RT VIVA
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
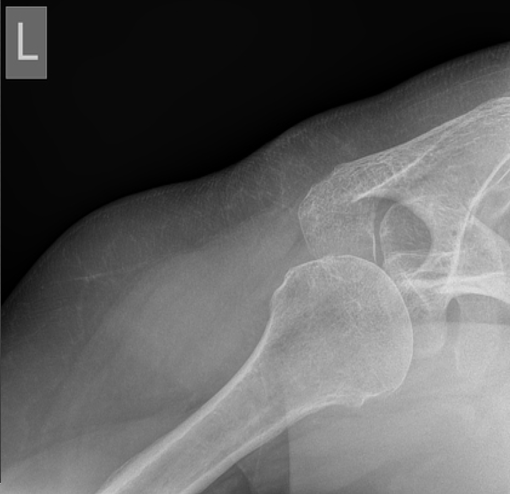
What is this view?
Westpoint view
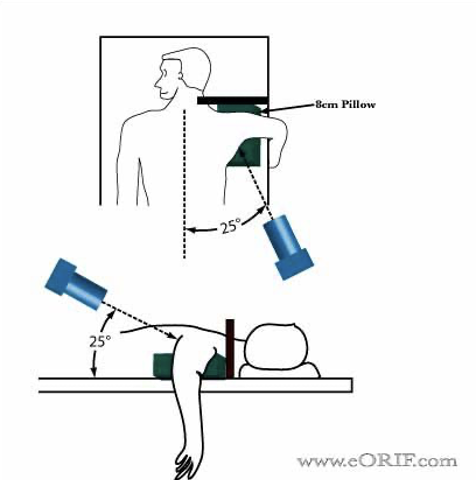
Positioning for a Westpoint View of the shoulder
Patient is prone
Affected shoulder placed on a sponge, elevating it 8cm
Arm is abducted 90deg with forearm hanging over table
IR is placed at superior part of the affected shoulder
Tube rotation: 25 deg to mid-sagittal plane and 25 deg caudal angulation
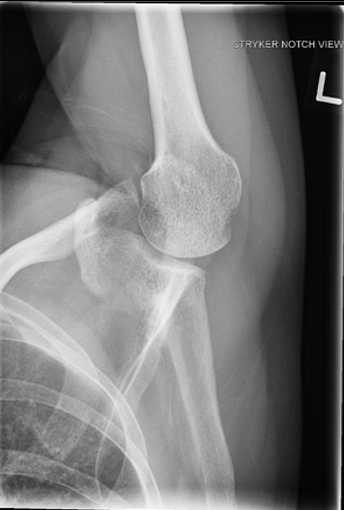
What is this view?
Striker View
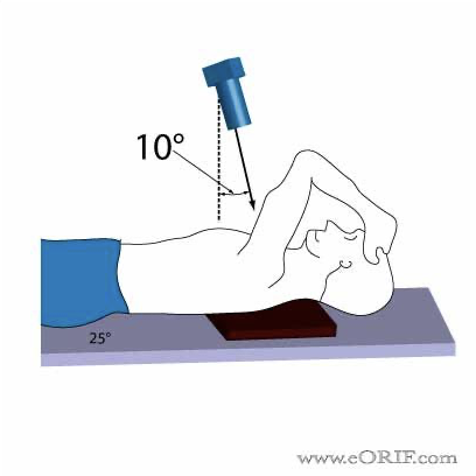
How to position for a Striker view?
