Perioperative Nursing Care and Processes
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Perioperative Care
care that clients receive before, during, and after surgery
Informed Consent
Client's agreement after understanding procedure details.
-description of procedure and alternatives
-name and qualifications of person performing the procedure
-risks/benefits
-explain right to refuse
-explain natural disease process and its course
-explain expected outcome, recovery, rehab plan and treatment course
-must make sure patient understands
Nurse role during consent
-not getting the consent but Witnessing
medication safety after surgery
-patient can be AAO x4 but overestimates ability while on medication or forget what wires and IV they are attatched too annd can fall
interventions
prevent blood clots, venous thrombus, pulmonary embolism
-ambulation is the most important thing
pulmonary safety after surgery
cough/deep breath (2 hrs)
-incentive spirometer (10-20x an hour) (blow out, suck slow and deep to fully expand the lungs)
encourage pain meds
so patient is more comfortable ambulating or doing respiratory exersizes
report
abnormalities
to prevent DVT
-early ambulation
-compression stockings/ted hose
Preoperative Phase
Begins with surgery decision, ends before surgery when client is transferred to OR or procedure bed
Intraoperative Phase
Begins at OR transfer, ends at PACU transfer.
Postoperative Phase
Begins at PACU admission, ends with recovery from surgery and follow up with MD.
Surgical procedures are classified in 3 ways
1.urgency
2.Risk
3.purpose
Elective Surgery
Surgery planned in advance, not urgent.
Urgent Surgery
Requires prompt attention but not emergency.
Emergency Surgery
Immediate surgery needed to save life.
risk could be either
minor or major
Purpose could be
-diagnostic (biopsy)
-curative (removal of mass)
-preventative
-ablative
-palliative (wont cure but increases comfort)
-reconstructive (boob job)
-transplantation
-constructive
anesthesia states
-Loss of consciousness (for endoscopy or colonoscopy deep sleep)
-Amnesia (forget it)
-Analgesia (pain meds)
-relaxed skeletal muscles (intubation)
-Depressed reflexes (intubation)
General Anesthesia
Induces loss of consciousness via inhalation or IV.(Intubation/ventilator)
-patient needs to be cleared by cardio or respiratory
pacemaker patient?
need to be checked B4 surgery call manufacturer
Regional Anesthesia
Blocks sensation in specific body area by injecting anesthetic agent near a nerve or nerve pathway around operative site.
-obstetric, knee, bone
Topical Anesthesia
Applied to surface of skin or mucous membranes.
-burns/open wounds
Moderate Sedation analgesia
Used for short, minimally invasive procedures. (conscious sedation/analgesia)
Induction Phase
From anesthesia administration to incision readiness.
Maintenance Phase
From incision to near procedure completion.
Emergence Phase
Client wakes from anesthesia, ready to leave OR.
types of regional anesthesia
-nerve blocks
-spinal
-epidural
nerve block anesthesia
bone replacement shoulder knee hip
spinal anesthesia
obstetrics/back surgery
epidural
delivering a baby
if patient does not understand the procedure from the physician
call them back to explain
Advanced Directives
Legal documents outlining patient's healthcare preferences.
-nurses responsibility with informed consent
-includes living will and durable power of attorney
living wills
A legal document stating a person's desires on what measures should or should not be taken to prolong life when his or her condition is terminal.
Durable power of attorney
exists when person executes a person as power of attorney which will become or remain effective in the event he or she should later become disabled can even be chosen by patient if they are AAOx4
NANDA
Nursing diagnosis classification system for patient care.
