Unit 2 BIO Test: Biochemistry of food
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How many covalent bonds can carbon make with other atoms?
4 covalent bonds, it's tetravalent
This type of fatty acid is liquid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fatty acids.
Fatty acids are bonded by a chain of this element...
carbon
What are the 6 most common elements in living things?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur

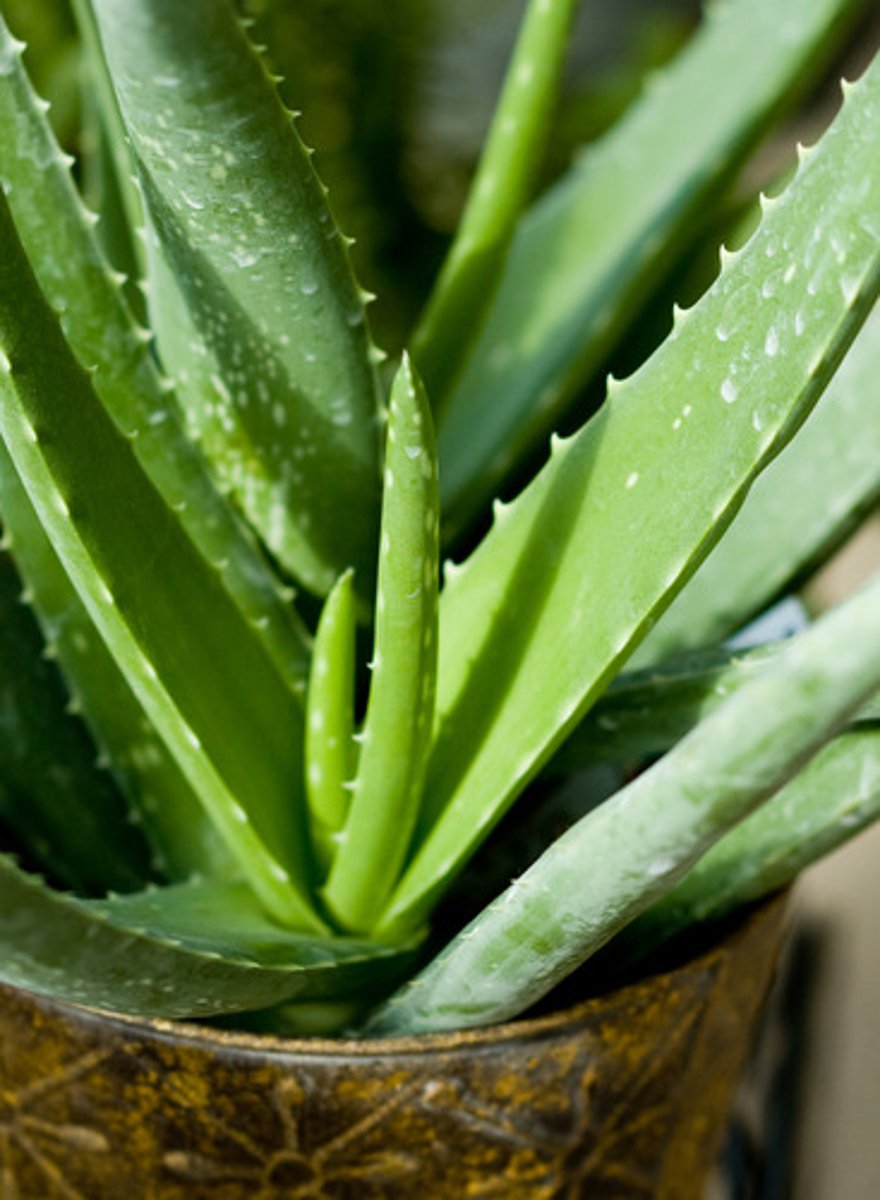
A scientist is analyzing a sample of tissue from an aloe vera plant. Which of the following elements will be found in the greatest amount in the sample?
carbon and oxygen
3 multiple choice options

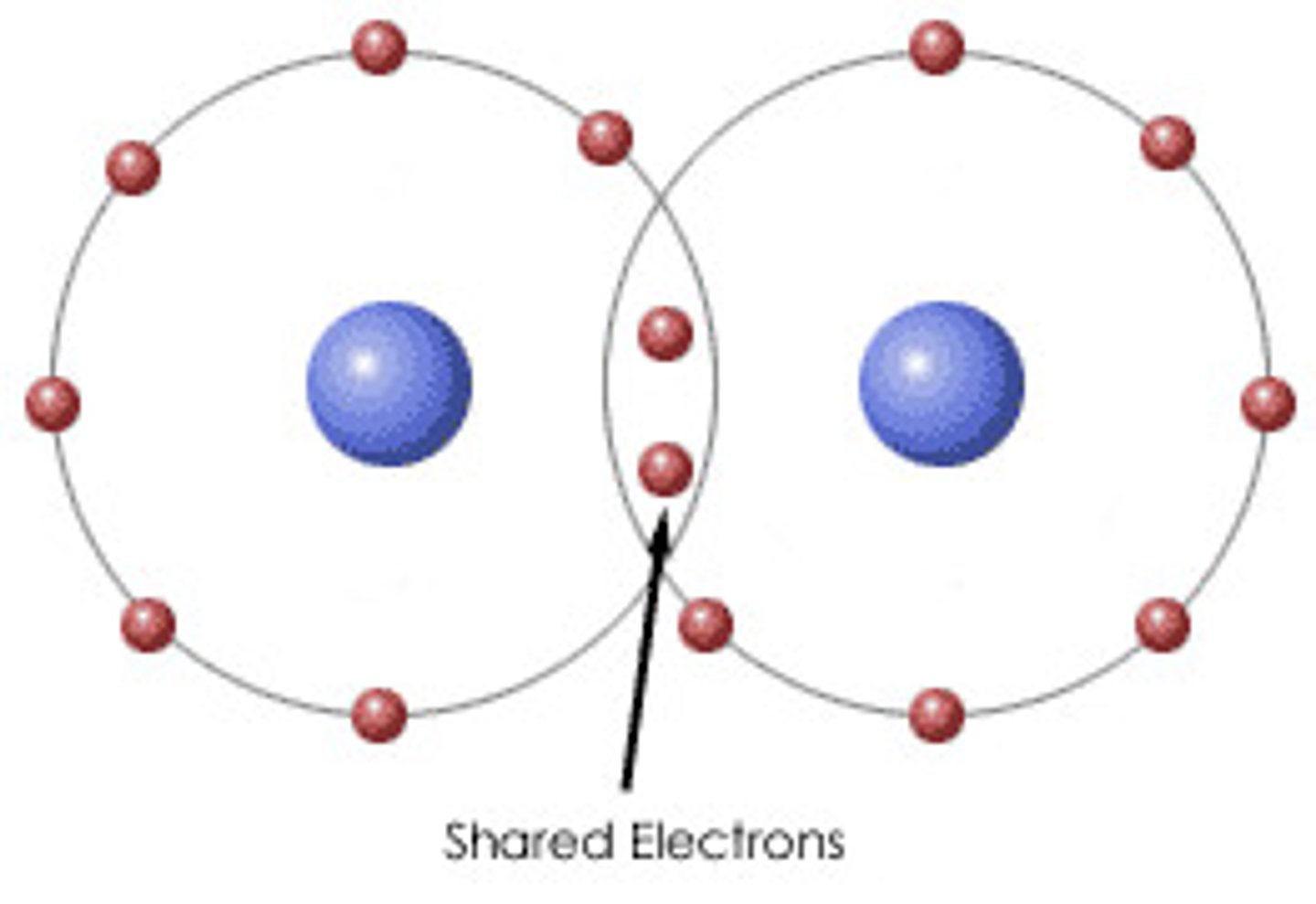
A covalent bond is formed between atoms when:
electrons are shared between atoms
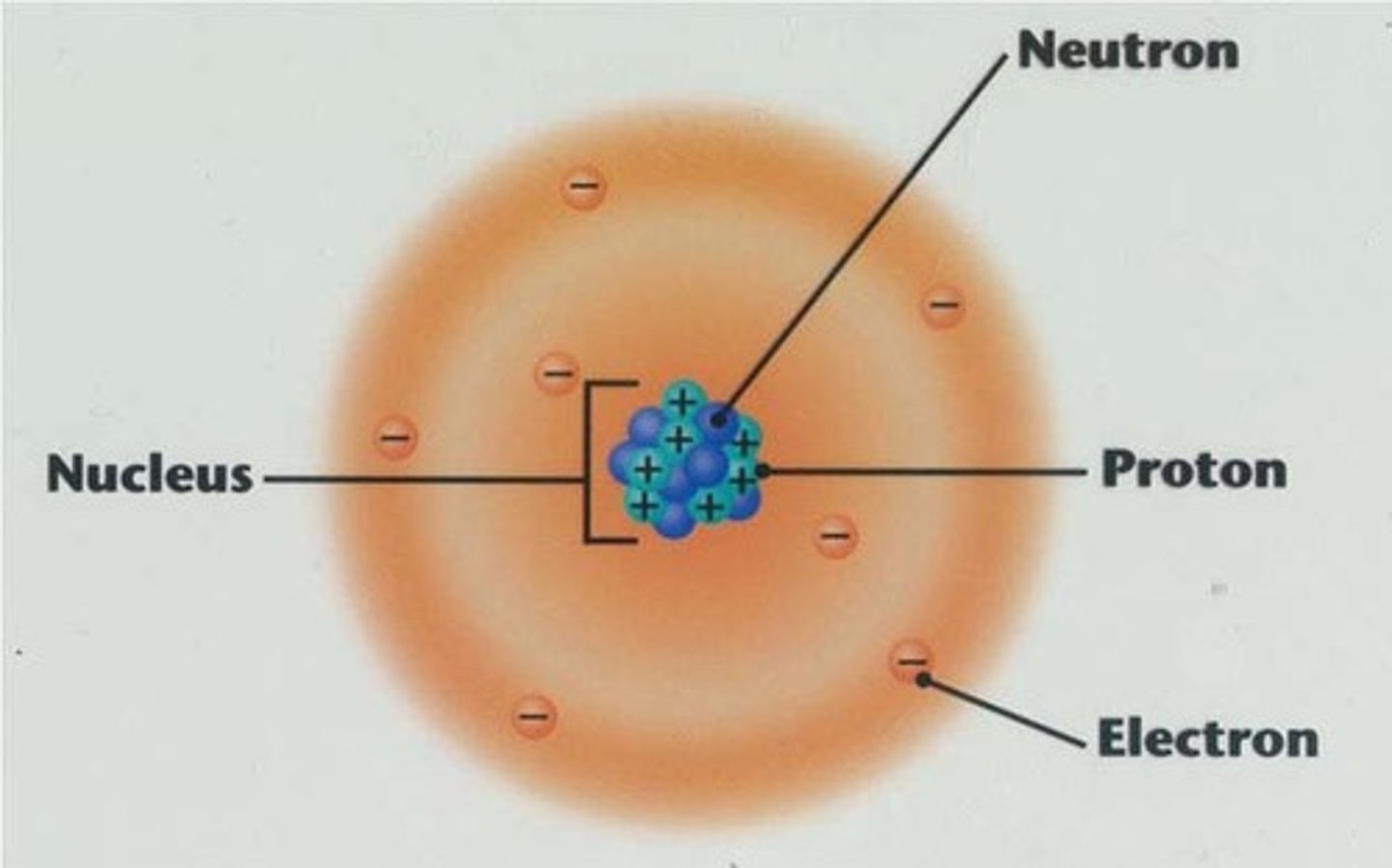
An electron
has a negative charge
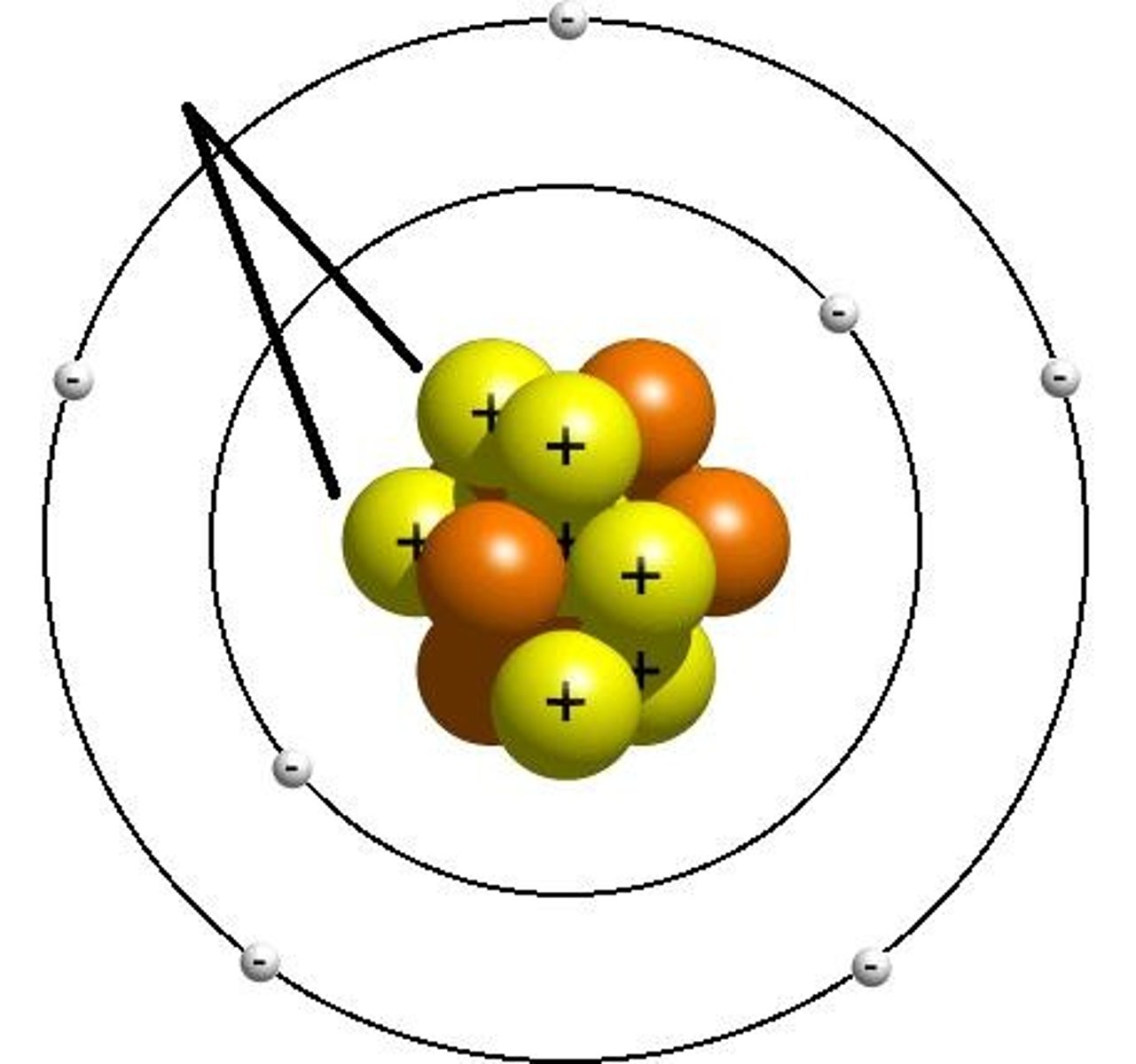
An electron is located...
on the shells of an atom.