Mid-coronal plane of the pt is parallel to detector
Pt rotated 30-45 deg towards the affected side, this shows the glenohumeral head
Affected arm is flexed and abducted anteriorly, resting the hand on the forehead while maintaining internal rotation
10-15 deg cephalic angulation
CP= mid-axilla at level of glenohumeral head
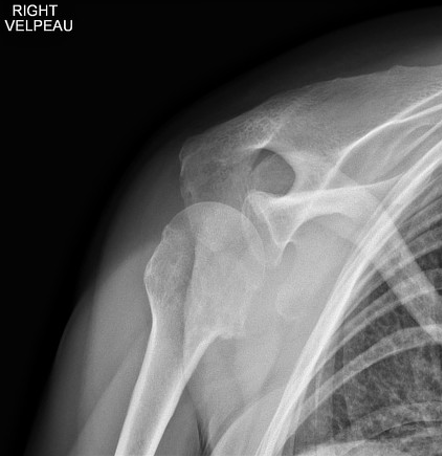
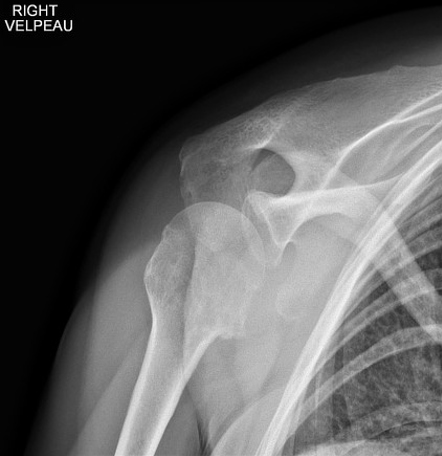
What does a Valpeau view show?
Shows Gleno-humeral relationship but does not require abduction of arm
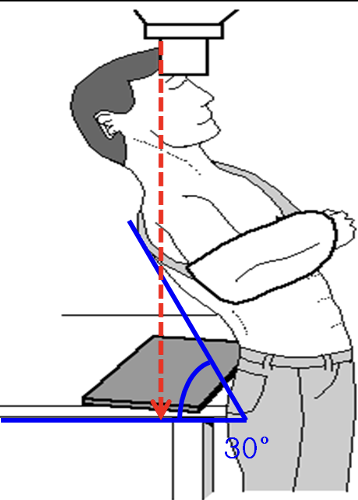
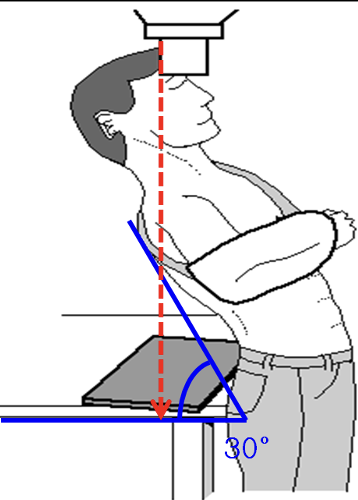
Positioning for a Valpeau view
Detector placed behind patient on table around height of sacrum
Pt erect
Lean them posteriorly 30 deg over the detector
Xray tube is perpendicular to the detector, centred at the glenohumeral joint
MCU Collimation and Positioning
Centre Point: 5cm above symph (middle of pelvic brim)
Centre Point (KUB): level of Iliac crests or just above to include the upper poles of the kidneys to the bottom of the bladder
Angulation: No angle, no foreshortening of the pelvic or uterine structures
Rotation: Generally true AP position required (shown by alignment of the sacral structures with the symph)
Collimation: Bladder, urethra and distal ureters
Collimation (KUB): Include the Upper poles of the kidneys
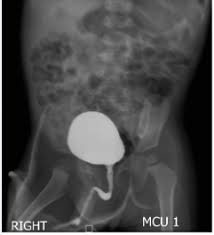
Pt and Room Prep - MCU
Pt Prep
NBM morning before
Allergies to CM
Everything set up before child is in the room
Parent present- check their pregnancy, lead apron
Reassurance and distraction techniques
Give the child a bottle while on table for comfort
Minimum staff
Calm atmosphere
Room Prep
Table flat for catheterisation
Absorbent pads on table
Table horizontal for procedures, absorbent pads
CM ready
Paediatric settings on equipment
Catheterisation- frog position
Urine specimen pottle, antibiotics
Pt and Room Prep - Barium Swallow and Meal
The patient needs to be NBM* on the day. No smoking or chewing gum for 8-12 hours prior
Explain procedure- hold barium in mouth until ready to swallow, raise hand to let us know you will swallow
Glasses and Jewellery removed
The fluoro table needs to be upright, with footrest and handles attached.
Barium needs to be mixed with a cup, straw and spoon handy.
