Parasitology Exam 1
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Symbiosis
Interactions between two or more species
Commenalism
One species benefits, the other is not affected
Mutualism
Both species benefit
Parasitism
One species benefits, the other is harmed
Mutualism Example
e.coli produces vit B and K
Commenalism Example
Staphylococcus Epidermis
Permanent Parasites
tapeworms in vertebrate intestines
temporary parasites
female mosquitos on host blood
obligatory parasites
plasmodium
faculative parasites
free living amoeba
biological vector
host where development occurs
mechanical vectors
organisms that transport pathogens without being infected themselves
Parasite Disease I
parasites reproduce slower and with fewer offspring
Parasite Disease II
usually chronic
Parasite Disease III
more difficult to control than other diseases
Visceral Ameobae Example
Entamoeba histolytica
Visceral Flagellate example
Giardia lamblia
Visceral Ciliates
Balantidium coli
Visceral Coccidia Example
Cryptosporidium parvum
Blood and Tissue Coccidia Example
Toxoplasma gondi
Blood and Tissue Piroplasm Example
Plasmodium
Blood and Tissue Flagellates
Leishmania and Trypanosoma
Helminths
platyhelminthes(flatworms) and roundworms(aschelminthes or nematoda)
Platyhelmithes
Flukes(trematode) and Tapeworms(cestodes)
Nematodes
Pin worms, hook worms, ad filarial worms
Eukaryote cytoskeleton
actin and microfilaments
Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have organelles and no cell wall
Multicellular fungi
mold
unicellular fungi
yeast
which eukaryotes have cell walls?
Planta(cellulose) and fungi(chitin)
ciliphorian nucleus
macronucleus and micronucleus
Anaerobic organelles
hydrogenosomes and mitosomes
Apicomplexan
secretory organs that allow host invasian
kinetoplast examples
leishmania and trypanosoma
kinetoplast
kDNA in a single large mitochondrion
longitudinal binary fission
cell divides longitudinally, creating two daughter cells
binary fission
split
schizogony
parasites multiply asexually in the host and then disrupt the cell wall
cyst functions
protection, morphogenesis, transmission
Visceral Protozoa
E. histolytica, E. gingivalis, Balantidium coli
Non-visceral protozoa
Naeglaeria fowleri, Anacthomoeba spp., Balamunthia mandrillas
Entamoeba histolytica locations
tropics, sub-tropics, poor sanitation
E. Histolytica diseases
Amebiases, Amoebic dysentary
Amebic dystentary symptoms
Amebic colitis, amebic liver abcess
Amebic dysentery
blood and mucus mixed with feces, dark, odor, acidic, 6-8 bpm
Bacillary dysentery
blood and mucus, 10 bpm, odorless, bright, alkaline, sticky
Amebiasis treatments
metronidazole and tetracycline
Disease coused by naegleria fowleri
Primary Amoebic meningoencephalatitis(PAM)
PAM affects the
central nervous system(CNS)
How does N. Fowleri enter humans
nose, amoeba
what forms does N. Fowleri have?
