fml its plant and animal biology
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
Features of plants
They can morph
unique tissues and organs that are different from animal cells
have rigid cell walls that contain cellulose
contain chloroplasts with chlorophyll and have vacuoles
Cuticle
Outer waxy layer on leaves (reduces water)
Cell wall
Multi-layered structure (protects cells)
Middle lamella
separates primary and secondary cell wall
Plasmodesmata
Cytoplasmic connections between cells
Cellulose
Glucose molecules forming a long chain
Plant cell wall structure
Primary cell wall = contains cellulose
Secondary cell wall = hemi-cellulose and lignin, which provide cell wall strength and thickening
Secondary growth = seen in trees due to the thickening of the secondary cell walls, between individual cells is the middle lamella. Contains pectin and calcium
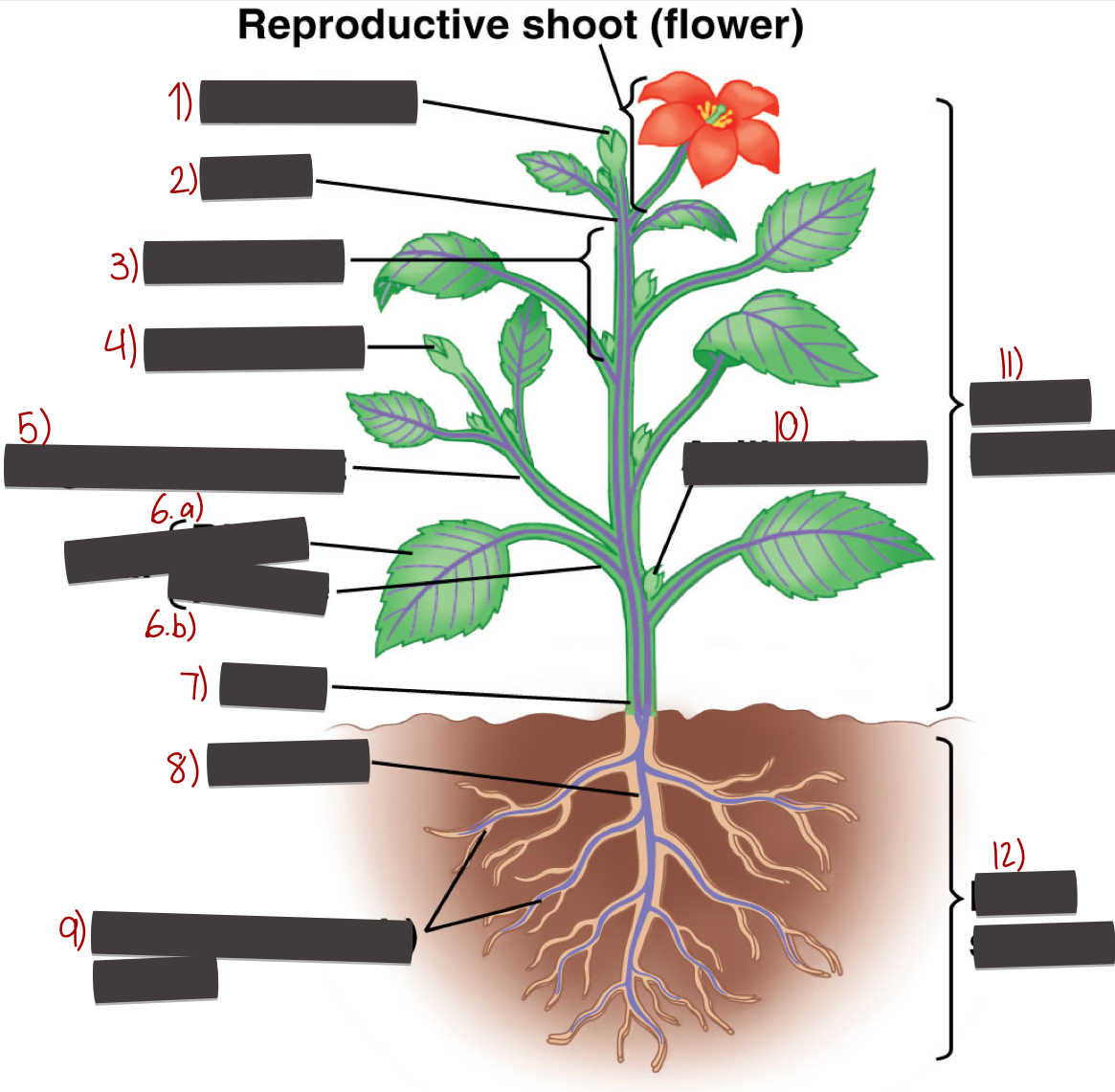
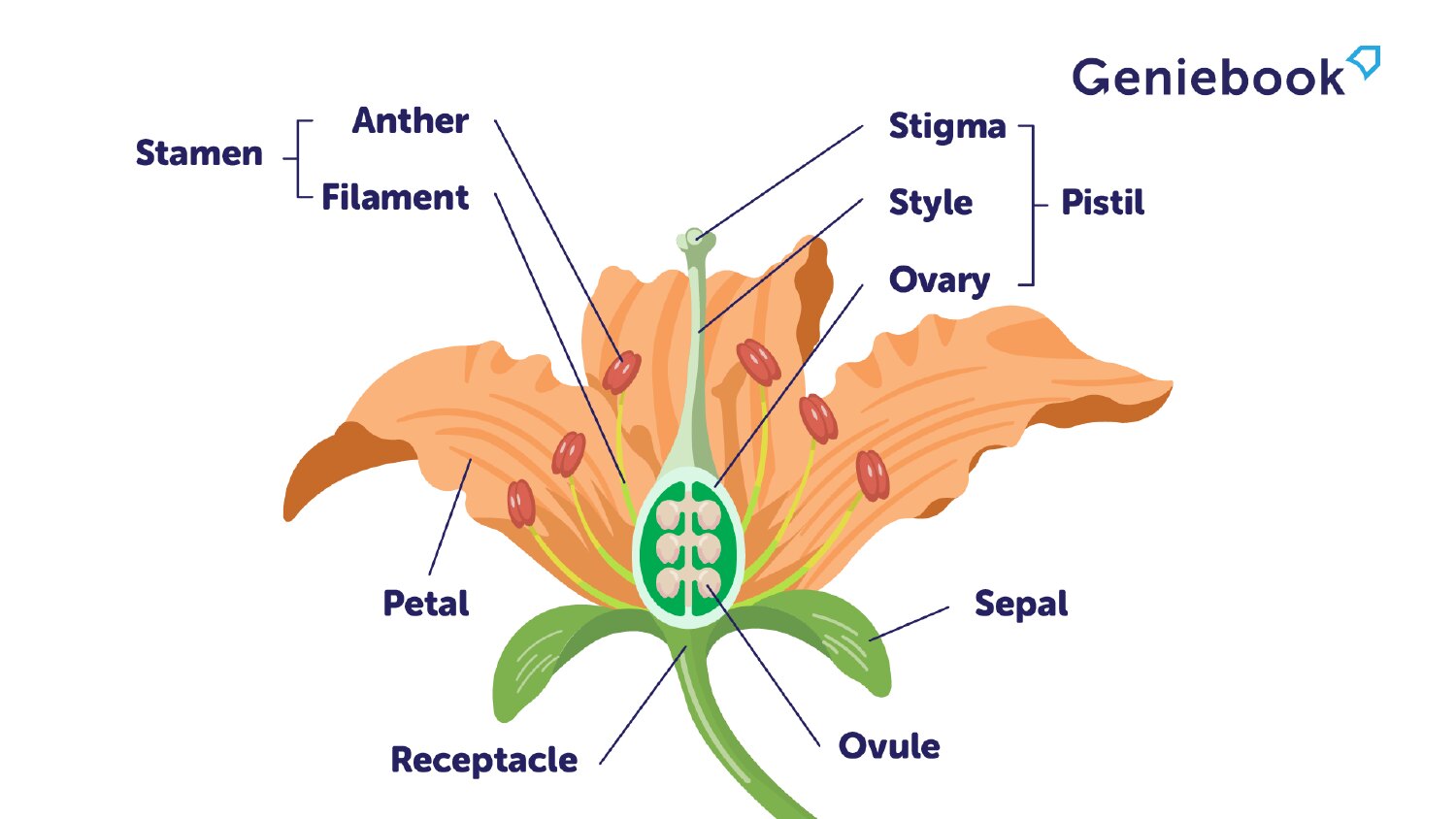
Parts of a flower
1) Apical bud
2) Node
3) Internode
4) Apical bud
5) Vegetative shoot
6.a) Blade
6.b) Petiole
7) Stem
8) Taproot
9) Lateral roots
10) Axillary bud
11) Shoot system
12) Root system
Functions of leaves
primary site for photosynthesis (sugar is formed from carbon dioxide and water and oxygen are produced)
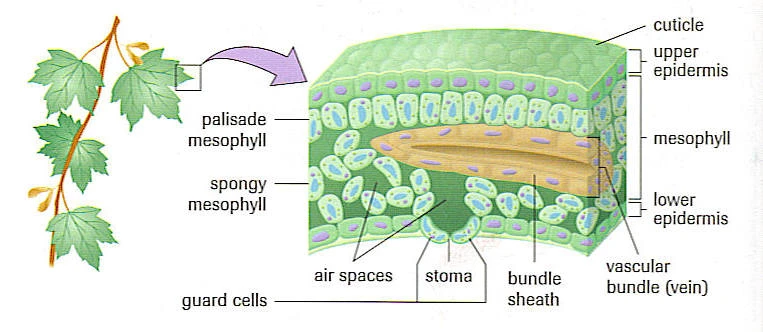
Features of a leaf
Have an upper epidermis and a lower epidermis. In between are mesophyll cells palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll. Also has cuticle
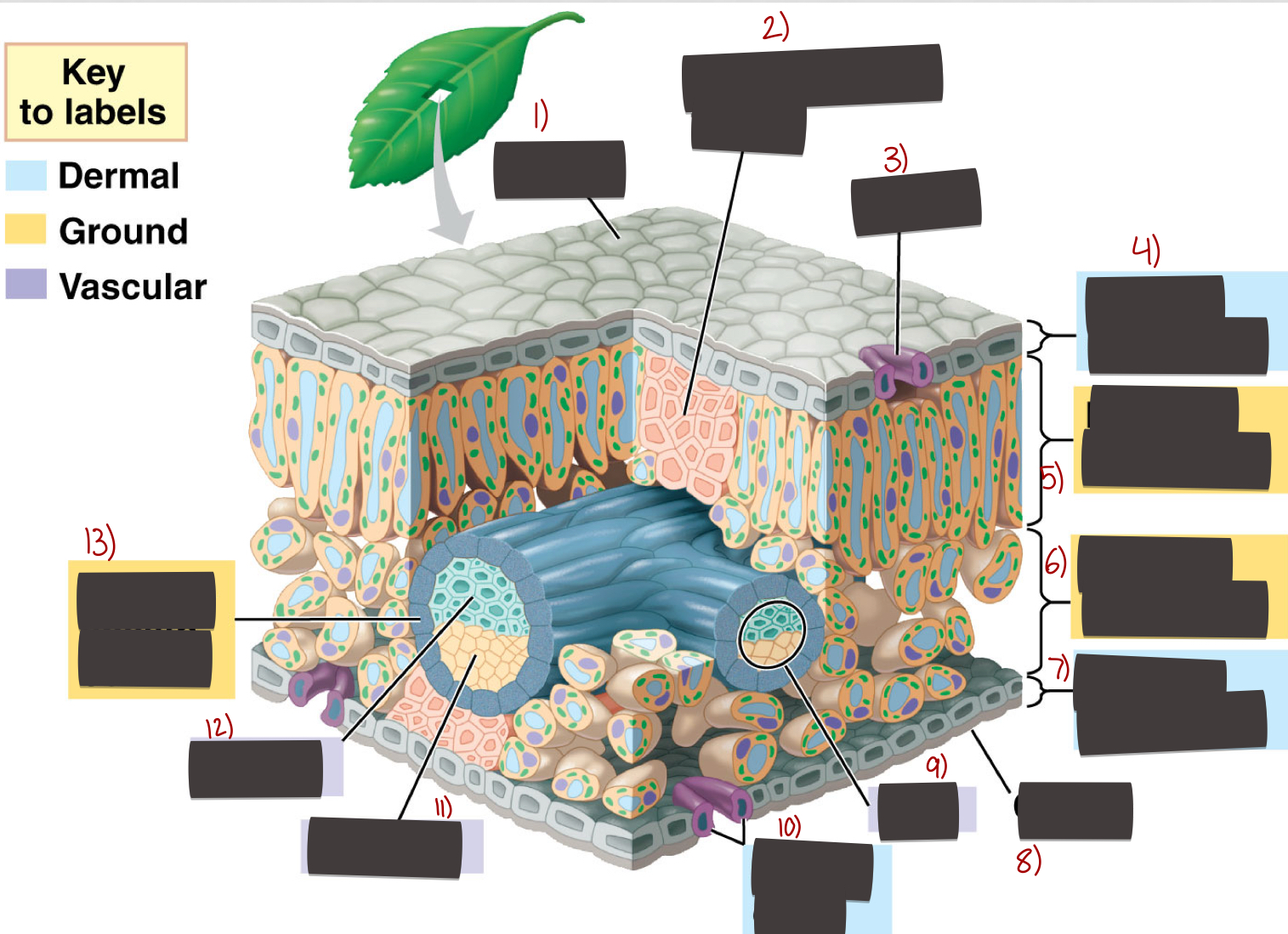
Parts of a leaf
1) Cuticle
2) Sclerenchyma
3) Stoma
4) Upper epidermis
5) Palisade mesophyll
6) Spongy mesophyll
7) Lower epidermis
8) Cuticle
9) Vein
10) Guard cells
11) Phloem
12) Xylem
13) Bundle-sheath cell
Functions of Stems
Provide physical support to the plant and are also involved in movement of water and nutrients up the plant through the vascular system. Allows for continued growth through the apical meristem. Contains axillary buds that give rise to side shoots
Can be used for storage of food and water
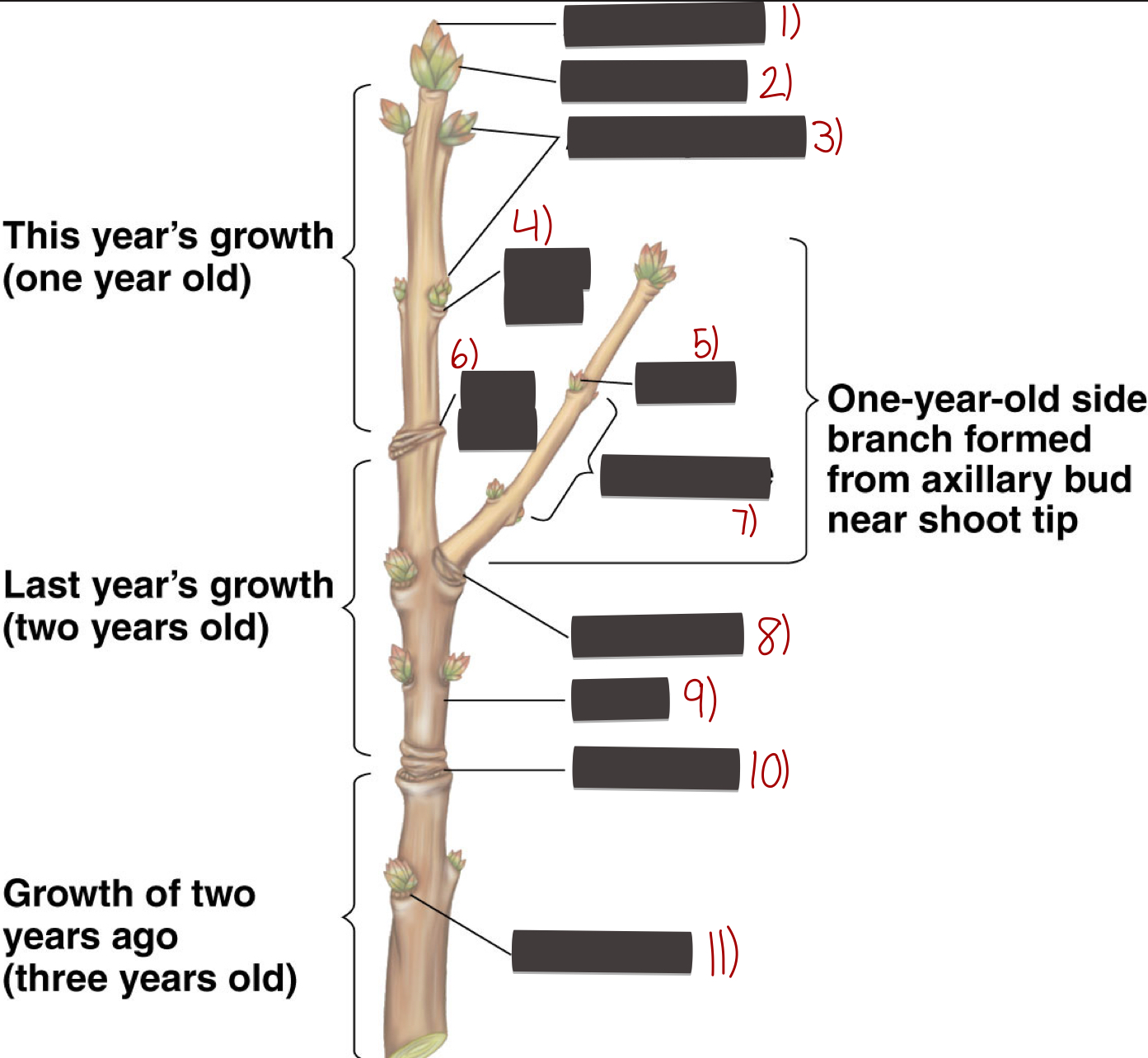
Parts of a stem
1) Apical bud
2) Bud scale
3) Axillary buds
4) Leaf scar
5) Node
