Econ - Supply and Demand vocab
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
demand
The willingness and ability to purchase an item
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantity demanded of a good or service at different price levels
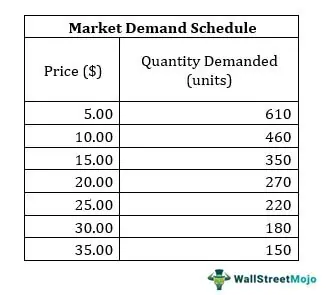
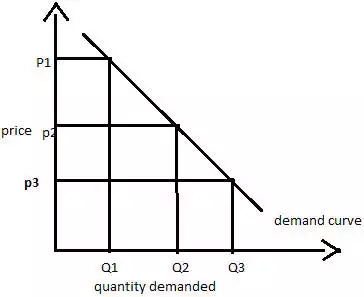
demand curve
a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good/service and the quantity demanded within a specified time frame (Any time the price changes…the quantity demanded will change)
(supply to the sky, demand to the sand)
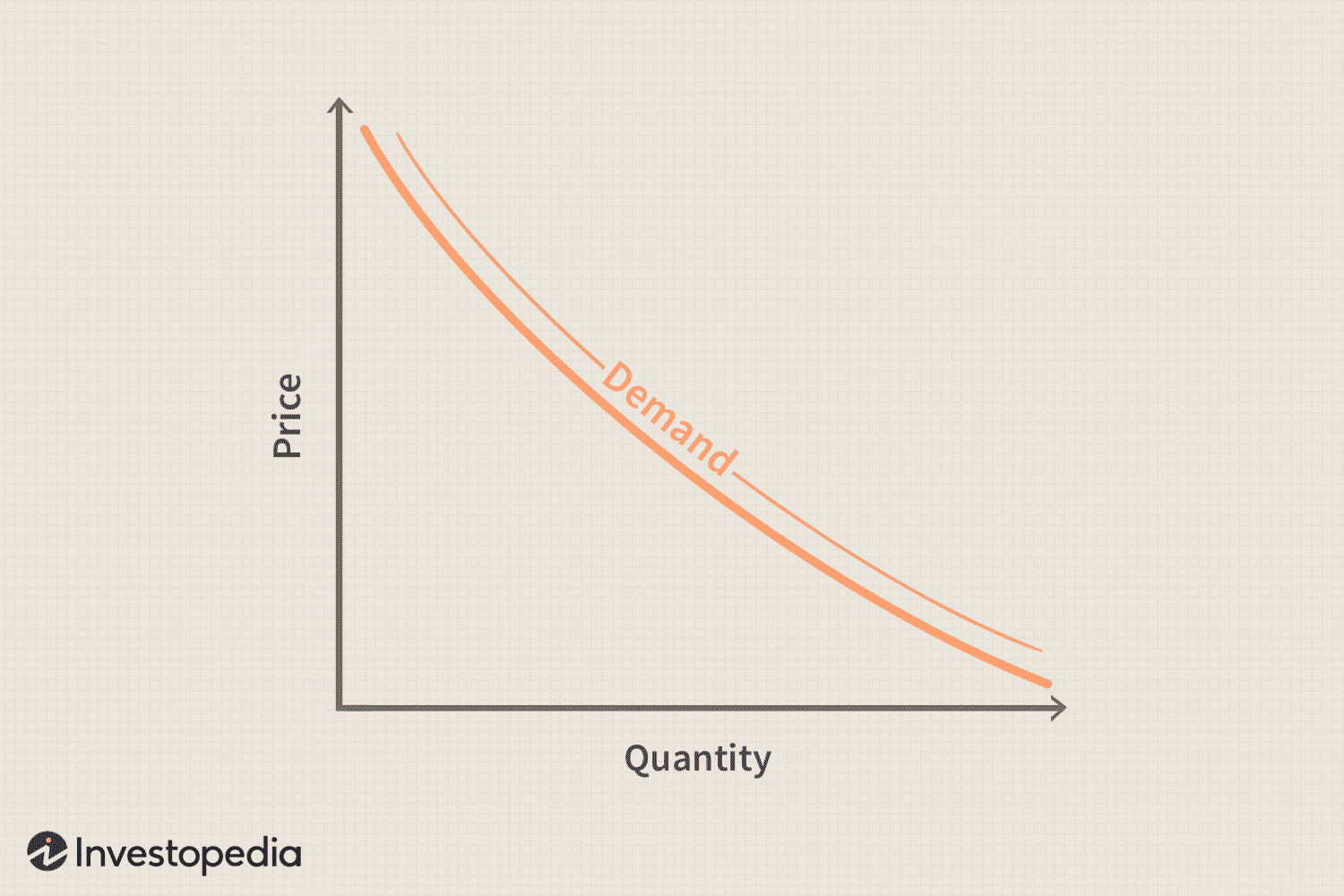
law of demand
as the price goes up - quantity demanded goes down
law of diminishing marginal utility
the more you consume, the less satisfaction you receive from consumption. (lower prices are needed to entice more buying)
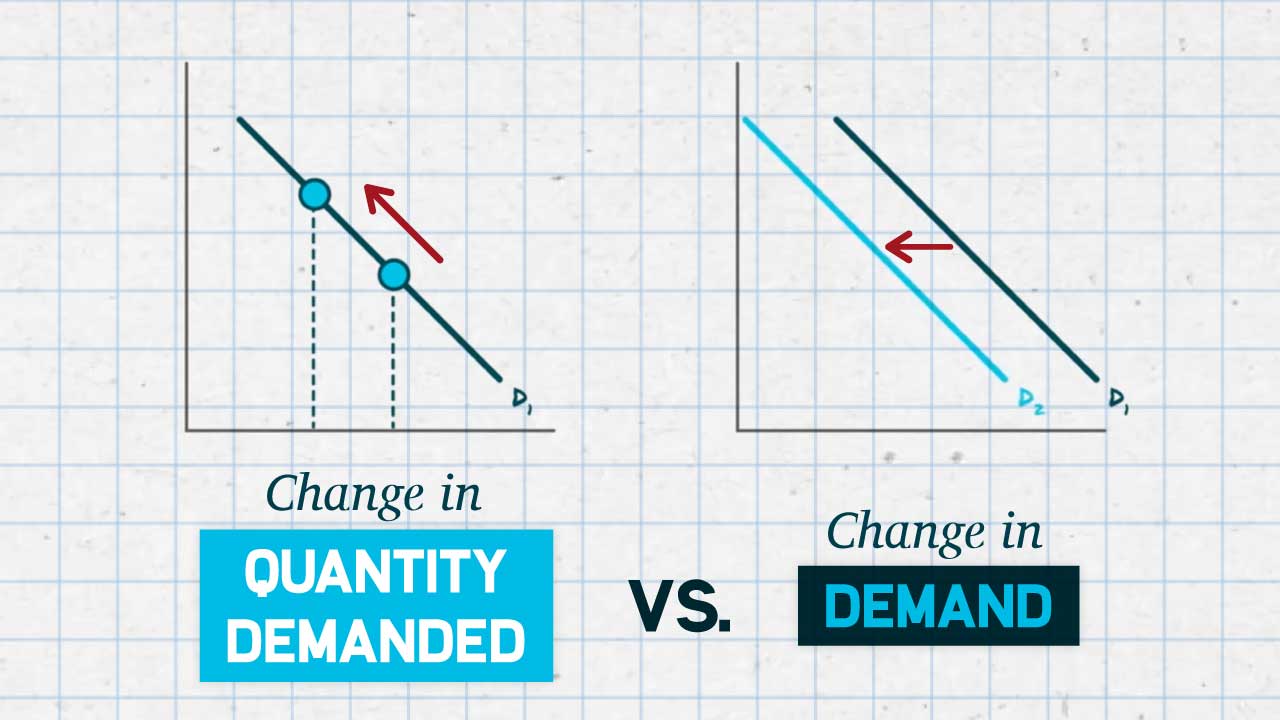
change in quantity demanded
a change in the quantity demanded due to price change
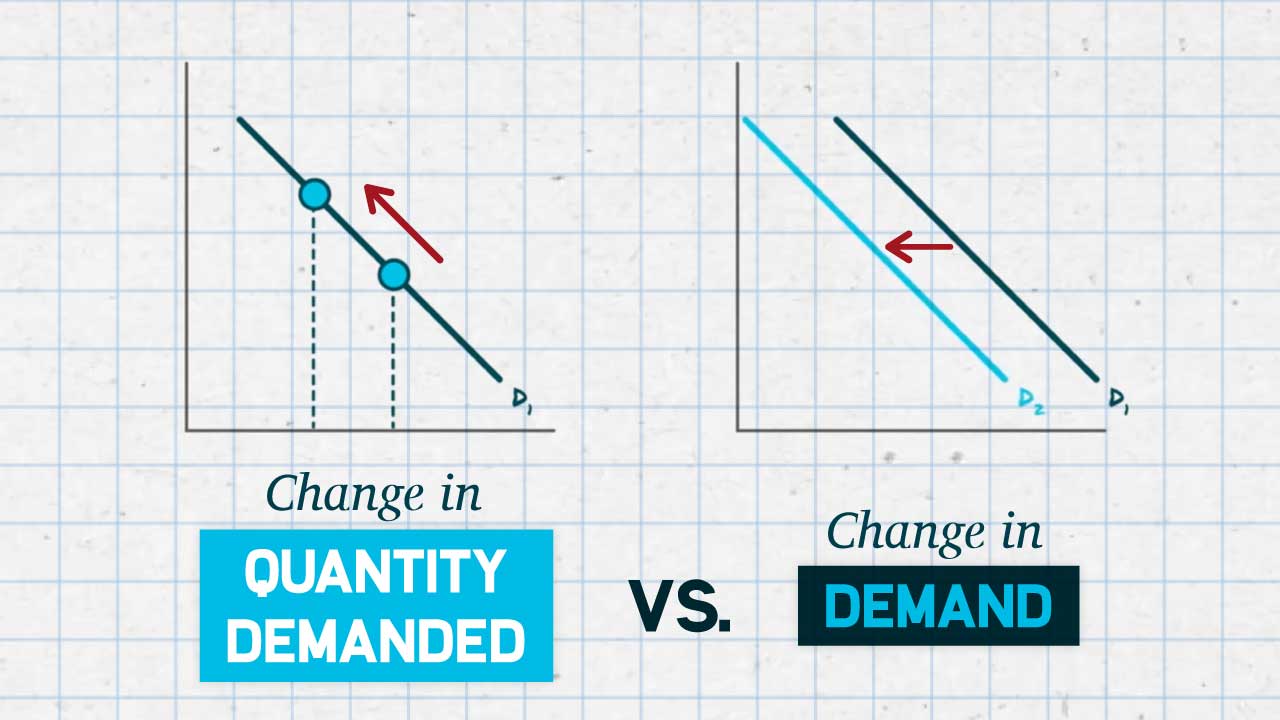
a shift in demand
a change in the quantity demanded due to an outside factor (other than price)
substitutes
used in place of another product (competitors)
complements
Commonly purchased items together

supply
How much of a product or a service will be produced and sold.
law of supply
as price goes up - quantity supplied goes up
Supply has a direct relationship as opposed to demand (indirect)
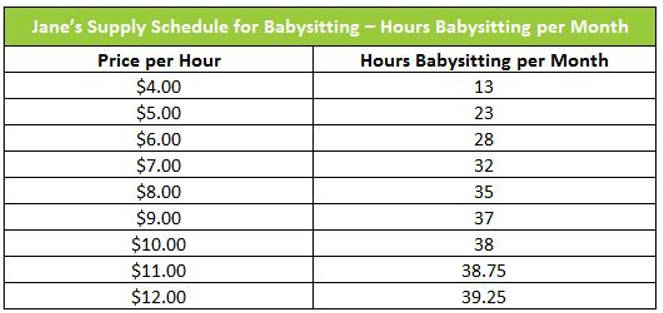
supply schedule
a table that shows the quantity supplied at each price
supply curve
a graph that shows how a change in the price of a good or service affects the quantity a seller supplies. (supply to the sky, demand to the sand)
quantity supplied
The number of goods produced/sold at each price level.