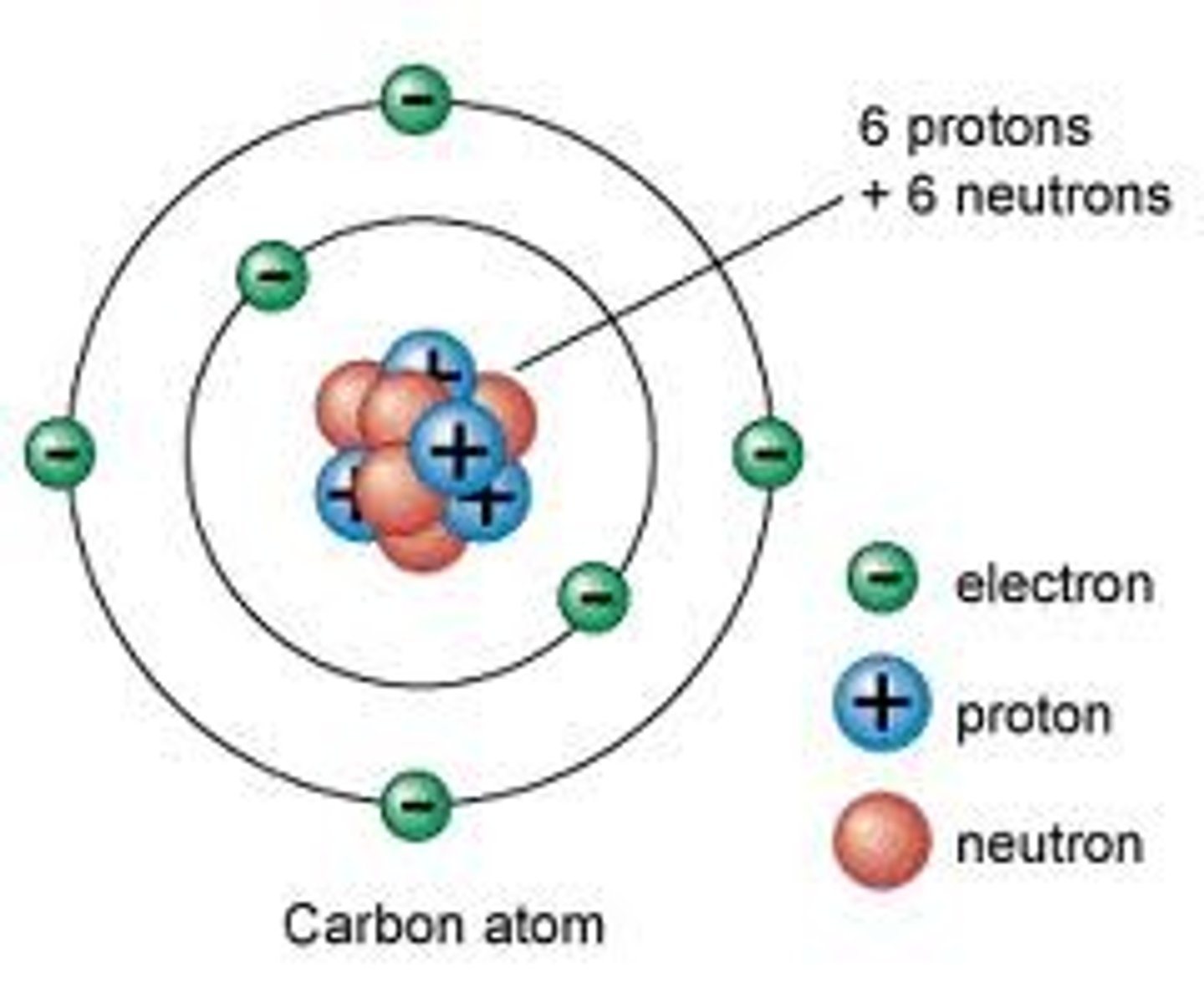
Positively charged atomic particles are called:
protons
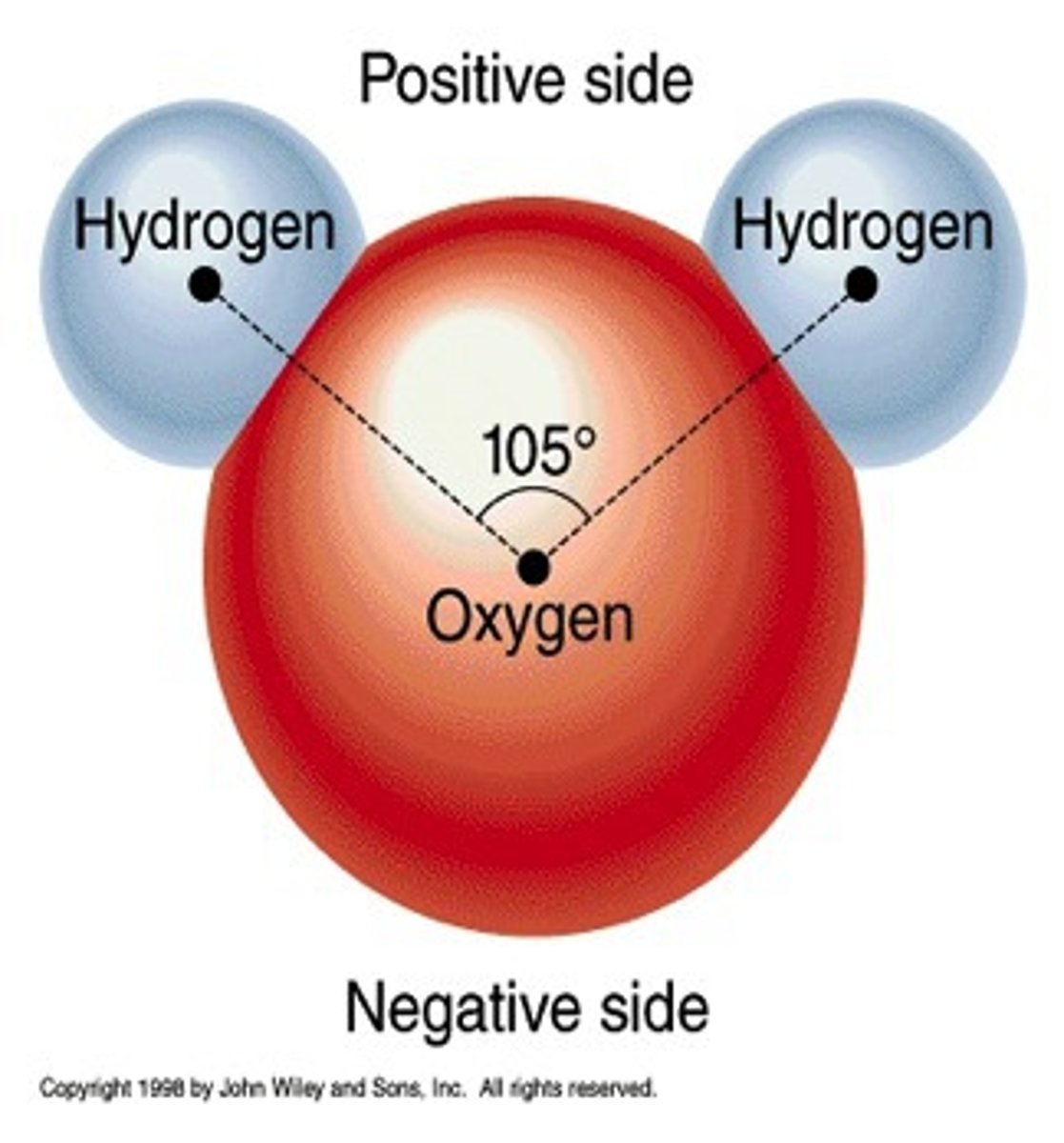
Water is a polar molecule because
different parts of the molecule have slightly different charges
hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
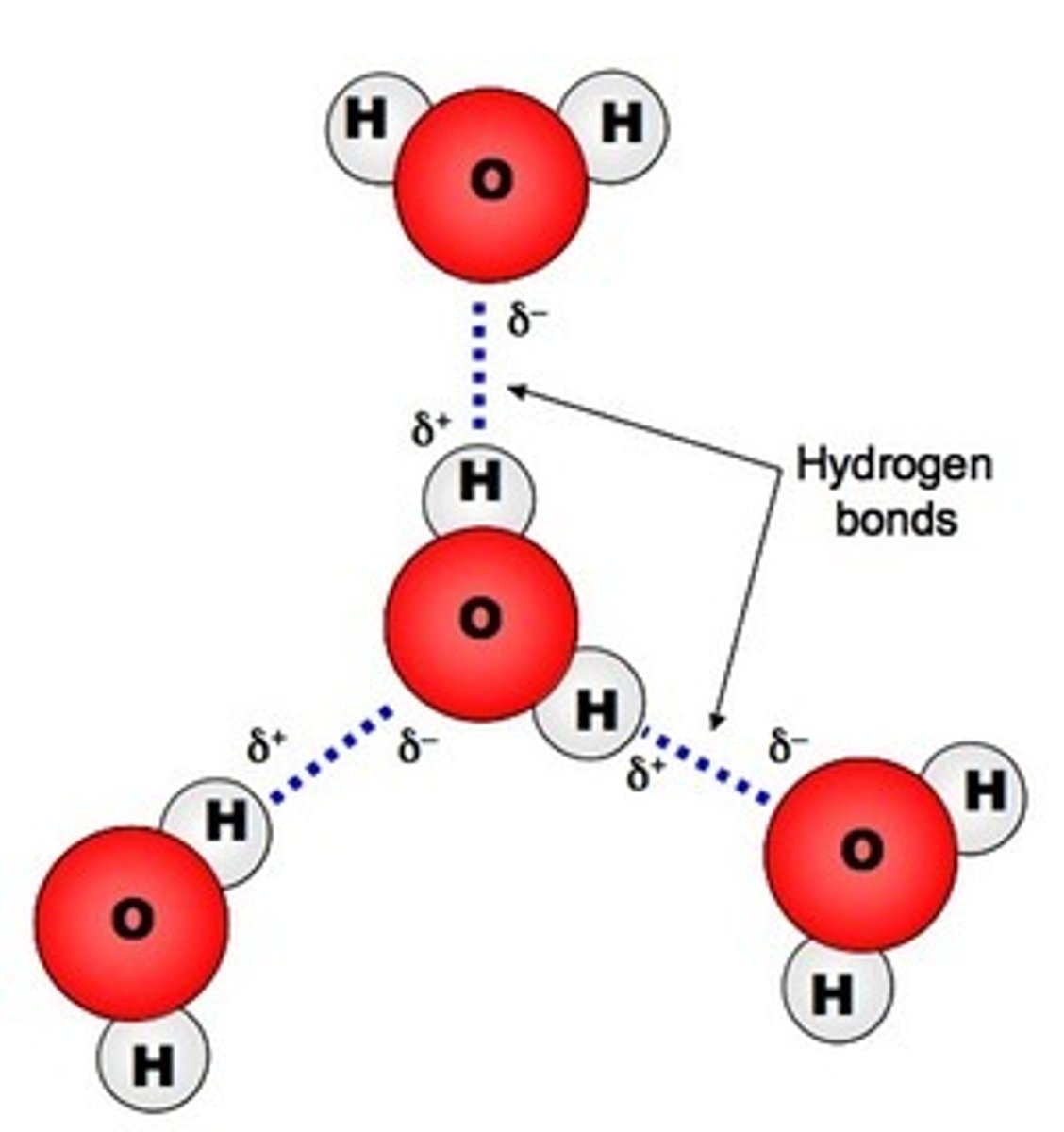
Cohesion
the sticking together of particles of the same substance.