Other consistencies of food such as a biscuit and banana need to be at hand
*For elderly and stoke pts there is risk of choking, aspiration pneumonia. Before beginning, check if they can safely drink water before commencing
Clinical Indications for Ba Swallow
Dysphagia
Gastro-oesopghageal reflux (GERD)
Sensation of food sticking
Regurgitation of food
Stroke
Lap band or gastric sleeve surgery
?Foreign object
? Rupture - eg: sword swallower
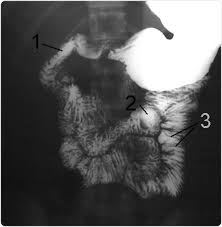
Risks for MCU
UTI and Bleeding
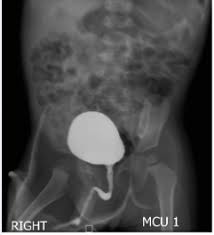
Clinical Indications for MCU
Vesicoureteric reflux (VUR)
Recurrent UTIs
Congenital abnormalities
Posterior urethral valves
Unstable bladder
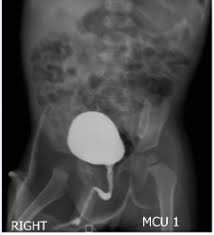
3 Ds for MCU
Distension – The bladder has been fully distended, enough contrast media has been introduced to show the bladder fully expanded.
Delineation- The bladder has been fully delineated, the contrast media has ensured that it is clearly distinguishable within the pelvis, even though it is a soft tissue structure. The contrast media has ensured that any abnormalities in the bladder wall will be demonstrated
Density – The contrast media has a high atomic number, it is probably iodinated CM, it attenuates the the x-rays and allow us to clearly visualise the soft tissue structure of the bladder
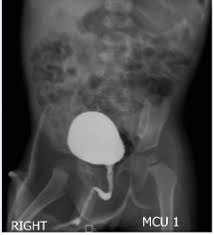
Ways to reduce nephrotoxic affects of CM if the pt was suffering from renal insufficiency
Use a low-osmolar contrast media such as Omnipaque
Radiation Protection for MCU
Collimate only to the ROI - bladder, urethra and ureters. Kidneys if needed
Undercouch
Staff wear lead
Low exposures
Radiation lights when screening
Suspend low exposures when radiation not in use
Low frame rate
Key Imaging steps- MCU
Key imaging steps
AP control- bladder stones, spinal anomalies
AP- filled bladder
Oblique- R and L filled bladder to see vesicoureteric junction (diverticula), grade 1 VUR
Oblique micturating- beginning, middle, end
AP film to include renal areas at the end
If reflux occurs, pick up child then take a post drainage film
Radiation Protection for Ba Swallow
1- Warning lights for x-ray on
2- Fluoro rooms should not be used as corridors. Where possible porters should not be knocking on the suite door when patients arrive. Sometimes you may need to lock the suite door for both radiation protection and privacy reasons.
3- Undercouch technique with II as close as possible to patient
4- Last image hold, scroll through previous run
5- Only those directly helping with procedure in room- when helping patient be aware of high dose areas around the unit.
6- Pb gowns, thyroid shields, glasses
7- Ceiling mounted glass screens, Pb skirts around II
8- Limiting screening times and the use of magnification
9- ID and pregnancy check
CM for Swallows and Meals
Swallow: Double contrast (air from granules and dense barium)
Fizzy Granules - Sodium Bicarbonate
Barium in water
Meal: Double Contrast (Air from granules and dense barium
Fizzy Granules - Sodium Bicarbonate
Barium in water
3 Ds for Ba Swallow and Meal
Density - CM needs to be dense enough to not be diluted by GI contents
Delineation - CM needs to delineate the ROI – GI tract is similar densities to surrounding organs and often overlapped by other anatomic structures
Distension – CM needs to either be dense enough to distend the anatomy or have dual CM to distend the ROI – i.e. fizzy granules during a Ba Swallow
Routine Views - Ba Swallow
Pharynx & Upper Oesophagus:
AP chin raised
Lateral (shoulders slightly off lateral)
Lower Oesophagus:
AP
RAO (Oesophagus posterior to the heart)
Lateral
Trendelenburg RAO
Why is an oblique projection ideal for Ba Swallow?
