16 - anti-heart failure drugs
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
b. Na+/K ATPase pump inhibitor
MOA of digoxin
a. HMG coA reducatse inhibitor
b. Na+/K ATPase pump inhibitor
c. Na/Ca exchanger blocker
d/ Na/Cl symporter blocker
a. increased digoxin toxicity
Digoxin + Furosemide
a. increased digoxin toxicity
b. decrease digoxin toxicity
c. no drug interaction
d. NOTA
a. Captopril
which of the ff drugs cold cause dry cough due to increased bradykinin level?
a. Captopril
b. Losartan
c. Aliskiren
d. Verapamil
b. CCB
Which if the ff drugs are generally not useful in CHF management
a. Beta blockers
b. CCB
c. ACEI
d. AT-1 receptor blockers
d. Nesiritide
A human B-type natriuretic peptide
a. Losartan
b. Fusinopril
c. Inamrinone
d. Nesiritide
Systemic circulation (poor oxygen) → right atrium → right ventricle → lungs (Oxygen Rich) → left atrium → left ventricle → systemic circulation
Normal Blood Circulation
Low Stroke Volume (Low CO)
Low Inotropy,
High Preload, &
High Afterload (vasoconstriction),
Increased cardiac remodelling
Problems w/ Heart Failure Drugs
Increase Inotropy, Low Preload, Low Afterload, Slow or reverse cardiac remodelling
Goals of therapy for Heart Failure:
Left HF
does not deliver enough oxygen-RICH blood through the body
tired, out of breath
pulmonary edema/ congestion
Right HF
unable to pump blood from right ventricle to the lungs
build-up of blood in the veins
peripheral edema/congestion
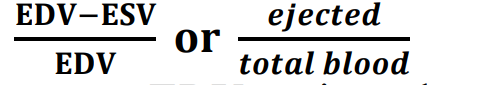
Rejection Fraction formula
Ejection diastole volume (EDV)
active relaxation
Ejection systole volume (ESV)
active contraction
120 mL
Normal EDV:
50 mL
Normal ESV:
50-70 EF
Normal Ejected Fraction:
41-49 EF
Borderline of EF:
<40 EF
Borderline of Systolic EF:
Preload
volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole (End diastolic pressure)
Afterload
Resistance left ventricle must overcome to circulate blood
Digoxin
Milrinone
Dobutamine & Dopamine
POSITIVELY INOTROPIC DRUGS
Digoxin
MOA: (-) of Na/K ATPase pump
Result: Increase Inotropy, (-) Chronotropy (HR)
N/V, Anorexia, AV block, Neurologic symptoms (blurred vision, greenish yellow halo), seizure
Digoxin A/E:
Lanoxin
Digoxin’s Brand Name:
Digoxin Fab fragment
Antidote for Digoxin toxicity:
hypokalemia
Digoxin + diuretics (loop) = can cause what disease?
Milrinone
Tx for acute HF
MOA: (-) PDE3 = degradation of cAMP
Results: increase Ca = inc inotropy
Dobutamine & Dopamine
MOA: (+) B- receptor = inc inotropy
Tx: HF, Cardiogenic Shock
ACE-Inhibitors
1ST line for Heart Failure (-pril)
Decrease afterload, cardiac remodelling,
S/E: Dry cough
Increase survival time
ARBs
sartans
Same as ACEIs
NO dry cough (RARE)
NESERITIDE
Human B-type natriuretic peptide
(+) Guanyl Cyclase = Inc cGMP
Use: Acute HF
ΒETA-ADRENOCEPTOR BLOCKERS
once contraindicated in heart failure because of their negative inotropic effect
Rationale of use: protects the heart cells from damaging effects of NE
Spironolactone
Eplerenone
Examples of Aldosterone Blockers that improve survival time
Loop diuretics & Thiazides
Diuretics for for pulmonary edema
HYDRALAZINE AND NITRATES
Dec preload and afterload
Use: If px can’t tolerate ARBs & ACEI
Isosorbide dinitrate
Hydralazine
HYDRALAZINE AND NITRATES’ drugs: