Infectious Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract Andgenitourinary Tract
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
COLITIS
Inflammation of the colon (large intestine)
DIARRHEA
An abnormally frequent discharge of semi-fluid or fluid fecal matter.
DYSENTERY
Frequent water stools, accompanied by abdominal pain, fever and dehydration.
ENTERITIS
Inflammation of the intestines, usually referring to the small intestine.
GASTRITIS
Inflammation of the mucosal lining of the stomach.
GASTROENTERITIS
Inflammation of the mucosal linings of the stomach and intestines.
HEPATITIS
Inflammation of the liver.
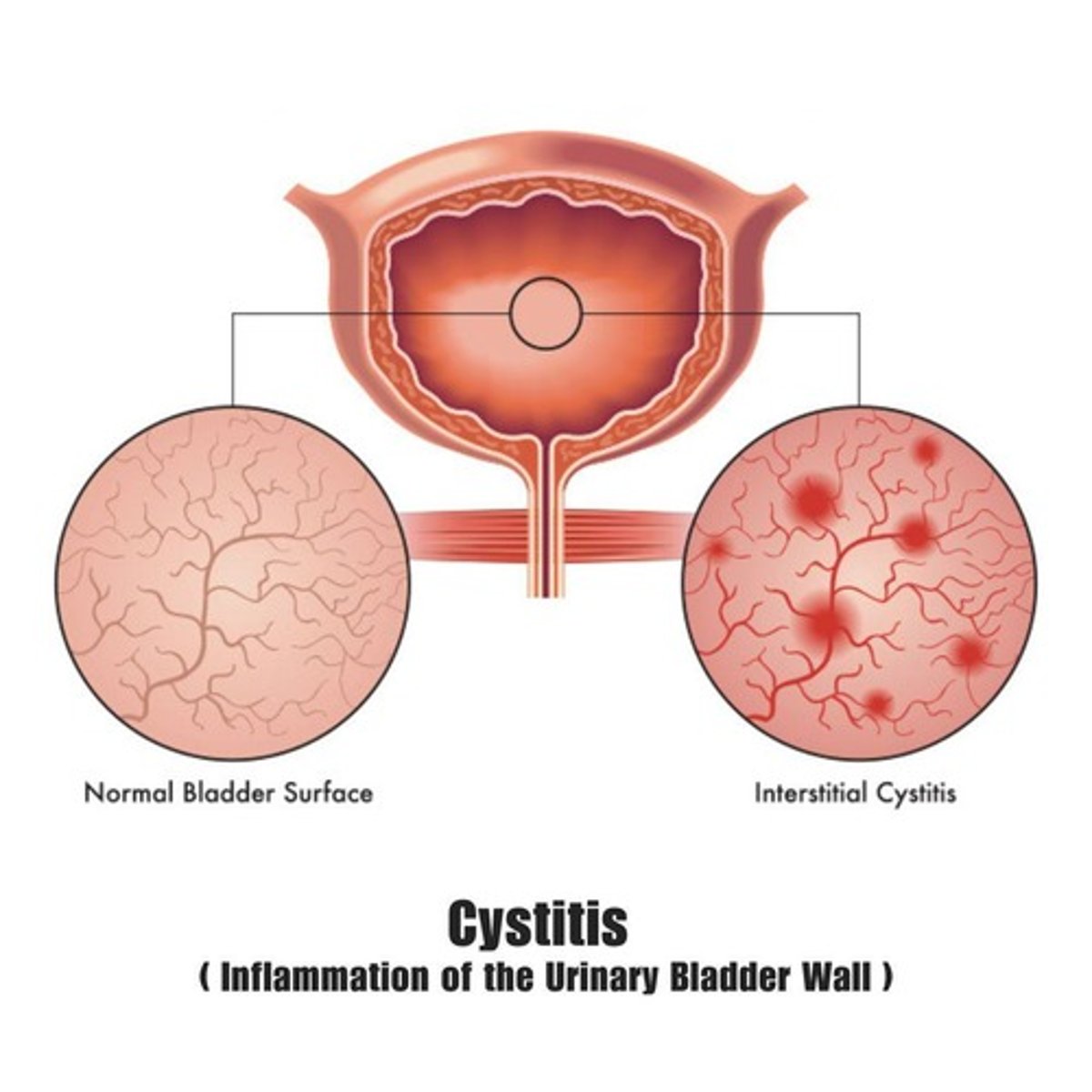
CYSTITIS
Inflammation of the urinary bladder; most common type of UTI; most common cause is Escherichia coli.
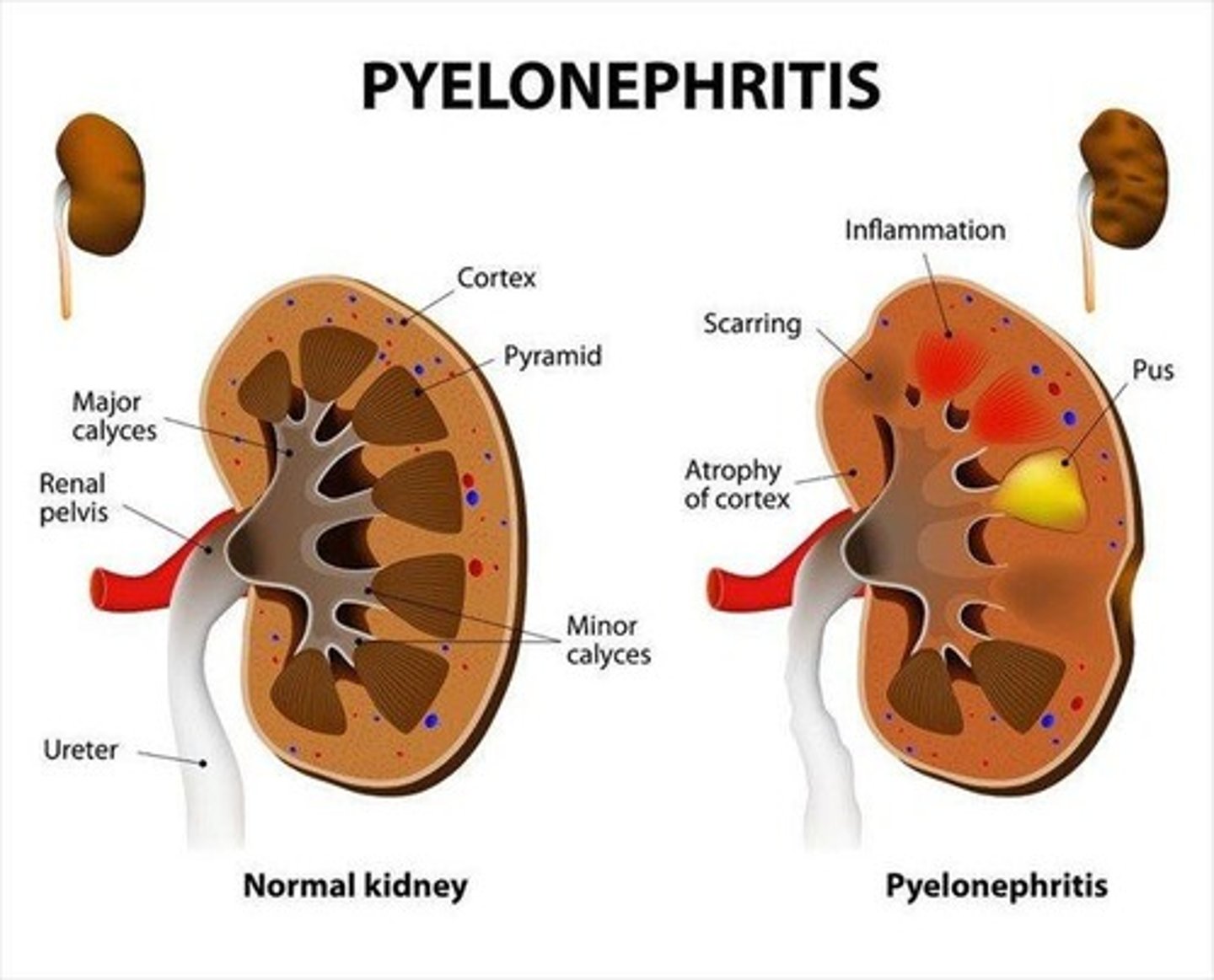
NEPHRITIS
Inflammation of the kidneys; Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal parenchyma; E. coli is the most common cause.
URETERITIS
Inflammation of one or both ureters; usually caused by the spreading of infection upward from the urinary bladder or downward from the kidneys.
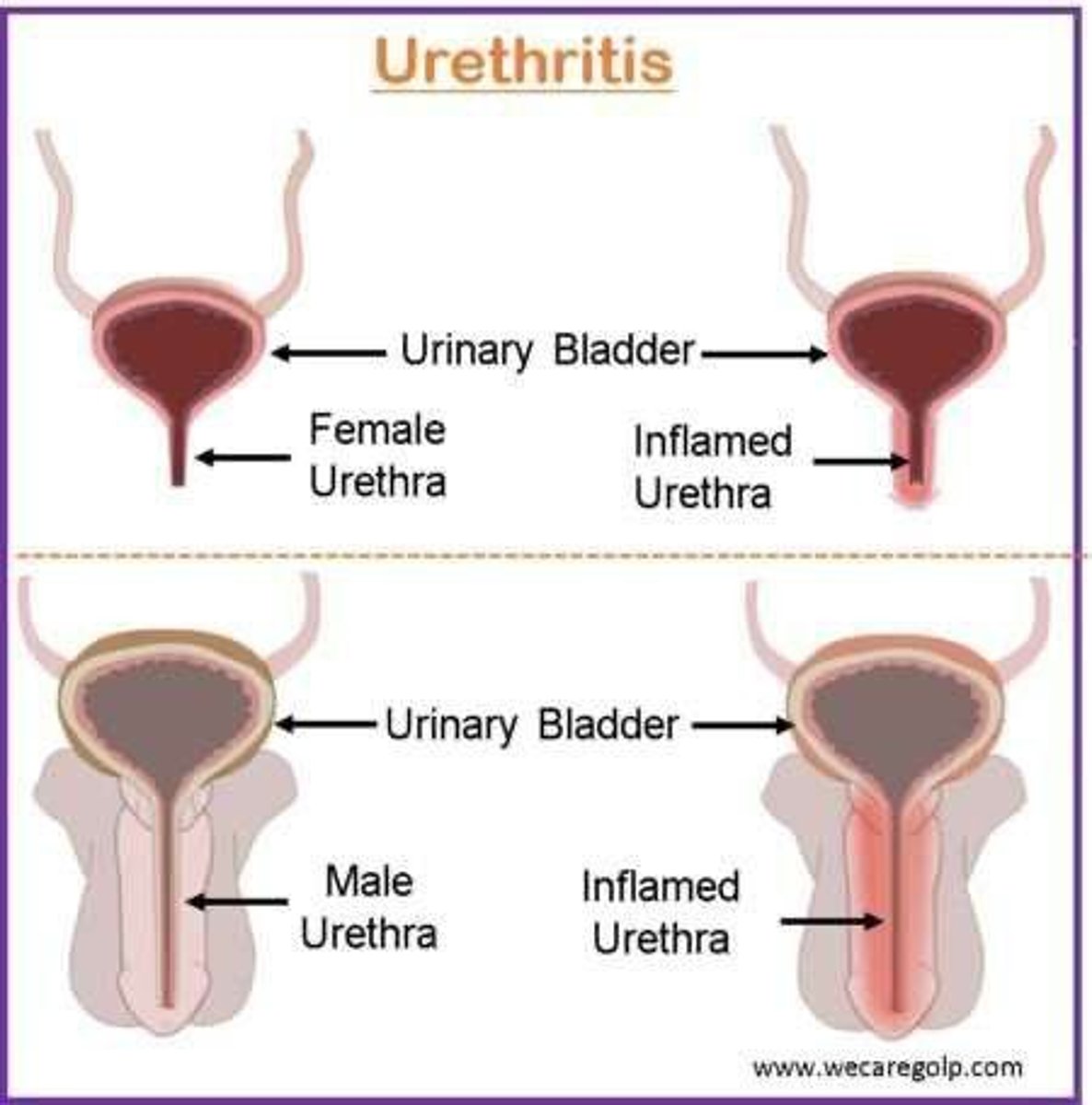
URETHRITIS
Inflammation of the urethra; most common cause is Chlamydia trachomatis, but Neisseria gonorrhoeae, ureaplasmas, and mycoplasmas can also be the cause.
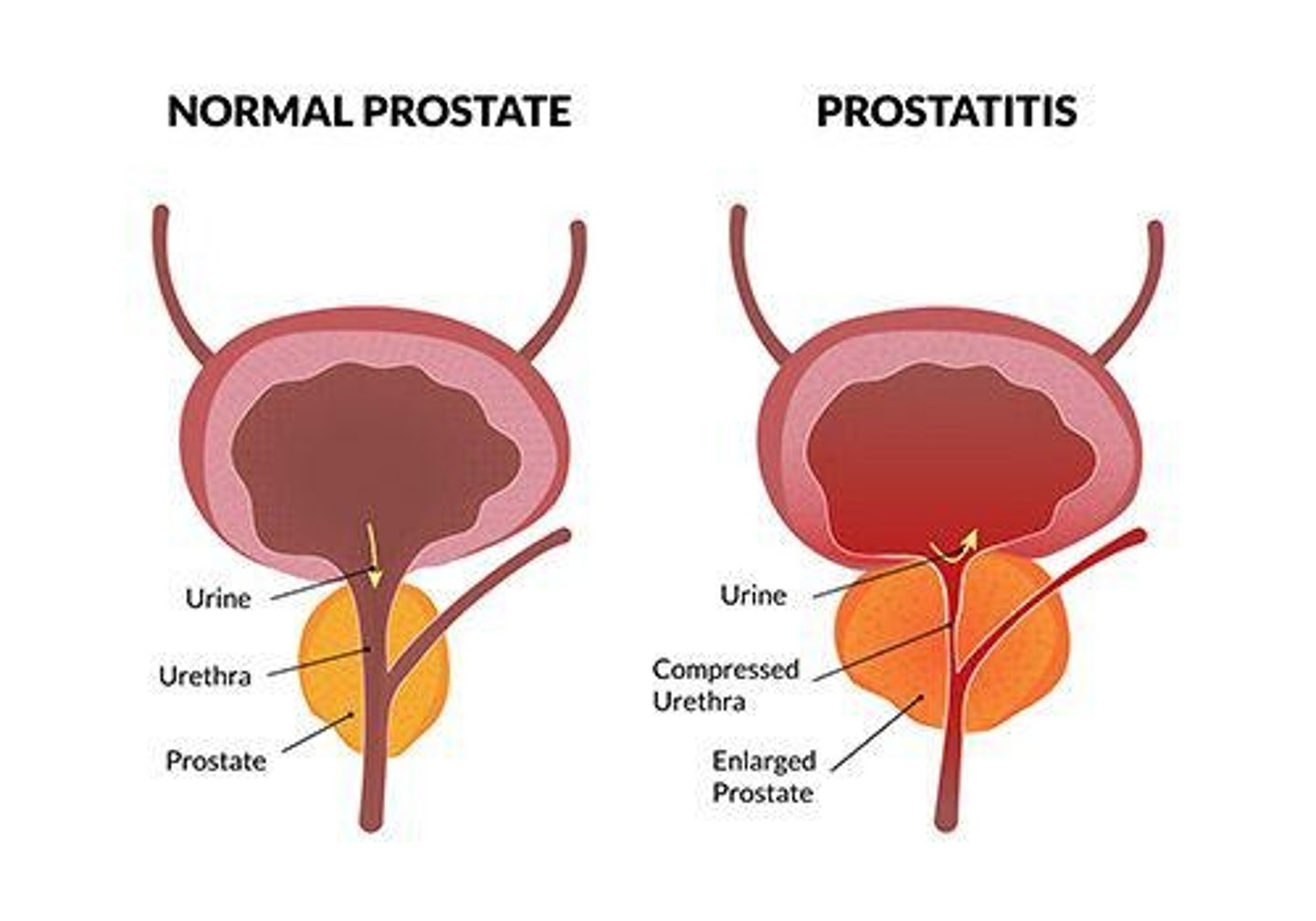
PROSTATITIS
Inflammation of the prostate gland; most often, prostatitis is not an infectious disease.