AP- Prevents superimposition of the Heart and Spine over the esophagus
Lateral- Prevents superimposition of the Shoulders over the esophagus
Why speech therapist are often involved in Video Swallows?
Speech therapists can analyse the various stages of swallow (bonus point for: Oral preparatory, Oral propulsive, Pharyngeal, Oesophageal) and prescribe treatment such as swallowing/coughing exercises (to improve muscle tone) or special diets to prevent aspiration.
Types of CM
Iodinated – positive CM. intravenous or intracavitary. Is water soluble and commonly used in Contrast CT, angiography, HSG, IVU and Intracavitary
Barium – Used in imaging of the digestive system. Not water soluble and commonly used in barium swallows, meals, follow throughs (eg SBFT) and enemas
Air – negative CM (less radio-opaque) used with Barium for enemas
CO2 – negative agent (less radio-opaque). Easily reabsorbed by the body
Aftercare for Barium
Barium Aftercare:
Drink plenty of fluids
Fiber to remove from the body
Stools may be white (normal)

Aftercare for Omnipaque
1.Drink plenty of fluids
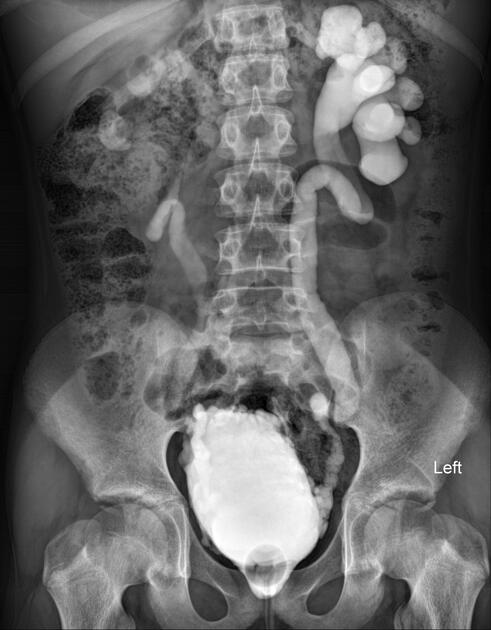
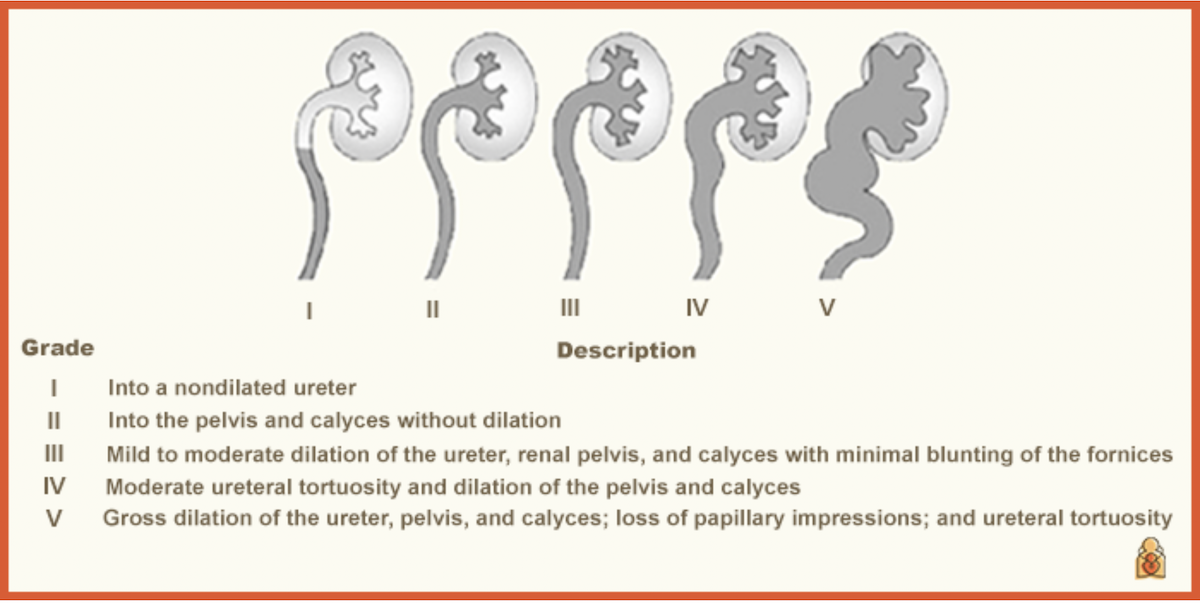
VUR Scale for MCUs and how this appears on the image
Into a non-dilated ureter
Into the pelvis and calyces without dilation
Mild to moderate dilation of the ureter, renal pelvis and calyces with minimal blunting of the fornices
Moderate ureteral tortuosity and dilation of the pelvis and calyces
Gross dilation of the ureter, pelvis and calyces, loss of papillary impressions and ureteral tortuosity
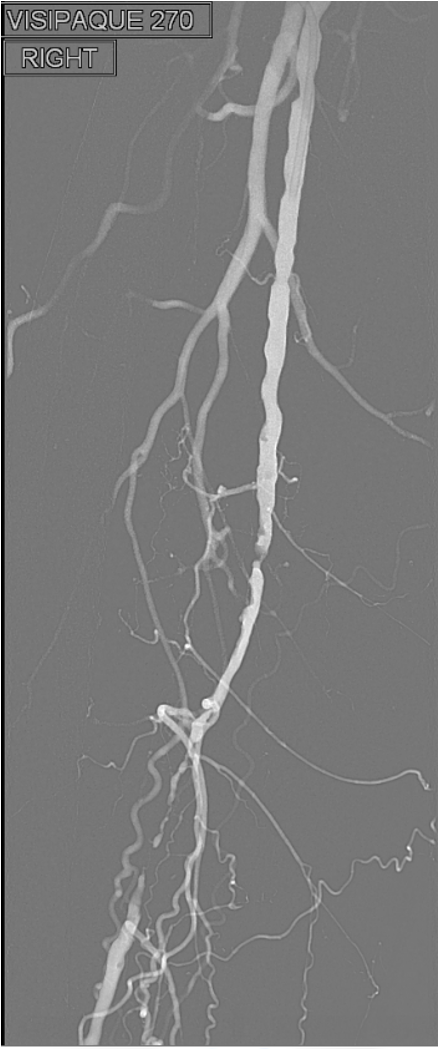
Peripheral Angio Equipment
DR Flat panel C-arm
Sterile procedure equipment:
Gloves, gowns, Towels, drapes, II covers
Gauze, scalpel, needles, scissors, syringes, bowls, catheters, wires, sheaths
Saline, Heparin, Lidocaine, CM, skin prep solution
Monitoring equipment
Blood pressure cuff, oximeter, pulse
Oxygen
Ultrasound machine
Anaesthetic Equipment
Risks and complications of Angiography (peripheral and coronary)
Swelling, bleeding, or infection at catheter insertion site
Contrast media reactions
Vessel dissection caused by catheter
