Introduction to Human Anatomy, Physiology, and Body Organization
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
337 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of the body and its parts.
Physiology
The study of the functions of the body and its parts.
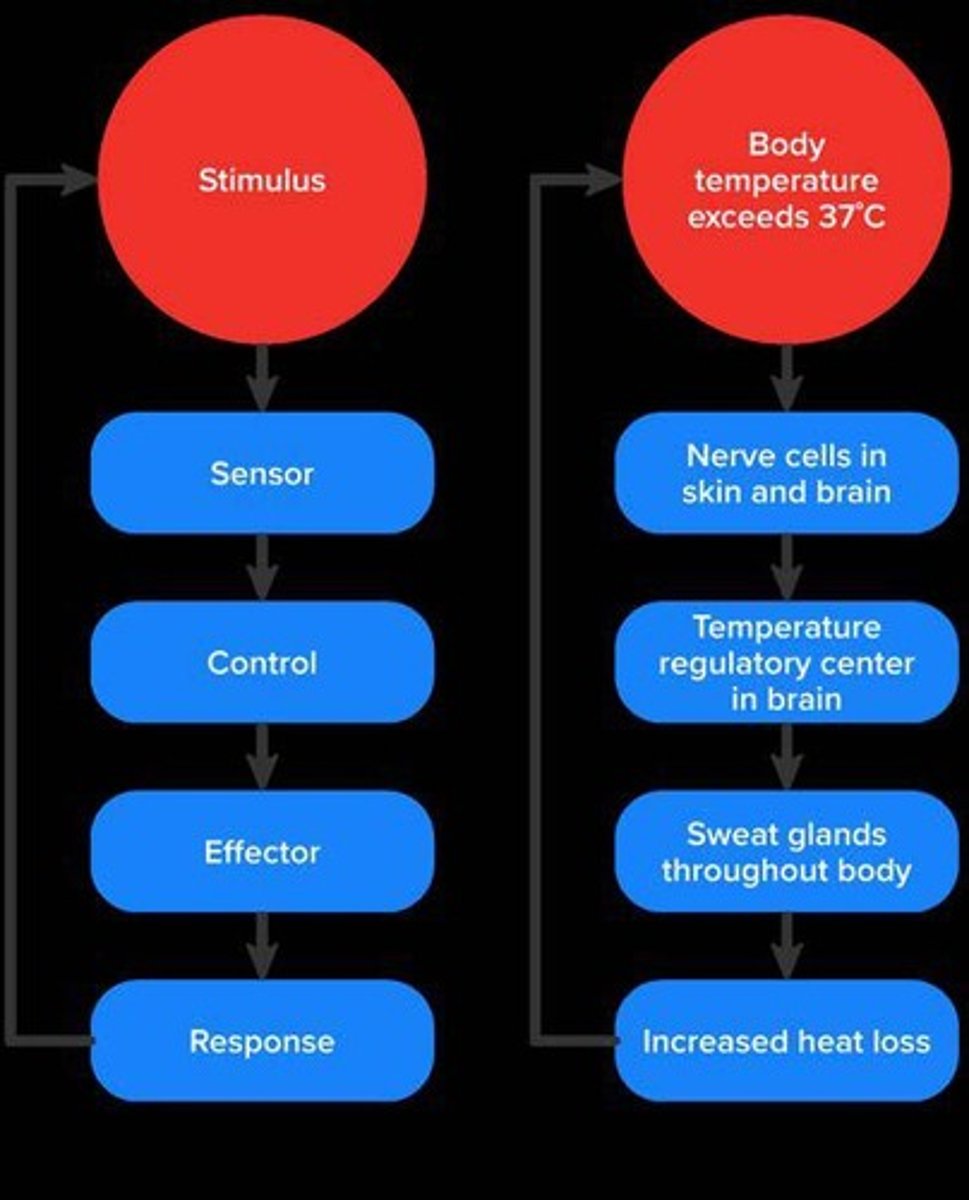
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body.
Chemical Level of Organization
The level of organization that includes elements, atoms, and bonding.