UPPER UTI
Includes infections of the kidneys (nephritis or pyelonephritis) and ureters (ureteritis).
LOWER UTI
Includes infections of the urinary bladder (cystitis), the urethra (urethritis) and in men, the prostate (prostatitis).
INDIGENOUS MICROBIOTA
Microorganisms found at and near the outer opening of the urethra and within the distal urethra of both men and women.
VAGINAL MICROBIOTA
Adult vaginal microbiota contains many species of Lactobacillus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria, Clostridium, Actinomyces, Prevotella, diphtheroids, enteric bacilli, and Candida.
SUPERINFECTION
Overgrowth of other members of the vaginal microbiota due to the destruction of some members.
BARTHOLINITIS
Inflammation of the Bartholin ducts in women.
CERVICITIS
Inflammation of the cervix (part of the uterus that opens into the vagina).
ENDOMETRITIS
Inflammation of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterine wall).
EPIDIDYMITIS
Inflammation of the epididymis (elongated structure connected to testis).
PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes; also known as salpingitis.
VULVOVAGINITIS
Inflammation of the vulva (external genitalia of women) and the vagina.
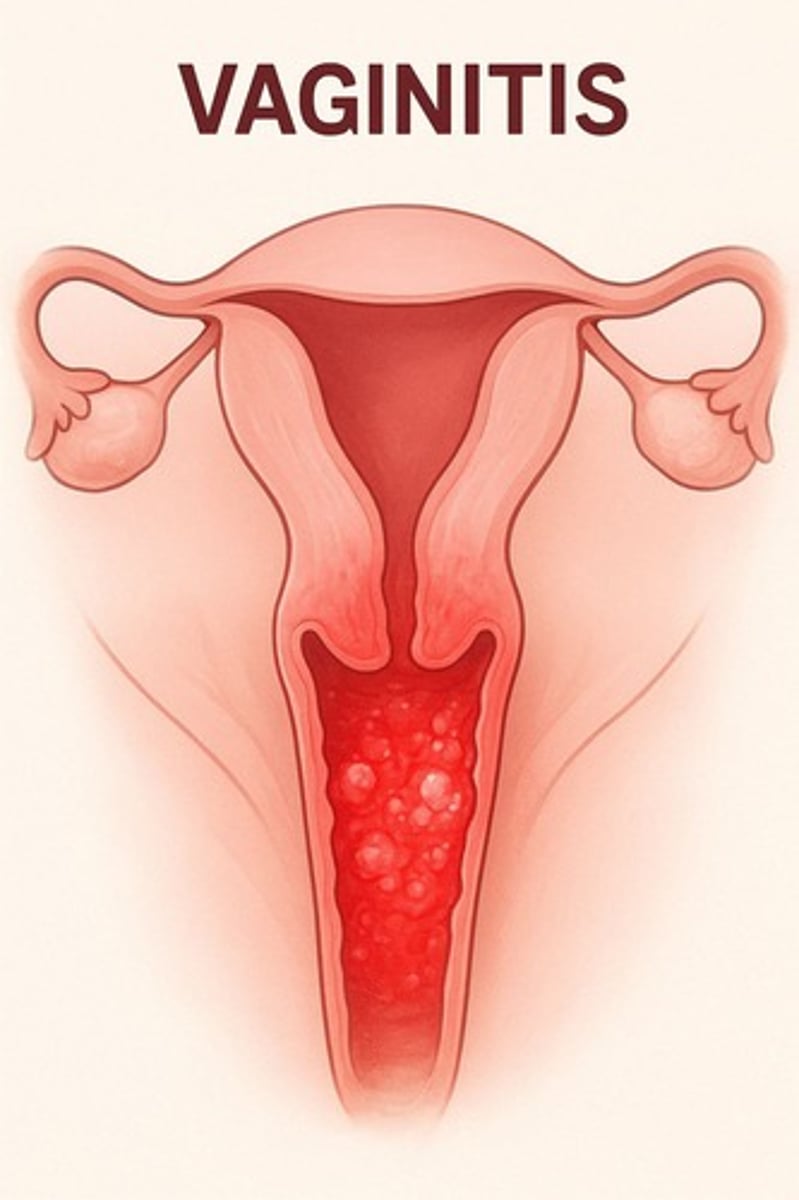
VAGINITIS
Inflammation of the vagina.
C. albicans
A yeast that is a common cause of vaginitis.
Trichomonas vaginalis
A protozoan that is a common cause of vaginitis.
STDs
Any infections transmitted by sexual activities affecting various body areas.
CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; estimates 20 million cases of STDs occur annually in the United States.
AIDS (HIV Infection)
Causative agent: Human Immunodeficiency Virus; transmission through sexual contact, blood transfusion, sharing needles, mother-to-child.
Chlamydial infection
Causative agent: Chlamydia trachomatis; often asymptomatic; females: abnormal discharge, pelvic pain; males: urethritis, painful urination.
Herpes infections
Causative agent: Herpes simplex virus; symptoms include painful grouped blisters/ulcers around genitals, anus, or mouth.
Gonorrhea
Causative agent: Neisseria gonorrhoeae; symptoms include discharge, pelvic pain, bleeding in females and pus, dysuria in males.
Syphilis
Causative agent: Treponema pallidum; primary: painless chancre; secondary: skin rash, fever, lymphadenopathy; tertiary: neurological & cardiovascular damage.