6) Bud scar
7) Internode
8) Leaf scar
9) Stem
10) Bud scar
11) Leaf scar
Meristems
Actively growing regions found at the tips of hoots an roots of plants allow for continued growth
Functions of roots
Anchor the plant/tree in the soil
Absorbs water and nutrients from the soil
large surface area
growth occurs through meristems
storage of nutrients
Tissue types in plants
Dermal - found on the outside layer of plant tissues, provides protection to the plant
Meristematic - found at the growing tips
Ground - there are three types ( parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma)
Vascular - there are twp types ( xylem and phloem)
Parenchyma cells - ground tissue
The most common type. These cells are thin-walled and capable of photosynthesis when they contain chloroplasts. They are involved in producing sugar during photosynthesis and they can store food
Collenchyma - ground tissue
Thicker walls for flexible support. These cells dont store food. They constitute living cells. Provides structural support to plants
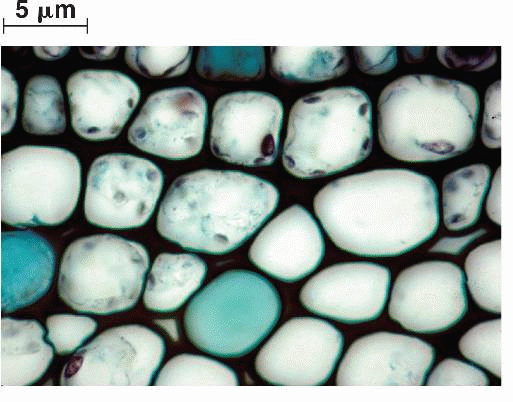
Sclerenchyma - ground tissue
Hollow, nonliving support cells. Their function in mainly in providing support and rigidity to plants
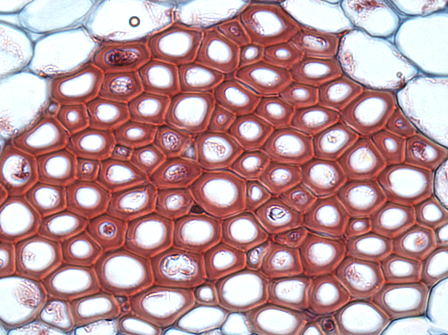
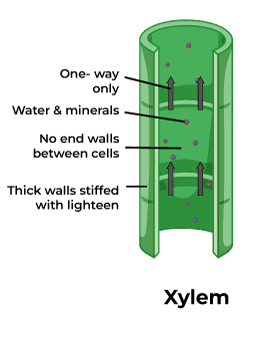
Xylem - Vascular tissue
Moves water and nutrients up the plant, from the roots. It consists of cells called tracheids and vessel elements which have pores in them and also are nonliving
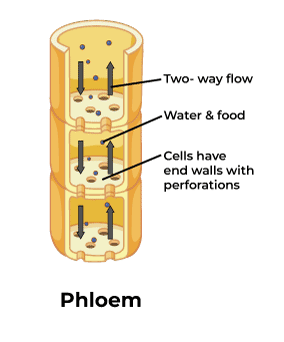
Phloem - Vascular tissue
Moves sugar and water solution from leaves to other parts of the plant. consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells which are living
Vascular cambium
Ring of actively dividing cells found separating the xylem and phloem. Cell divisions result in the formation of secondary xylem and secondary phloem. Cause “growth rings” in large trees
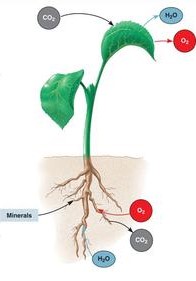
How roots take up water
Through osmosis - movement of water from concentration of low solute (soil) to one of higher concentration of solute. Roots hairs provide greatly increased surface area for absorption of water and nutrients.