Inorganic Compounds
Compounds that do not contain carbon, such as water, acids, and bases.
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Cell Membrane
The outer boundary of a cell that regulates what enters and exits the cell.
Membrane Transport
The process by which substances move across the cell membrane.
Cellular Organelles
Specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions.
Nucleus
The organelle that contains the cell's genetic material and controls cellular activities.
Protein Synthesis
The process by which cells produce proteins based on genetic instructions.
Tissue Level of Organization
The level of organization that involves groups of similar cells working together.
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers body surfaces and lines cavities.
Connective Tissue
Tissue that supports and protects other tissues and organs.
Muscle Tissue
Tissue responsible for movement in the body.
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that mediates perception and response through nerve impulses.
Types of Tissues
The four basic types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
Course Organization
The structure and sequence of topics covered in the Anatomy & Physiology course.
Terms to Know
A callout at the end of each topic that lists important terms covered.
Glossary
An alphabetical list of terms and definitions provided at the end of each lesson.
Chemical Reactions
Processes that involve the transformation of substances through breaking and forming bonds.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
Ions
Atoms or molecules that have gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a charge.
Acids
Substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution.
Bases
Substances that accept hydrogen ions (H+) or release hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution.
Biology
The study of life and living things.
Gross (Macroscopic) Anatomy
The study of body structure visible with the unaided eye.
Microanatomy
The study of body structure using a microscope or other magnification device.
Human Anatomy
The scientific study of the body's structure, specifically of homo sapiens (humans).
Dissection
The process of cutting apart a body to observe its physical attributes and the relationships between structures.
Imaging Techniques
Methods developed to visualize structures inside the living body, such as cancerous tumors or fractured bones.
Cytology
The study of cells.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Macroscopic Observation
Observation of structures visible without the aid of magnification.
Microscopic Observation
Observation of small structures that can be observed only with the use of a microscope or other magnification devices.
Anatomists
People who study anatomy.
Greek Root of Anatomy
The word 'anatomy' comes from a Greek root that means 'to cut apart'.
Human Physiology
The scientific study of the body's function in humans.
Anatomy Specializations
Areas of specialization within anatomy, including gross and microscopic anatomy.
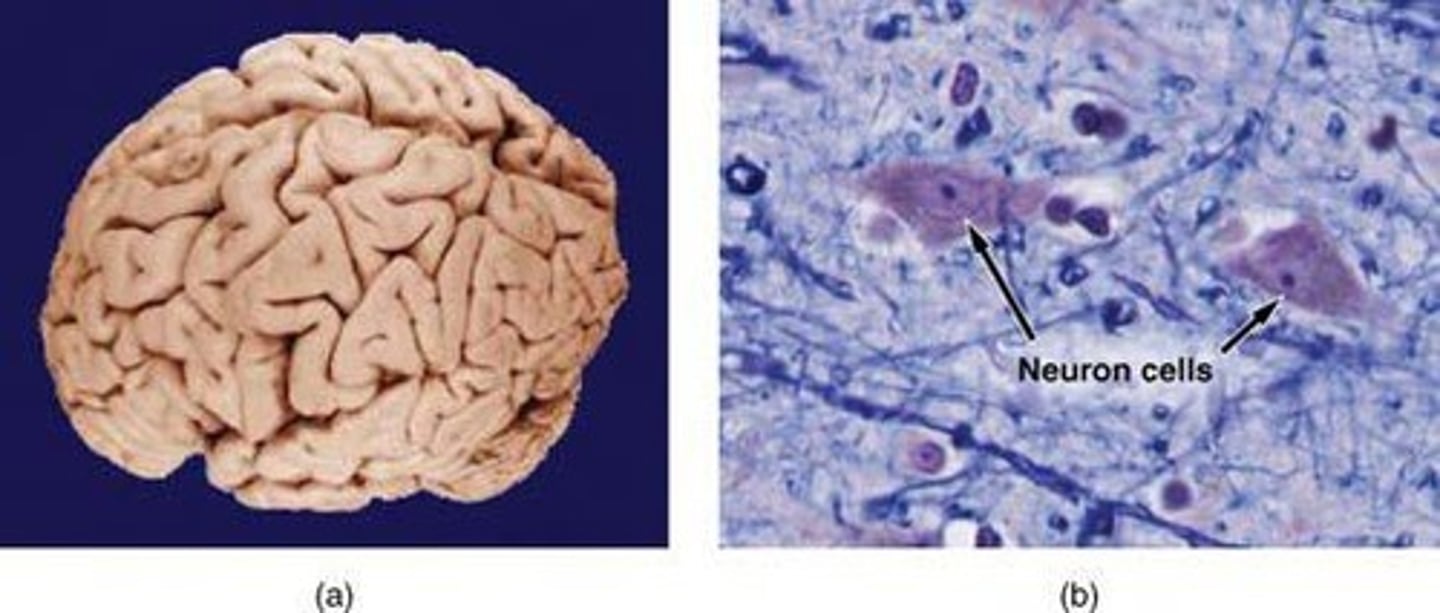
Light Micrograph
An image produced by a microscope showing structures at magnification.
