alcohols and derivatives aldehydes and ketones
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
are alcohols water soluble
short chain alcohols are water soluble but long chain (>5) insoluble
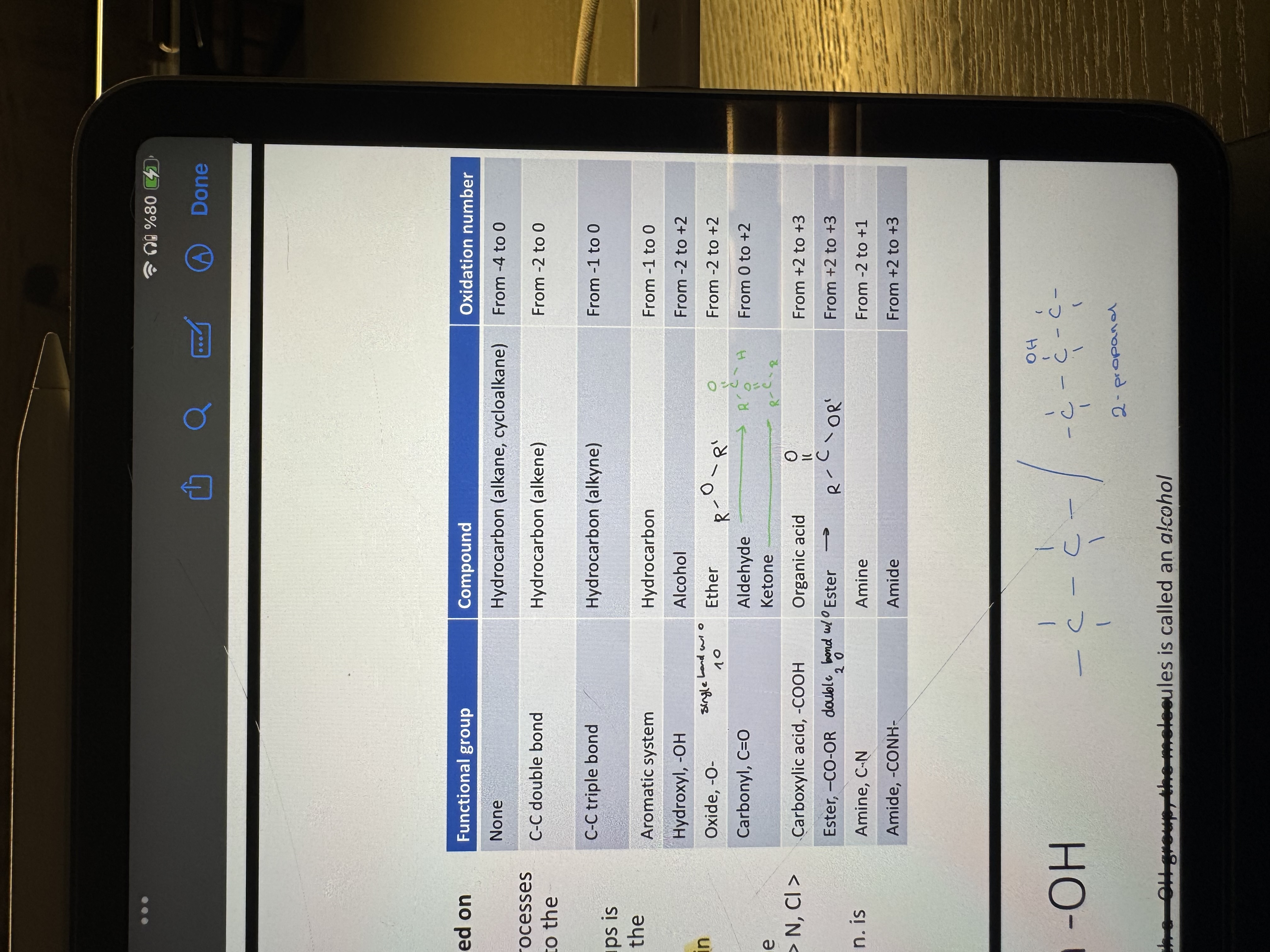
study and memorize the functional groups based on their oxidation state
what is the name of the benzene that is an alcohol
phenol
what are alcohols used as
disinfectants, paint thinners, recreational purposes
why does alcohol have a hydrophobic effect (bu tam doğru bi soru mu anlamadım ama hydrophobiccen direk delta S>0 yani entropy var)
due to entropy increase (increased mobility/ disorder/ degrees of freedom)
what kind of alcohol is in hand sanitizers
ethanol
how do hand sanitizers work
at 70% ethanol the interactions between proteins and water are replaced by interactions with ethanol. these weak forces destabilize the structure of proteins, that lose their function. viral proteins constituents of the capsid destabilized, and the virus loses its infectivity
is ethanol ampiphatic
yes it’s both hydrophobic (Ch3CH2-) and hydrophilic (-OH)
what does thio- indicate
presence of sulfur
what is the substituent in thiols
-SH sulfhydryl group
why are thiols more volatile than alcohol
because sulfur is a poor hydrogen bond acceptor
what do thiols react with to form a thioester
acids
why are ethers even more volatile
because it has dipole dipole interactions
are ethers soluble in water
poorly soluble in water
what is alcohols’ reactivity due to
-the polarized c-o bond
-the presence of lonr pairs on the oxygen, making the alcohol a nucleophile
what happens if we oxidize an alkane twice
first oxidation it becomes an alcohol
second oxidation it becomes a ketone/aldehyde (primary alcohol creates aldehyde secondary alcohol creates ketone)
alcohols properties
on/off switch to signal events inside/ outside the the cell
breakdown/ synthesis intermediate metabolites
attachment points for several chemical modifications (alcohols are reversable they can turn into something and then turn back on)
what do we get when we oxidize a phenol
quinone
what to alcohols react with to form esters
acids (organic or inorganic)
what are phosphate esters’ job in biology
-in dna and rna nucleotides are linked together via phosphodiester bonds
-amino acids with -OH functions can be modified to form phosphate esters, modifying the protein structure and function
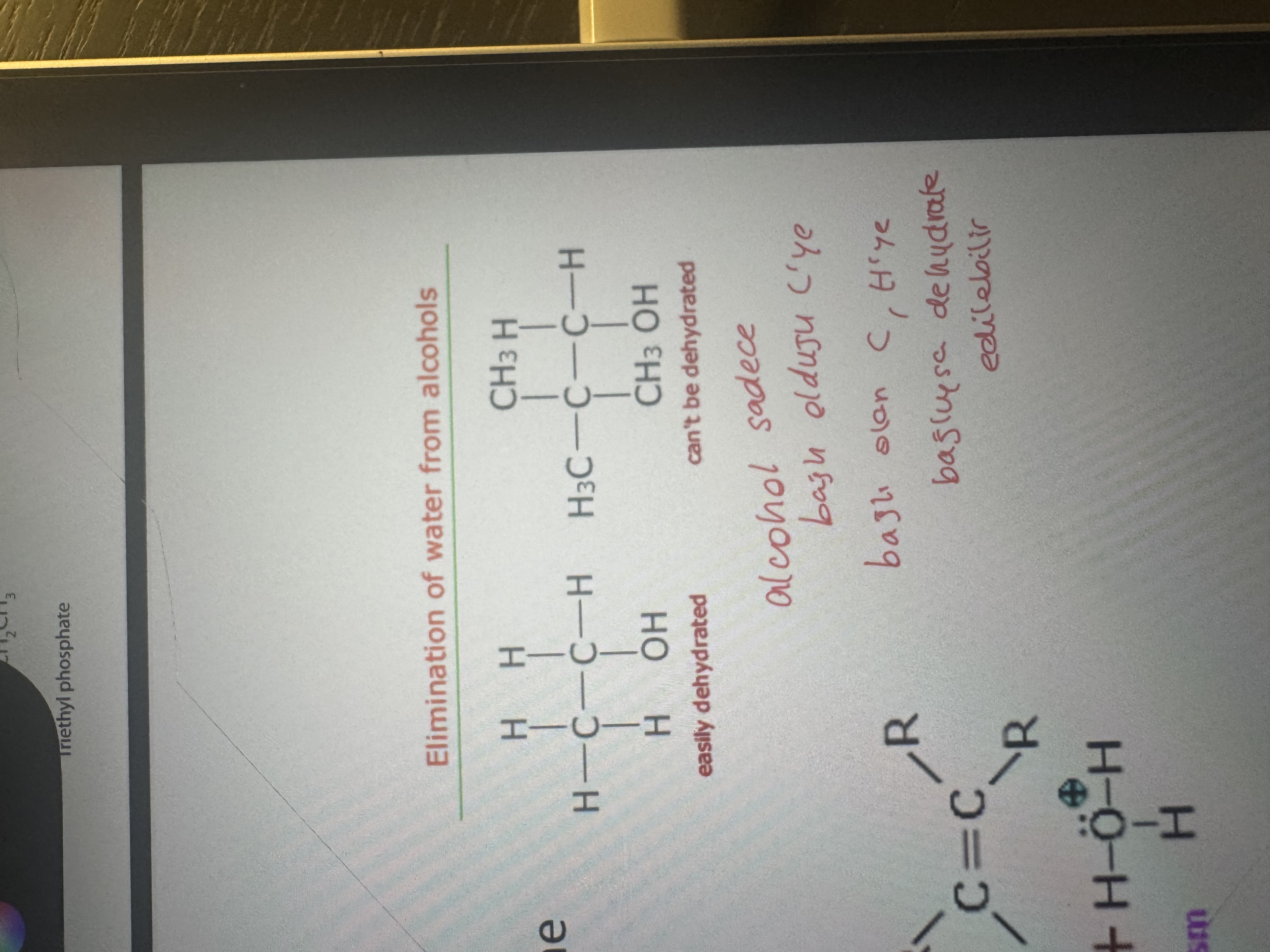
when can an alcohol be dehydrated
only if there is a hydrogen on the carbon next to the one carbon atom bearing the -OH function
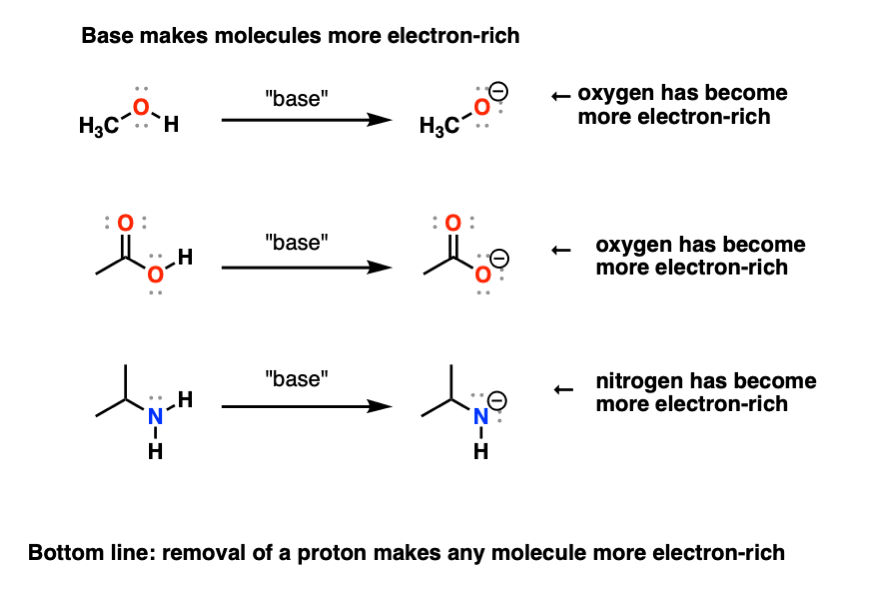
are alcohols acids or bases
they are amphoteric (electron withdrawing groups make the alcohol more acid and electron donating ones make them less acid) (positively charged acidic negatively charged basic most of the time)
which one is more acidic alcohols or thiols and why?
thiols are more acidic because the S-H bond is longer and weaker than the C-H bond
sulfur is more polarizable
thiols are very good nucleophiles (since the lone pairs are less attracted by the atom thanks to lower electronegativity)
with which method are the conjugated bases stabilized
resonance (electron delocalization in molecules when there is multiple lonr pairs)
what protonates alcohols
strong acids
what is protonation
the chemical process where a molecule or ion gains a proton
what is a cystine
a covalently-linked dimer from the oxidation of two cysteine molecules
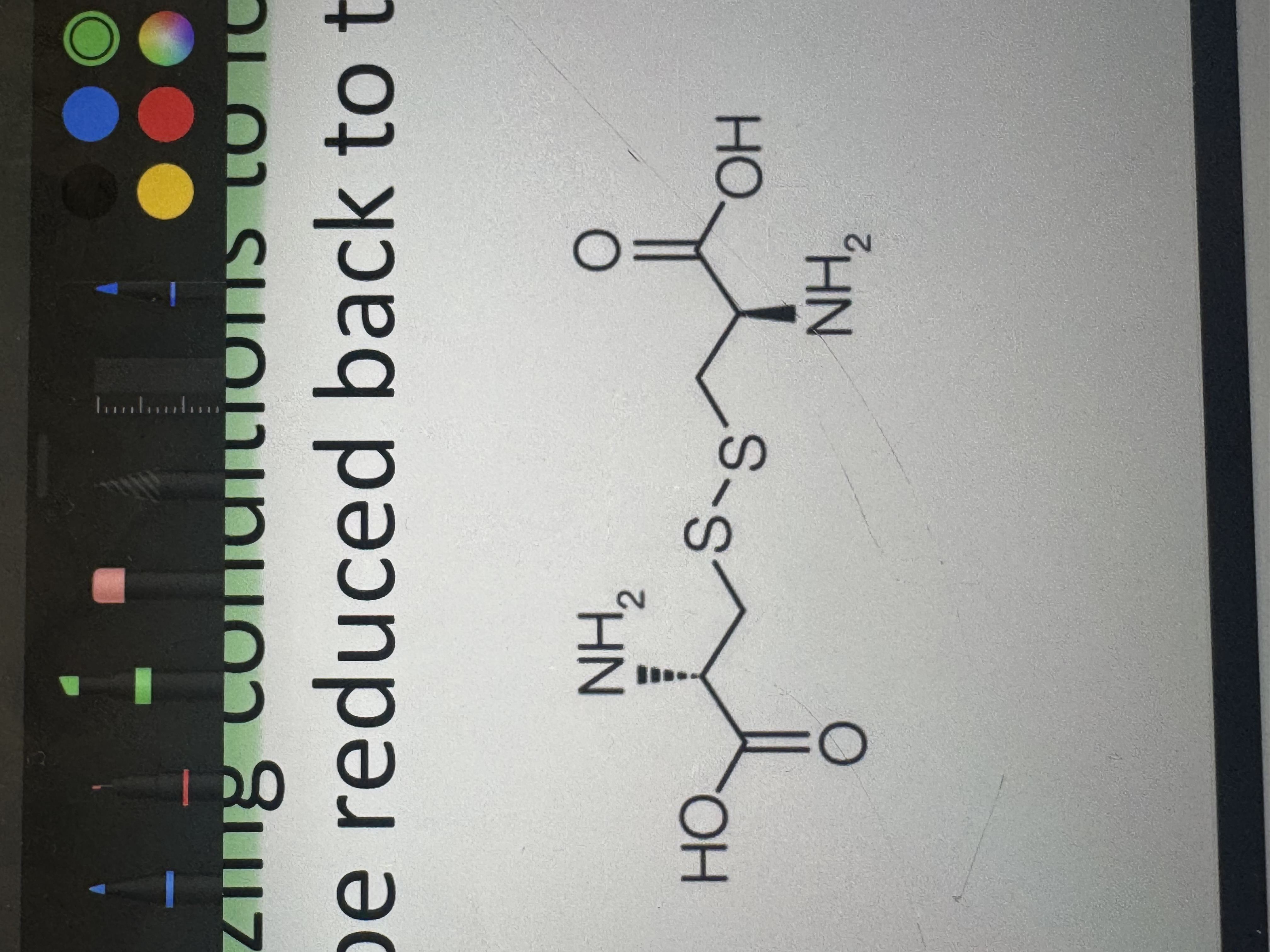
which amino acid has a thiol function
cysteine (natural component of proteins)
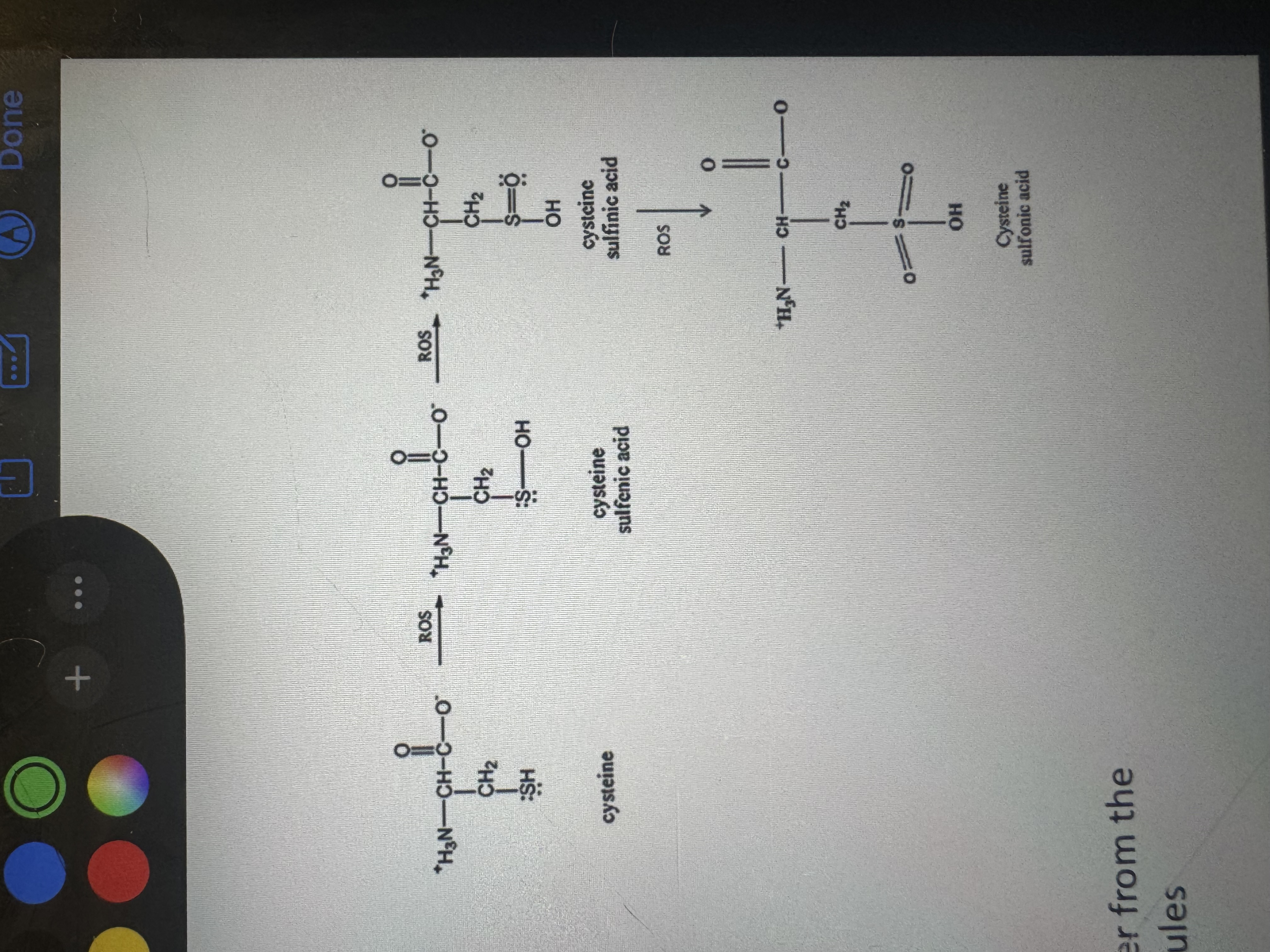
(under stress conditions it can be oxidized to a variety of acid forms)