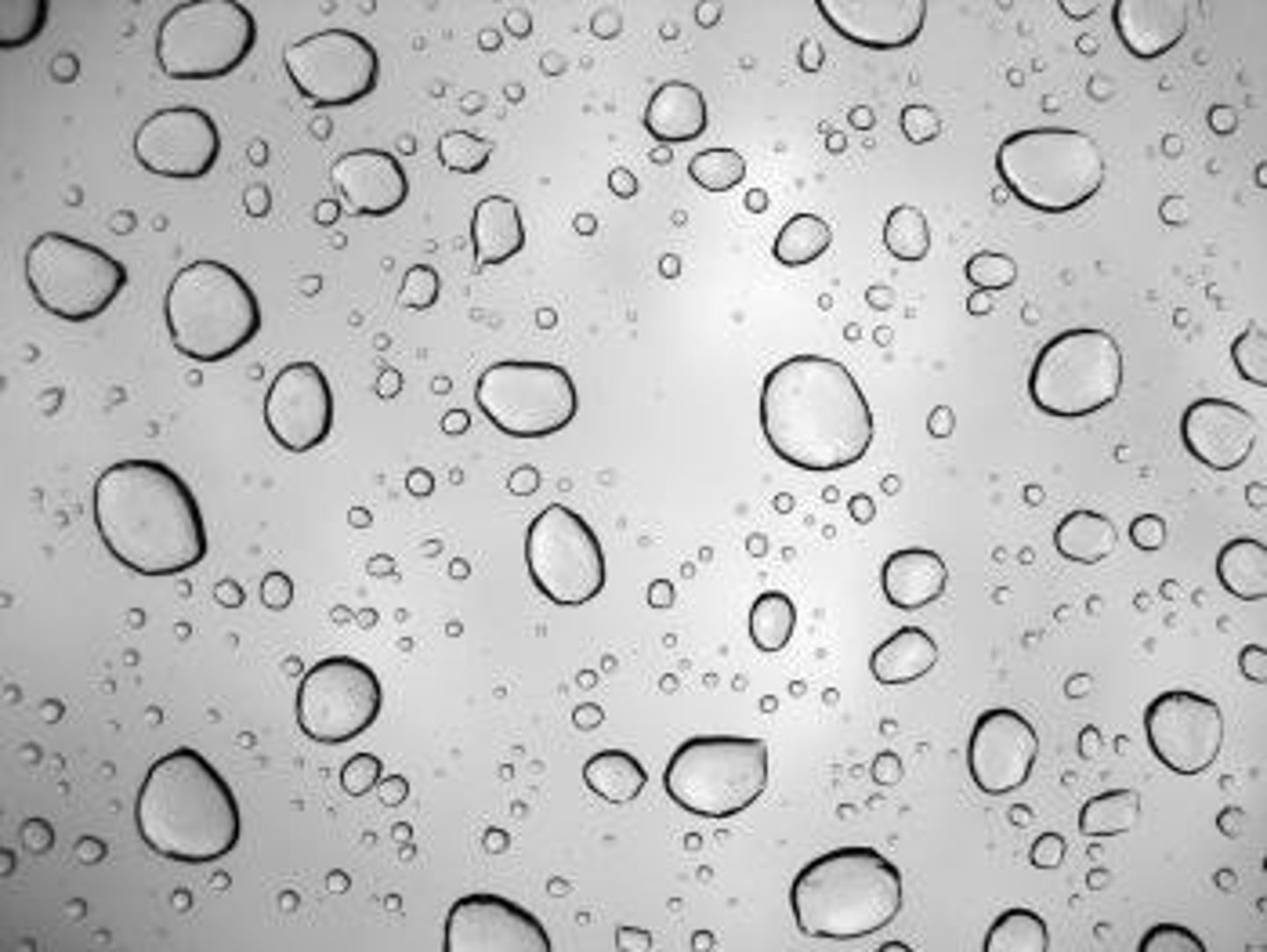

Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
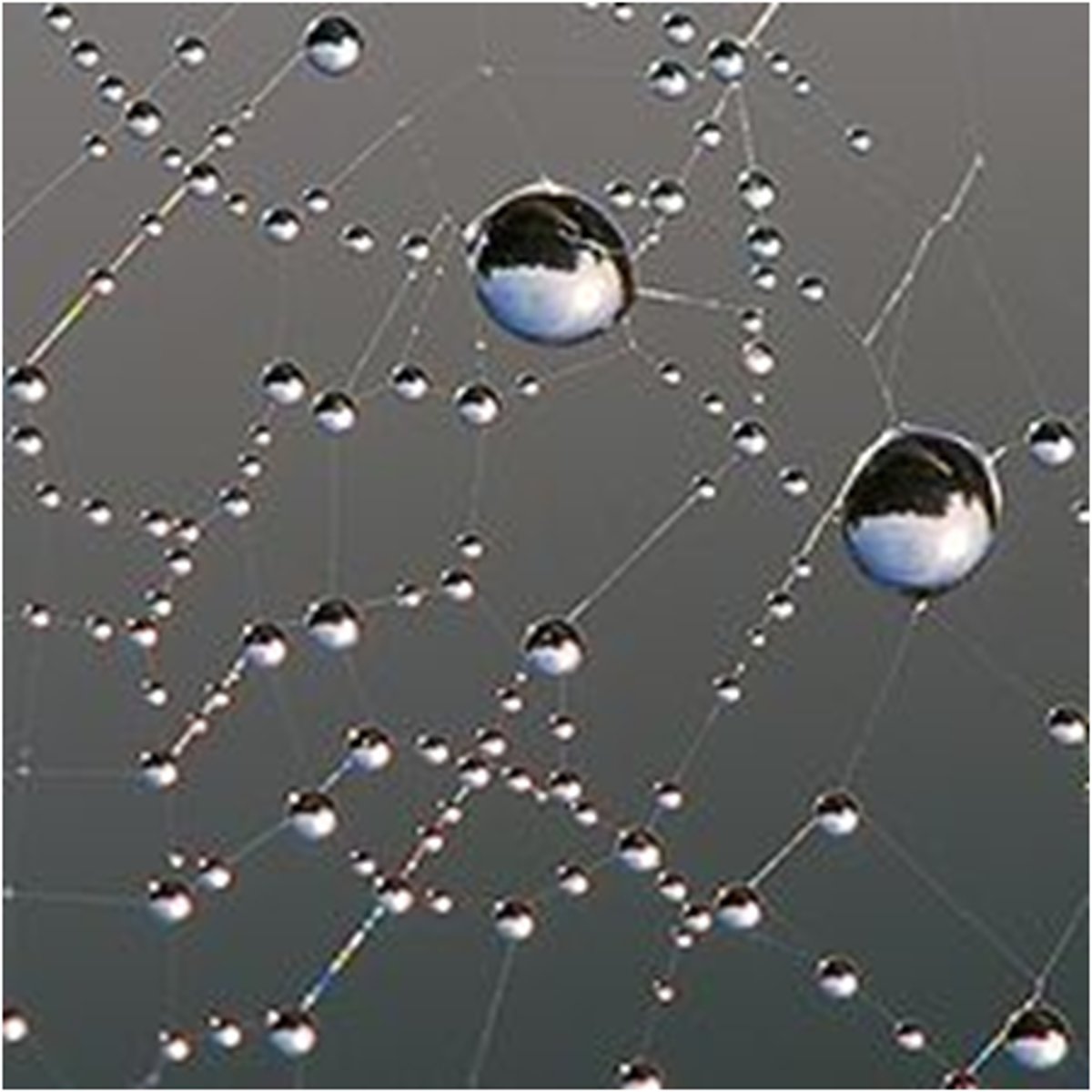

Surface tension (of water)
the intermolecular hydrogen bonds between molecules of water at the surface.
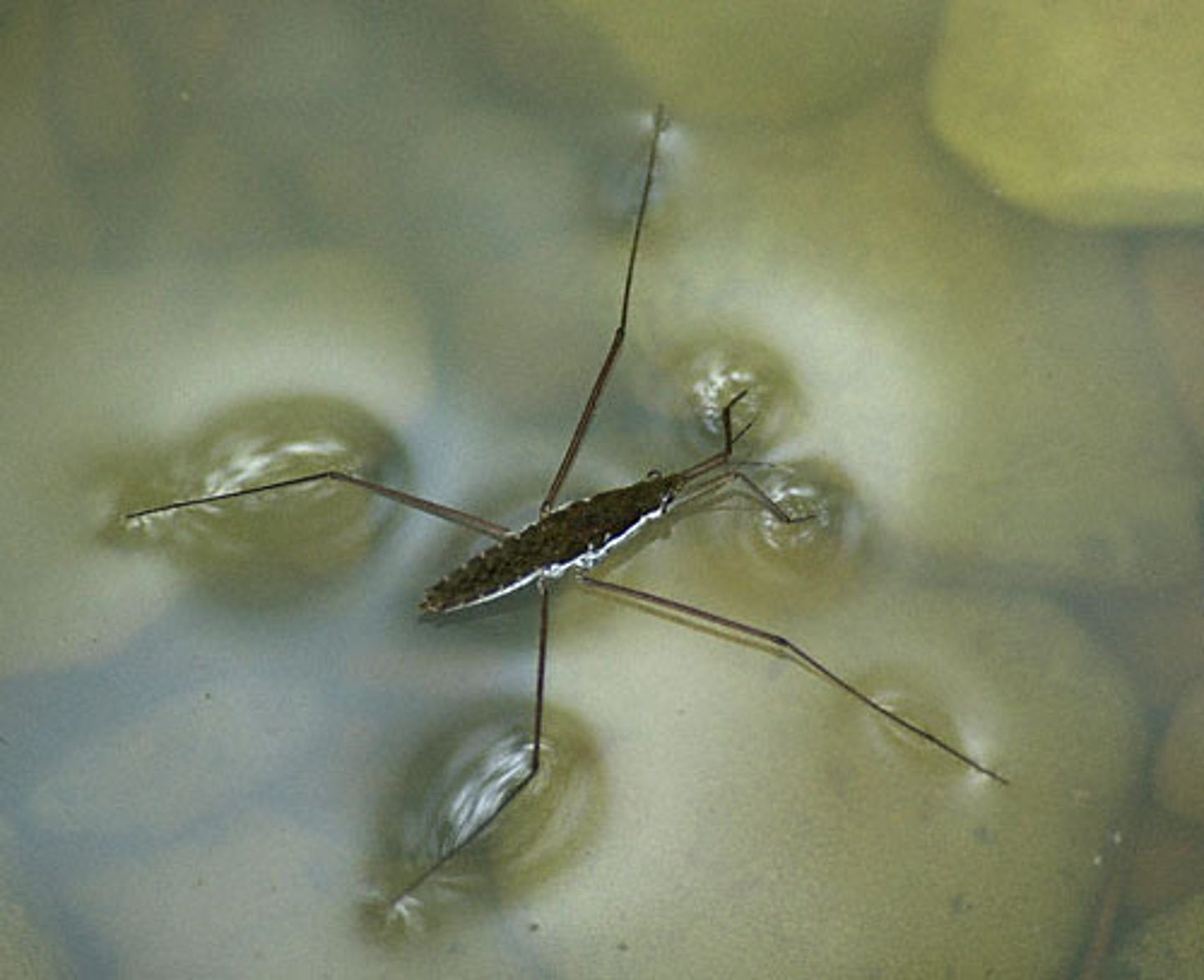

capillary action
tendency of water to rise in a thin tube due to adhesion and cohesion

water resists changes in temperature
water absorbs heat and releases heat slowly
3 multiple choice options

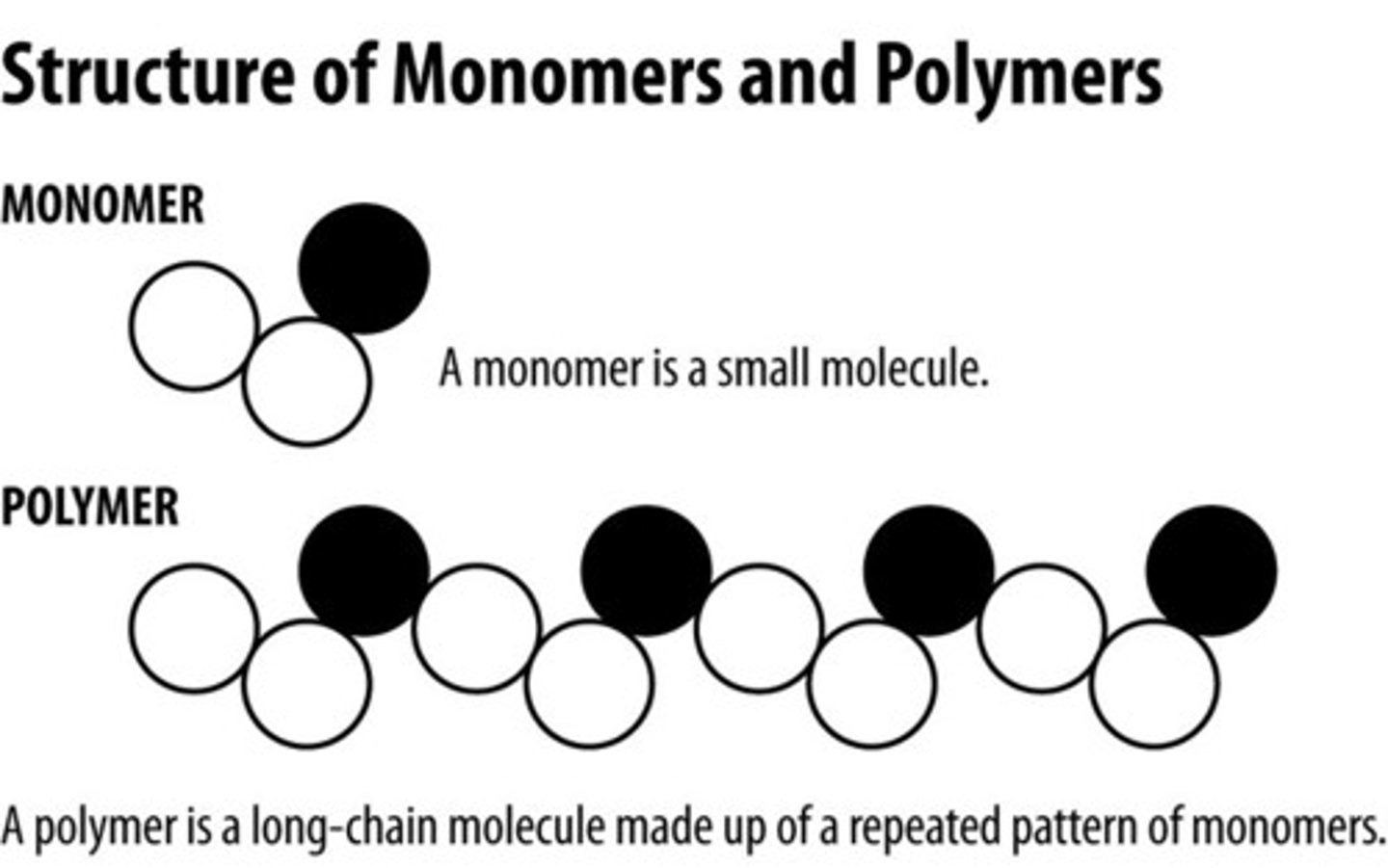
