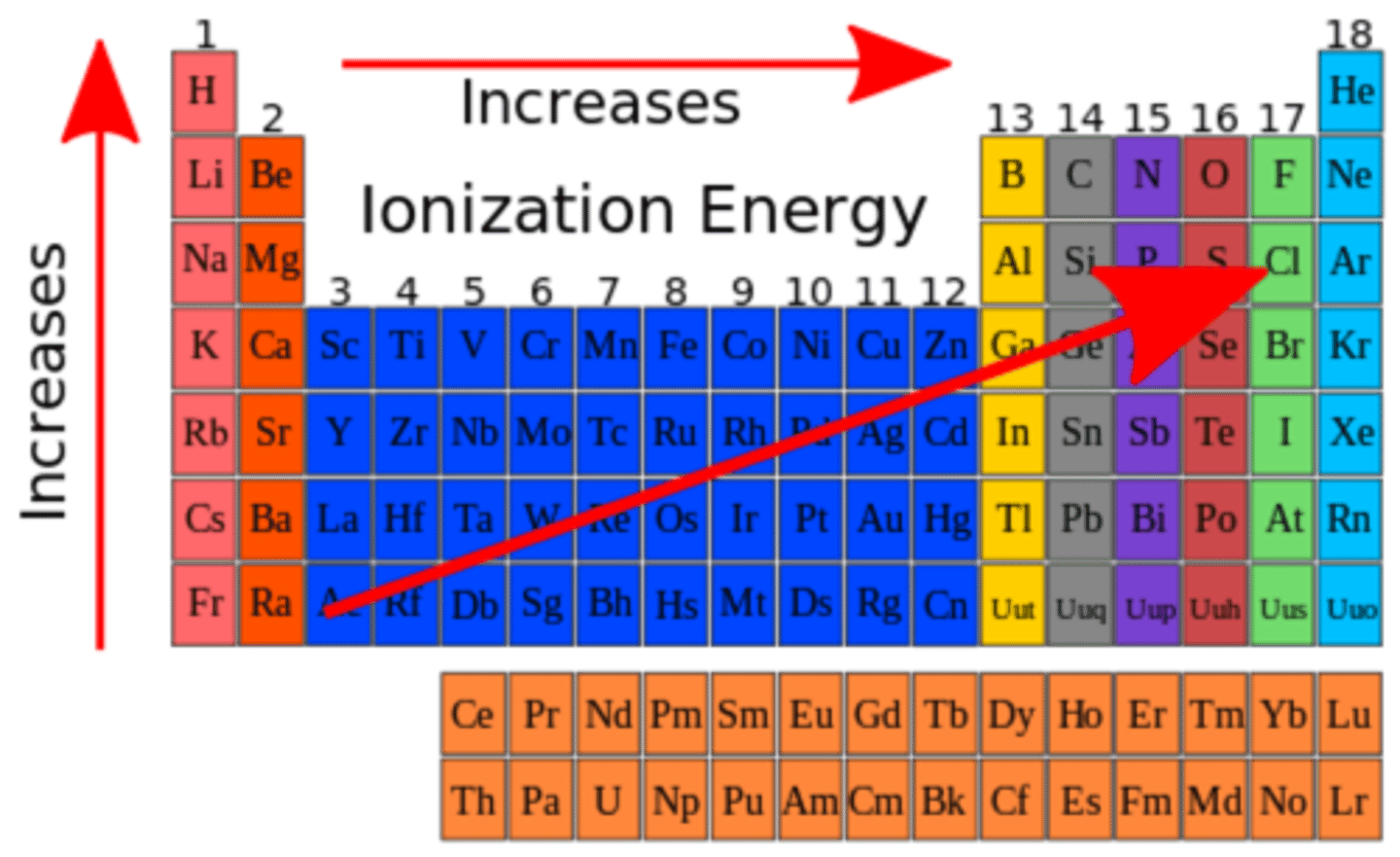
Periodic Trends: Ionization Energy
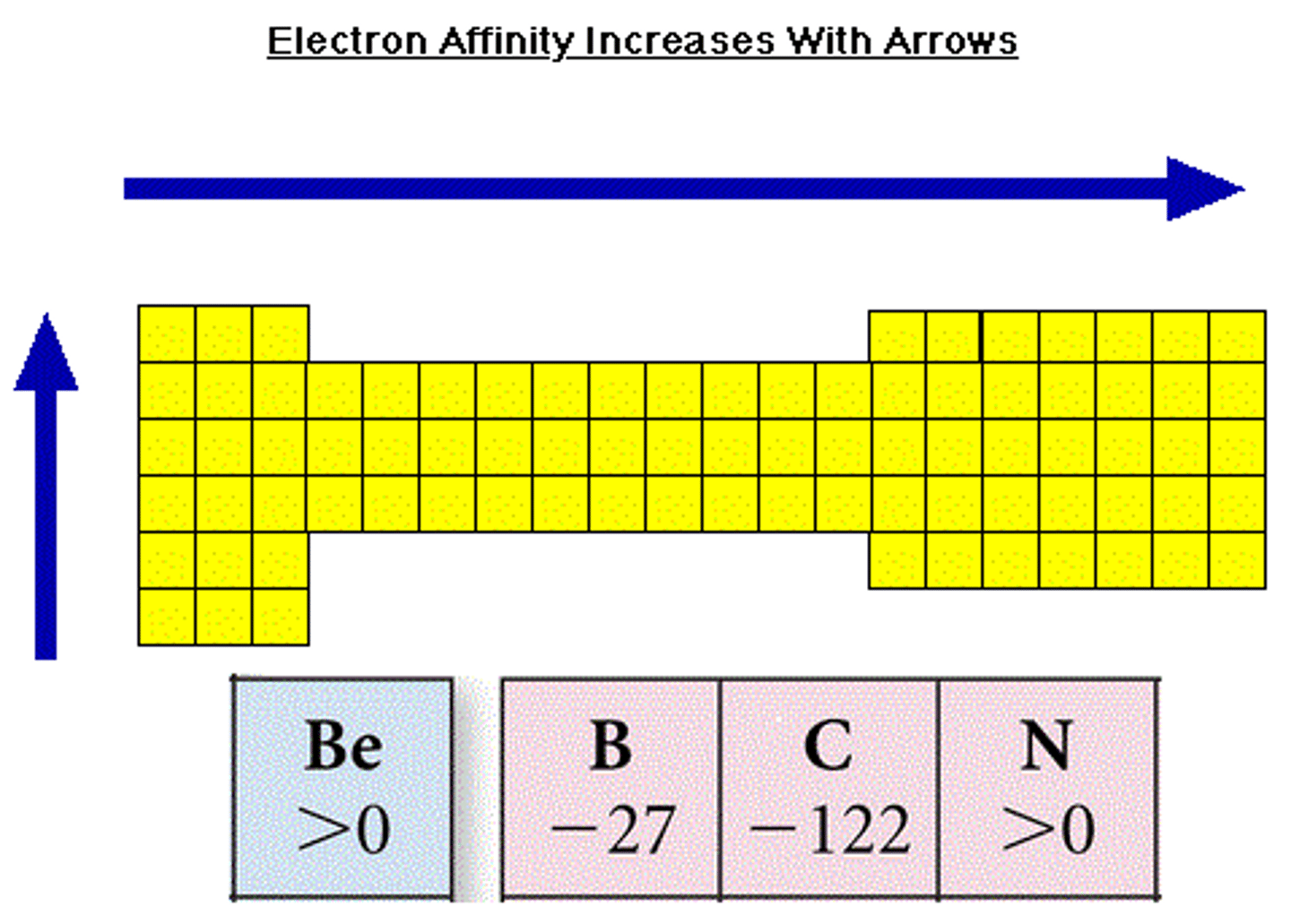
Periodic Trends: Electron Affinity
What are the 7 Strong Acids?
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO₃, H₂SO₄, HClO₄, HClO₃
What are the Strong Bases?
Group 1A Metal Hydroxides, Ca(OH)₂, Sr(OH)₂, Ba(OH)₂
What is a strong electrolyte?
Strong Acids, Strong Bases & Soluble Ionic Compounds
What is a non-electrolyte?
Organic Compounds, Weak Acids, Weak Bases
What is the sign for an endothermic reaction and where does heat go?
Positive Sign (+), Heat goes out of system
What is the sign for an exothermic reaction and where does heat go?
Negative Sign (-), Heat goes into system
What is the formula for Kinetic Energy?
KE= (1/2)mv² (JOULES)
mass --> kg
velocity --> m²/s²
What is the calorimetry equation where you use moles and the coefficient?
Hrxn= (grams * coefficient)/(# moles)
What is the Nonmetal Activity Series?
F>O>Cl>Br>I>S
What is the 1st Solubility Rule?
All compounds with group 1A and NH₄⁺ metals are soluble
What is the 2nd Solubility Rule?