Thrombus/embolus formation – risk of causing stroke
SOB/Fluid overload in patients with known CHF
Perforation

Safe use of Contrast Media and types used
Check the bottle is sealed, and has not been opened
Check bottle for any damage
Check expiry date, type (Omni 300), concentration and volume
Types=
Visipaque 270 (better for angiography as iso-osmolar)
Omnipaque 300
Safety for patient= Over 150mL used in total, saline IV used for hydration helping in elimination of CM from the body
Pt Prep for Angio procedures (peripheral or coronary)
Must include INR or clotting check, GFR or creatinine level check
Previous contrast reaction or history of allergies
Pregnancy check if female and within pregnancy age-range
NBM 4 hours pre-procedure, but fluid intake is encouraged
Pt bring their usual medication/provide a list of medications they take ( ask whether taking metformin, aspirin or other blood thinning medications )
Pts asked to arrive at the Radiology dept before the scheduled appt time
Pt asked to sign a consent form which lets them know what occurs in the procedure and that they understand the risks and complications it may cause
Contraindications for Angio procedures
Coagulopathy-low or fast clotting time
Uncontrolled hypertension
Arrhythmia
CM allergy
Pregnancy
High creatinine levels

4 Step Imaging Procedure for Angio
Beginning:
1. Seldinger technique to introduce catheter. Imaging of the guidewire and catheter to the vessels of interest
Middle:
CM is injected through the catheter and a series of diagnostic images are taken to assess the anatomy of the region for any abnormality
Once the cause for symptoms and any abnormality identified a treatment plan is discussed and agreed. Treatment goes ahead (balloon, stent insertion or drug eluting balloon)
End:
A final series of images are taken to see if treatment was effective i.e. return of normal blood flow
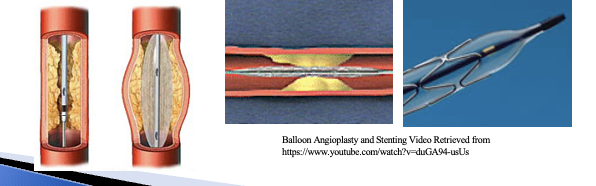
Interventional Techniques and Devices
PTCA- Angioplasty balloon, stent insertion or drug eluting stents
These are used to treat stenosis from atherosclerosis (vessel plaque) in the heart and other areas
Radiation Protection in Angio
Pt Protection
ID, Pregnancy