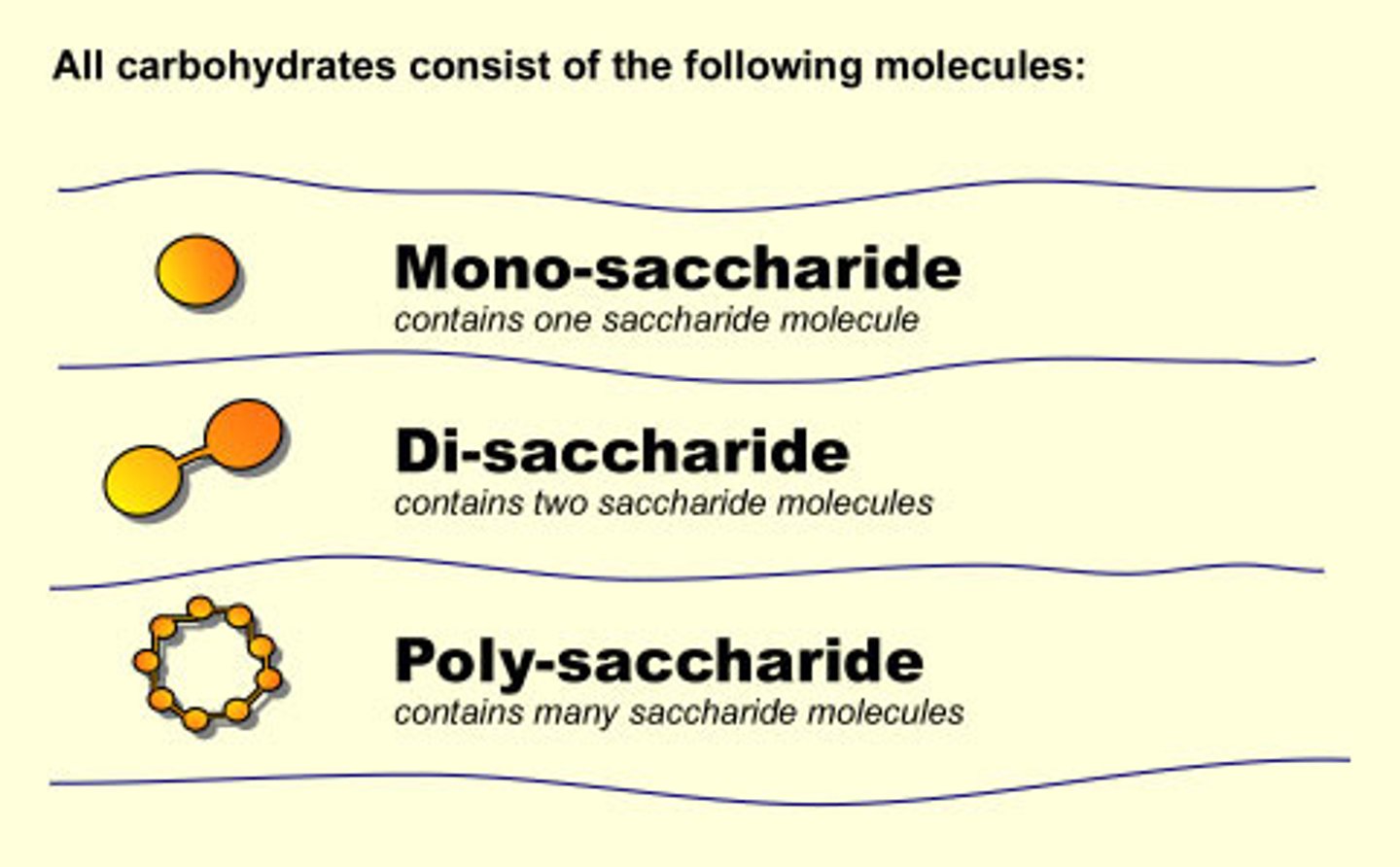
Macromolecules (biomolecules) are large molecules that are made of smaller molecules called:
monomers
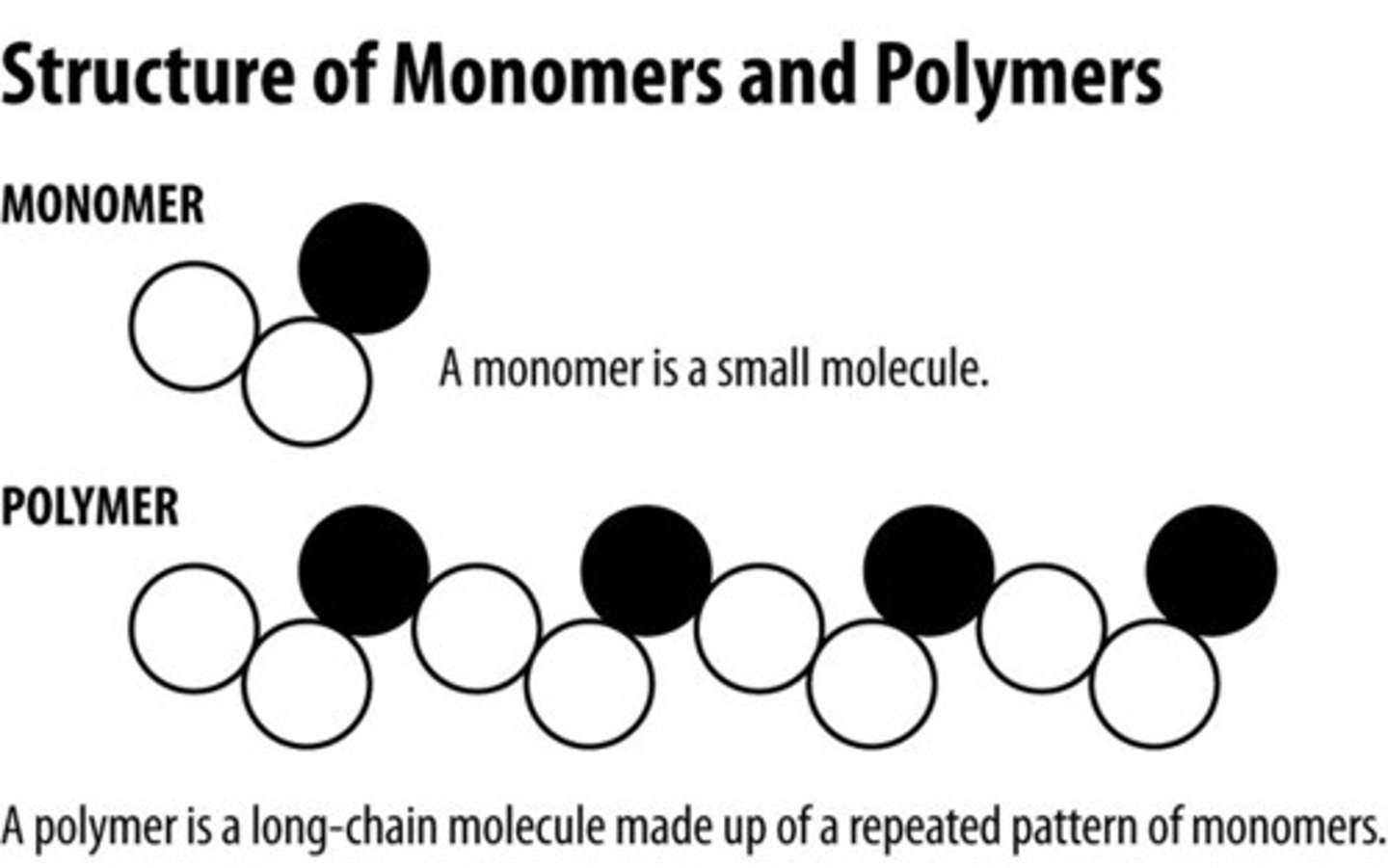
Monomers (smaller molecules) join together to form
polymers
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction that…
breaks polymers apart into monomers
3 multiple choice options
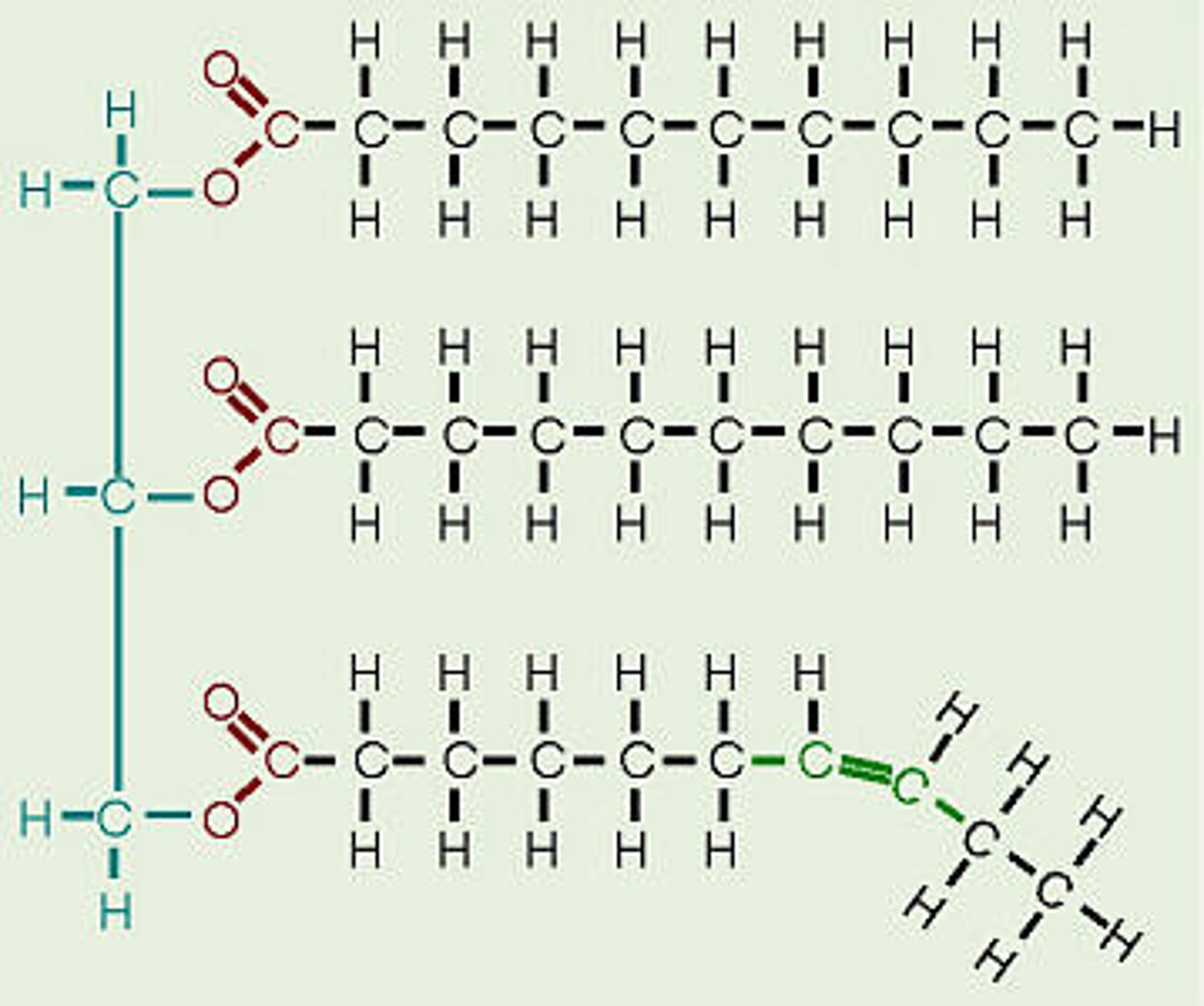
One type of macromolecule is made of long hydrocarbon chains. The hydrocarbon chains may be saturated or unsaturated. Which type of molecule is this?