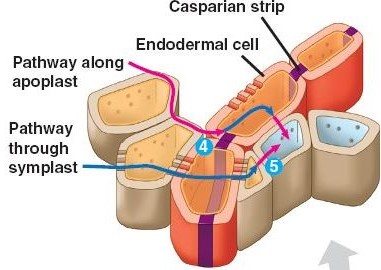
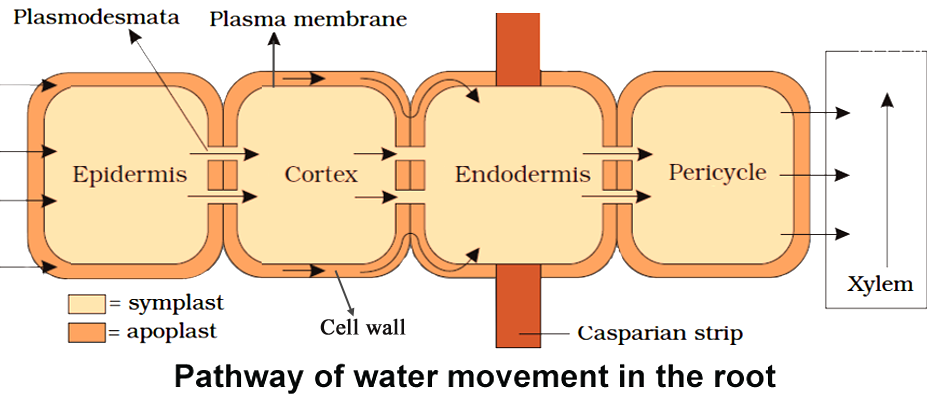
What happens when water enters the roots
Moves in between cells (apoplast) or through the cells themselves (symplast). Once it reaches a layer of cells called the endodermis, the water is redirected to move via symplast. This allows for control of water uptake
Water movement
Once inside the xylem tracheids and vessel elements, water molecules adhere to each other by hydrogen bonding as well as to the walls of xylem vessels. Creates a column of water internally. Water travels upwards to the leaves. Travel rate can be 15 meters per hour
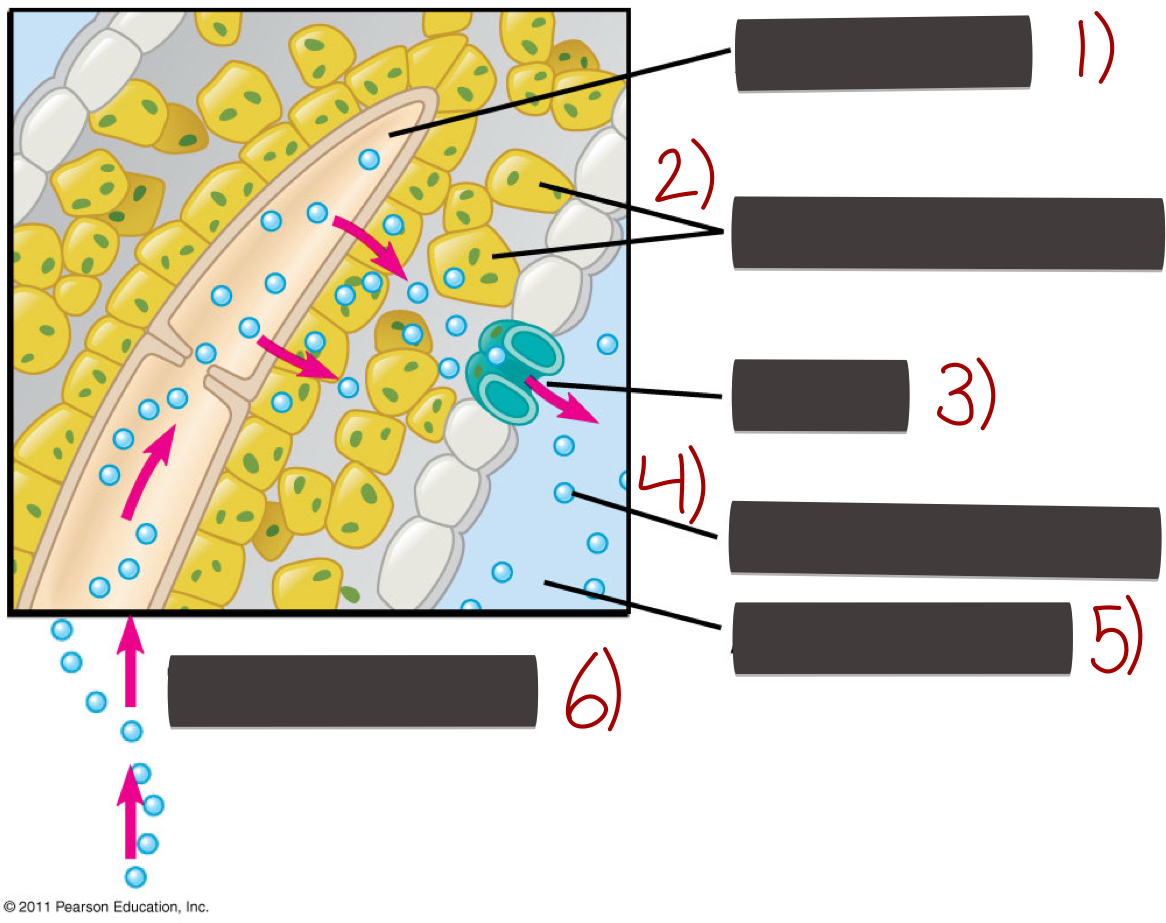
Loss of water through transpiration
1) Xylem sap
2) Mesophyll cells
3) Stoma
4) Water molecule
5) Atmosphere
6) Transpiration
Water flow up the plant (tree)
Loss of water due to transpiration creates a “water deficit” or negative water potential inside the leaf. Causes a “pull” of water into the leaf from the xylem. This in turn pulls water up the xylem from the roots. “Transpiration pull” main force that brings water up the plant
Stomata
Located in the epidermal layer of leaf cells. More stomata on the underside of leaves as it is cooler. Need to stay open to take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis

Functions of stomata
Stomata open when there is lots of water, when there is sunlight, when potassium ion levels are high inside. Causes water to flow in. Stomata will close when there is not enough water, when dark or when potassium levels are low
How do plants adapt
Reduce leaf size to store water
Dry down but grow again when it rains
Close the stomata during the day, open them at night when it is cooler
Stomata be located deeper inside the leaf than the epidermis
Leaves have thick waxy cuticles
Fewer Stomata
Xerophytes
Plants adapted to dry with features like reduced leaves (spines), thick cuticles, sunken stomata, and CAM photosynthesis to minimize water loss. Examples include cacti, succulents, and aloe.
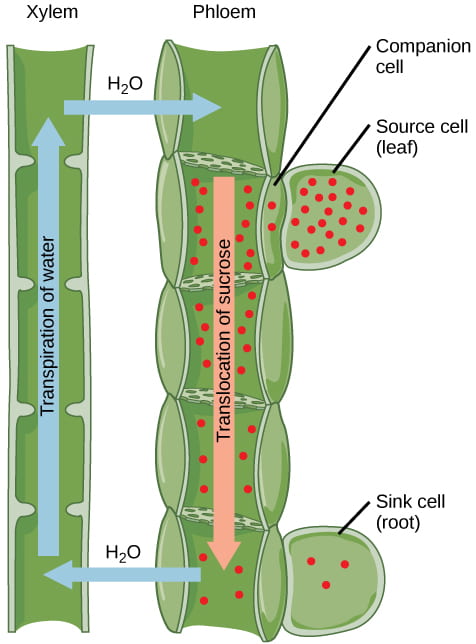
Function of phloem
During photosynthesis sugar is produced in the leaves that must be transported to other parts of the plant
This requires movements from the source
Sugar (sucrose) is loaded into the phloem cells by sucrose transporters. This causes a high osmotic pressure which draws in water from the xylem
This causes pressure to build up, which forces the flow of sugar down the plant
The turgour pressure causes the sugar solution to move via “bulk flow” to reach cells that need it. The sugar is “unloaded” here
4 reasons why plants are so important
Oxygen Production – Plants produce oxygen through photosynthesis, which is essential for life.
Food Source – They provide food for humans and animals, forming the base of the food chain.
Climate Regulation – Plants absorb carbon dioxide, helping to reduce greenhouse gases and regulate temperature.
Habitat & Biodiversity – They provide shelter and sustenance for various organisms, supporting ecosystems.
3 differences between plant cells and animal cells
1) Cell wall
2) Chloroplasts
3) Vacuole
Various constituents that make up a plant cell wall
Cellulose – A structural polysaccharide that provides strength and rigidity.
Hemicellulose – A branched polysaccharide that binds cellulose fibers together.
Pectin – A gel-like polysaccharide that helps in cell adhesion and flexibility.
Lignin – A complex polymer that provides rigidity and water resistance, especially in woody plants.
Proteins – Structural and enzymatic proteins that help in cell wall maintenance and signaling.
Water – Maintains turgor pressure and flexibility.
Minerals (Calcium & Magnesium) – Strengthen the wall structure and contribute to signaling pathways.
Different cell types found in plant leaves
Epidermal Cells – Form the outer protective layer, preventing water loss and pathogen entry.
Guard Cells – Regulate gas exchange by controlling the opening and closing of stomata.
Palisade Mesophyll Cells – Contain many chloroplasts and are the primary site of photosynthesis.
Spongy Mesophyll Cells – Loosely arranged cells that facilitate gas exchange.
Xylem Cells – Transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves.
Phloem Cells – Transport sugars and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Bundle Sheath Cells – Surround vascular bundles and play a role in photosynthesis (especially in C4 plants).