1600x Magnification
A magnification level that makes structures appear 1600 times larger than with the unaided eye.
Supplemental Materials
Additional resources such as videos and links that provide more insight or details about a topic.
In-lesson Videos
Videos identified with the 'Watch' callout to help understand the topic or concept being taught.
External Links
Links identified with the 'Learn More' callout that allow downloading additional details about a topic.
Assessment Exclusion
Supplemental materials will not be included in the assessments.
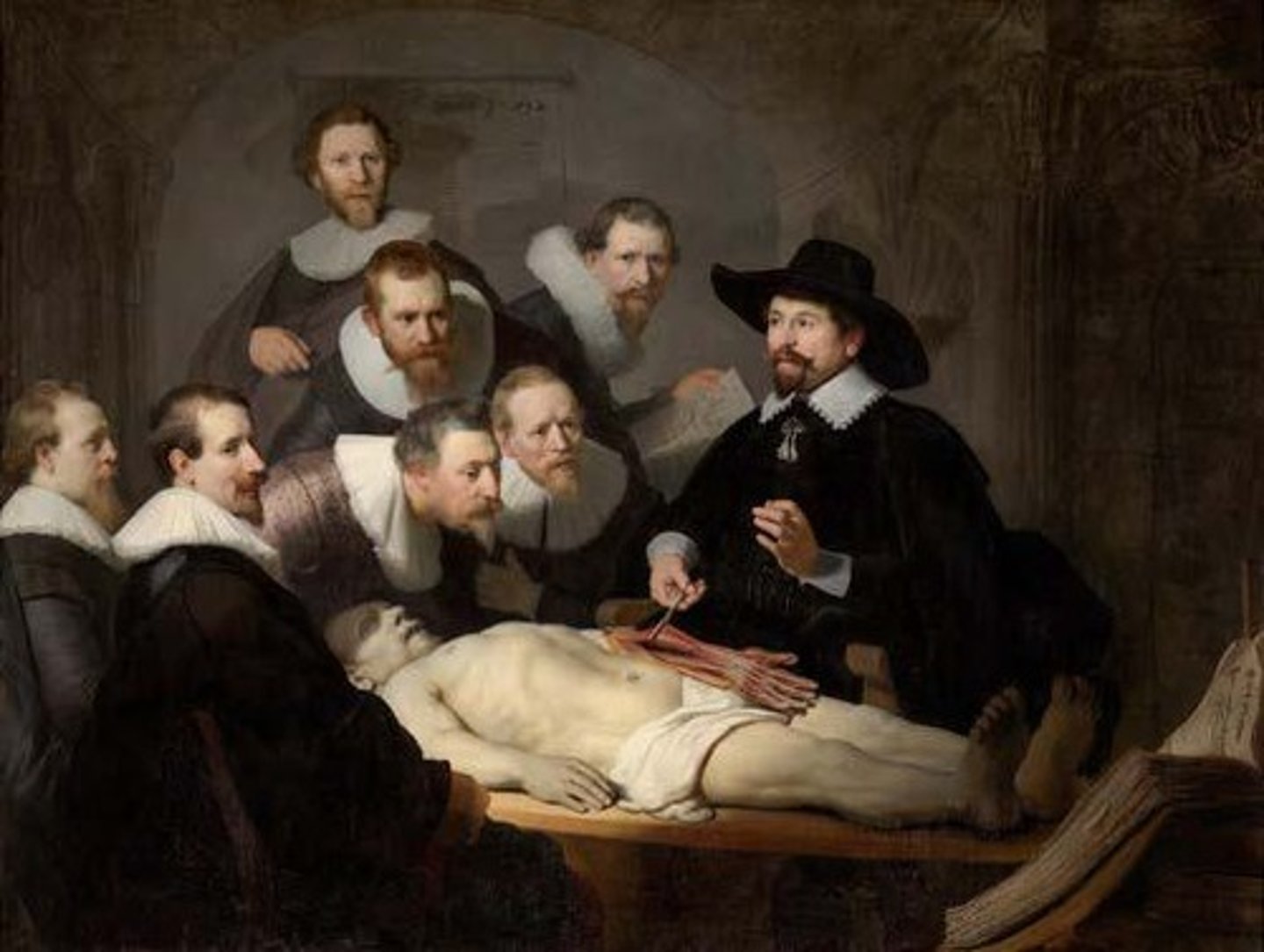
Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp
An oil painting by Rembrandt van Rijn depicting physicians attending the dissection of a cadaver.
Physiology Definition
The word 'physiology' comes from the Greek root which means 'the theory or science of nature.'
Neurophysiology
The study of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves and how these work together to perform functions as complex and diverse as vision, movement, and thinking.
Internal equilibrium
The balance maintained by living things in response to changes in the internal environment.
Function
The role or activity of a body structure.
Electrochemical signal
A signal that travels along nerves, facilitating communication within the nervous system.
Blood sugar concentration
The level of glucose in the blood, which must be maintained for homeostasis.
Body temperature regulation
The process of maintaining a stable internal temperature in hot or cold environments.
Eyelid function
The ability of the thin flap of skin to clear away dust particles and allow vision.
Skin cells
Cells that make up the outer layer of the skin.
Nerve cells
Cells that transmit signals in the nervous system.
Muscle cells
Cells that contract to produce movement.
Structure-function relationship
The concept that the form of a structure is closely related to its function.
Human hand anatomy
The unique arrangement of bones in the human hand that allows for manipulation of tools.
Thumb opposition
The ability of the thumb to move in opposition to the fingers, enabling grasping.
Fluid production in eyelids
The process by which eyelids produce tears to keep the eye moist.
Blink reflex
The automatic response of the eyelid to close in response to stimuli.
Anatomy and Physiology connection
The relationship between the study of body structures and their functions.
Components of the body
The various parts that make up the human body and their roles.
Maintaining life
The processes that support the survival of living organisms.
Course overview
An introductory summary of the materials to be learned in a course.
Lesson items
Key topics and concepts to keep in mind as one progresses through a course.
Biological approaches
Methods used to study the body from both structural and functional perspectives.