Lipids
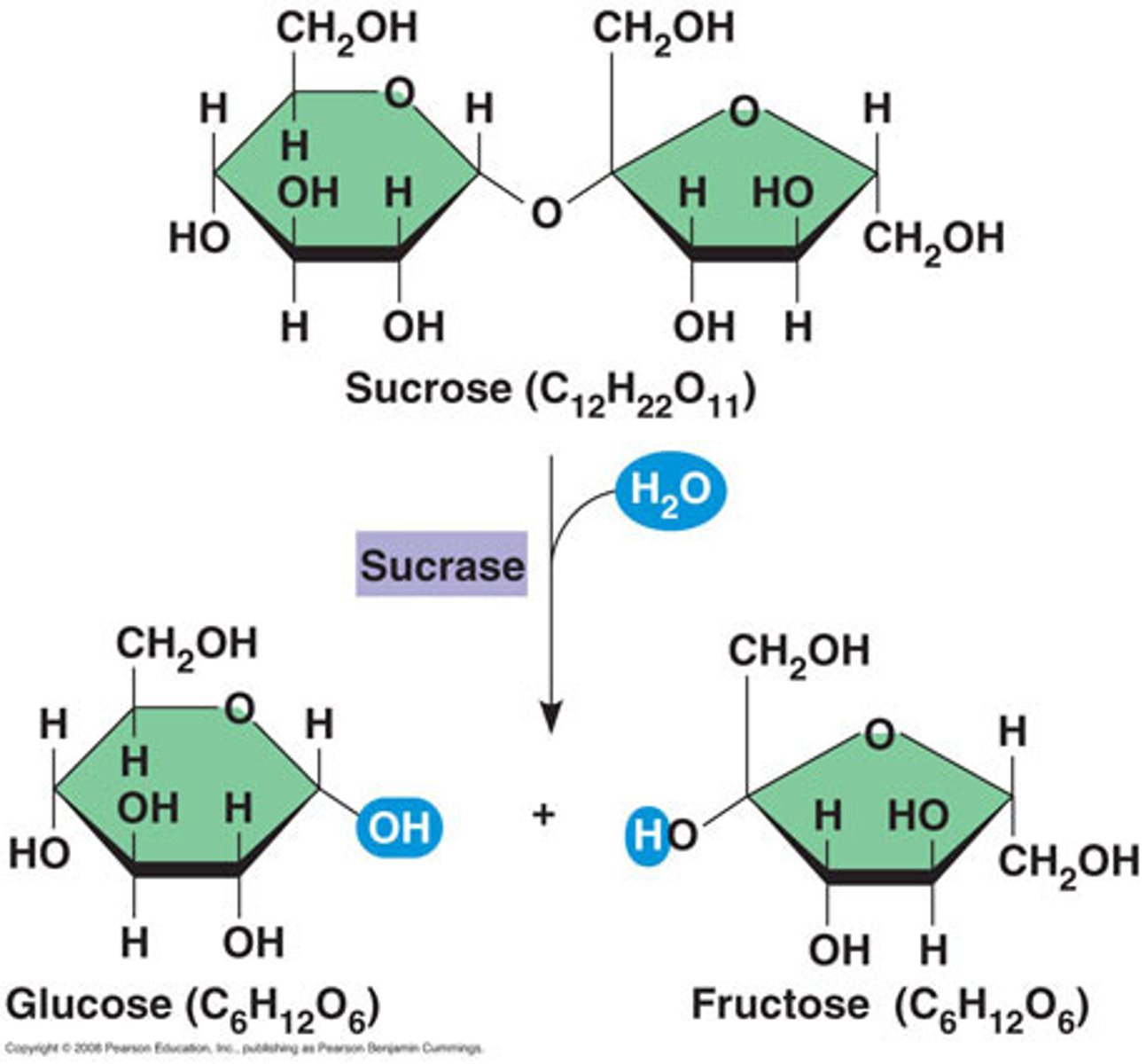
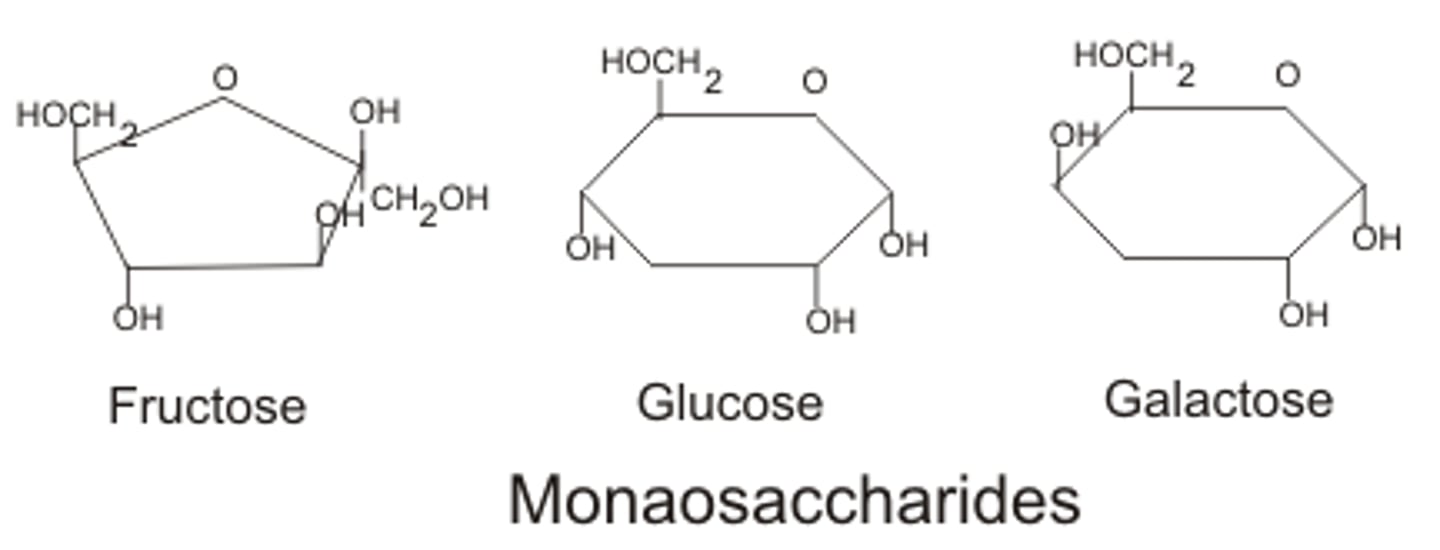
Carbohydrates can be simple molecules or complex macromolecules. Many of these simple carbohydrates are called:
monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
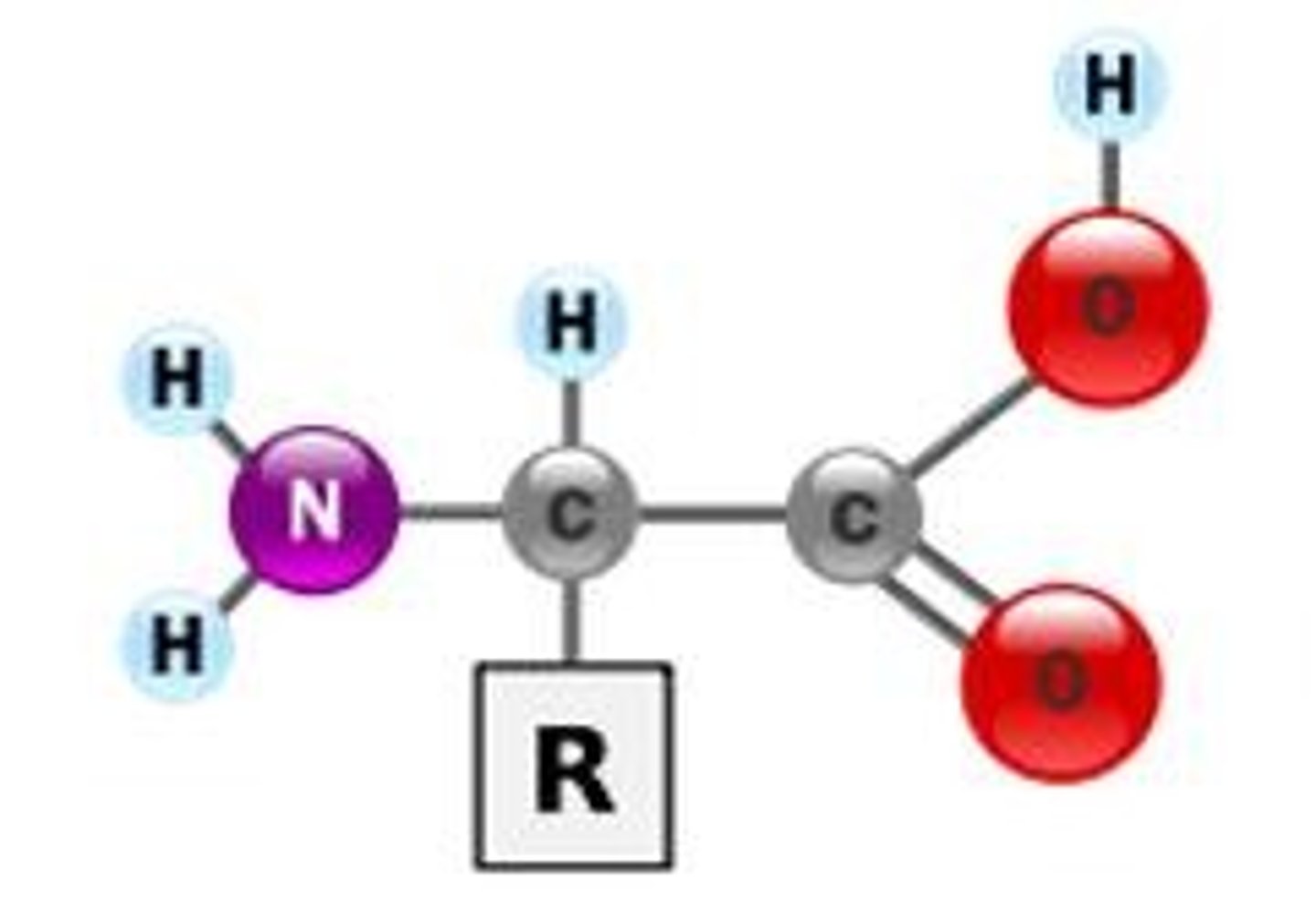
amino acids
monomers of proteins
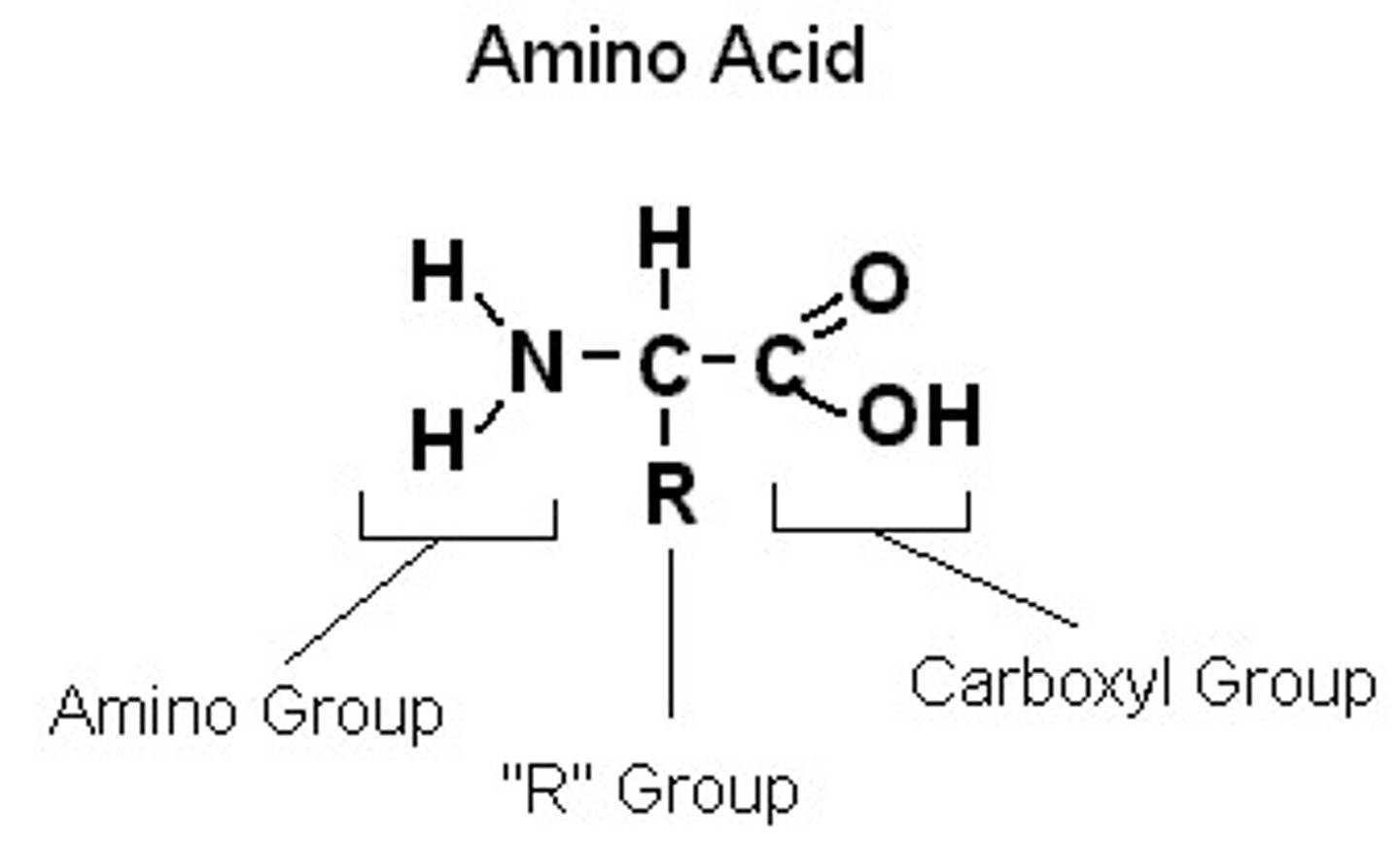
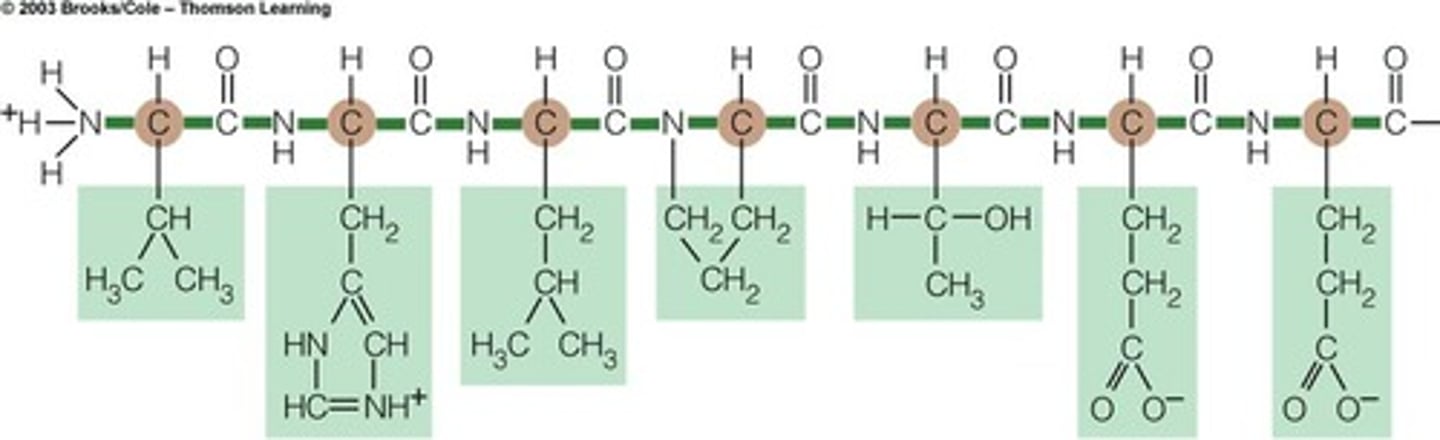
Proteins
Chains of amino acids
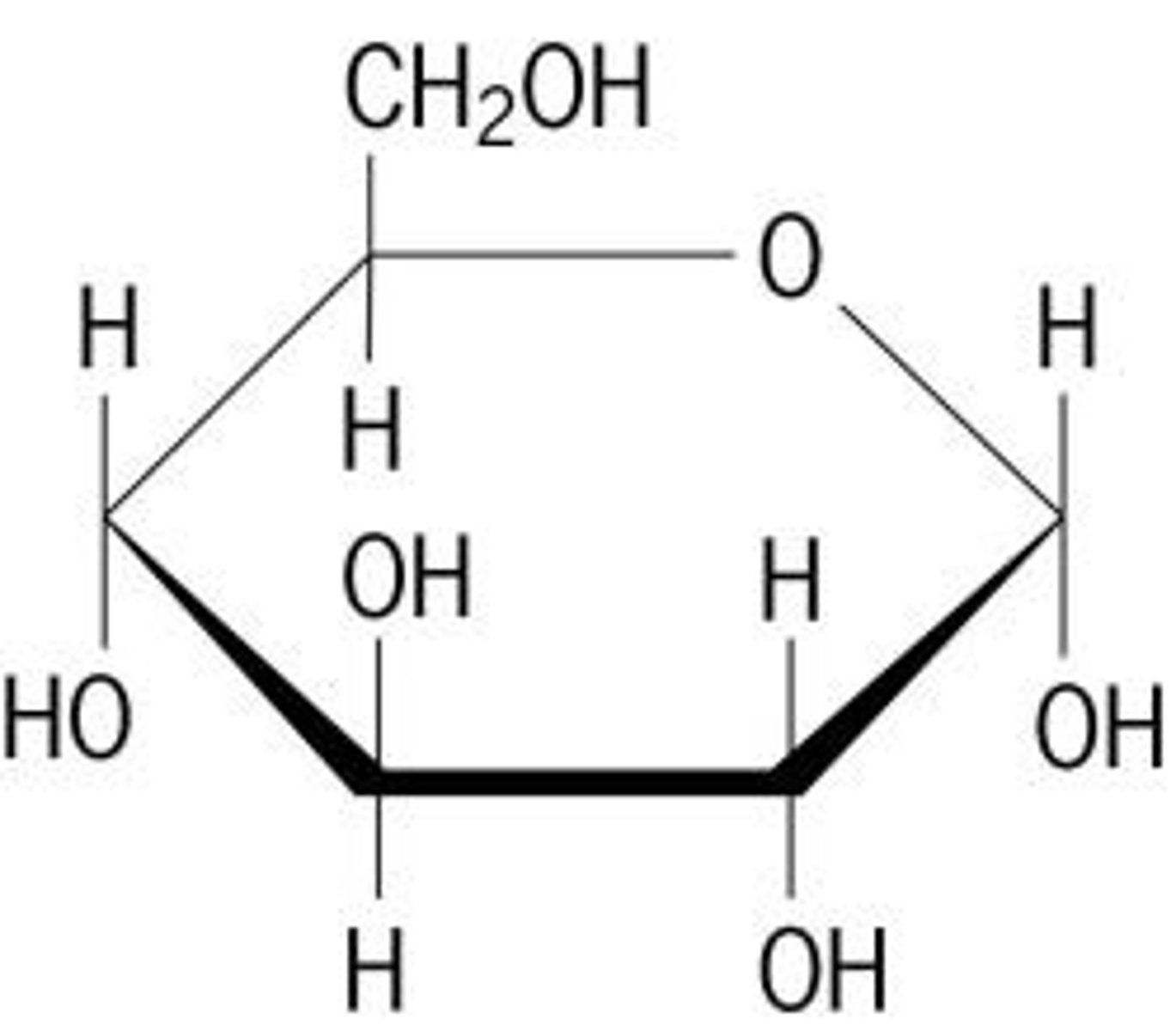
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
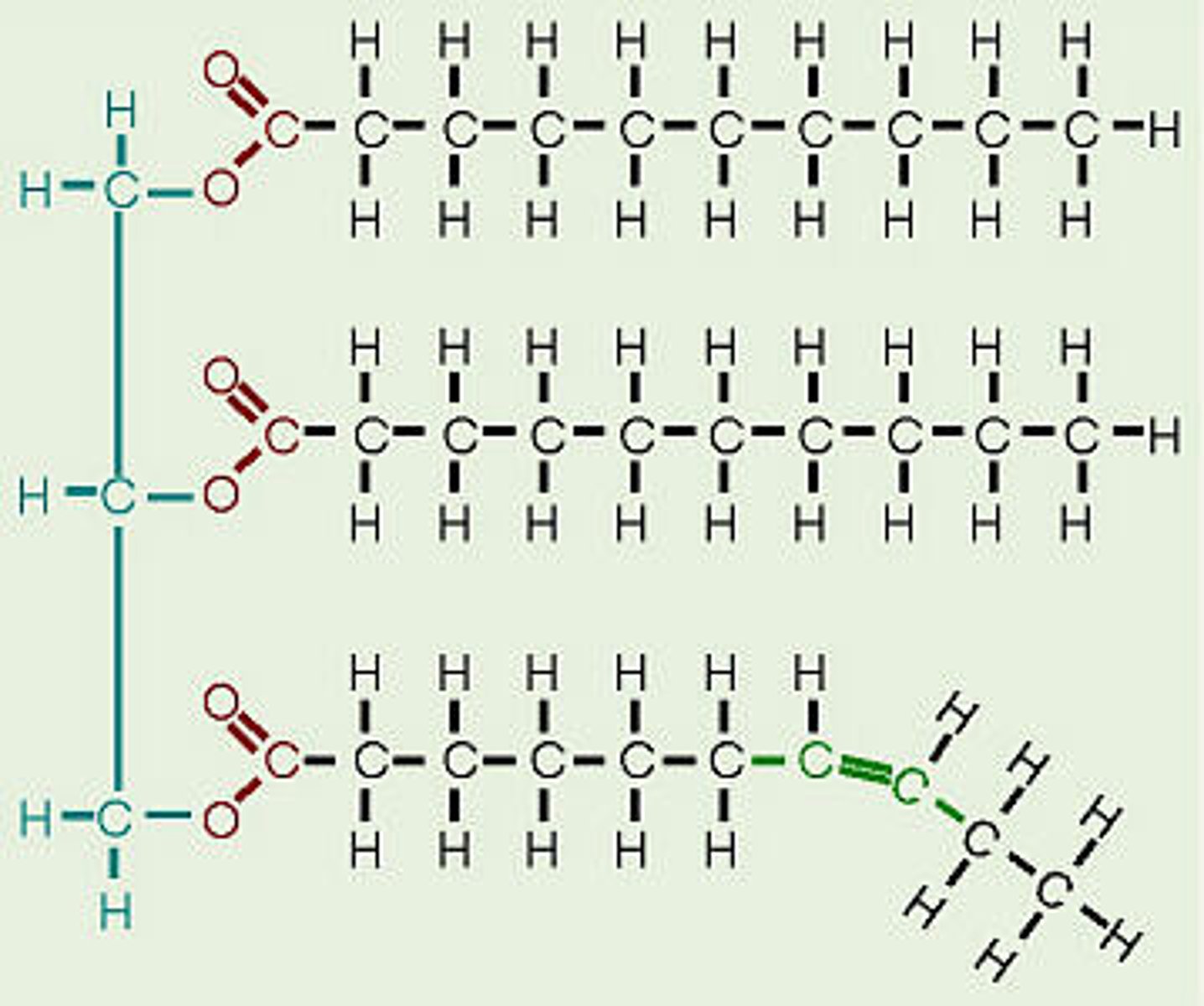
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