nursing process for perioperative care
-Assessment
-Health history
-Medical history
-allergies (previous reactions to anesthesia)
-Physical assessment
-diagnosis
-nanda
-Impaired comfort
-Risk for infection
-OI/ planning
-Implementing
Client Risk Factors
-Developmental level
-Medical history
-Medications
-Previous surgeries
-Nutrition
-Use of alcohol, illicit drugs, or nicotine
-Activities of daily living and occupation
-Coping patterns and support systems
-Sociocultural needs
stop blood thinners
7 days before surgery
nutrition is important
it influences healing
medications
some may need to be given even if HCP says they are PO (ask Dr)
alcohol/illicit drugs
could influence heart rate and also may need to up-dose drugs
sociocultural needs affect
transplant patients, can they afford after care and necessary medications
tests before surgery
-CBC
-CMP
PTINR
-COMPLETE PANEL
-12-LEAD ekg
-If previous heart issue they need Eccho
-verify labs
-F- pregnancy tests
patient belongings
-make sure you remove everything a secure
jewelery, underwear
-dentures, hearing aids, contacts, glasses
(document what they had with them how you secured it or if you send it home with a family members.
anticoagulants
precipitate hemorrhage
-stop these
herbal meds
-can stop blood clotting
Diuretics
electrolyte imbalances, respiratory depression from anesthesia
Tranquilizers
increase hypotensive effects of anesthetic agents
Adrenal steroids
abrupt withdrawal may cause cardiovascular collapse
(prednisone/cortisone)
-we want to gradually withdraw them
-elevate glucose level and impact healing
Antibiotics in mycin group
respiratory paralysis when combined with certain muscle relaxants
if you notice these medications on your patients MAR
-notify physician and ask if you should hold
Pre-Surgical Screening
-chest xray
-ECG
-CBC
-Electrolyte levels (basic metabolic panel or complete metabolic panel)
-urinalysis
other screening dependent on client individual history
-female-pregnancy tests
nursing role in pre-surgical testing
-Ensure that tests are explained to the client.
-Ensure that appropriate specimens are collected.
-Ensure that results are recorded in client records before surgery.
-Ensure that abnormal results are reported.
CONTACT HCP
Teach client
-Surgical events and sensations
-Pain management
-Physical activities
1.Deep breathing
2.Coughing
3.Incentive spirometry
-Leg exercises (foot pumps)
-Turning in bed
-Early ambulation
(get patient to walk from PACU to bed to expel carbon dioxide)
Nursing Interventions to meet psychological needs
-Establish therapeutic relationship and allow client to verbalize fears and concerns.
-Use active listening skills to identify anxiety and fear.
-Use touch to demonstrate genuine empathy and caring.
-Be prepared to respond to common client questions about surgery.
never give
false reassurance
leg exersises to increase venous return
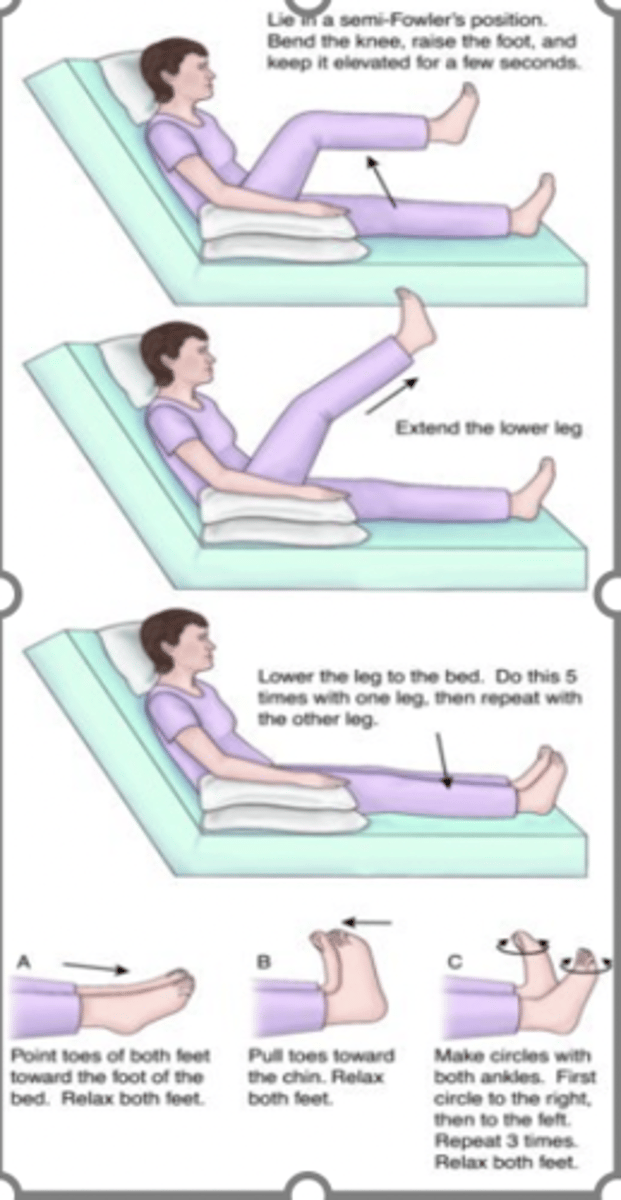
preoperative prep
-Hygiene and skin preparation (chlorahexidene shower twice night before surgery and morning of eliminates bacteria on skin)
-Elimination
-Nutrition and fluids (NPO needs fluid and diabetic must have dextrose)
-Rest and sleep
-Preparation and safety the day of surgery (family must pick them up no ride share)