How plants reproduce
Asexual = (through vegetative means) offspring are all genetically identical
Sexual = (involving male and female gametes) genetic diversity
Sexual reproduction
Female and male gametes are found in the flowers
Requires the transfer of the male gamete to the ovules to initiate fertilization
Male gametes produced in anthers
Female gametes are found in the ovary
Requires the fusion of male and female gametes to produce a zygote followed by seed production
Male gamete = pollen grains
Female gamete = ovules
Pollination and fertilization
Process of transfer of the male pollen to the female stigma is called pollination
Pollen can be transferred by wind, this requires production of very large amounts of pollen each spring
Pollen can also be transferred by insects
Insect pollinated flowers are attractive and produce nectar to reward the pollinators
After pollination
a fruit is formed, not all fruits have seeds and dont need pollination to form a fruit
Steps in fertilization (double -fertilization)
Pollen grain has 2 sperm nuclei
pollen grain germinates on the stigma of the same plant specie and produces a germ tube
Germ tube grown down the style
Reaches the ovary it seeks out the opening in the ovule called micropyle
One sperm nucleus fuses with the egg nucleus inside the ovule to form the zygote
Second sperm nucleus fuses with the polar nuclei to form the endosperm which is the food storage
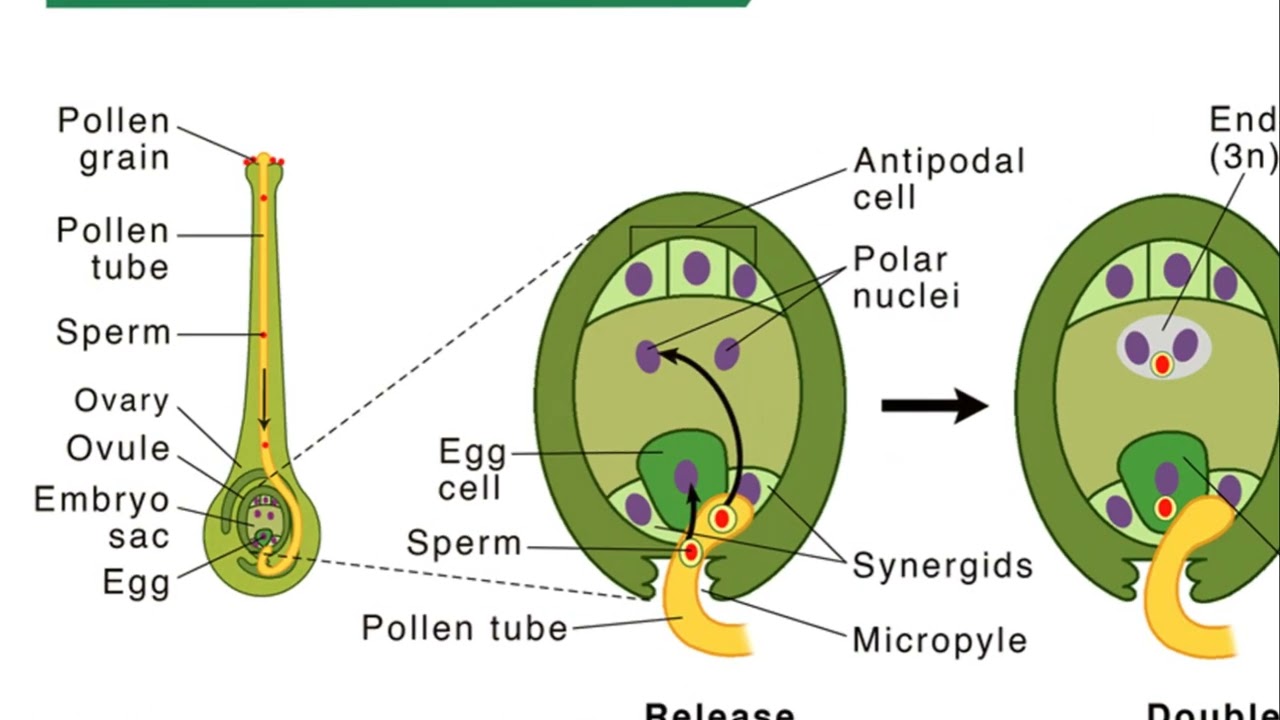
Development of the zygote
Zygote divides several times to form an embryo
Embryo differentiates to form a root and shoot apex
Ovary expands and the wall becomes the seed coat
Each fertilized ovule forms one seed
Each seed has one or cotyledons depending if its a monocot or dicot plant species
Seeds will germinate to form a root and shoot and the plant has now been propagated sexually
Self-pollination
Where pollen from the same flower fertilizes ovules form the same flower. More efficient as the pollen and ovules are found in the same flower
Cross-pollinated
Where pollen form one flower fertilizes ovules from a different flower. Less efficient but evolutionary more advantageous as more genetic diversity is created. Plants have developed mechanisms to try and increase cross pollination
How do plants increase cross-pollination
Wind and insects seen in coconut
Male and female flowers separate (monoecious)
Male flowers mature earlier
Produce male and female flowers on different plants (dioecious)
Make male pollen incompatible with stigmas of the same plant
How to spread seeds far and wide
Lots of seeds that spread by wind
float on water
seed spiny so that catch to animals
aerodynamic
fruits attract seed inside them are spread
fruits fleshy and attractive for animals to eat
Why do some plants not produce seeds
Most plants are diploid like in humans, allowing normal meiosis to occur and gamete production
Some plants are polyploid, greater than 2 sets of chromosomes
plants cannot pair chromosomes in meiosis, causing no gametes to form. No seeds produced
Banana is triploid
Potato is tetraploid
Strawberry is octaploid
Plant responses to physical injury
Injury causes cells to break and release contents
Enzymes are produced to heal the injury
Oxidation reactions cause browning that helps heal the wound
Other chemical reactions occur to start the process of cell division
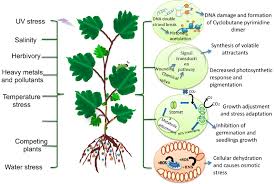
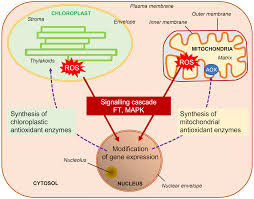
Plant stresses cause chemical changes
To express genes to produce chemical products to deal with the stress
The response may occur in a matter of minutes, chemical signals are produced. Which signal other parts of the plant that something is going on
Causes changes to help the plant recover from the stress
Internal clock - Turn east at night, face west in day
Stem growth occurs on the west side at night, causes flowers to turn to east waiting for the sun to rise
Stem growth occurs on west side in daytime, causes flowers to bend east in the day-waiting for sun set
Gravitropism
Plants response to gravity
Positive : Roots frow down
Negative : Stems grow against gravity