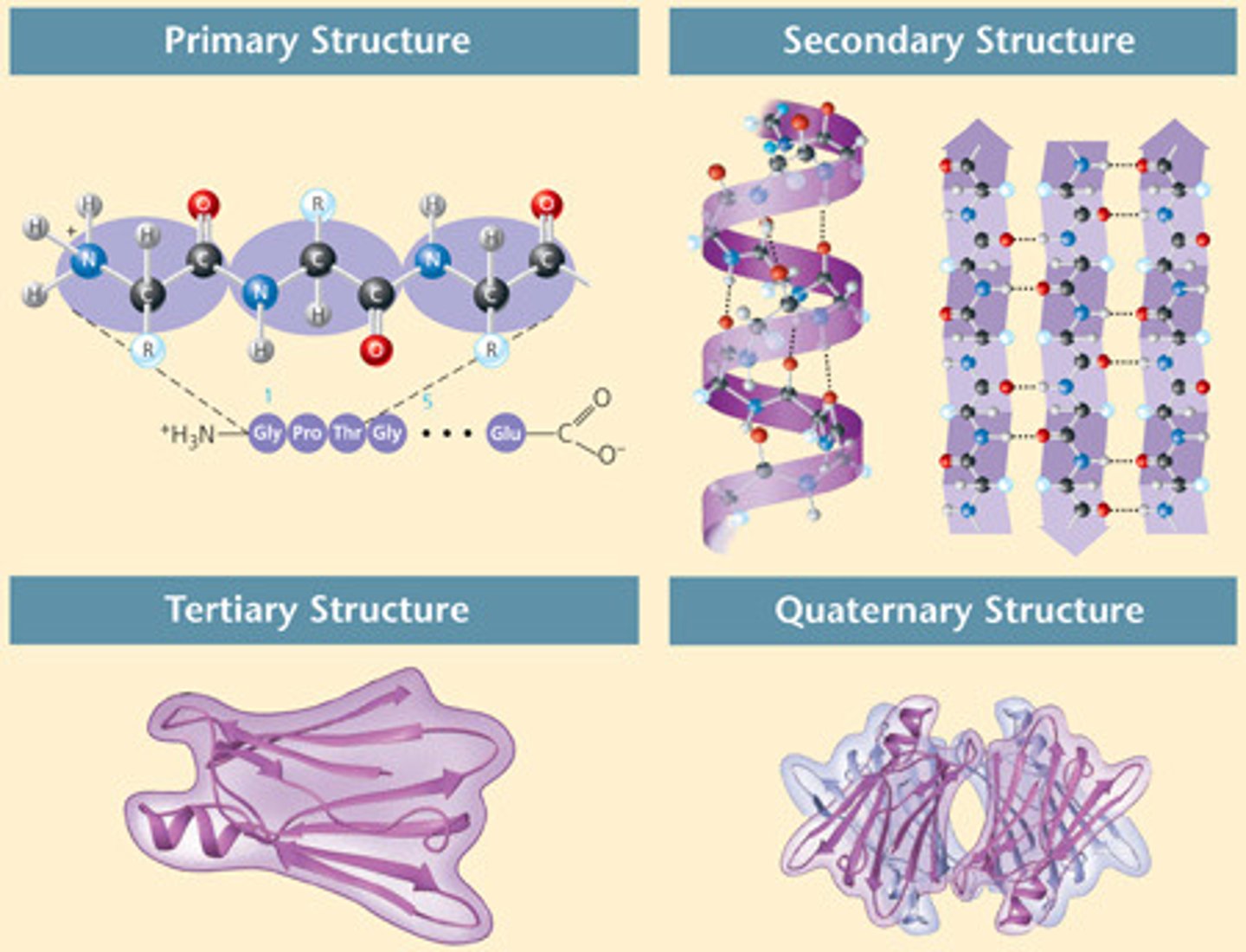
Protein functions include
structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances
Carbohydrate functions
short term energy storage and structure

nucleic acid monomers are
nucleotides
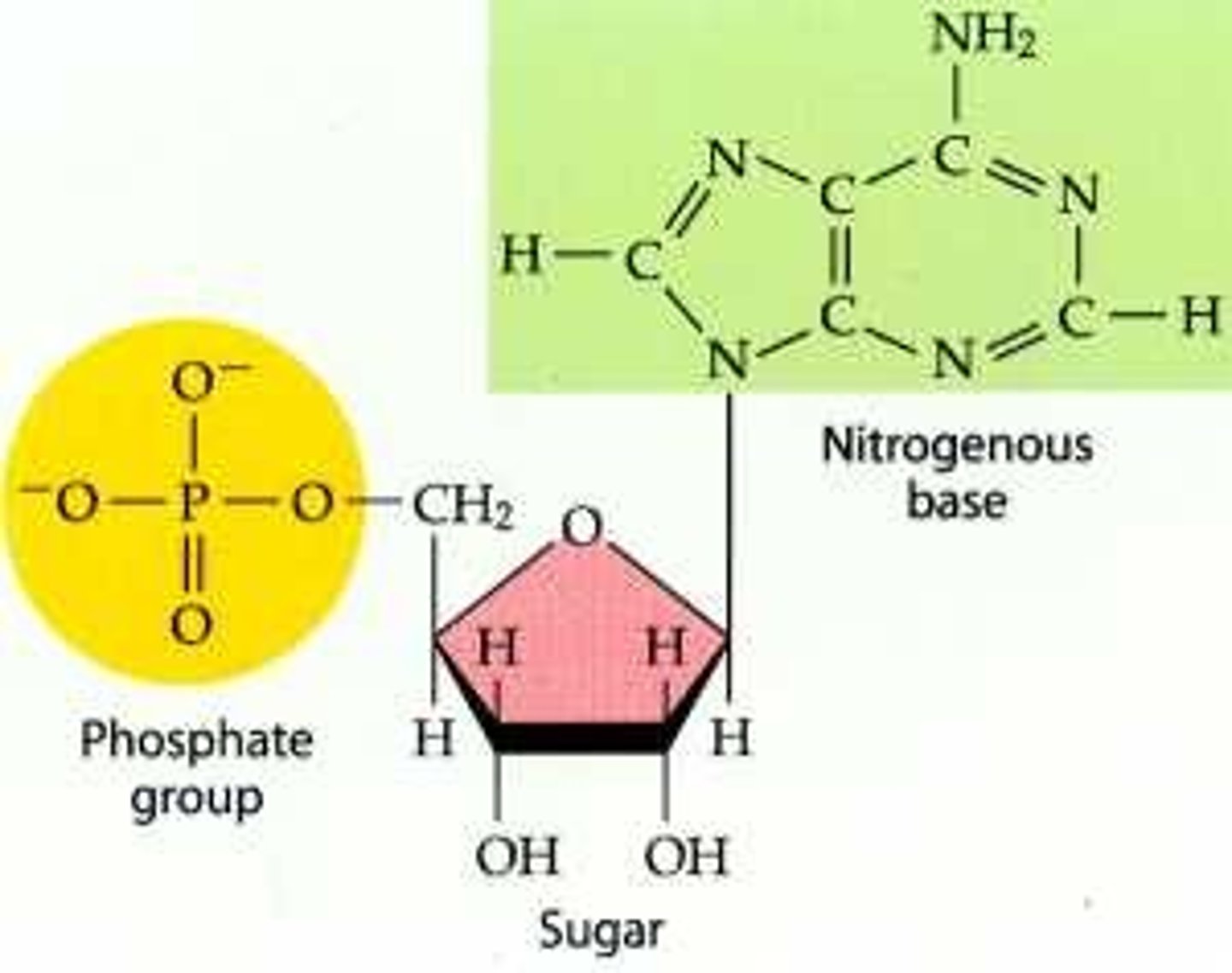
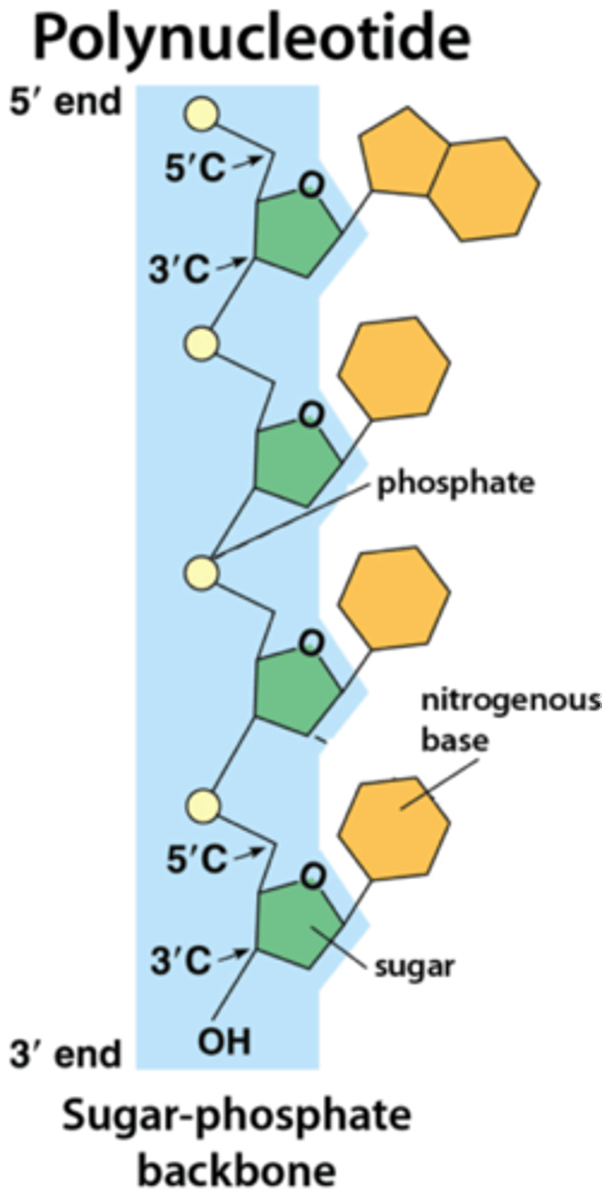
Nucleic acid polymers
DNA and RNA
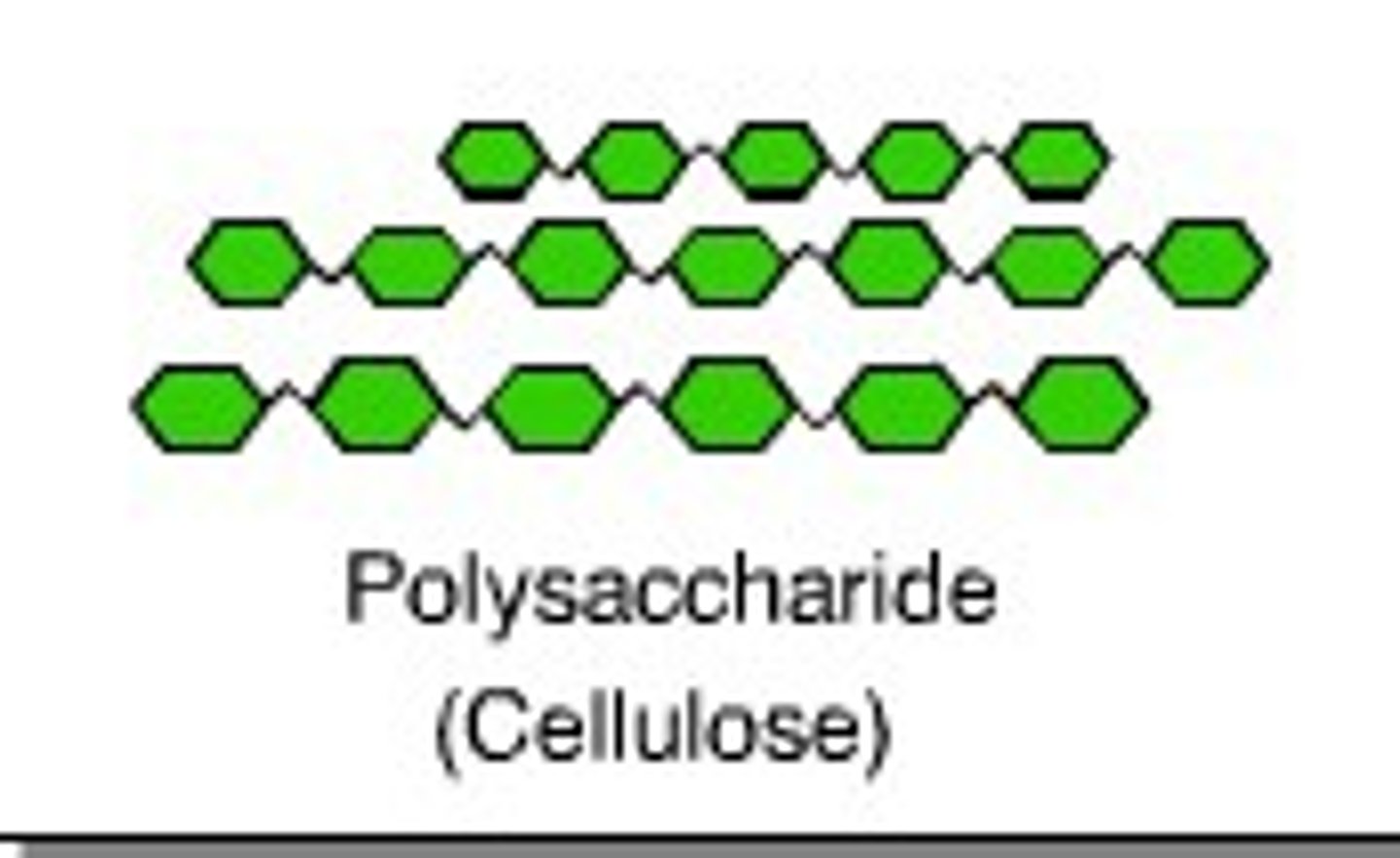
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many plants.
false positive
a test result that comes out positive when it should not; often caused by contamination.
false negative