change in quantity supplied
a change in the quantity supplied due to price change
a shift in supply
a change in the quantity supplied due to an outside factor (other than price)
subsidy
the opposite of taxes…the government PAYS companies to produce something (increase in supply)
equilibrium price
the price on which the consumers and producers agree on
equilibrium quantity
when supply and demand meet (the amount of an item that consumers want to buy is equal to the amount being supplied by its producers)
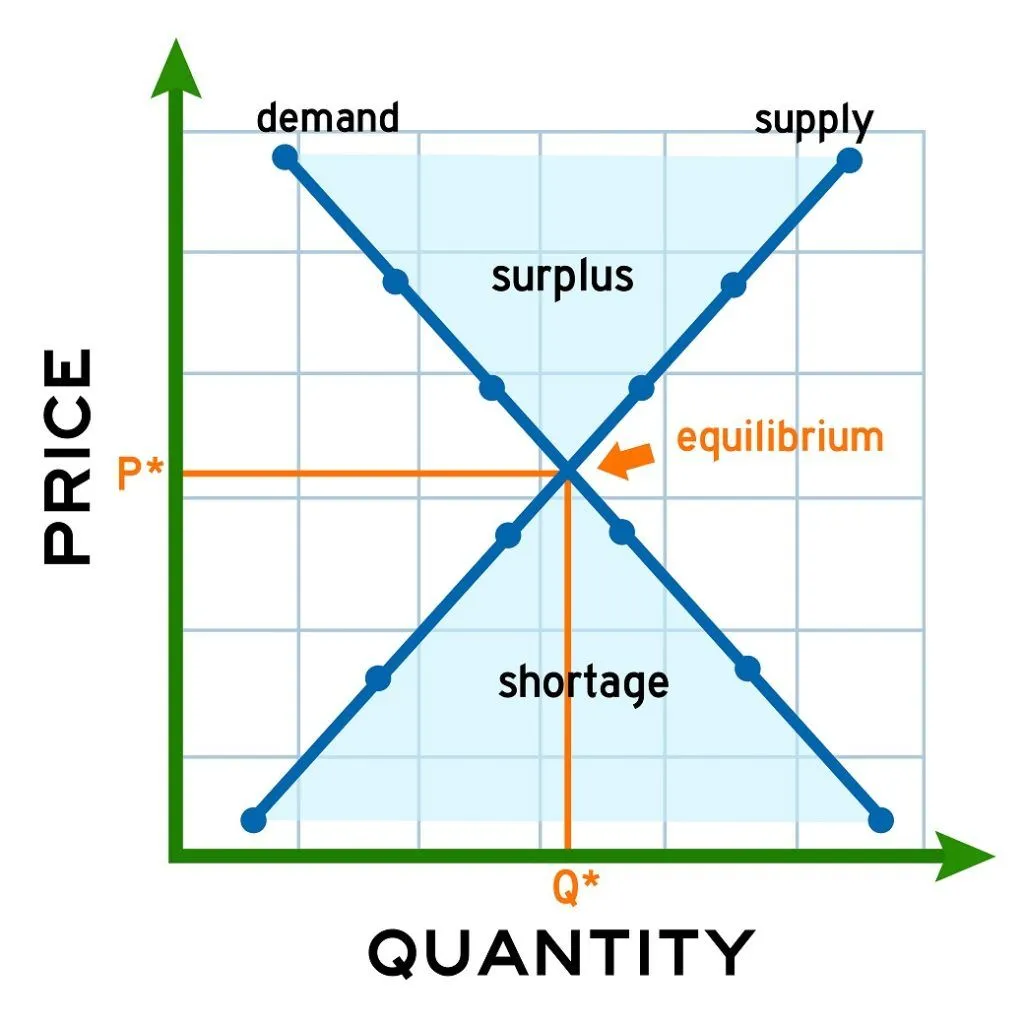
surplus
supply is greater than demand - causes businesses to lower their prices

shortage (what is it? what are the effects?)
demand is greater than supply - causes businesses to increase their prices
price ceiling
highest price allowed by the government - leads to lower prices and shortages
price floor
the minimum/lowest price allowed by the government - leads to higher prices and a surplus