All ionic compounds that contain Nitrate/ite, Perchlorate/chlorate, acetate, or bicarbonate are soluble
What is the 3rd Solubility Rule?
Ionic compounds that contain Cl, Br, CN and I are soluble UNLESS combined with Ag, Hg, Pb
What is the 4th Solubility Rule?
Ionic compounds that contain Sulfate/ite are soluble unless combined with Ag, Hg, Pb, Ca, Ba, Sr
What is the 5th Solubility Rule?
Most ionic compounds that contain phosphate, carbonate, hydroxide, sulfide, oxide, chromate, dichromate and fluoride are INSOLUBLE unless paired with Group 1A metals or NH₄⁺
Acetate
C₂H₃O₂⁻ OR CH₃COO⁻
Giga
1.0x10⁹
Mega
1.0x10⁶
Kilo
1.0x10³
Deci
1.0x10⁻¹
Centi
1.0x10⁻²
Milli
1.0x10⁻³
Micro
1.0x10⁻⁶
Nano
1.0x10⁻⁹
Pico
1.0x10⁻¹²
Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion
C= (F-32)/1.8
Heat Equation
q=mc∆T
Density
Density=mass/volume
1cm³ equals what
1ml
How do you calculate number of protons, neutrons & electrons for an atom?
Electrons --> Equal to Protons in a NEUTRAL ATOM
Protons --> Atomic Number
Neutrons --> Atomic Mass - Atomic Number
Covalent bonds are formed between..
two nonmetals
Ionic bonds are formed between..
one nonmetal and one metal
Sulfate
SO₄⁻
Sulfite
SO₃⁻
Thiosulfate
S₂O₃²⁻
Peroxide
O₂²⁻
What atoms form diatoms?
H, N, O, F, Cl, I, Br
What is a binary acid?
An acid that contains an H and one other element
What is an oxyacid?
An acid that contains H, O and one other element
Naming Binary Acids
Hydro- prefix
Roof of Nonmetal for the middle of the name
Add -ic suffix
Naming Oxyacids
hypo- & -ous --> Oxyacid with least oxygens
-ous
-ic
per- & -ic --> Oxyacid with the most oxygens
"ous" =
"ite"
"ic" =
"ate"
How do you know if you need to complete a limiting recent calculation?
You will see amounts for each reactant
What is the formula for percent yield?
% yield = actual/theoretical
What are the steps to the empirical formula?
1. Go from grams to moles
2. Divide by lowest number of Moles
3. Multiply entire compound to get to whole number
M₁V₁=M₂V₂
only use when dealing with the same compound
2 Concentration & 1 Volume
1 Concentration & 2 Volumes
Solution Stoichiometry
Titration
Energy equation
∆E=q+w
(heat + work)
I calorie = how many Joules
4.184
Work Equation
w=-P∆V
P--> atm
V --> L
When given bonds how do you find Hrxn?
Reactants-Products
When given compounds how do you find Hrxn?
Products-Reactants
What is the light spectrum in order of least harmful to most?
Radio, Micro, Infrared, Visible, UV, X-Ray, Gamma
As Frequency Increases, Wavelength & Energy..
Wavelength --> Decreases
Energy --> Increses
What is the equation relating wavelength and frequency?
speed of light = wavelength(λ) x frequency(v)
What is the Light energy equation
Energy (J) = h x frequency(v)
h = planks constant
What is the Balmer-Rydberg Equation
(1/λ)=R*(1/m²-1/n²)
m=1 --> Lyman Series (UV)
m=2 --> Balmer Series (Visible)
m=3 --> Paschen Series (IR)
(m2= initial; n2=final)
What defines Paramagnatism?
Substances that have unpaired electrons
What defines Diamagnetism?
Substances with NO unpaired electrons
What is the formal charge equation?
Formal Charge = VE- 1/2 BE - LPE
If ∆Electronegativy = 0 ..
Non-Polar Covalent
If ∆Electronegativity < 2
Polar Covalent
What is the gas equation?
PV=nRT
p = pressure
v = volume
n = amount of substance
r = ideal gas constant
t = temperature
What is a Sigma (δ) bond?
All single bonds are sigma bonds
What is a Pi (π) bond?
Found in double and triple bonds
1 mol of any gas =?
22.4 L STP
1 torr = mm hg?
1 mm hg
1 atm= psi?
14.7
1 atm= Pa?
101325
1 bar=Pa?
1X10^5 Pa
Balmer-Rydberg Constant (R)
1.097x10⁻²