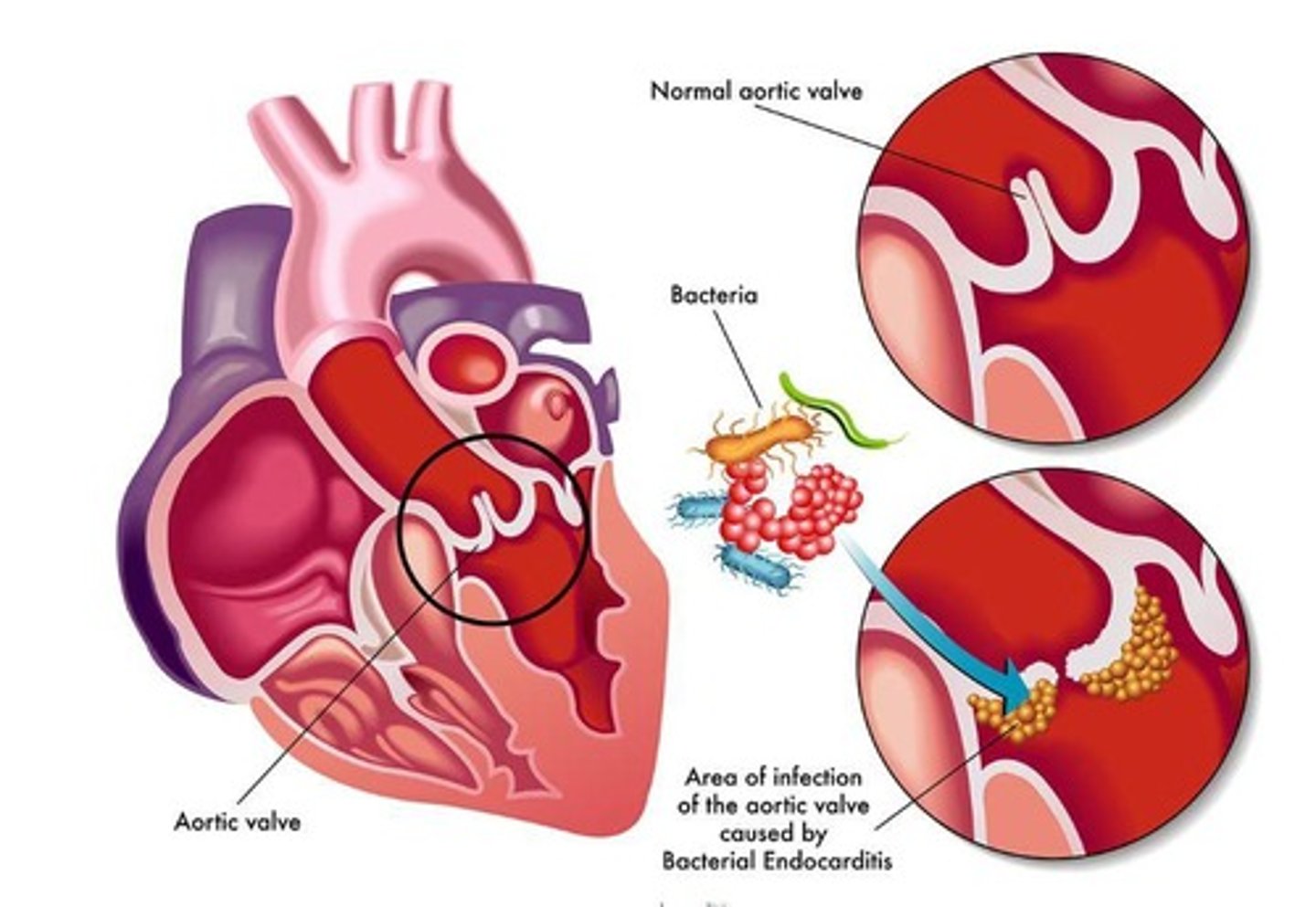
Endocarditis
Inflammation of the endocardium—the endothelial membrane that lines the cavities of the heart.
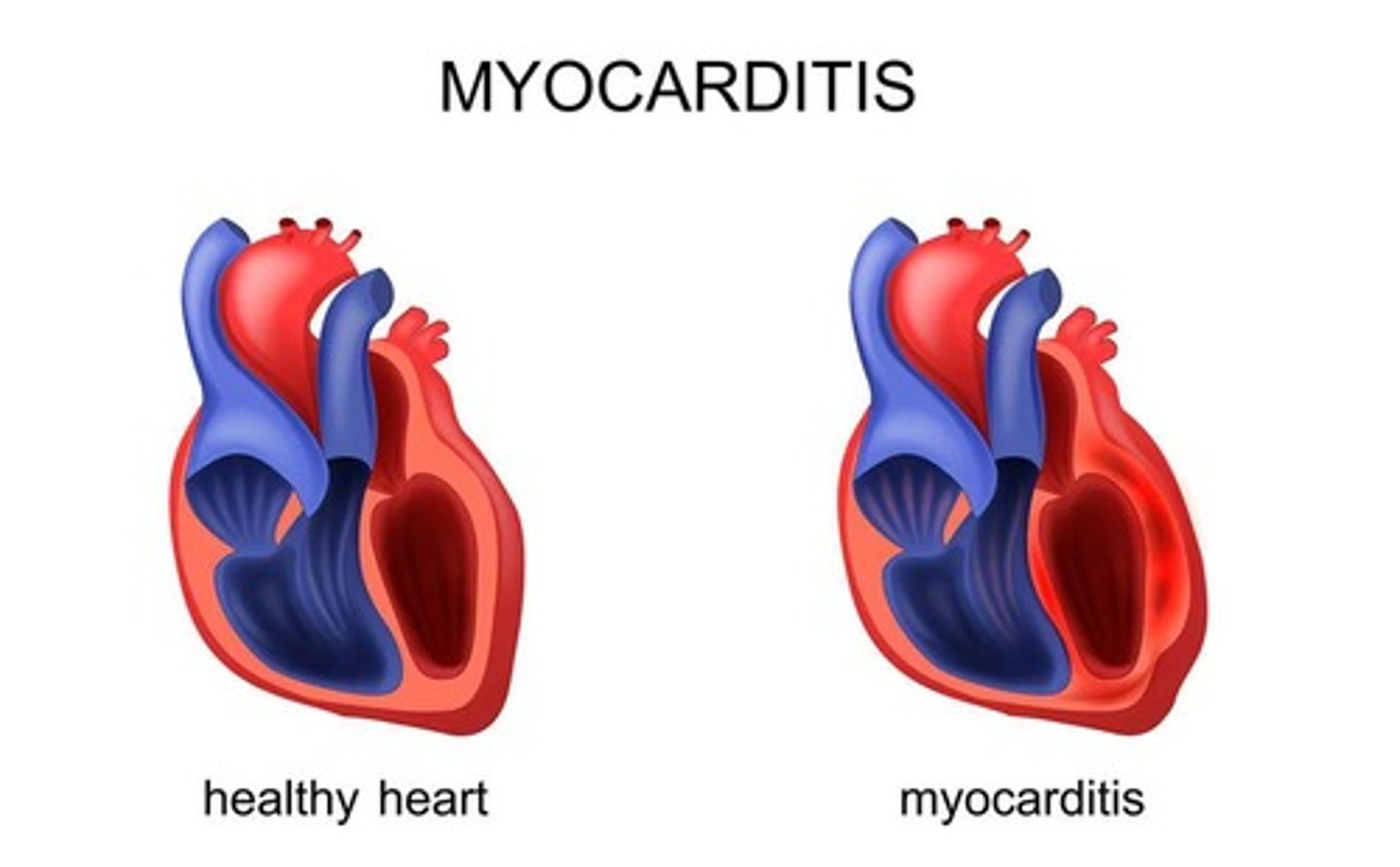
Myocarditis
Inflammation of the myocardium—the muscular walls of the heart.