Pulsed fluoro, low screening settings, high kV-low mAs
II in close to patient
alarms, collimated field, programmed positions, tube underneath- scatter projected to the floor
Staff Protection
Pb aprons, screens, glasses
X-ray tube- under couch, limiting numbers within room, badges,
adjusting table height to bring II in close
MRTs leave room for full exposure runs
Post Procedure Care for Angio
Catheter removed – compression (or angioseal or another closure device can be used)
Patient taken to the ward.
Bed rest- min 4 hours. Head up 30 degrees
Nurses on the ward will carry out regular observations such as pulse and blood pressure measurements.
There may be a small amount of bruising in the groin or wrist (arterial entry)
Any specific Instructions (dependent on the procedure performed) given to patient from nurse (leaflet inserted in patient’s notes)
Drink plenty of fluid (flush CM)
If sedation given, no driving for 24 hours
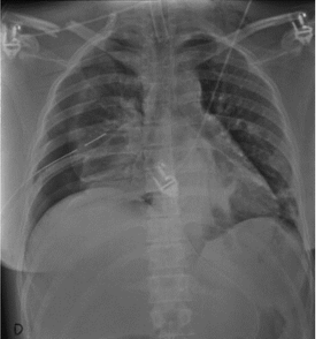
Mobile CXR review for pathology
Lung fields – Equal transradiancy, fissures, apices.
Trachea – Central with slight deviation to the R around the aortic knuckle.
Hilum – The left hilum should be higher than the Right. The hila should be concave in shape and look similar, so compare the shape and density of them.
Heart, & Mediastinum- check for normal shape and size, clear edges. Cardiothoracic ratio.
Diaphragms and Costophrenic angles – R diaphragm should be higher than the left as heart pushes L side down. Well defined acute angles
Bones and Soft Tissue - Check for rib #s and subcutaneous emphysema
Difficulties with Imaging of Mobile CXR
Difficulty with:
ensuring the correct SID of 15cm is used,
the angulation of the detector is perpendicular to the CR, Difficulty ensuring no rotation as the patient is obviously unwell
that the patient is able to sit erect (may have to support the IR with sponges/pillows to keep it vertical)
the patient may not be able to take an adequate inspiration
needing to be as quick and efficient as possible as the referring Dr will be waiting for result so that treatment can begin
needing to navigate around oxygen, drains or extra staff.