what is the hybridization of the carbon atom in carbonyl groups
sp2
what is the composition of carbonyl groups
planar with 120 degree angles between the bonds
what are the carbon atoms adjacent to a carbonyl are called
carbon 2 and carbon alpha
what is a keto-enol tautomerism
when at least a hydrogen is present on the alpha carbon, aldehydes and ketones can go under a rearrangment (tautomerization) to an enol
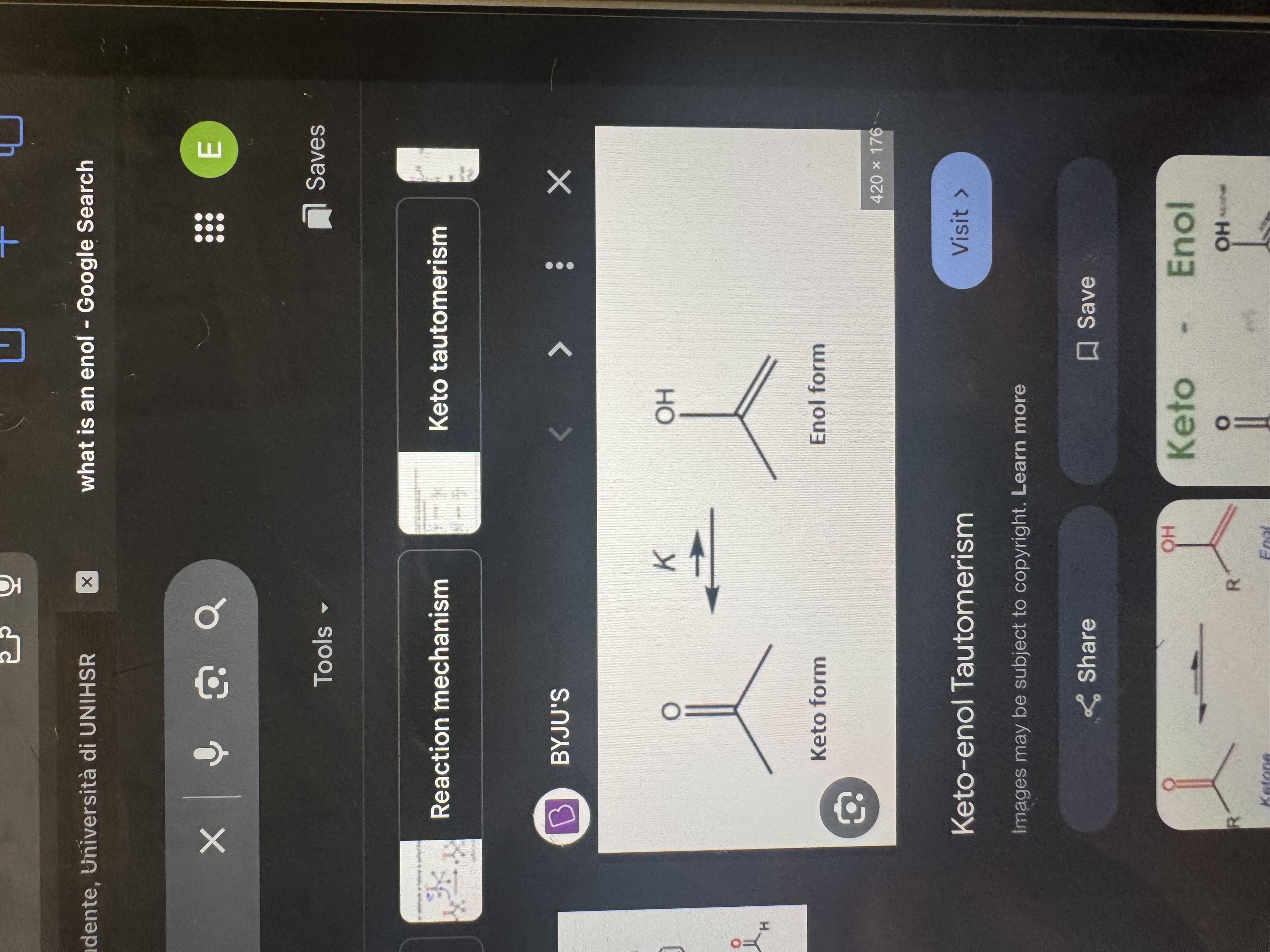
keto and enol properties

which is more stable and favorable keto form or enol form
keto form
what is an enol
alkene molecule containing a hydroxyl group
why is the keto enol tautomerism not a resonance
because it involves the movement of atoms, specifically a proton and the relocation of electrons, resulting in two different chemical compounds with distinct features (yani sadece bondun yeri değişse resonance olur ama burda o ya h de bağlandığı için sayamayız galiba)