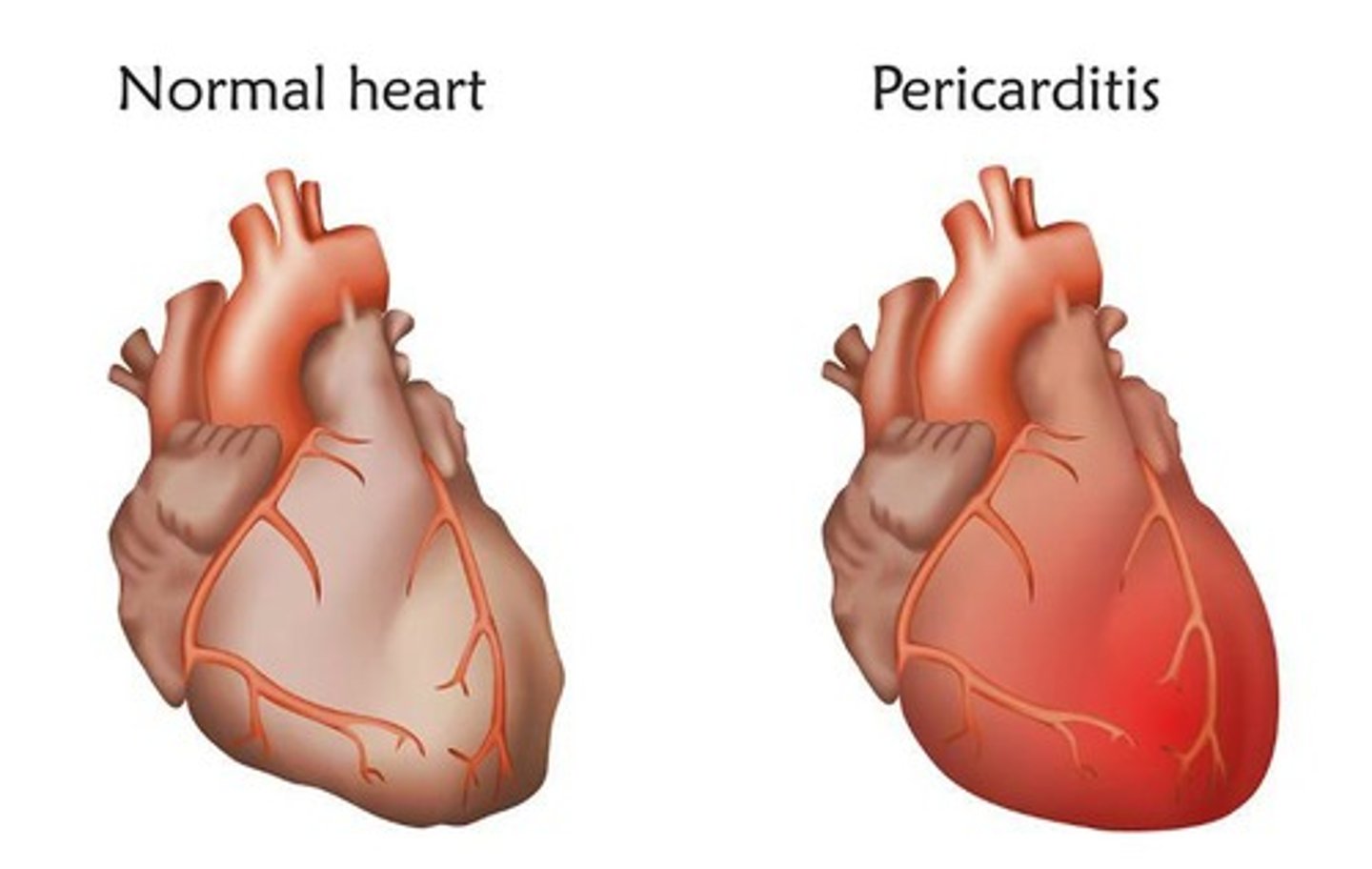
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the pericardium—the membranous sac around the heart.
Bacteremia
The presence of bacteria in the bloodstream; it can be, but is not always, a sign of disease.
Transient bacteremia
The temporary presence of bacteria in the blood.
Septicemia
A systemic disease in which the patient experiences chills, fever, and prostration (extreme exhaustion), and has bacteria and/or their toxin in their bloodstream.
Lymphadenitis
The inflammation and swelling of the lymph nodes.
Lymphadenopathy
Diseases of lymph nodes.
Lymphangitis
Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels.
CNS (central nervous system)
Consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the three meninges that cover the brain and spinal cord.
There are no indigenous microbiota of the nervous system.
True
trauma (fracture or medical procedure), via the blood and lymph to the CSF, or along the peripheral nerves.
Microbes gain access to the CNS through?
Encephalitis
Inflammation of the brain.
Encephalomyelitis
Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges that surround the brain and spinal cord.
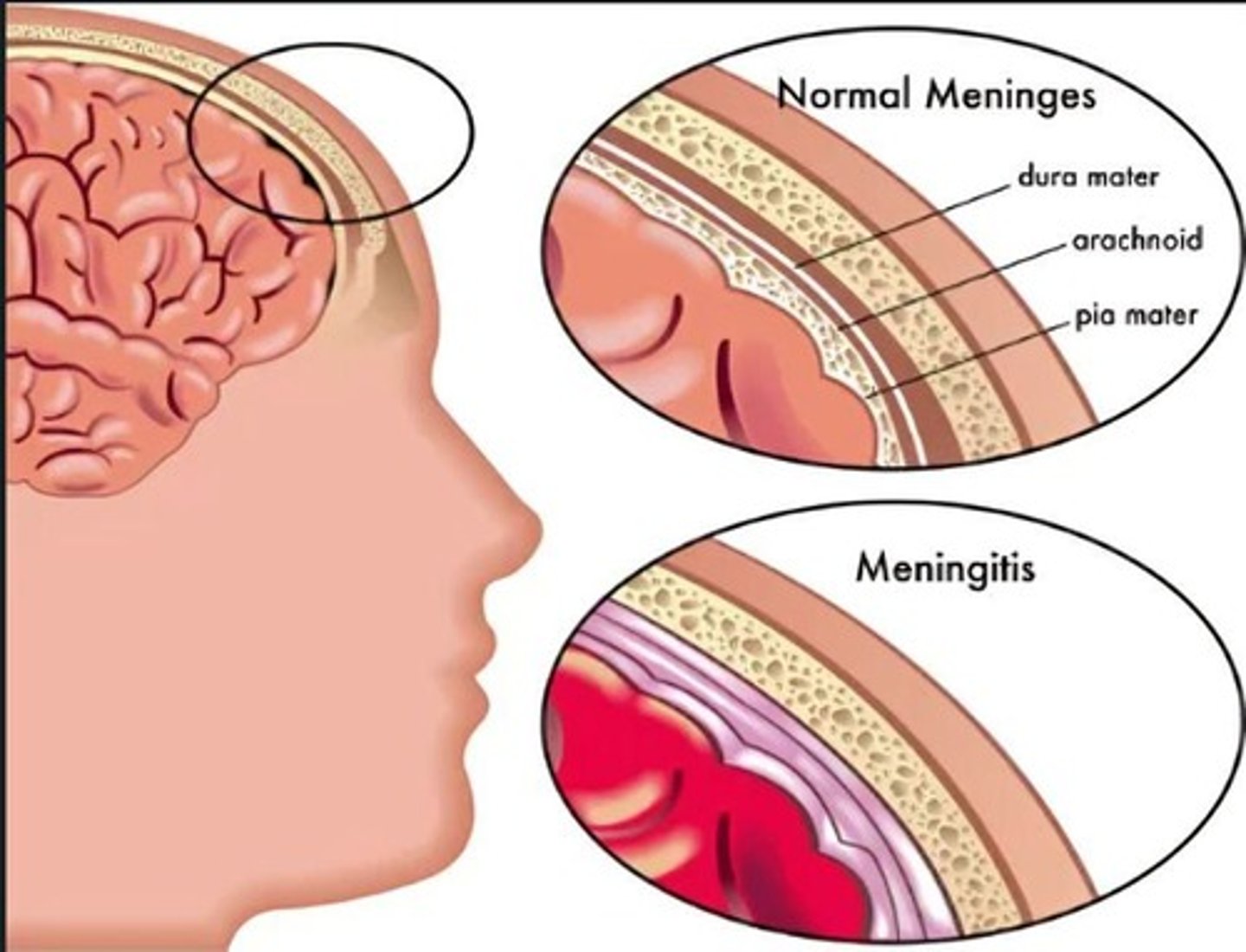
Meningoencephalitis
Inflammation of the brain and meninges.