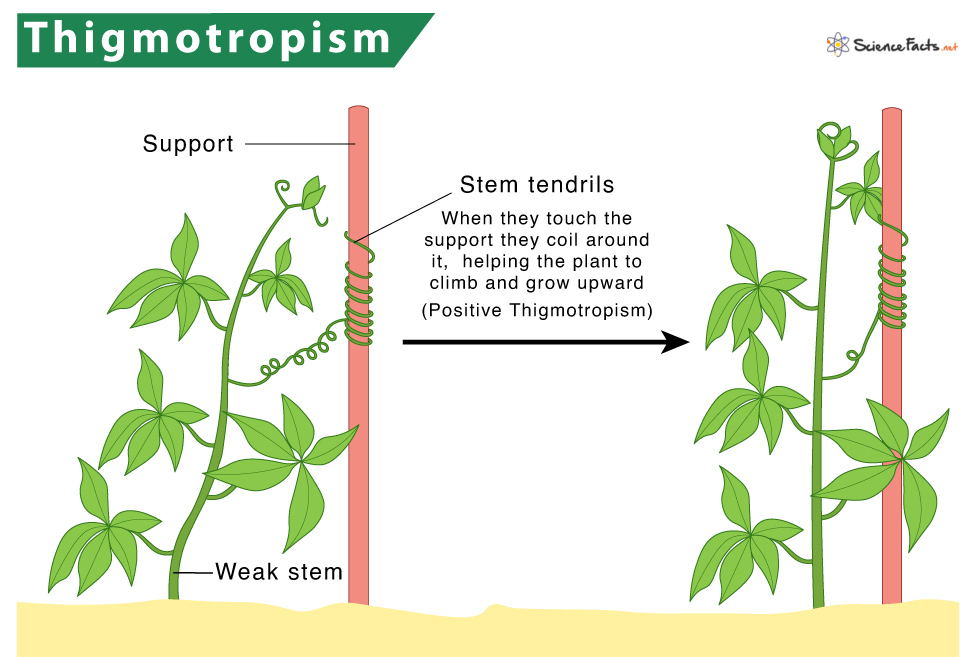
Thigmotropism
Thigma means touch in greek
Touching certain plants changes its behaviour
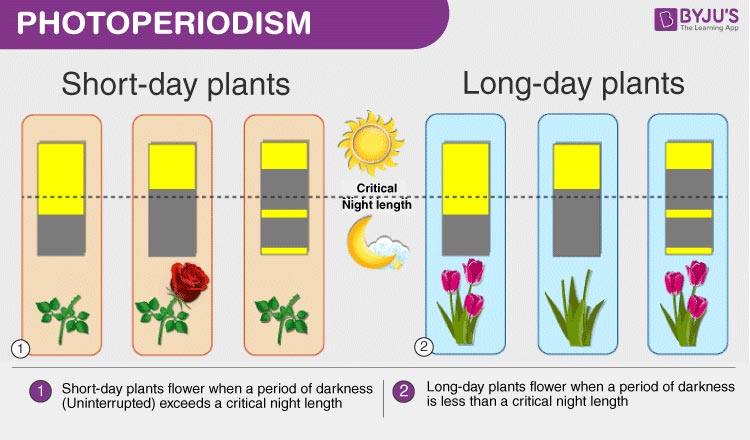
Photoperiod
Plant responses to different lengths of time of exposure
Phytochrome protein senses light
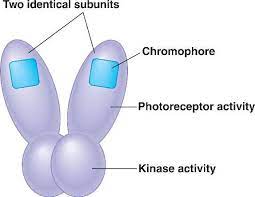
Phytochrome is activated by red light
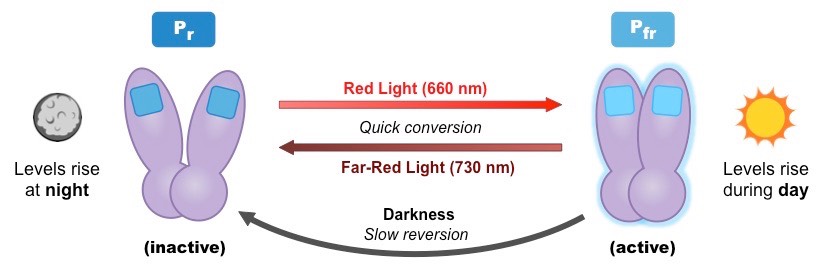
Phototropism
Plants respond to light by growing towards it so they get maximum exposure
Auxin production
Is a hormone that increases cell elongation
Hormones respond ot environmental changes
Auxin - stimulates cell elongation and regulates branching and organ bending
Cytokinins - stimulate plant cell division and promote later bud growth
Gibberellins - Promote stem elongation, helps seed break dormancy and used stored reserves
Brassinosteroids - Chemically similar to the sex hormones of animals, induce cell elongation and division
Abscisic acid - produces stomatal closure in response to drought, promotes seed dormancy
Strigolactones - regulate apical dominance, seed germination and mycorrhizal associations
Ethylene - Mediates fruit ripening
Photosynthesis
Production of sugar in plants using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of light. Solar energy is used to produce energy which is used to produce organic molecules. Takes place in plants and trees, algae and kelp, and photosynthetic bacteria
6CO2 + 12H2O = C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2
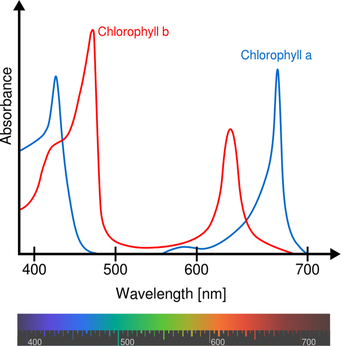
Chlorophyll
Plants only respond to light in the visible spectrum. These are tow forms of chlorophyll - ‘a’ and ‘b’. Chlorophyll ‘a’ absorbs light around 440 nm (blue) wavelength and also 680-700nm (red)
Pigments
Pigments that are orange and yellow called carotenoids. They absorb light around 480-500nm. Carotenoids pigments show up when chlorophyll is broken down in the fall season to produce vivid colours of leaves. They also are anti-oxidants that reduce oxidative damage due to sunlight and UV rays
Features of chloroplasts
Chlorophyll is contained within chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are found in mesophyll cells of leaves, they are surrounded by a double layer of cell membranes
Inside the chloroplasts are stacks of granum that are surrounded by the thylakoid membrane
The space around the granum is called stroma
Light is absorbed by the granum, except for green wavelength which is transmitted
Light energy is packaged into photons which strike the chlorophyll and cause it to emit higher energy electrons
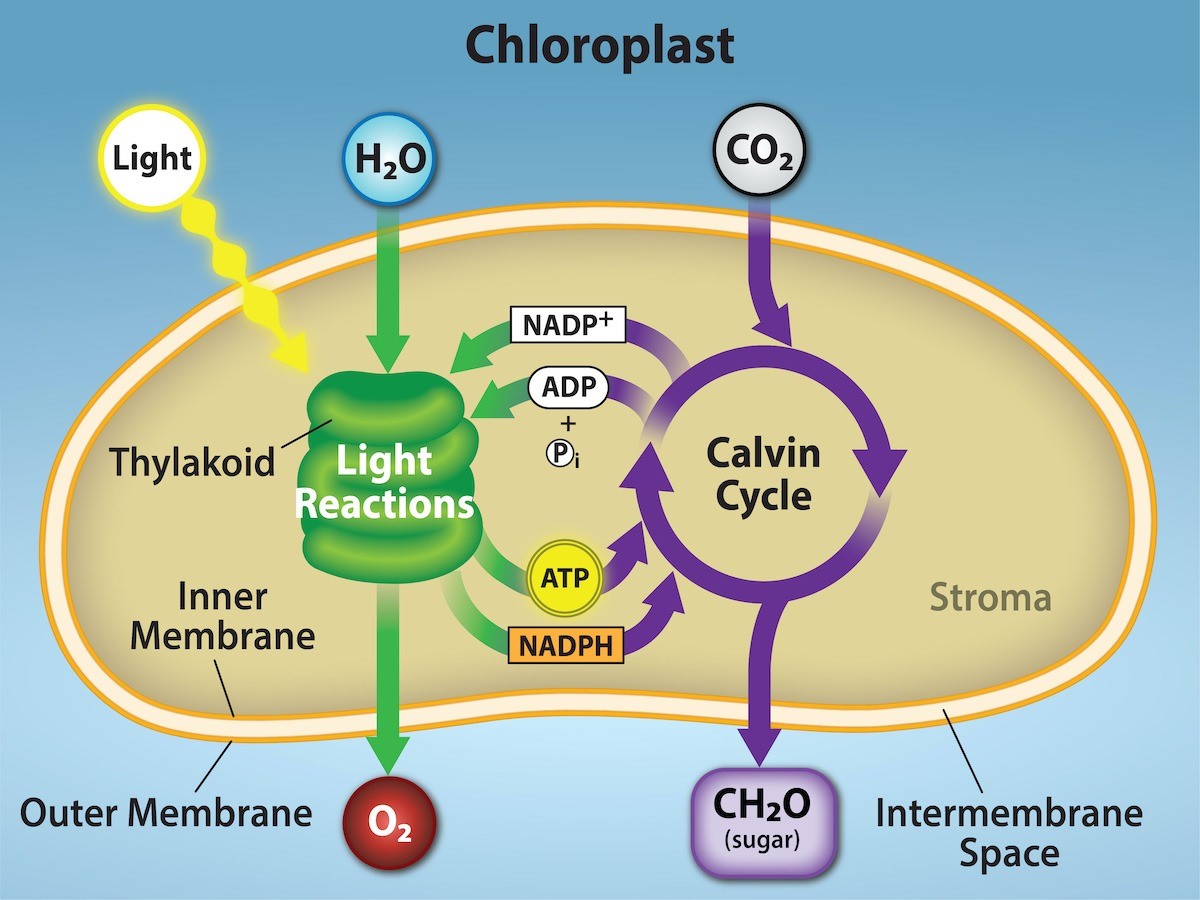
Photosynthesis reactions
During the light reactions, ADP and NADP are combined with p to form ATP and NADPH. This provides energy for the next step in photosynthesis. Oxygen is released from water
Calvin cycle which is light-independent in which energy form the light reactions is used to drive the formation of carbon molecules
Chlorophyll and pigment molecules are arranged in a light-harvesting complex called a photosystem. Inside is a primary electron accepter called pheophytin
The photosystem I and photosystem II are embedded in the thylakoid membrane
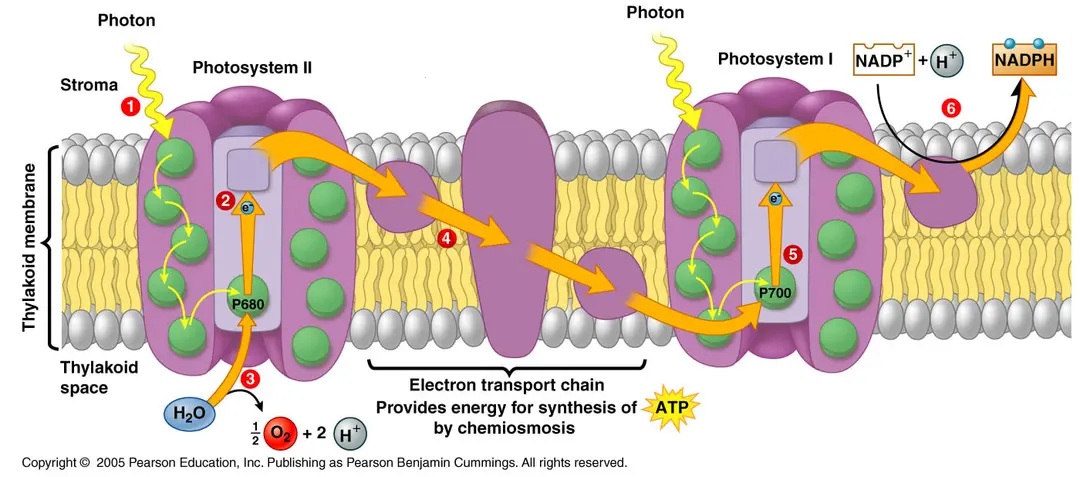
The photosystems
Photosystem I absorbs light in the range of 700nm. Photosystem II absorbs light in the range of 680nm
Electrons released from the splitting of water by light photons reach P680 first and chlorophyll energizes electrons to the primary electron acceptor
Electrons are transferred down an “electron transport chain” to Plastoquinone (Pq) then to the cytochrome complex (Cc) and then to plastocyanine (Pc)
At the point of reaching Cc, energy from the electron is used to generate ATP
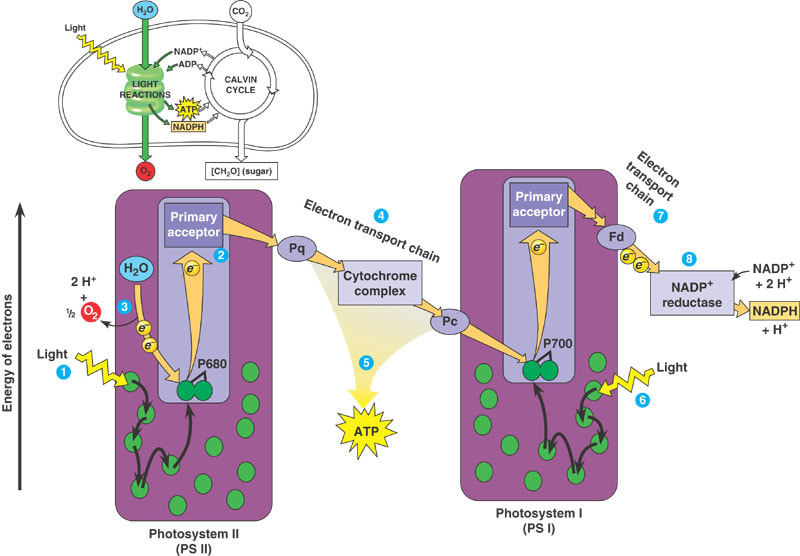
Electron transport chain
Light energy strikes Ps I (P700) and electrons are transferred to the primary electron acceptor
Electrons continue down the electron transport chain to the next molecule which is Ferredoxin
Energy form the electrons create the formation of NADPH using the enzyme NADP reductase
