Powers & Scientific Notation
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is a variable?
A symbol (usually a letter) representing an unknown number.
What is a constant?
A number on its own.
What is a coefficient?
A number multiplying a variable (e.g., 4 in 4x).
What is a term?
A single number, a variable, or a product of numbers/variables.
What is an expression?
A collection of terms (with + or – signs).
What is an equation?
An expression with an equals sign.
What does “raising a number to a power” mean?
Multiplying it by itself repeatedly.
Example: 2 × 2 × 2 = ?
23
Example: X × X × X = ?
X3
What terms also mean “power”?
Indices, exponents.
In 106, what is the base?
10
What is the exponent/power?
6.
Rule 1 — multiplying with same base:
am x an = am + n.
Rule 2 — dividing with same base:
am ÷ an = am - m.
Rule 3 — zero power:
a0 = 1/an.
Rule 4 — negative power:
a-n = 1/an.
Rule 5 — powers raised to powers:
(am)n = am x n.
Rule 6 — reciprocal rule:
1/an = a-n.
Simplify: 104 × 102.
106.
Simplify: 106 ÷ 103.
103.
Simplify: (a3 x a-6) / (a5).
a-8.
Simplify: (5×2)(2×3).
10×5
What do you do if bases are different?
None of the rules apply; keep bases separate.
What happens when a full term is raised to a power?
Every element is raised (e.g.,(3×2)4 = 34×8).
Example: (ab2)4.
a4b8.
What is the reciprocal of a number n?
1/n = n-1.
Reciprocal of 7?
1/7.
Reciprocal of 3/2?
2/3.
Reciprocal of 1.6?
1 / 1.6.
How do you remove a square?
Raise both sides to 1/2.
Example: a2 = 81.
a = 9.
R3 = 125.
R = 5.
What is scientific notation?
A way to express numbers using powers of 10:
a × 10^x.
What must “a” satisfy?
1 ≤ a < 10.
Rule for numbers > 1?
Count decimal “jumps” to the left; exponent is positive.
Example: 45.
4.5 × 101.
Example: 45,000.
4.5 × 104.
Example: 450,000,000.
4.5 × 108.
Rule for small numbers (< 1)?
Count decimal jumps to the right; exponent is negative.
Example: 0.45.
4.5 × 10-1.
Example: 0.0045.
4.5 × 10-3.
Example: 0.0000045.
4.5 × 10-6.
If the decimal moves left, what happens to the power?
Power increases.
If the decimal moves right?
Power decreases.
Why is it called a seesaw?
As one side increases, the other decreases.
Covert 3.02 × 104.
30200.
Convert 8.9 × 10-2.
0.089.
Convert 4.81× 10-5.
0.0000481.
Method for Multiplying?
Multiply the “a” numbers; add the exponents.
Example: 300,000 × 50,000.
3 × 105 × 5 × 104 = 1.5 × 1010.
Method for dividing?
Divide the “a” numbers; subtract exponents.
Example: 450,000,000 ÷ 90,000.
4.5 × 108 ÷ 9 × 104 = 0.5 × 104 = 5 × 103.
Requirement for adding/subtracting?
Powers of 10 must match.
Example: (2.6 × 104) + (4 × 103).
2.6 × 104 + 0.4 × 104 = 3.0 × 104.
Example: (1.2 × 106) - (5.0 × 108).
Convert 1.2 × 10^6 → 0.012×10^8:
-4.99 × 108 ≈ -5.0 × 108.
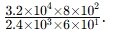
Example from notes:
Apply multiply/divide rules → simplify → express with 2 s.f.
25,000×4,000,000.
2.5 × 104 × 4 × 106 = 1.0 × 1011.
25,000÷5,000,000
2.5 × 104 ÷ 5 × 106 = 0.5 × 10-2 =5 × 10-3.
1.8 × 10-2 + 2 × 10-3.
Convert second term → 0.2×10^{-2}.
Sum = 2.0 × 10-2.
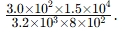
In what order do you do this?
Multiply → divide → express to 2 s.f.
Why are powers useful in algebra?
They provide condensed ways to express repeated multiplication.
Why is scientific notation essential in science?
It allows huge or tiny numbers to be written and calculated efficiently.