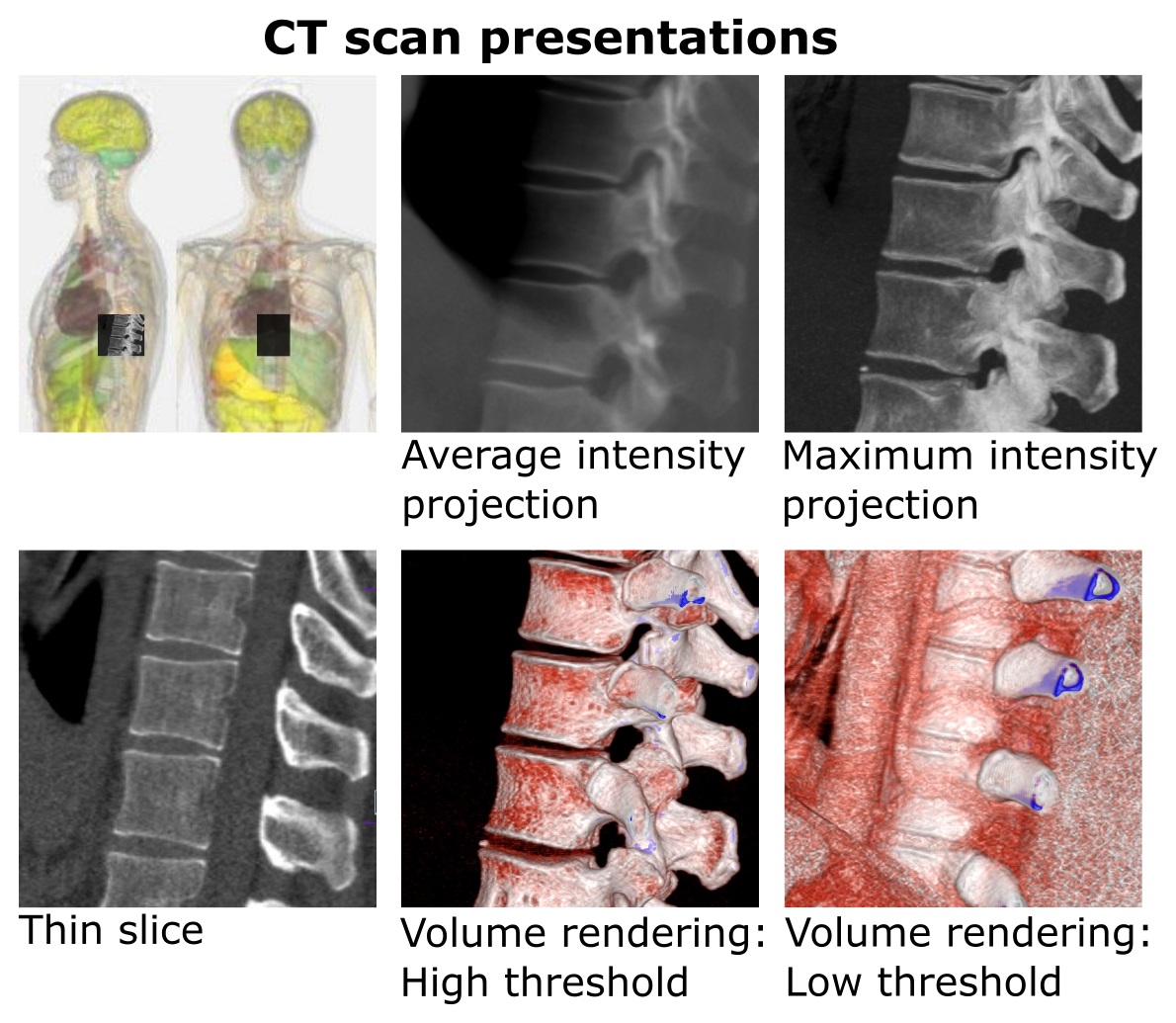
What is the abbreviation: MIP
Maximum Intensity Projection - a 3D imaging technique that highlights the brightest structures in a set of images
What is the abbreviation: DFOV
Display Field of View - determines how much of the scan field of view is reconstructed onto an image
What is the abbreviation: VR
Volume Rendering - VR uses thin slices to create a 3D structure that represents all depths of tissues
This can be manipulated in the 3D plane to show pathological changes and likely relationships resulting from trauma to be easily spotted
Artefact definition
Discrepancies in the reconstructed CT image which don’t represent the true attenuation coefficients (true structure) of the object scanned
Define SOL
Space Occupying Lesion - either a tumour, abscess or haematoma
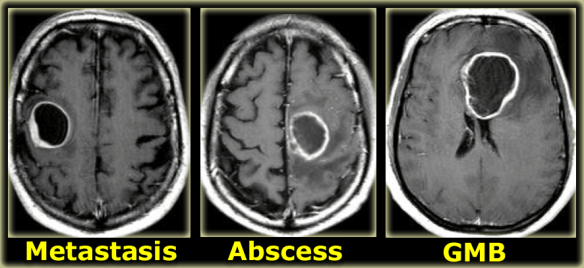
Clinical Indications for a CT Head
? Degenerative Change
? Dementia
? Stroke
? SOL
? Tumour
? Mets
Infection or inflammatory change - abscess, encephalitis, meningitis
Congenital conditions
Endocrine conditions
Anatomical landmarks required for axial slices in a scout view
Include all of brain stem and bones base of skull (base of medulla oblongata)
Last slice should be through the vertex
Angled to include only the bony supraorbital margin
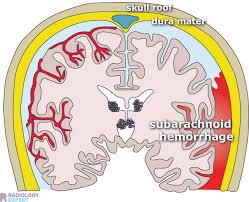
Define: SAH
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage - blood collects beneath the arachnoid mater in the subarachnoid space (occurs near site of a skull #)