End result of electrons being released from water is the production of ATP and NADPH and the production of oxygen
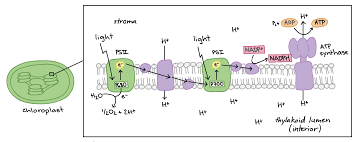
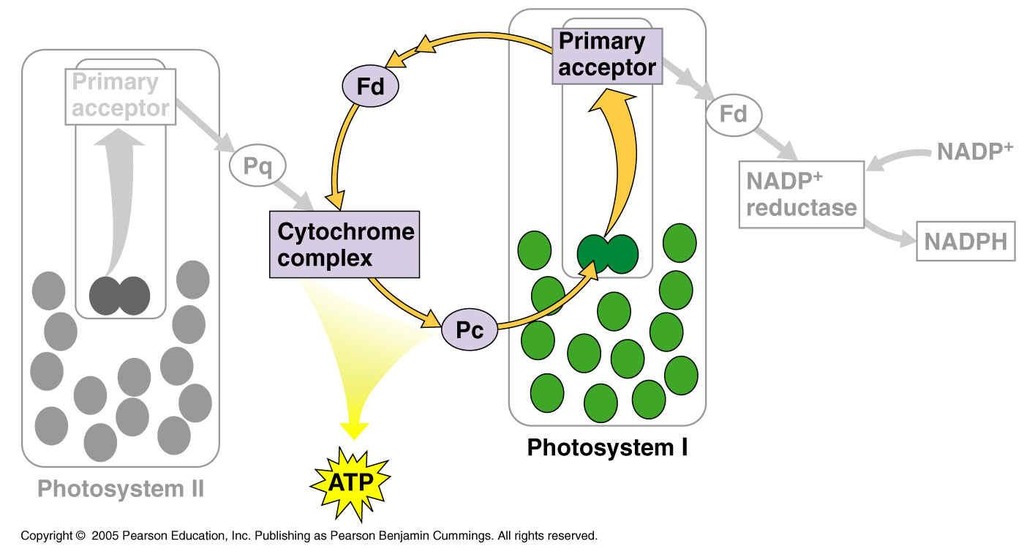
Cyclic electron flow
Occurs when electrons from ferredoxin are transferred back to cytochrome complex instead of moving on to NADP reductase
Results in no NADPH being formed but ATP is still produced
Cells undergo cyclic electron flow if there was sufficient NADPH present or if the cells needed more ATP to be produced
ATP production occurs through ATP synthase, which is driven by a flow of protons through the thylakoid membrane and into the stroma of the chloroplast. This process is called chemisomosis
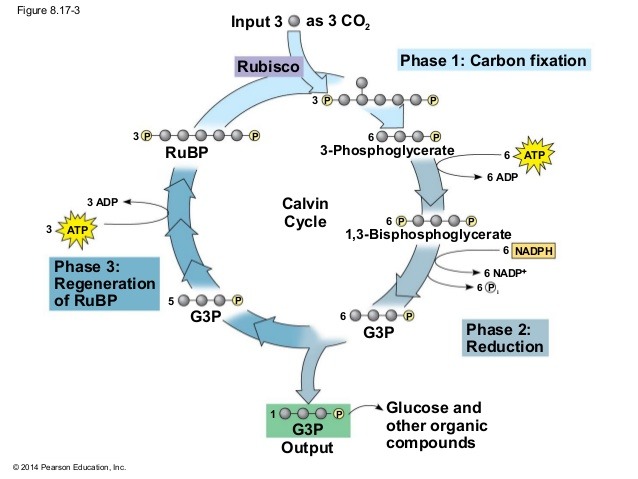
Calvin cycle
Also called the C3 cycle
results in the conversion of carbon dioxide to sugar using energy (ATP, NADPH) from the light reactions
also called “carbon fixations” about 160 × 10^12 kg/yr is fixed by plants
Occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts
Calvin cycle steps
Reactions starts with ribulose-1,5-biphosphate (RuBP) adding CO2 molecule to form (2X) 3-phosphoglycerate
The enzyme involved here is called rubisco = ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase. this is the most abundant enzyme on Earth
Next step is a requirement for ATP to produce 1,3-biphosphoglycerate (3C)
Then NADPH is required to form glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, goes on to form sugar
RuBP is reformed to continue the cycle
Energy in the form of ATP is required for
Plants growing in hot climates
Close their stomata during the day to conserve water
causes CO2 levels in leaf cells to decline and oxygen builds up
Calvin cycle slows down as there is less CO2
Plants undergo “photorespiration” where in presence of oxygen, the phosphoglycerate molecule is oxidized to release CO2
cause up to 50% of the carbon to be lost
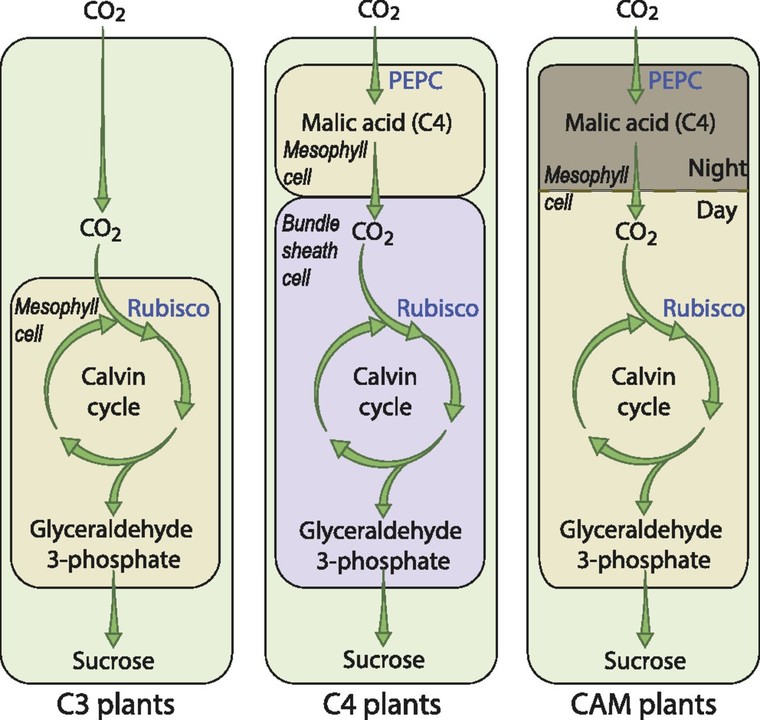
To avoid this loss plants have evolved a C4 pathway to fix carbon in hot climates
C4 pathways in plants
Use a molecule of malate (C4) instead of phosphoglycerate (C3)
produced in mesophyll cells in adding CO2 to a molecule of phospho-enol-pyruvate(PEP) to form oxaloacetate which is converted to malate
enzyme involved is PEP carbonxylase which has a higher affinity for CO2 than Rubisco and so can capture lower concentrations of CO2 in hot climates
Have specialized cells called “bundle shealth cells” These cells break down malate to release CO2 and form pyruvate
CO2 molecule is used in the calvin cycle to form sugar this allows plants to grow in hot climates
Reduces photorespiration
Other adaptations to hot climates
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) plants
Occur in plants such as cactus and pineapple
during the day stomata are closed
CO2 is taken up at night to produce organic acids
Stored in mesophyll cells at night
In day time light reactions continue and ATP and NADPH are produced
Crassulacen acid is broken down to release CO2
Used in the calvin cycle which can operate while the stomata are closed during the day
Short summary of photosynthesis
Product of photosynthesis is used in plant to from cellular structures and tissues
stored in roots and tubers as starch
other uses are for fruits and seeds
photosynthesis requires, light energy, chloroplasts, water, electrons, photosystems, electron transport and calvin cycle
plants need to have adaptations to survive in hot climates to reduce photorespiration
include C4 and CA<
Carbon fixation is a very important process for plants
Body organization
1) Organ system
2) Organ
3) Muscle tissue
4) Muscle cell
Four main categories of animal tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Organ systems
Digestive
Circulatory respiratory
Excretory
Endocrine
Reproductive
Nervous
Immune and lymphatic
Integumentary
Skeletal
Muscular
Epithelial tissue shape
Cuboidal (dice) - cube
Columnar (bricks) - rectangular
Squamous (floor tiles) - flat
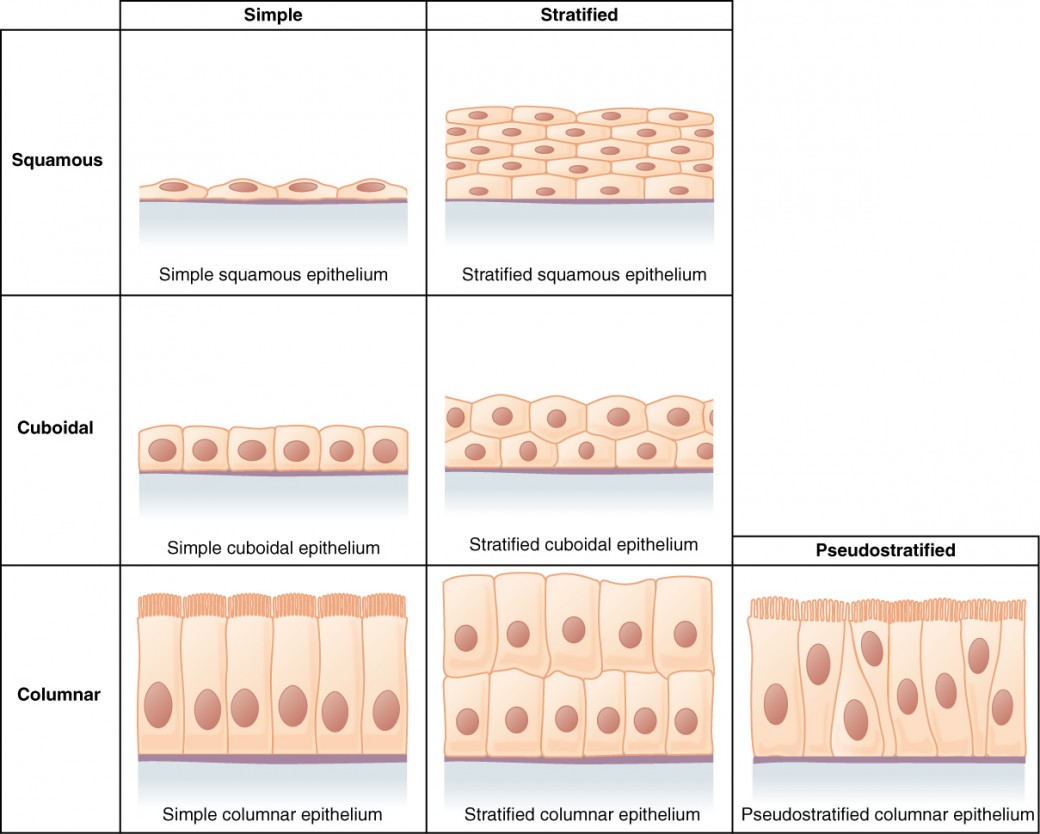
Epithelia tissue layer
Simple epithelial - a single layer of cells that provides a barrier and functions in absorption, secretion, and sensation.