a test results that comes out negative when it should be positive; often caused by not stirring solutions, not enough solution, or human error.
Foods with carbohydrates
Grains, Fruits, Vegetables and Sugars

Foods with proteins
Meat, Beans, Dairy products, Soy, Eggs and Nuts

Foods with lipids
butter, cheese, red meats, chocolate, ice cream

Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose - carbohydrates small molecules, also called simple sugars
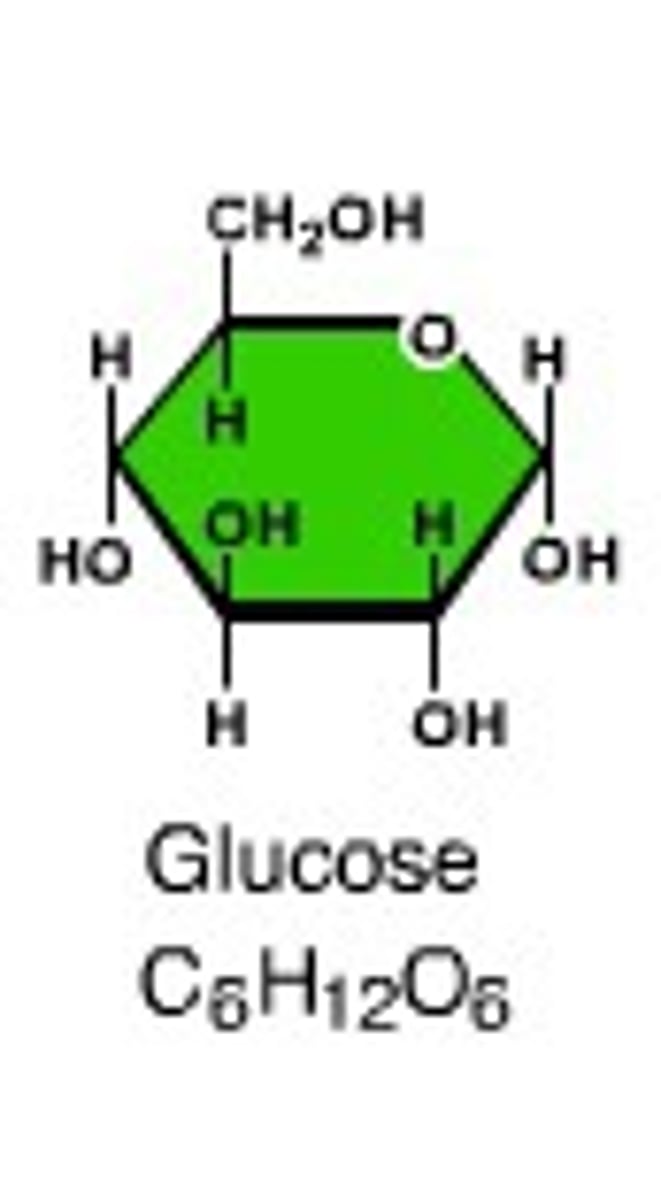
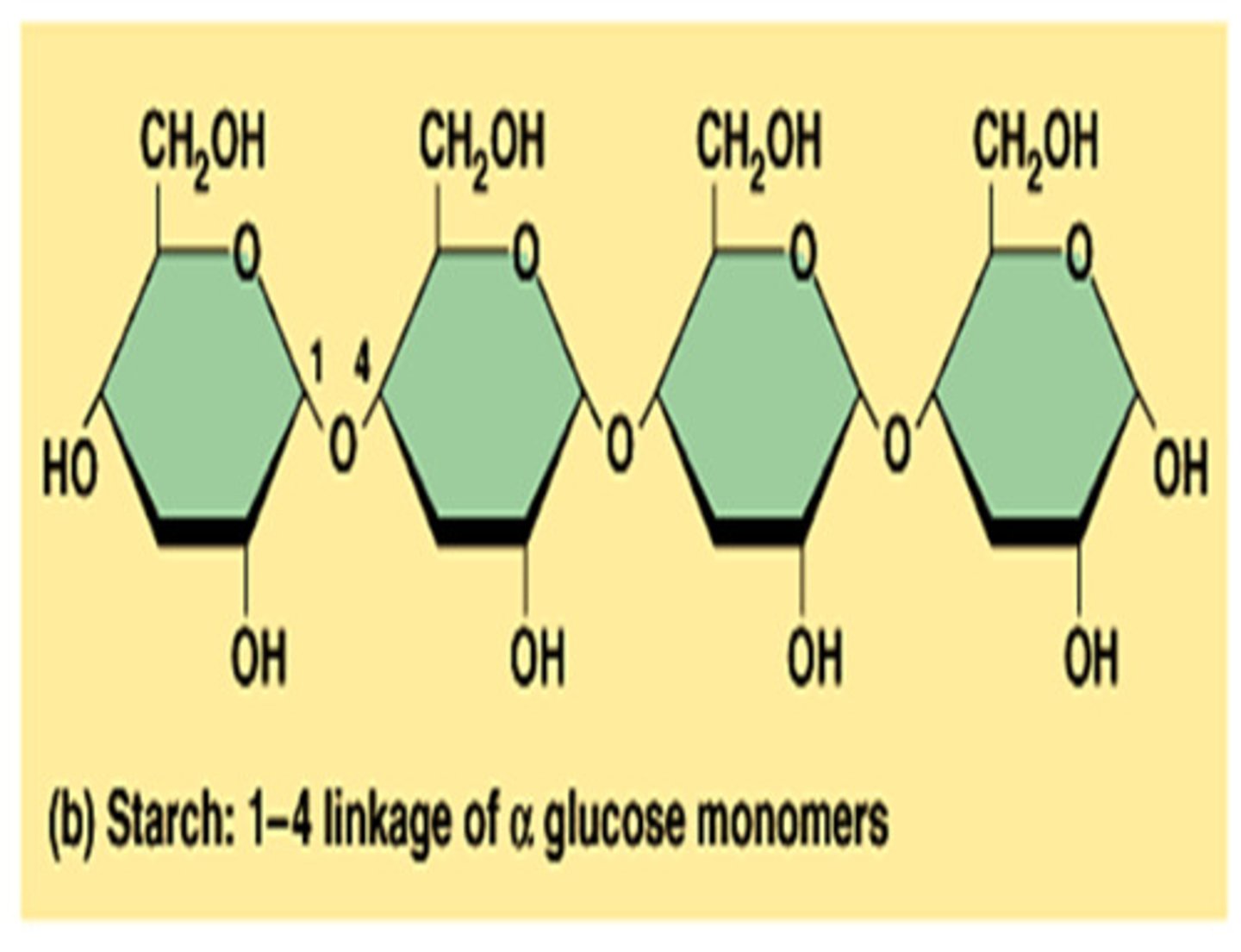
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides. Also called complex carbohydrates.