Myelitis
Inflammation of the spinal cord.
Causes of Meningitis
Can be caused by ingestion of poisons, the ingestion or injection of drugs, a reaction to a vaccine, or a pathogen.
Pathogen types for Meningitis
If caused by a pathogen, it might be a virus, a bacterium, a fungus, or a protozoan.
Viral Meningitis
Sometimes referred to as 'aseptic meningitis,' because in about 50% of the cases, the pathogen cannot be identified.
Viral Meningitis causes
May be caused by a virus that specifically infects the meninges, or may be the result of an immune reaction to a virus that does not specifically infect the brain (e.g., chickenpox, measles, and rubella).
Types of viruses causing Meningitis
Include enteroviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, mumps virus, arboviruses, poliovirus, adenoviruses, measles virus, herpes simplex, and varicella virus.
Viral infection
Most common causes of Meningitis
Enteroviruses
Major cause of Viral meningitis in the United State
Bacterial Meningitis
Historically, the three major causes have been (1) Haemophilus influenzae (the primary cause in children), (2) Neisseria meningitidis (the primary cause in adolescents), and (3) Streptococcus pneumoniae (the primary cause in the elderly).
Less common causes of Bacterial Meningitis
Include Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella, and Klebsiella.
Major causes of Bacterial Meningitis in neonates
Include Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B, β-hemolytic streptococci), Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes.
Bacterial Meningitis
Early neurologic symptoms include fever, dizziness, headache, convulsions, stiff neck, minor paralysis, sore throat, coma, and vomiting.
Haemophillus Influenzae
Primary cause of bacterial meningitis in Children
Neisseria Meningitidis
Primary cause of bacterial meningitis in Adolescence
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
Primary cause of bacterial meningitis in Elderly
Streptococcus agalactiae, Escherichia coli and other members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, and Listeria monocytogenes.
Primary cause of bacterial meningitis in neonates
Protozoa causing CNS disease
Include Toxoplasma and Trypanosoma.
Amoeba causing CNS disease
May cause meningoencephalitis; examples include Naegleria and Acanthamoeba.
Fungus causing CNS disease
Cryptococcus neoformans.
Toxins causing CNS disease
Include botulinum toxin (the exotoxin that causes botulism) and tetanospasmin (the cause of tetanus).
Opportunistic infections
Opportunistic pathogens are microbes that usually do not cause disease but can become harmful under certain conditions.
Opportunistic infections (OIs)
Infections that rarely occur in healthy, immunocompetent individuals, often causing only mild infections, but are life-threatening in immunosuppressed individuals.
Aspergillosis
A mould infection that can become a systemic infection in immunosuppressed individuals.
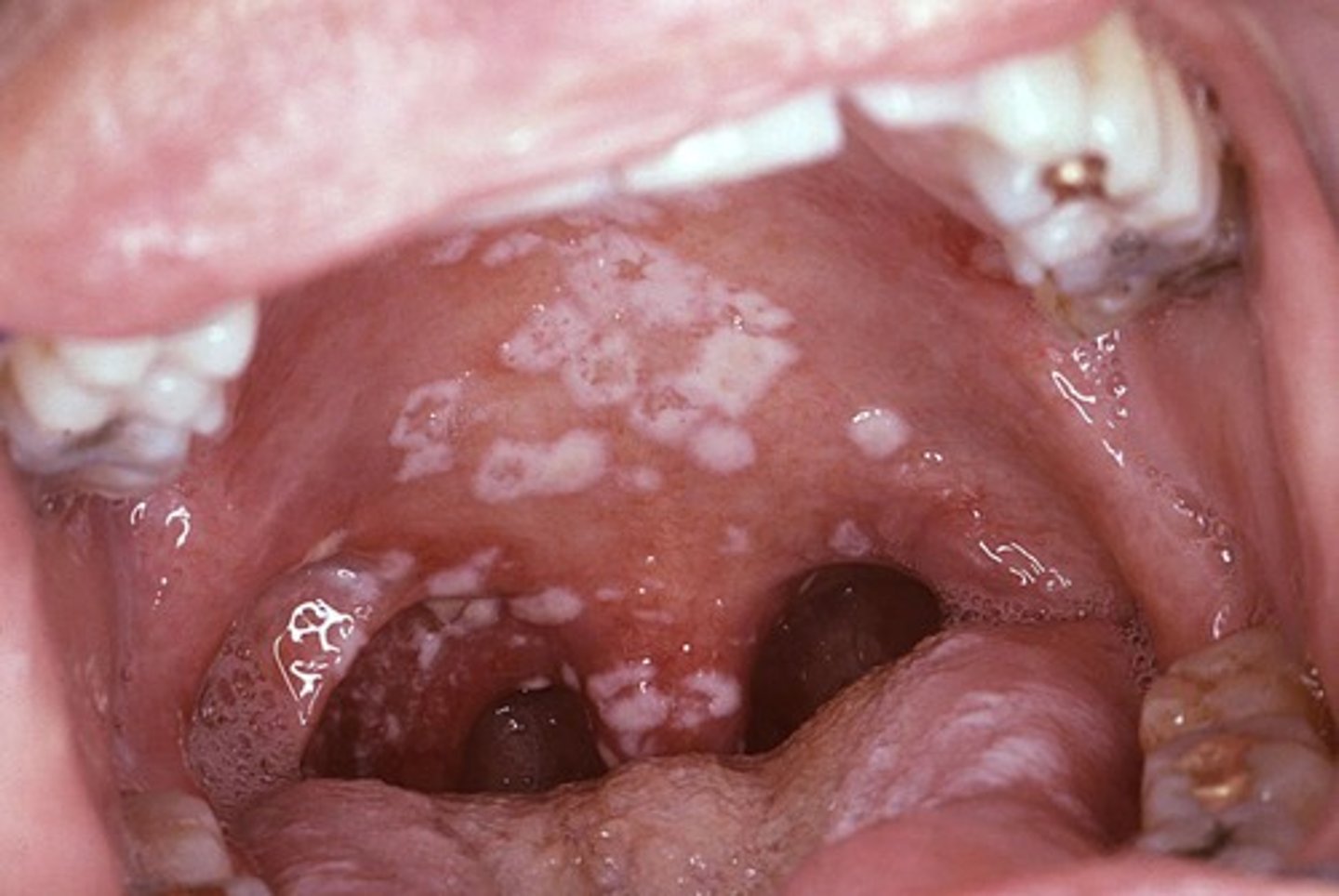
Candidiasis
A yeast infection of the mouth (thrush), throat, or vagina that can become a systemic infection in immunosuppressed individuals.