Stratified epithelial - multiple layers of cells that protect underlying tissues.
Pseudostratified epithelial - single layer of cells but look like multiple layers
Connective tissue and five types
Mainly binds and supports other tissues.
It contains cells that are loosely arranged in a liquid, jellylike or solid matrix
Loose connective tissues
Adipose tissues
Blood
Fibrous or dense tissues
Cartilage
Bones
Loose connective tissue
Binds to epithelia to underlying tissues and holds organs in place
Composed of loosely woven collagen and elastic fibers
Fibers and other components of the connective tissue matrix are secreted by fibroblasts
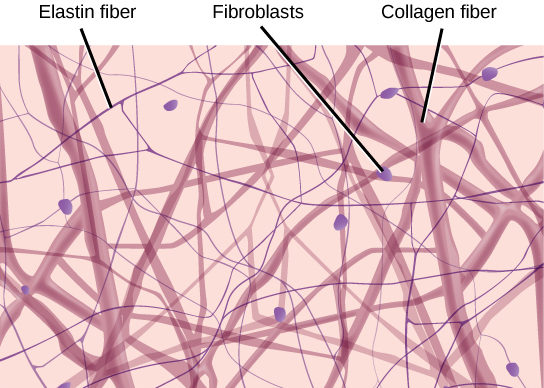
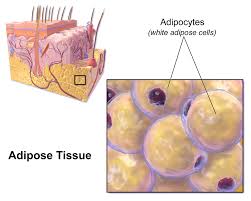
Adipose tissue
Stores fat for insulation and fuel
Each adipose cell contains a large fat droplet that swells when fat is stored and shrinks when the body uses fat as fuel
Blood
Composed of blood cells and cell fragments in blood
Matrix is a liquid called plasma, consisting of water, salts, and a variety of dissolved proteins
Suspended in the plasma are erythrocytes, leukocytes and cell fragments called thrombocytes
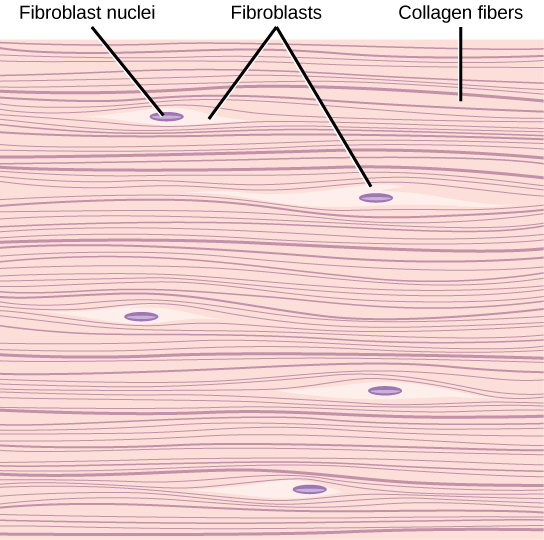
Fibrous (or dense) connective tissue
Found in tendon
Attach muscles to bones and ligaments
Connect bones at joints
Fibrous connective tissue from the tendon has strands of collagen fibers lined up parallel
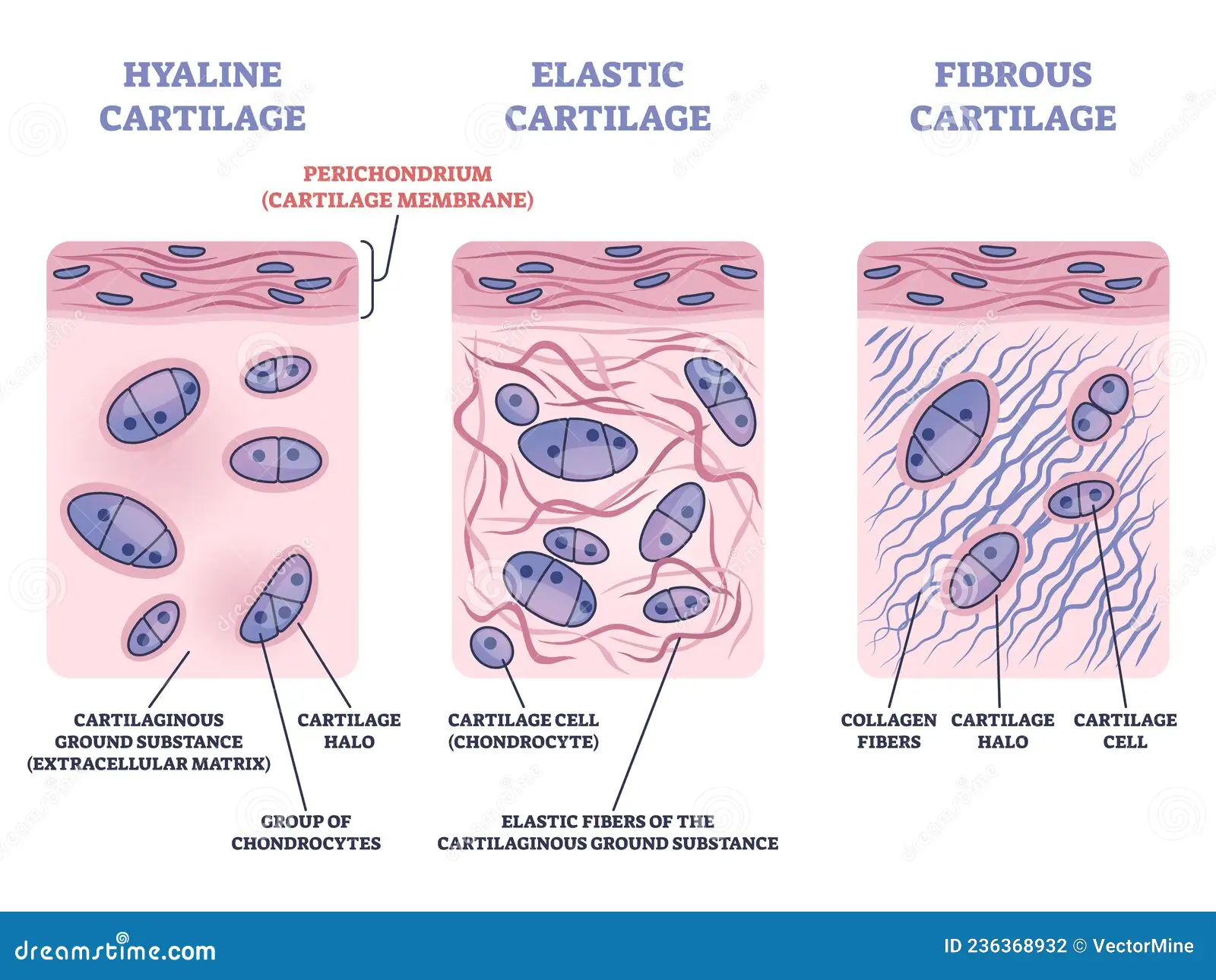
Cartilage
Strong and flexible support material (found in nose, ears and rib cage)
Has an abundance of collagenous fibers embedded in a rubbery matrix made of a substance called chondroitin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate is a protein-carbohydrate complex
Chondrocytes secrete collagen and chondroitin sulfate
Composite of collagenous fibers and chondroitin sulfate makes cartilage a strong yet somewhat flexible support material
Bones (osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts)
Mineralized and forms the skeleton
Large amount of two different types of matrix material
Organic matrix is similar to the matrix material found in other connective tissues, including some amount of collagen and elastic fibers
The inorganic matrix consists of mineral salts-mostly calcium salts-that give the tissue
Microscope structure of hard mammalian bones consists of repeating units called osteons or Haversian systems
Osteoblasts are immature cells active in making bone for growth and remodeling
Osteoblasts deposit bone material into the matrix and, after the matrix surrounds them, they continue to live, but in a reduced metabolic state as osteocytes
Osteocytes are mature bone cells found in lacunae of the bone interconnected by the canaliculi (spider-shaped and are responsible for maintaining bone tissue)
Osteoclasts are active in breaking down bone for bone remodeling, and they provide access to calcium stored in tissues
Multinucleated cells secrete acids and proteolytic enzymes to dissolve collagen and mineral coating
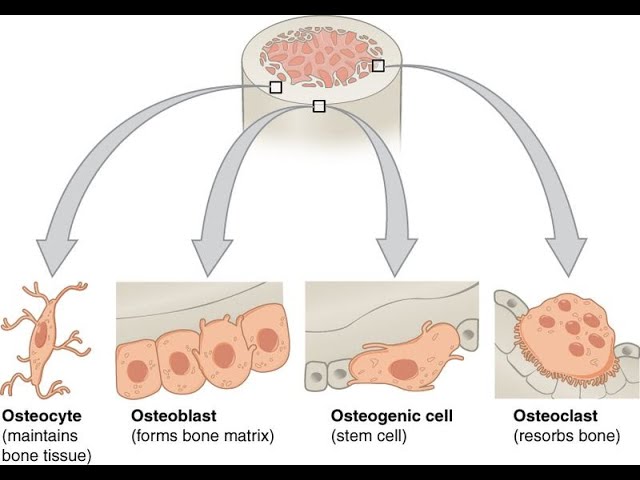
Types of bone cells (connective tissue)
Osteroblasts - immature cells active in making bone for growth and remodeling
Osterocytes - mature bond cells found in lacunae of the bone interconnected by canaliculi
Osteroclasts - active in breaking down bone for bone remodeling and they provide access to calcium stored in tissues
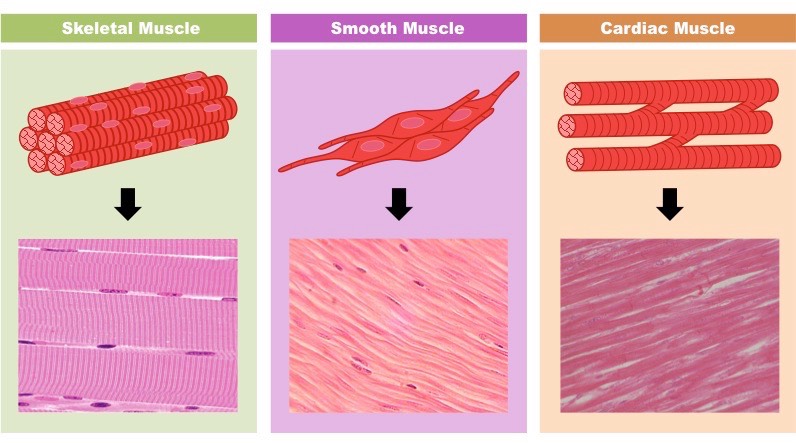
Muscle tissue and the three types
long cells called muscle fibers which contract in response to nerve signals
Three types of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle - attached to bone sand is responsible for voluntary body movement
Smooth muscle - mainly lines internal organ and is responsible for involuntary body activities
Cardiac muscle - responsible for heart contraction to help pump blood throughout the body
Nervous tissue
Sense stimuli and transmits and electrical signals throughout the animal
What the nervous tissue contains
Neurons - nerve cells that transmit nerve impulses
Gilal cells - help nourish, insulate, and replenish neurons
Dendrites - short branching which transit electrical signals form adjacent cells to the neuronal cell body
Long axons - which carry electrical signals from the cell body to other cells
Three animal categories (eating style)
Herbivores - eat mainly autotrophs (ex. cows and rabbits)
Carnivores - eat other animals (ex. sharks, spider and snakes)
Omnivores - regular consume animals as well as plants or algal matter (ex. human and bears)