cyst, amoeba, flagellate
What do acanthomoeba and balamunthia mandrillas cause
Granulous Amoebic encephalitis(GAE)
Acanthomoeba keratitis
caused by wearing dirty contacts
Acanthomoeba Cyst shape
square
Acanthamoeba spp. treatments
miltefosine
single infectious cilliate
balantidium coli
largest parasitic protozoan
balantidium coli
B. Coli enzyme
hyaluronidase
Gastrointestinal flagellate
Giardia lambia
genitourinary flagellates
trichomonas vaginalis
Giardia Lambia Trophozite characteristics
median bodies, adhesive disc, 4 pairs of flagella
G. Lambia reproduction
longitudinal fission
G. lambia resevoirs
dogs, beavers, sheep
G. Lamblia Symptoms
greasy stool
G. lambia effects
flattening of villi
G. lambia diagnosis
ELISA, IgA antibodies, PCR
G. lambia treatment
metronidazole
Trichomonas vaginalis unique features
undulating flagella, hydrogenosome
T. vaginalis raises pH by
disrupting lactic-acid producing bacteria
Best pH for T. Vaginalis
5-6
What sex experiences symptoms of T. vaginalis
female
T. vaginalis treatment
metronidazole
Genus Leishmania
Visceral, Cutaneous, Mucocutaneous
Genus Trypanosoma
African sleeping sickness, chagas
Hemoflagellate transmission
bloofdfeeding insect vectors
hemoflagellate organs
liver and spleen
hemoflagellate common structures