Cytomegalovirus infection
Can cause eye disease that can lead to blindness and serious problems for immunocompromised individuals or infected newborns.
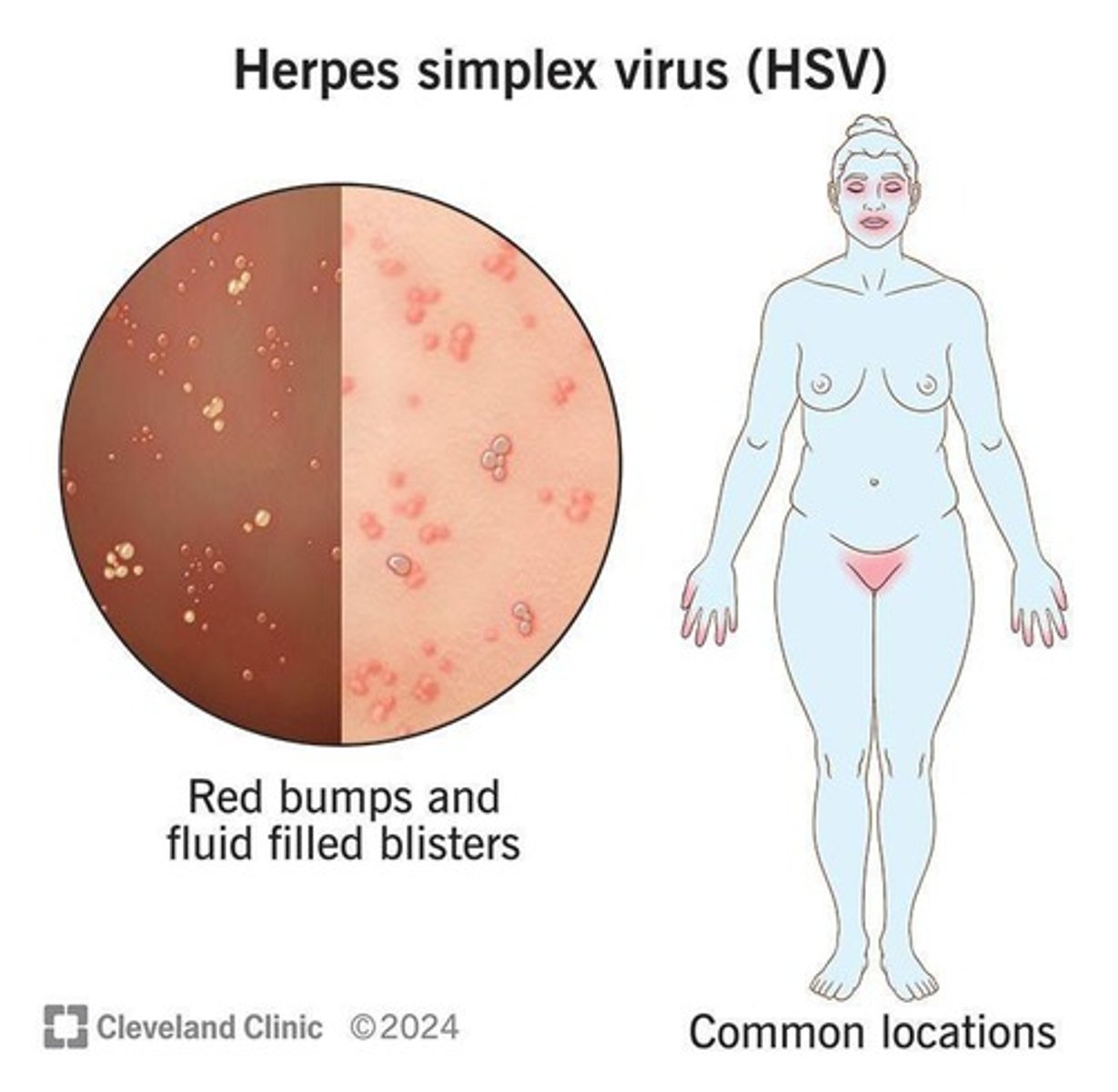
Herpes simplex virus infections
The cause of oral herpes (cold sores) and genital herpes, which are more frequent and severe in immunosuppressed individuals.
Malaria
A parasitic infection that is more common and severe in immunosuppressed individuals.
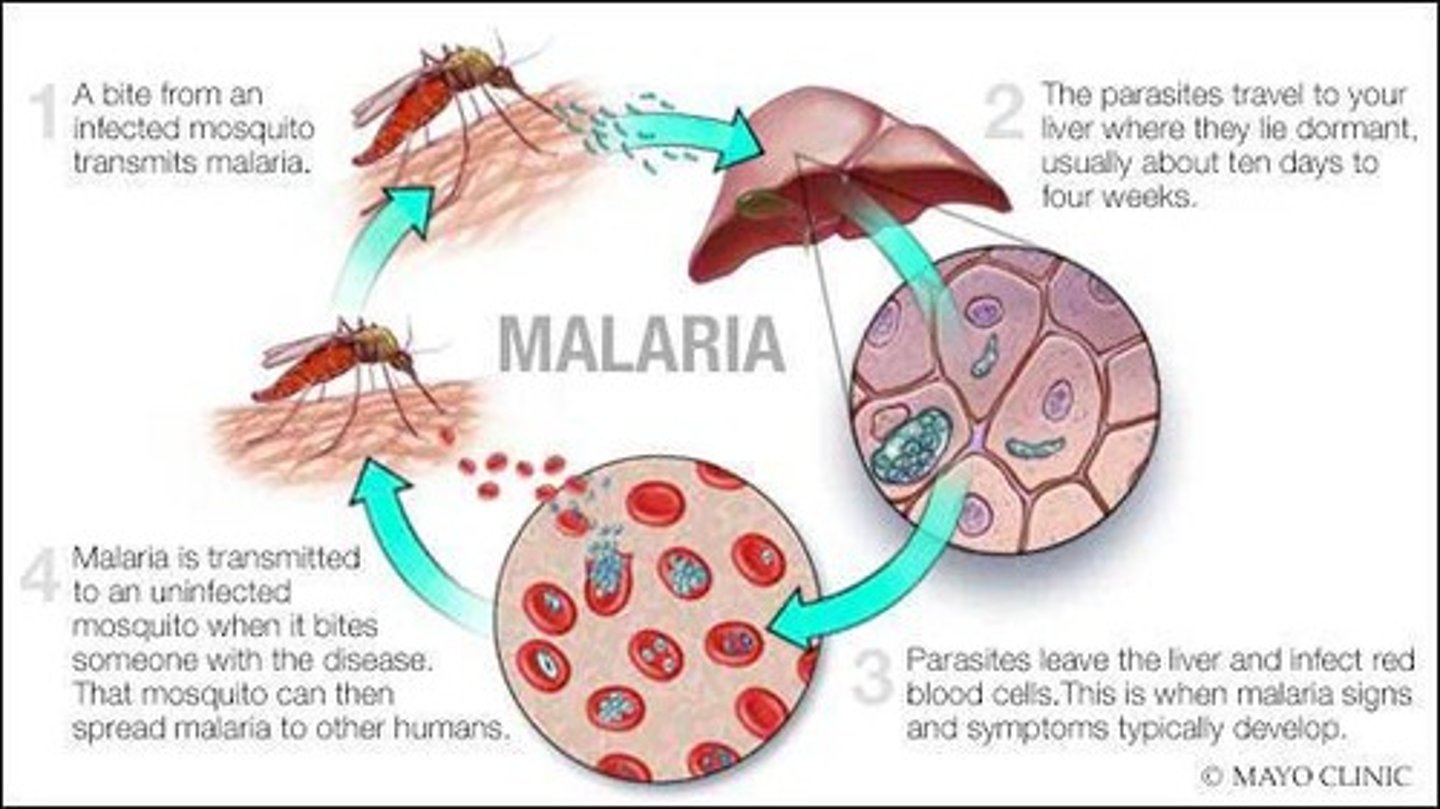
Plasmodium spp.