sunumun 16-17. sayfasındaki anlamadığım yerler var onları deganoya sormayı unutmamak için not alıuorım
wowoowowow
what are methanal - ethanal - 2-propanone (dimethyl ketone) common names
methanal = formaldehyde
ethanal = acetaldehyde
2-propanone = acetone
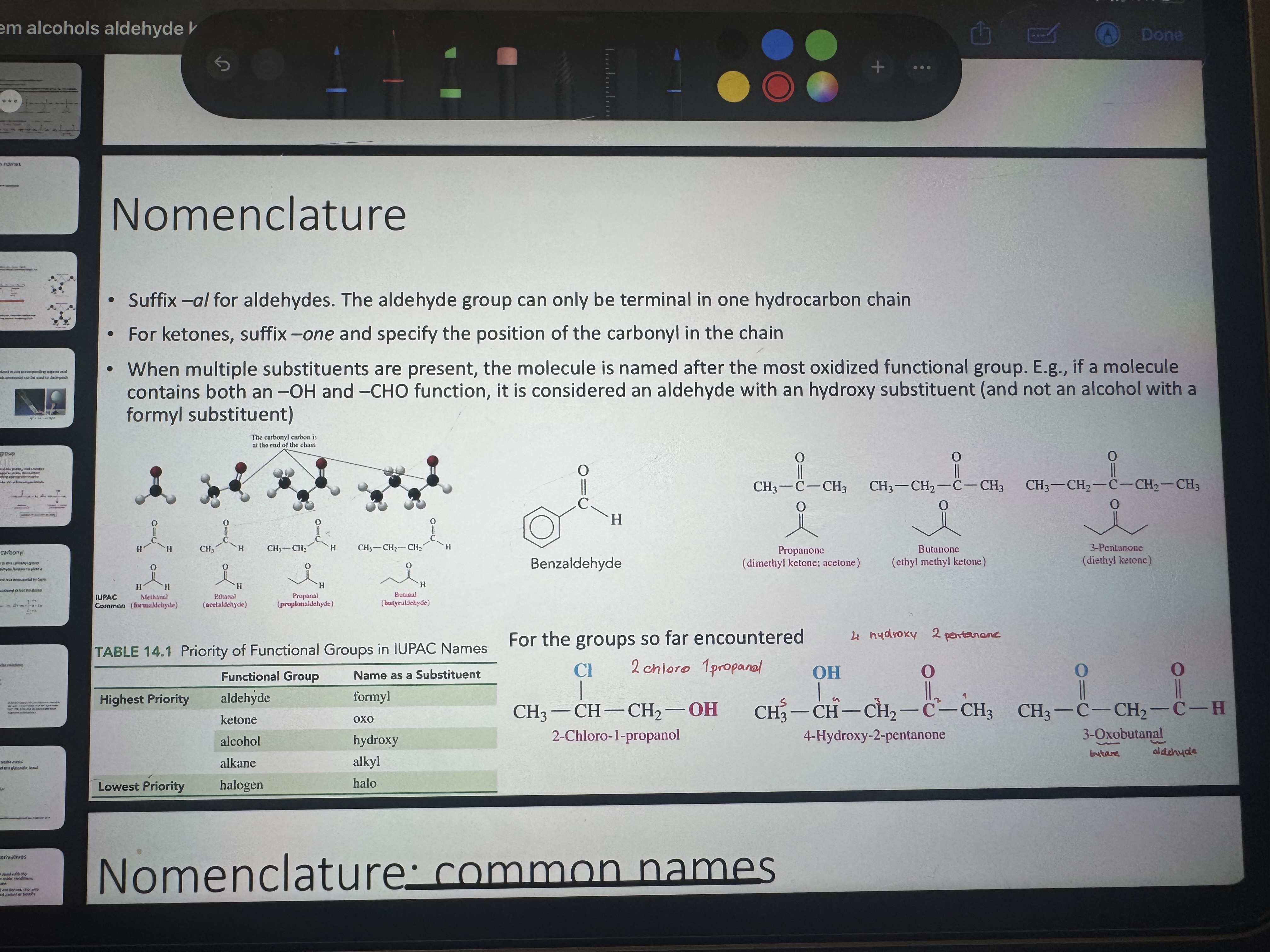
name all these
alr named on the photooooo
between nucleophiles and electrophiles which one is a donor and which one is an acceptor in a hydrogen bond
nucleophiles are donors (they attack) and electrophiles are acceptors
in a hydrogen bond is carbonyl an acceptor or a donor
carbonyl is an acceptor because carbonyls are electrophiles
going from alkane to aldehyde to ketone to alcohol does the boiling point increase or decrease
the boiling point increases
alkane 0 degrees
aldehyde 49 degrees
ketone 56 degrees
alcohol 97 degrees
why are pure ketones/aldehydes low boiling liquids
they have dipole dipole interactions and the carbonyl group has a strong dipole