Intraoperative care
Assessment
-Pre-op completion
-Marking site
-Diagnosis- NANDA
Risk for imbalanced fluid volume
Risk for injury
-Outcome identification /planning
-implementing
-Documenting
-Evaluating
-time out before to make sure all info is correct
normal urinary output
30 cc an hour
Postoperative Assessments
-Monitoring vital signs and recovery status.
-empty all drains /CATHETERS from PACU
-Helps you get accurate I/o
-COUNT ALL SPONGES AND MATERIALS USED
vital signs post op
- q15x4 (first hour)
-q30x2 (next hour)
-q1 hr x4 (every hour for the next 4 hours)
-systematic assessments every 10-15 mins
timeout
-verify patient name
-surgeon
-procedure
return of conciosuness
-make sure patient is AAO
-give small amount of liquid to make sure they can swallow
abdominal patient
-check back for bruising could be hematoma
-if patient is hypotensive and tachycardic could be bleeding
Ongoing Postoperative Care
-Assessment (CBC vitals head to toe)
-Diagnosis
-Acute pain
-Risk for delayed surgical recovery
-Outcome
identification and planning
-Implementing
-Evaluation
Postoperative Assessments and Interventions
Respiratory status (airway, pulse oximetry)
Cardiovascular status (blood pressure and heart rate)
Temperature
Central nervous system status (level of alertness, movement, shivering)
Fluid status (NS /LR)
Wound status
Gastrointestinal status (nausea and vomiting)
General condition
Important: Note comparisons with preoperative baseline values
Outcomes for surgical client
Receive respectful and culturally and age-appropriate care
Be free from injury and adverse effects
Be free from infection and DVT
Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance; skin integrity, normal temperature
Have pain managed
Demonstrate understanding of physiologic and psychological responses to surgery
Participate in rehabilitation process
hemmorrhage
-low BP high heart rate
shock
-BP drop
-WBC increase
when treating an infection
get culture first then get antibiotics
Thrombophlebitis
infiltration
pulmonary embolism
-ambulation, compression devices, ted hose, prophylactic meds (lovonox)
prevent respiratory complications
-elevate HOB
-Incentive spirometer
-cough deep breath
-ambulation (3x a day as per order)
-oral care (q shift and for intubating q4 hrs)
changing surgical dressing
-if you see bleeding circle area and call HCP
-let HCP know dressing has not been changed
-surgeon should do first surgery dressing change
- dressing must stay on for first 24 hours
nutriition
-clear liquid full liquid, advance as tolerated
prevent wound complications
Interventions
-Assess vital signs
-Maintain hydration
-Maintain nutritional status
-Proper hygiene
-Maintaining aseptic technique
Discharge Planning
Teaching:when and how to take medication and for how long
Wound care-report temperature or discharge from incision site
No heavy lifting more than 5 lbs
Don’t wash with soap just let water run
Make follow up day of discharge
Educate s/s to look for
If on narcotics no driving
Activity- be mobile walk around and use IS
Nutrition- eat good diet and take stool softener when on narcotics
Support systems- family to help or friends may need home health care involved
Thrombophlebitis
Inflammation of veins due to blood clots.