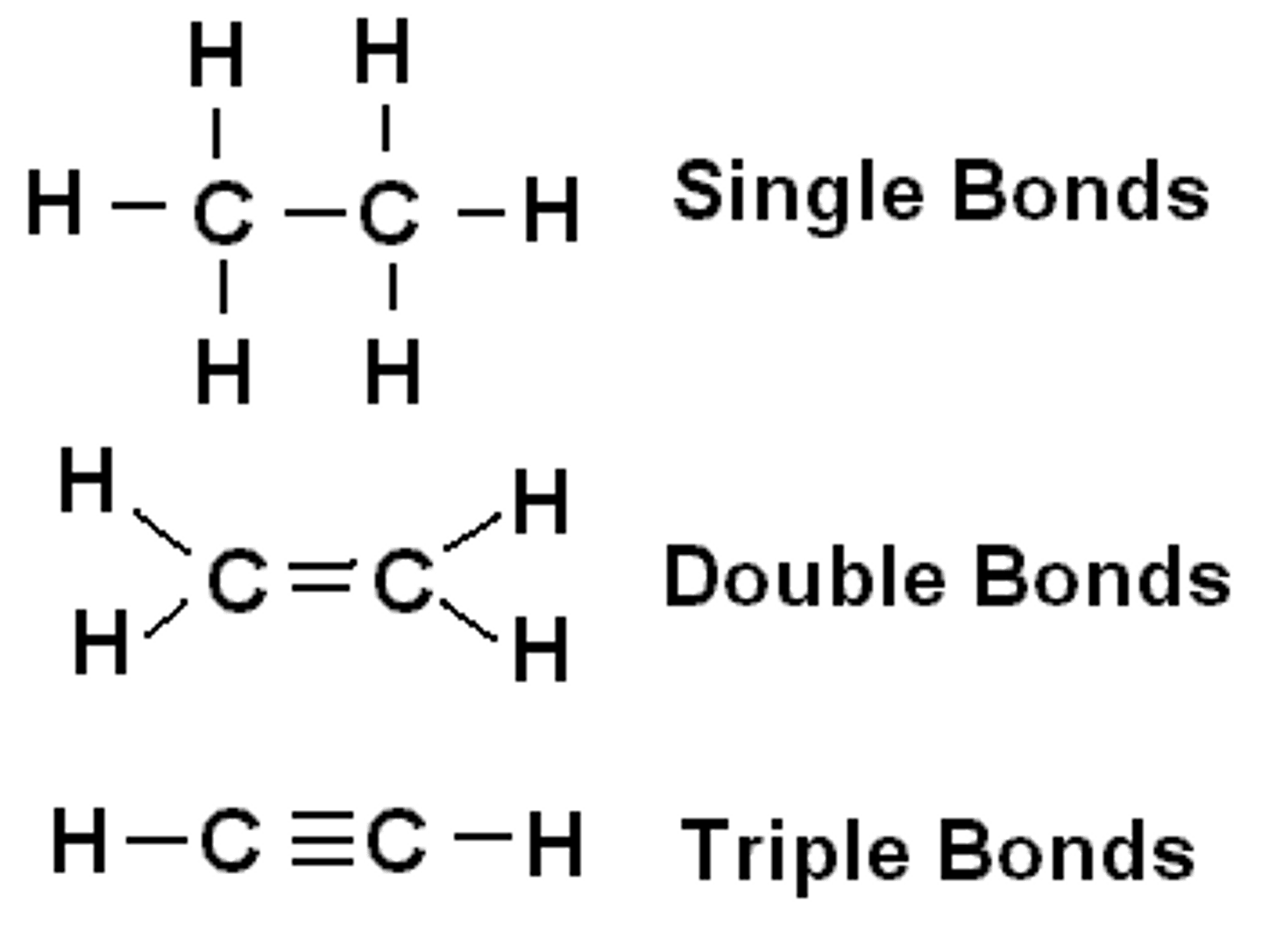
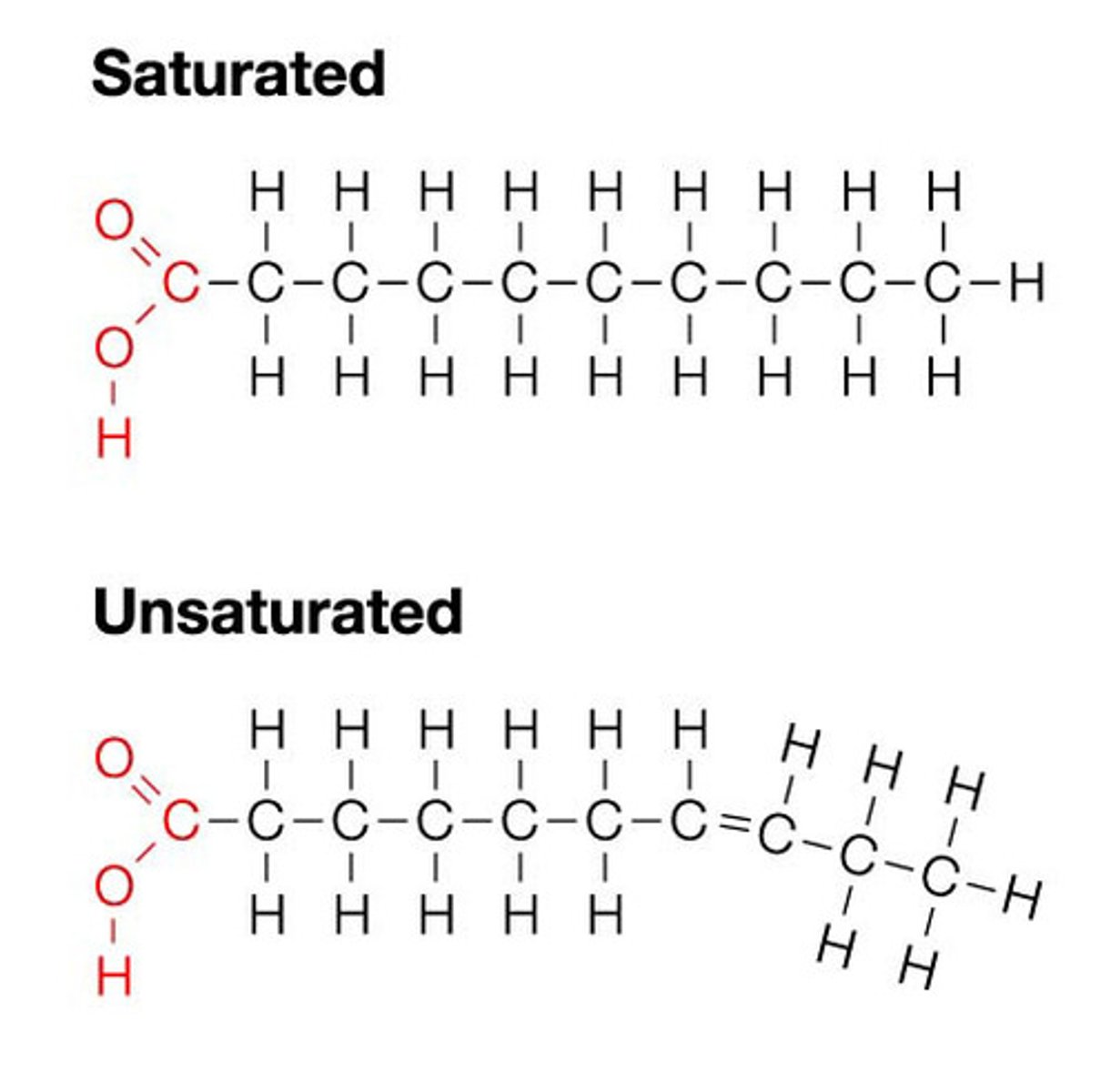
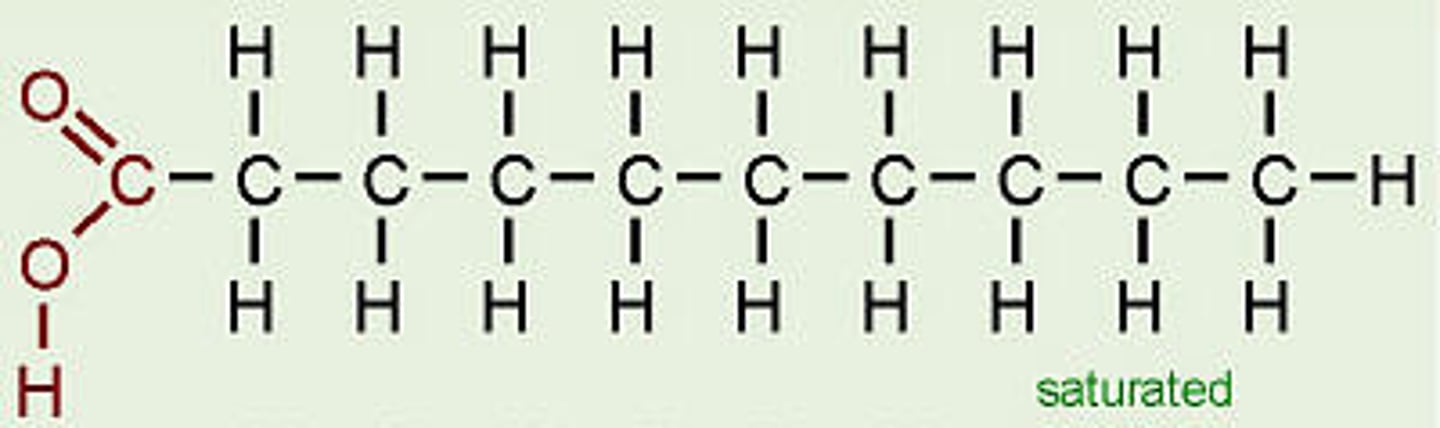
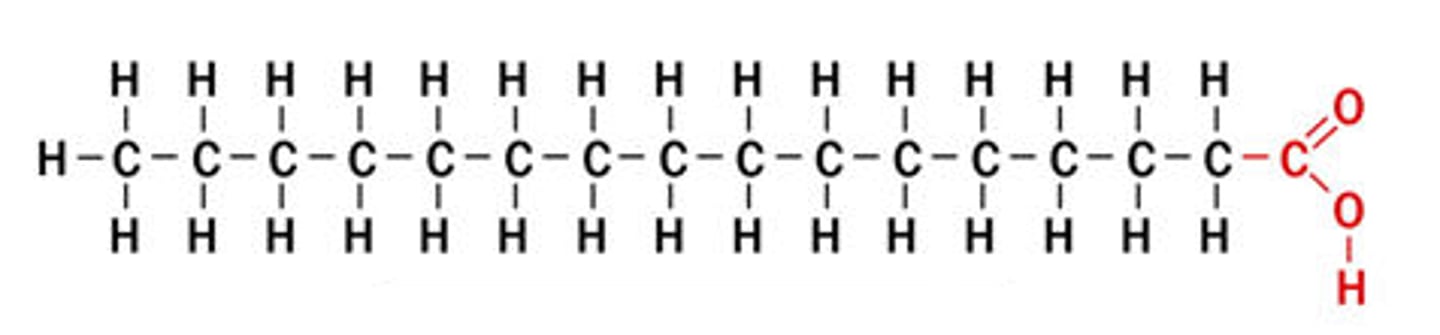
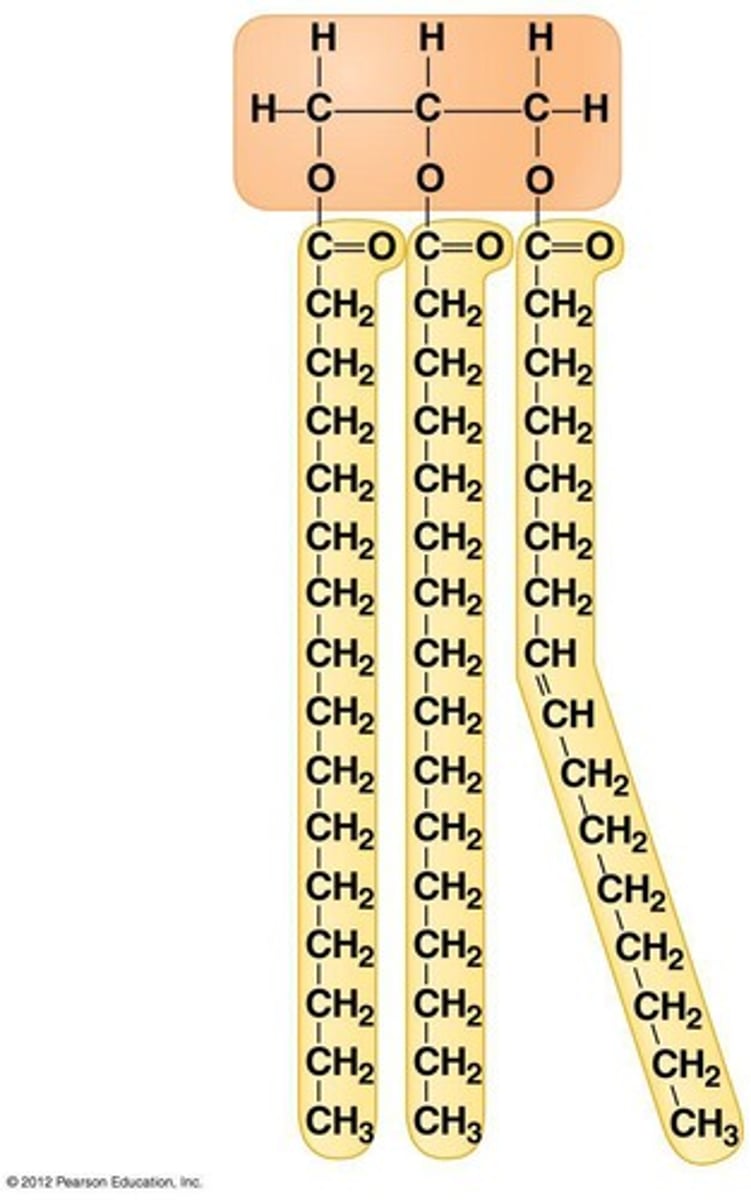
saturated fatty acid
molecule in lipids in which carbon atoms are bonded to as many hydrogen atoms as possible
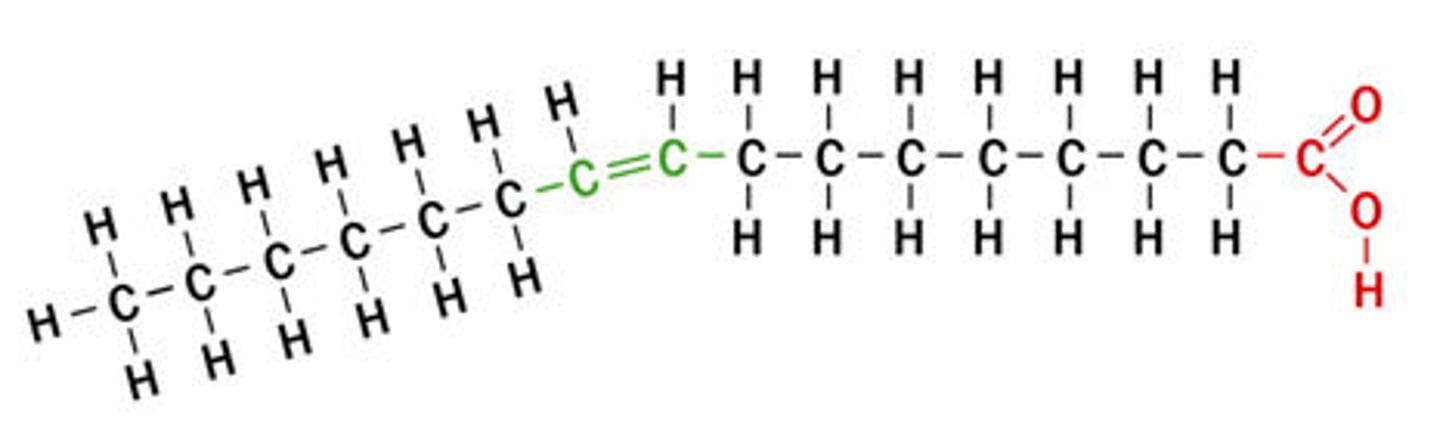
unsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid whose hydrocarbon chain contains one or more double bonds, with room for more hydrogens
Triglycerides
an energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
Polypeptide
long chain of amino acids that makes proteins