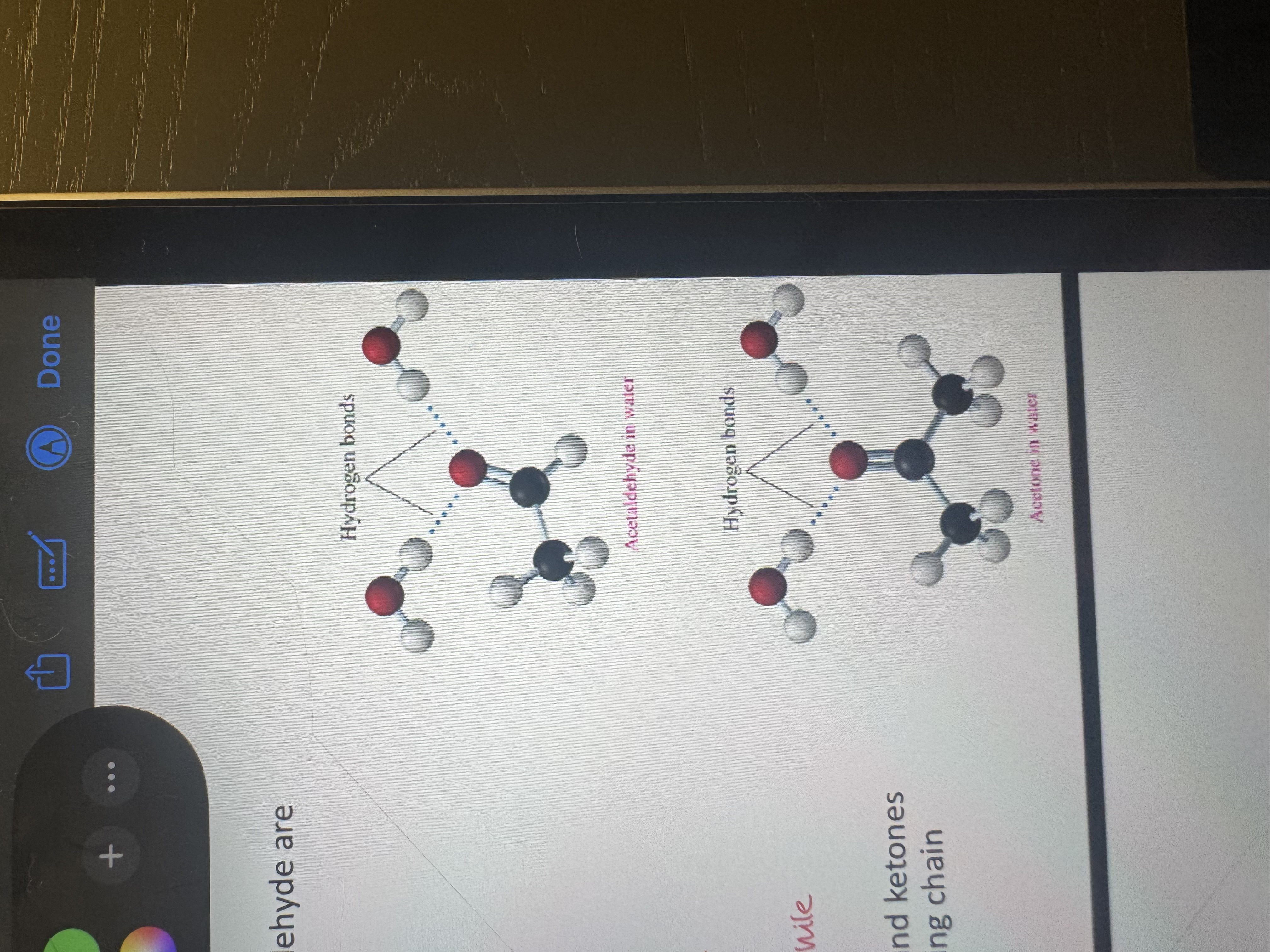
aldehyde and acetone in water creating hydrogen bonds
can aldehydes and ketones be oxidized to the corresponding organic acids
only aldehydes can ketones can’t
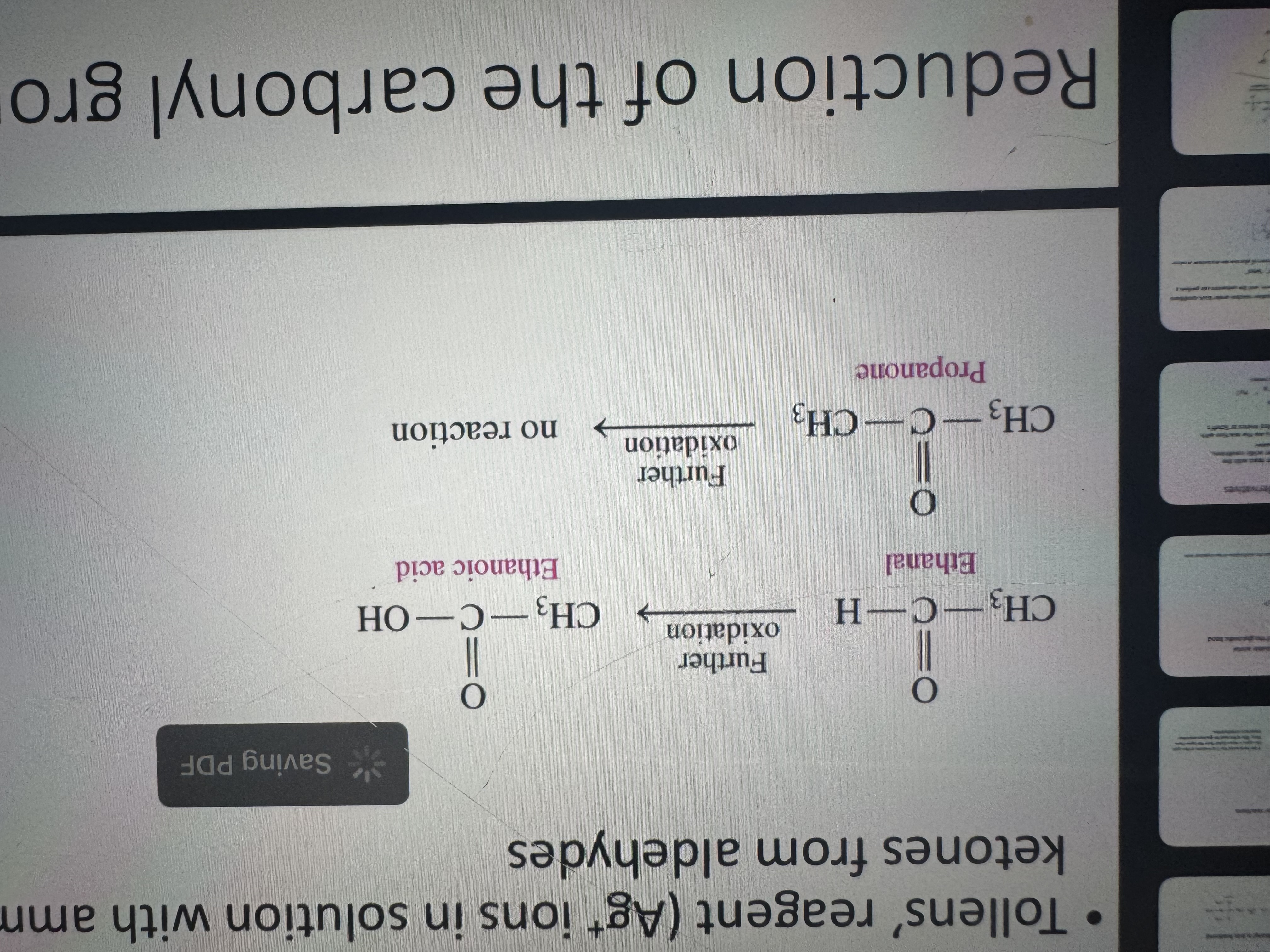
what is used to distinguish ketones from aldehydes
tollens’ reagent (Ag+ ions in solution with ammonia)

what are aldehydes and ketones reduces by
H2 or NaBH4 (sodium borohydride) and catalyst such as nickel, platinum, palladium
aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols

what do we get when an alcohol reacts with an aldehyde or ketone
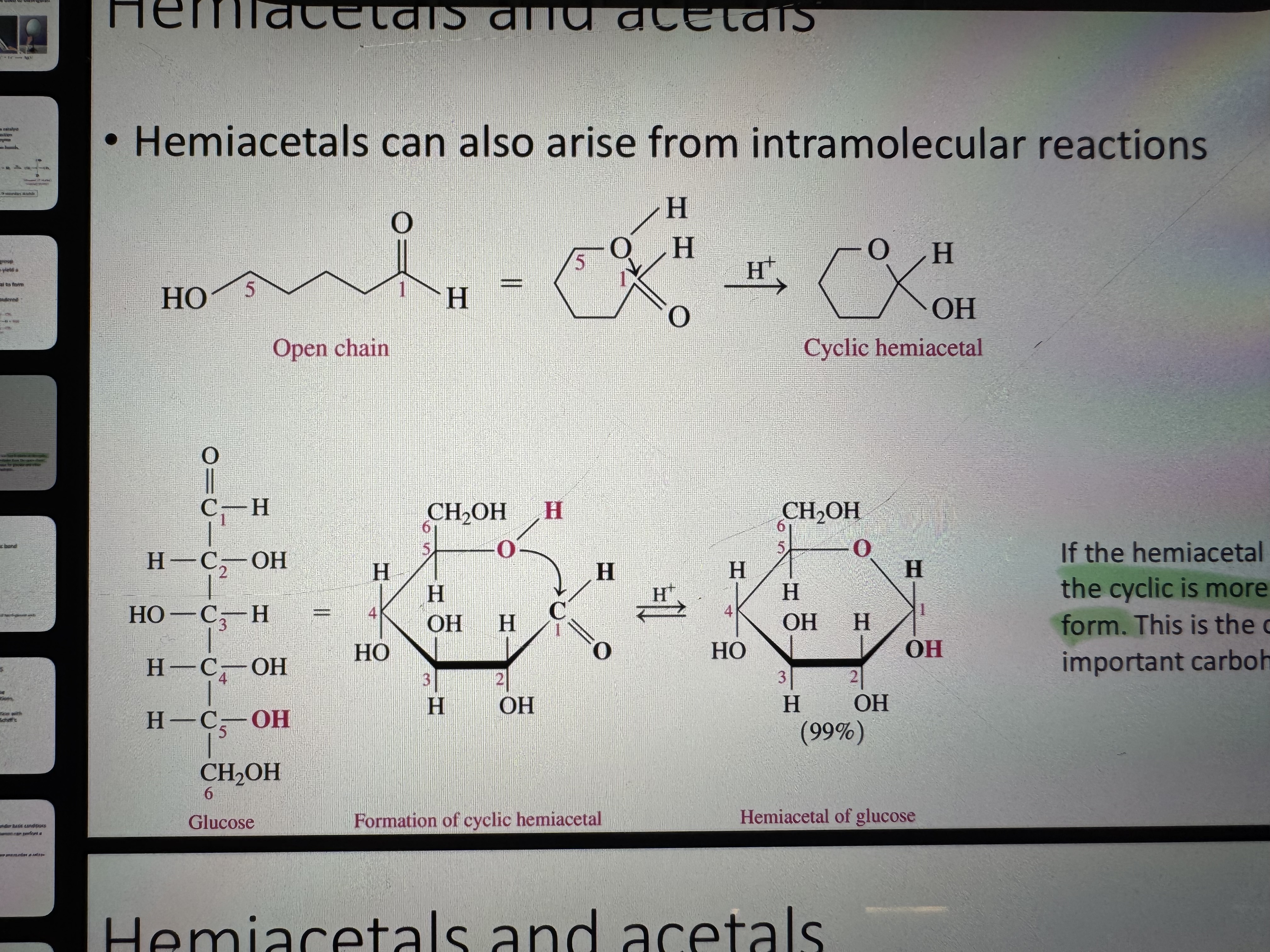
hemiacetal (very unstable)

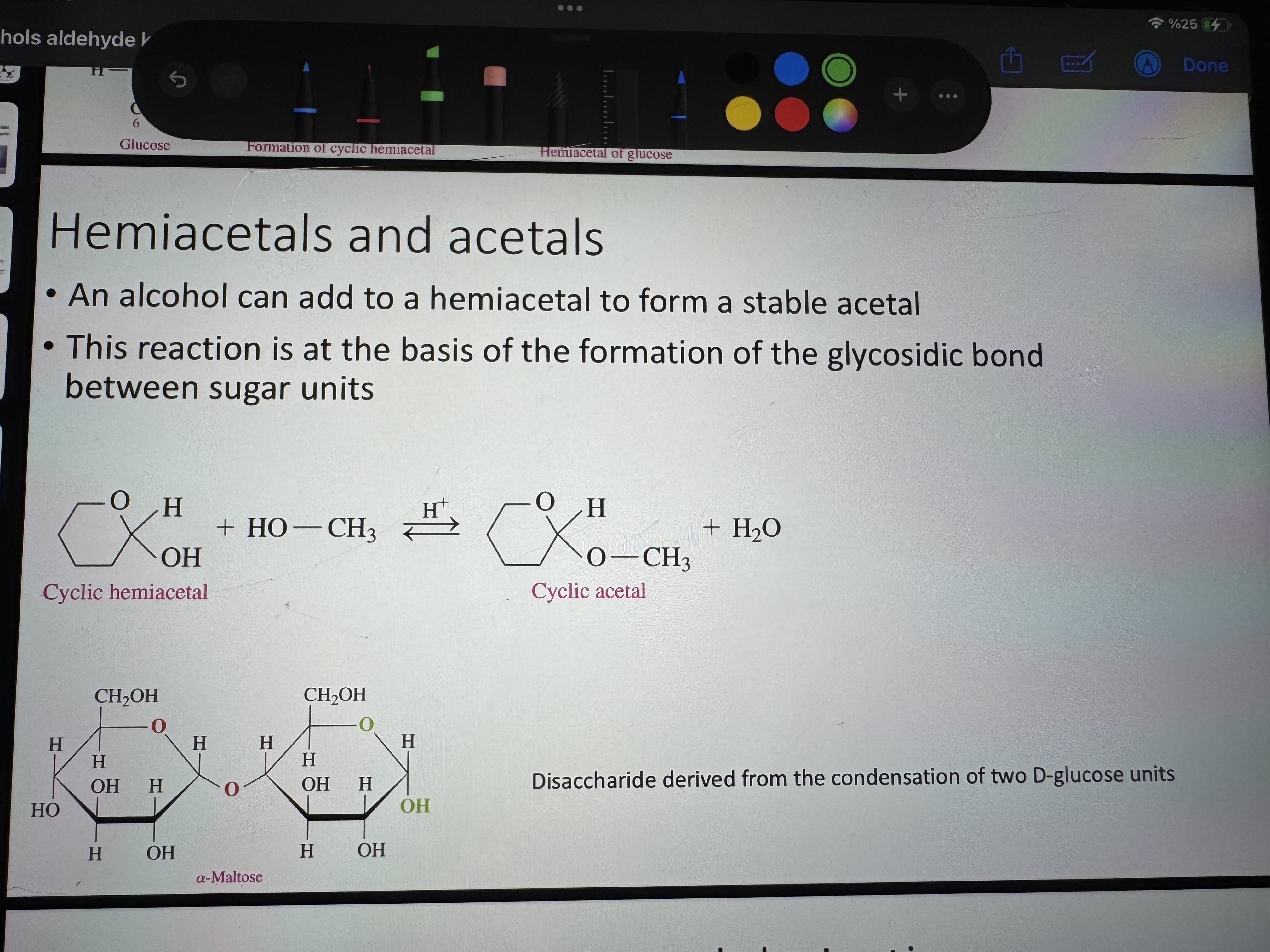
what forms when an alcohol is added to a hemiacetal
acetal (more stable than hemiacetal)

which one is more stable for hemiacetals cyclic form or open-chair form
cyclic form
formation of a cyclic hemiacetal