Malaria is caused by what microorganism?
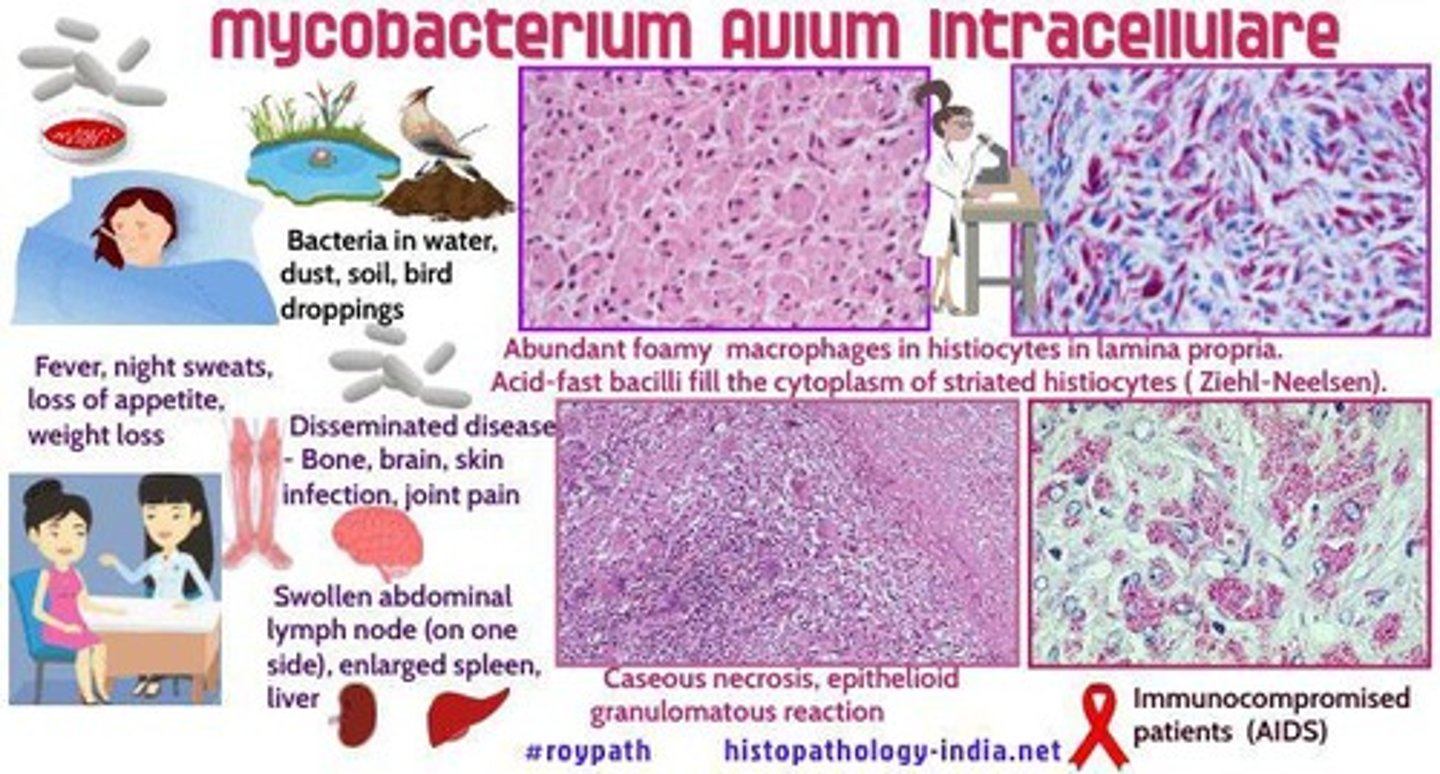
Mycobacterium avium complex
A bacterial infection that can cause recurring fevers, problems with digestion, and serious weight loss.
Pneumocystis pneumonia
A fungal infection that can cause a fatal pneumonia, primarily affecting people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or on immunosuppressive therapy.
Pneumocystis pneumonia
This Infectious disease was once the major killer of AIDS patients
Pneumocystis jirovecii
Pneumocystis pneumonia is cause by what microorganism?
Toxoplasmosis
A protozoal infection of the eyes and brain, contracted by eating contaminated undercooked meat or contact with cat feces.
Tuberculosis (TB)
A bacterial lower respiratory infection that can cause meningitis, more common and severe in immunosuppressed individuals.
Emerging diseases
New infectious diseases that continue to emerge due to changes in human demographics, ecological changes, increased travel, and weakened public health systems.
Reemerging diseases
Previously contained or eradicated diseases that are reemerging due to pathogen mutations and genetic recombinations.
Causes of emerging diseases
Include changes in human demographics and behavior, ecological changes like deforestation and climate change, and misuse of antibiotics.
Infectious diseases that have reemerged
Include cholera, dengue fever, diphtheria, malaria, Rift Valley fever, TB, yellow fever, and infections caused by methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Infectious diseases that have emerged in the last 30 years
Include Avian influenza, Cryptosporidiosis, E. coli O157 infections, Ebola hemorrhagic fever, Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, Hendra virus infection, HIV infection and AIDS.
pericarditis
inflammation is a key cause of chest pain that gets worse when you lie down and often feels better when you sit up and lean forward.
viral meningitis
Type of meningitis that is usually less severe
Acanthamoeba
a genus of microscopic, free-living amoebae found worldwide in various environments, including soil, fresh water, and even air. While most people are exposed to this throughout their lives without getting sick, it can act as an opportunistic pathogen and cause serious, though rare, infections in humans.
Avian influenza (bird flu) is an emerging infectious disease that appeared within the last 30 years.
True
Cryptosporidiosis is considered one of the more recently recognized emerging infections.
True
E. coli O157 infections — including those causing HUS — are part of the newer emerging disease group.
True
Ebola hemorrhagic fever is included among the emerging infectious diseases of the last 30 years.
True
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is an example of a newly emerged infectious disease of the last 30 years.
True
Hendra virus infection is a recently emerged infectious disease of the last 30 years.
True
HIV infection & AIDS are considered emerging infectious diseases of the last 30 years.
True
Human monkeypox is an example of an emerging infectious disease of the last 30 years.
True
Lassa fever is one of the infectious diseases recognized as an emerging disease of the last 30 years.
True