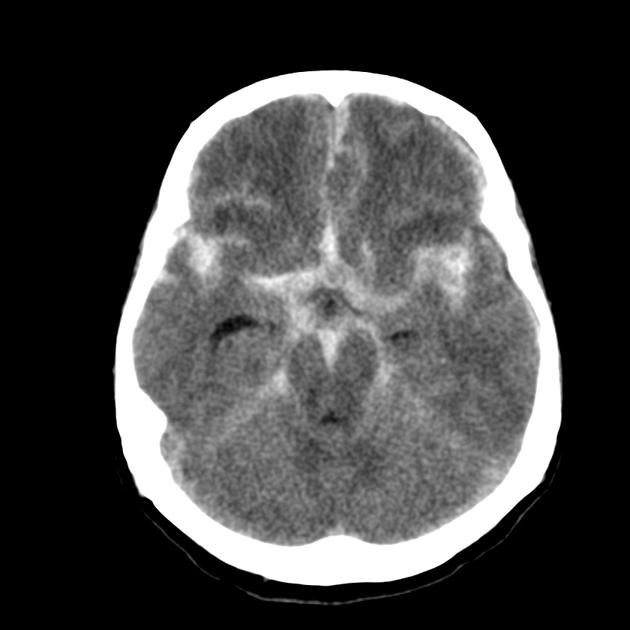
Define: SDH
Subdural Haematoma - Blood accumulates between the dura and arachnoid mater of the meninges, bleeding in the ventricles and causes a midline shift
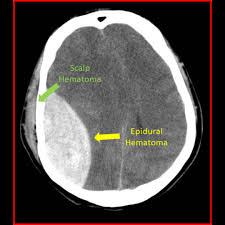
Define: EDH
Epidural Haematoma - arterial bleeding between the dura and the skull vault (associated with skull #)
Clinical Indications for CT
Benefits
Readily available
Fast to perform (1 min or less)
Highly accurate for intracranial injuries req surgical treatment
Sensitive for calvarial and skull base #s
Can be performed easily in patients who are intubated and being monitored due to severe injuries
Risks
Ionising radiation - pt dose
Insensitive to:
Vascular injuries
Diffuse axonal injury
Mild parenchymal contusion
Clinical Indications for MRI
Strengths
Uses magnetic field and radiofreq pulses to produce an image
No ionising radiation
Sensitive to brain parenchymal and vascular injury
Weaknesses
Takes longer than CT (20 mins)
Not readily available to every ED
Harder to monitor unstable pts in the MRI environment
Confused pts may need gen anaesthesia (avoid movement)
Does not demonstrate most calvarial/skull base #s
Ferromagnetic FB (bullets, metal fragments) in the pt may move during scanning and thus represent a contraindication
Pacemakers, some types of implants are contraindications to MRI as they malfunction and/or move in the MR environment
GCS
Glasgow Coma Scale
13+ Mild Brain Injury
9-12 Moderate brain Injury
>8 severe brain injury