the formation of acetal is at the basis of which bond’s formation
this reaction is at the basis of the formation of the glycosidic bond between sugar units
cyclic hemiacetal turning into cyclic acetal
compounds with R-NH2 structure reacting with the carbonyl group
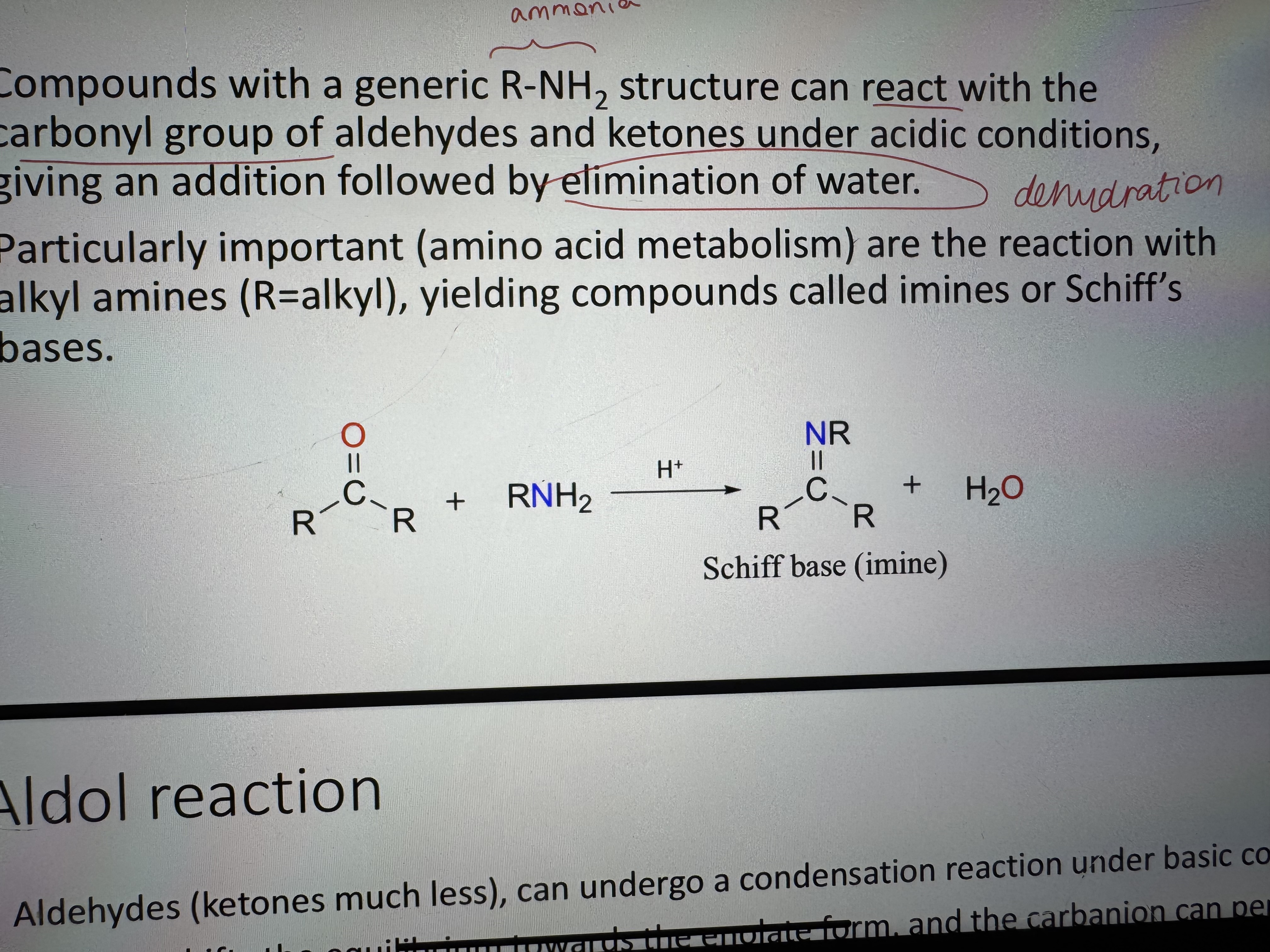
what is the product of a reaction between an ammonia and carbonyl group called
schiff bas (imine) + H2O
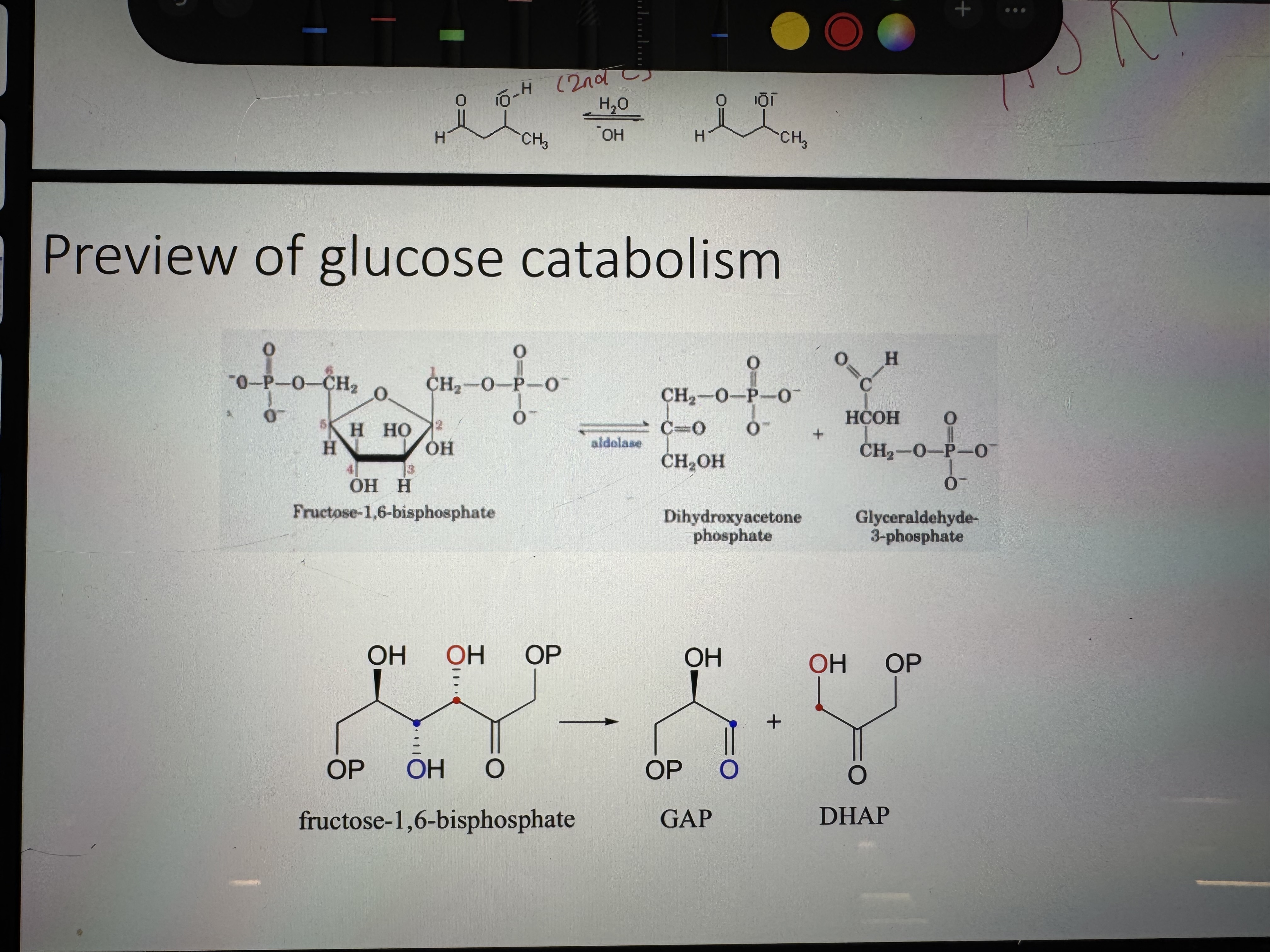
where is the aldol reaction most important
in the metabolism of glucose. in the breakdown of glucose we encounter a retro-aldol reaction
what is the product of an aldol reaction
3-hydroxy aldehyde (or ketone) “aldol”, “ketol”
what happens in an aldol reaction
the base shifts the equilibrium towards thr enolate form, and the carbanion can perform a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl
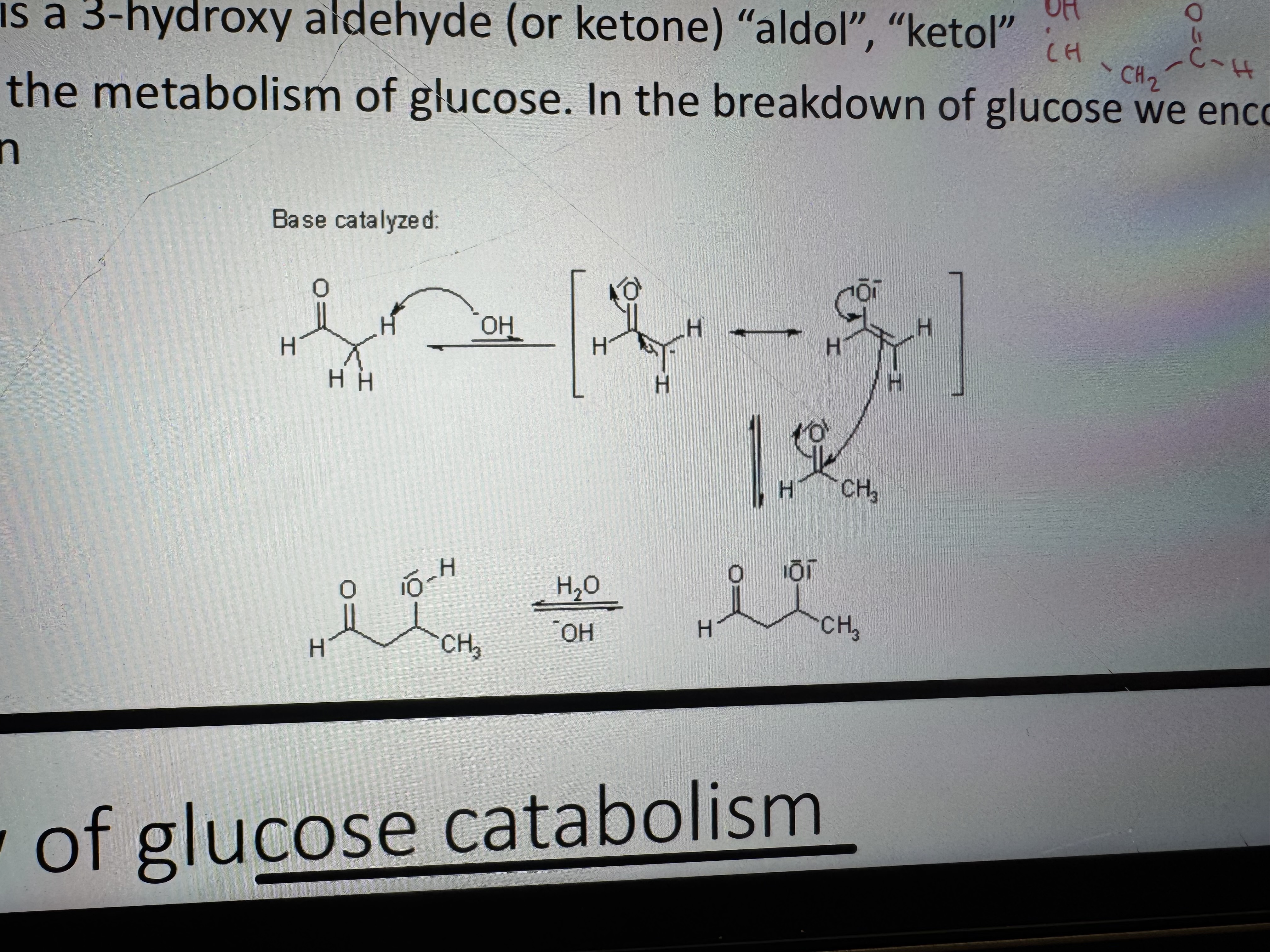
glucose catabolism