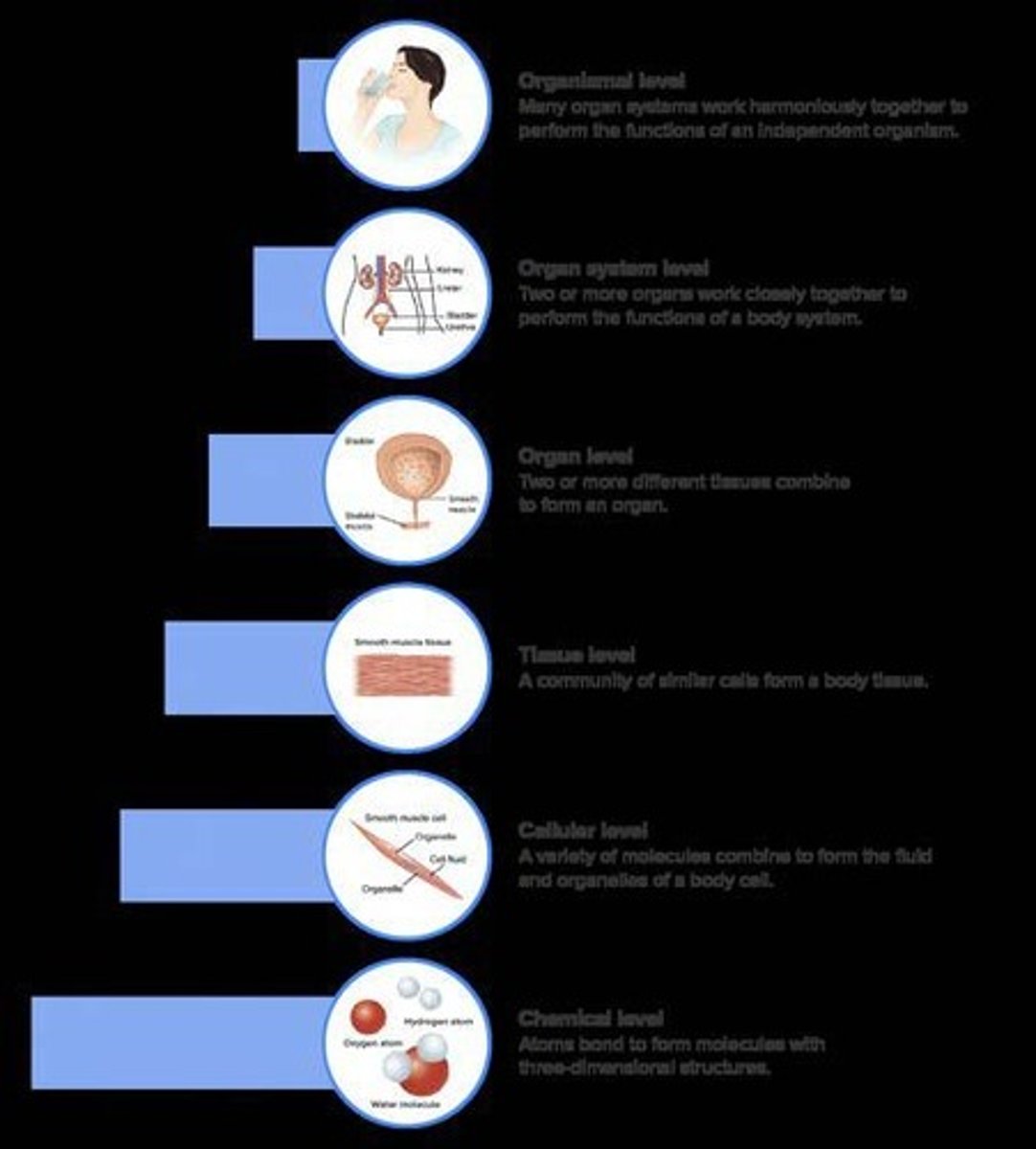
Chemical Level
The lowest level of organization with the smallest units; all matter is composed of elements.
Cellular Level
The smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism, containing organelles.
Tissue Level
Many cells combine to form a tissue.
Organ Level
A level of organization where different tissues combine to form an organ.
Organ System Level
A level of organization where different organs work together as a system.
Organism Level
The highest level of organization, representing a complete living entity.
Atoms
The smallest unit of any pure substance (element).
Molecules
Chemical building blocks formed by two or more atoms.
Types of Cells
The human body is composed of over 200 different types of cells.
Total Cells in Human Body
Approximately 37 trillion total cells.
Size of Cells
Cells can range from 0.1 micrometer to 1 meter in length.
Shortest Cell in Human Body
The granule cell located in the cerebellum, which is 4 micrometers long.
Longest Cell in Human Body
A neuron which can reach 1 meter.
Colors of Cells
Cells can be clear, white, yellow, brown, red, blue, and green.
Visible Spectrum of Light
Cells can span all colors of the visible spectrum.