kinetoplast and mitochondrion
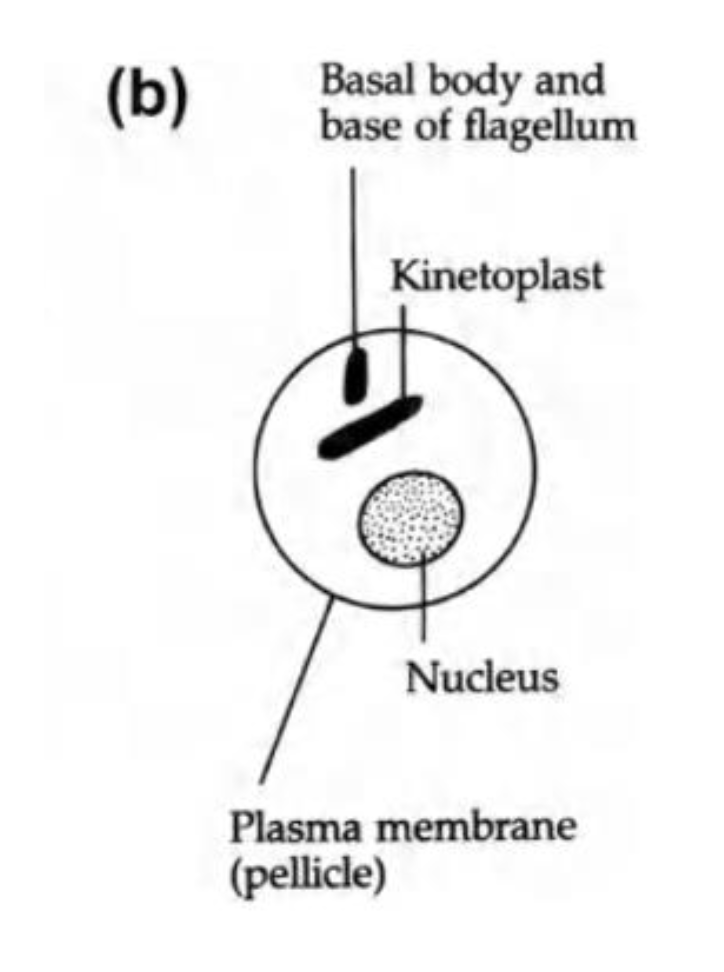
Amastigote
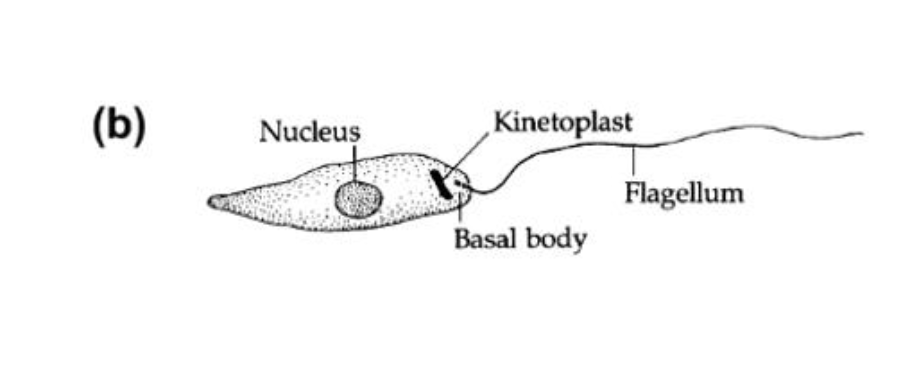
Promastigote
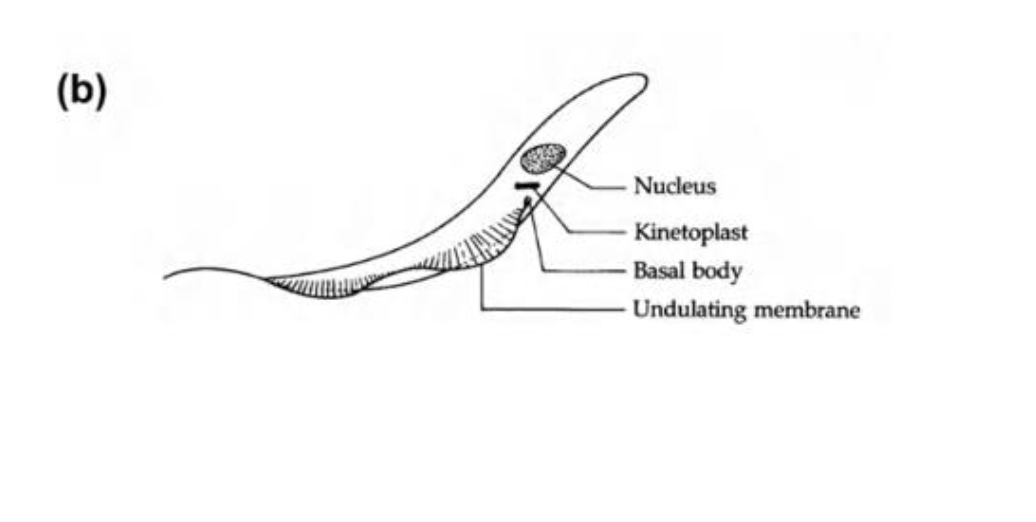
Epimastigote
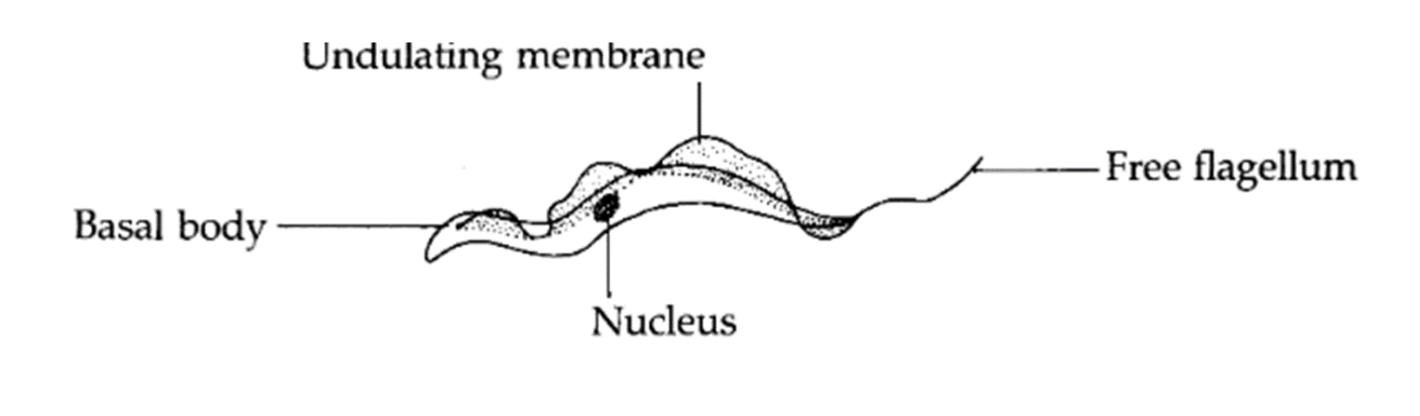
trypomastigote
Amastigote location
intracellular
promastigote location
insect vector and in the culture
leishmania vector
female sandflies
leishmania transmission
zoonotic, anthroponotic
most common leishmania
cutaneous leishmania
cutaneous leishmania transmission
sandflies, blood transfusion
cutaneous leishmania types
L. tropica, L. major, L. mexicana
cutaneous leishmania resevoirs
dogs, rats
cutaneous leishmania symptoms
skin sores
cutaneous leishmania regions
middle east, africa, mediteranian, india
cutaneous leishmania complications
leishmania recidiva, secondary bacterial infections
cutaneous leishmania diagnosis
amastigotes, promastigotes(cultured)
cutaneous leishmania treatment
miltefosine, liposomal amphoterican B
Visceral leishmaniasis organs affected
spleen, liver, bone marrow
Visceral leishmaniasis symptoms
sweeling of liver and spleen, fever, weight loss
Visceral leishmaniasis types
L.d. donovani, L.d. infantum, L.d. chagasi
Visceral leishmaniasis amastigote
in mammalian tissues
Visceral leishmaniasis promastigote
cultures or sandflies