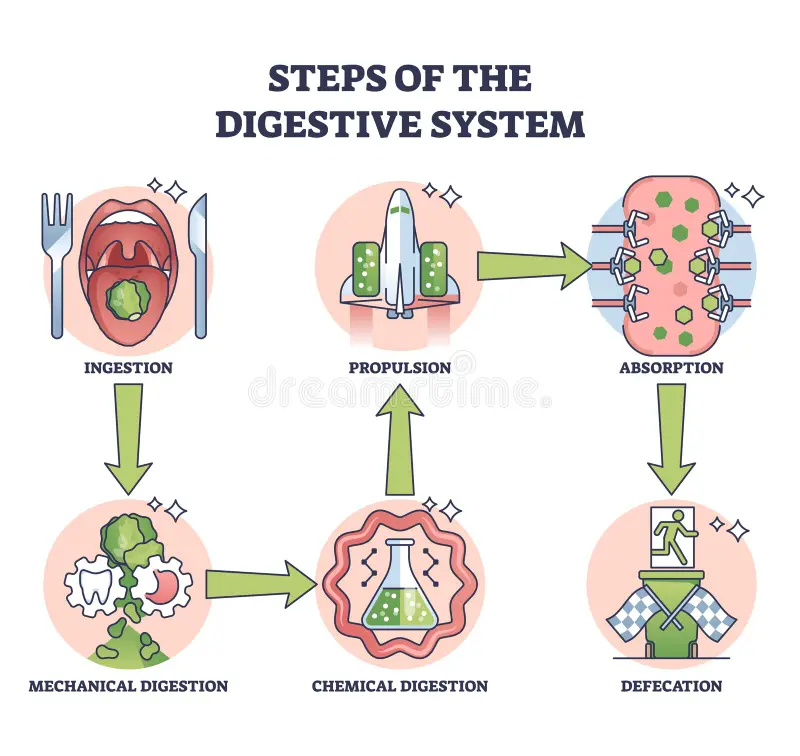
Main stages of food processing
1) Ingestion - is act of eating
2) Digestion - process of breaking food down into soluble molecule. Mechanical digestion: chewing and churning increases surface area of food for faster chemical digestion. Chemical digestion: process of enzymatic hydrolysis which splits bonds in molecules with addition of water
3) Absorption - is uptake of nutrients by body cells
4) Elimination - passage of undigested material digestive compartment
Gastrointestinal tract (mammalian digestive system)
Consists of a pathway by which food enters body and solid wastes of expelled.
Salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder which secrete digestive juices into gastrointestinal tract through ducts to help breakdown food
Food is pushed along by peristalsis, rhythmic contractions of smooth muscles
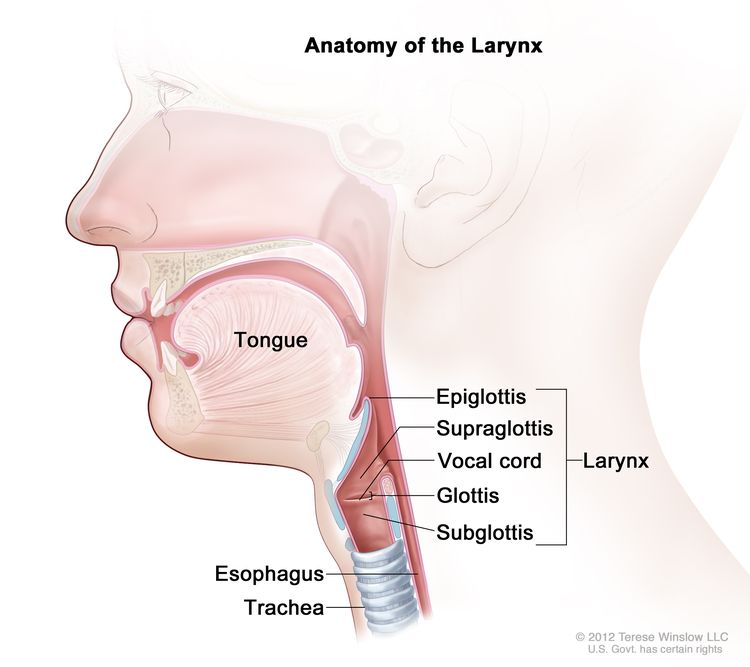
The oral cavity, pharynx and esophagus
Salivary glands - deliver saliva to lubricate food, this contributes to mechanical digestion as it increases the surface area allowing chemical digestion to happen quickly with the usage of salivary amylase
Tongue shapes food into a bolus and provides help with swallowing
Throat region is called the pharynx which opens the esophagus and trachea (windpipe)
Swallowing causes the epiglottis to block entry to the trachea
The esophagus conducts food from pharynx down to stomach by peristalsis
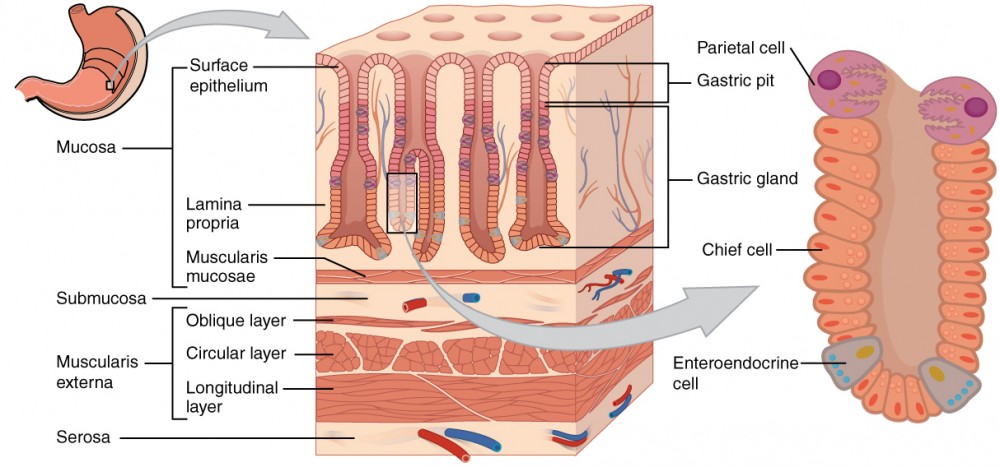
Digestion in the stomach
accordion-like folds and a very elastic wall
stores good and secretes gastric juice, which converts a meal to acidic chyme (gastric juice is made of hydrochloric acid and pepsin)
Coordinated contraction and relaxation of stomach smooth muscle churn the stomach’s contents (churning mixes and breaks down food)
Sphincters prevents chyme from entering the esophagus and regulate its entry into the small intestine
Parietal cells secrete Hydrogen (H+) and chloride (Cl-), separately
Chief cells secrete inactive pepsinogen which is activated to pepsin when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach
Mucous cells secretes mucous which protects stomach lining from gastric juice
Digestion in the small intestine (major organ)
Small intestine is longest section of alimentary canal
It is the major organ of digestion and absorption
First portion of the small intestine is the duodenum where chyme from the stomach mixes with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, gallbladder and the small intestine itself
Pancreas secretions
Secretes zymogens partly to prevent the enzymes form digesting the cells in which they are synthesized
Proenzymes are normally activated after entering the duodenum
Pro-enzymes
Trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen = activated into trypsin and chymotrypsin (breaks down small polypeptides)
Procarboxypeptidase = activated into carboxypeptidase (breaks down smaller polypeptides)
Prolipase = activated into lipase (break downs fats)
Proamylase and pronucleases = activated into amylase and nuclease (breaks down starch and carbohydrates, nucleotides)
Bile production by the liver
Small intestine, bile aids in digestion and absorption of fats
Bile is made in liver and stored in the gall bladder
Bile emulsifies fat (type of mechanical digestion)
Emulsification: transformation of large liquid droplets into small lipid droplets also increases surface area for chemical digestion of fats by lipases
Liver functions
Detoxifies the blood to rid it of harmful substance
Stores some vitamins and iron
Stores the simple sugar glucose as glycogen
converts glycogen to usable sugar when the body’s sugar levels fall below normal
Breaks down hemoglobin as well as insulin and other hormones
Converts ammonia to urea
Destroys old red blood cells
Absorption in the small intestine - villi and microvilli
Increases the surface area for absorption
Enormous microvillar surface area greatly increases rate of nutrients
Each villus contains a network of blood vessels and a small lymphatic vessel called a lacteal
Glycerol and fatty acids are absorbed by epithelial cells and are recombined into fats
Fats are coated with phospholipids, cholesterol and proteins to form chylomicrons
Amino acids and sugar pass through the epithelium of the small intestine and enter the bloodstream
Capillaries and veins from the lacteals in small intestine all converge to form the hepatic portal vein, which delivers blood to the liver and then on to the heart