Tissue
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organ
An anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types that work together to perform one or more functions.
Examples of Organs
Include the skin, bones, muscles, brain, lungs, stomach, and kidneys.
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body.
Skeletal System
Composed of bones which all have their individual functions yet work together as the skeleton to provide structure and protection.
Organism
A living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life.
Multicellular Organism
An organism that is a group of organ systems that work together to maintain life.
Levels of Organization
A framework that shows how individual building blocks can be grouped together to form increasingly complex structures.
Cell
The smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism.
Order of Levels
Indicates how each level increases in complexity as it is constructed.
Meaning in Language
In order for a sentence to have a meaning, it must contain specific words in a specific order.
Example of Word Organization
Version 1: The organization is this levels about lesson of. Version 2: This lesson is about the levels of organization.
Correct Organization
The second sentence has meaning and functions correctly due to the correct organization of its parts.
Components of Organization
Each level of organization must contain specific components (i.e., chemicals, cells, tissue, organs, and/or organ systems) in specific arrangements.
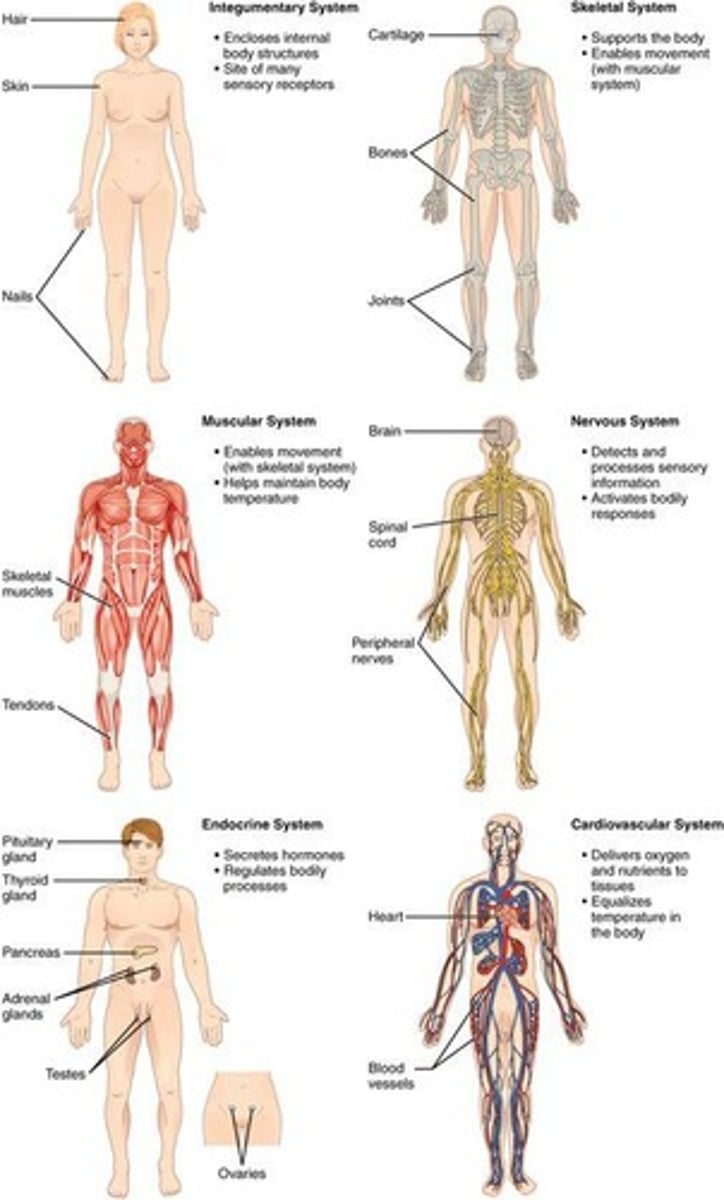
Organ Systems
Anatomy & physiology covers eleven distinct organ systems in the human body.
Integumentary System
The primary organ of this system is the skin which functions to cover the body.
Muscular System
The primary organs of the muscular system are muscles attached to the skeleton.