Exam 2 - Scramblases and Flippases
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
In the ER, are new phospholipids synthesized on the cytosol or ER lumen side of the membrane?
New phospholipids are built exclusively in the cystosolic side go the ER membrane.
If the addition of new phospholipids is asymmetrical, then how does the ER membrane manage to grow evenly?
A protein called scramblase adjusts for this asymmetry by randomly moving phospholipids from the cycstolic monolayer to the ER lumen side. They sense the asymmetric curvature and redistribute the phospholipids.
Why is it important and necessary for some organelles to have asymmetric membranes?
Asymmetric membranes allow organelles to have their distinct shape, like the stacks and tubules of the Golgi body.
Membrane asymmetry is also important to make vesicles
Where are flippases mainly found?
In the golgi body
What is the function of flippases?
They induce (create) asymmetry, they make the membrane more asymmetric by moving phospholipids from the lumen monolayer to the cytosolic side of the organelle membrane.
What is the difference between scramblases and flippases?
Scramblases removes phospholipids randomly while the flippases target specific phospholipids.
Scrablases try to fix asymmetry while flippases try to create asymmetry.
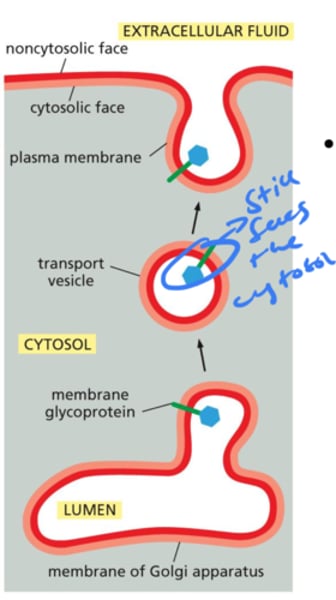
When the transport vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, which monolayer will face the cell cytosol? Look at the picture
Plasma membranes have conservation of orientation
The cytosolic monolayer always faces the cytosol
The noncystosolic, lumen side, that faces the inside of the vesicle will face the cell exterior when it reaches the cell membrane
In this case, the orange side will face the cell cytosol when the vesicle fuses with the membrane because it is facing the cell cytosol before fusion also.

Are glycolipids asymmetrically found on the cytosolic or non-cytosolic part of the membrane bilayer?
Non-cytosolic side
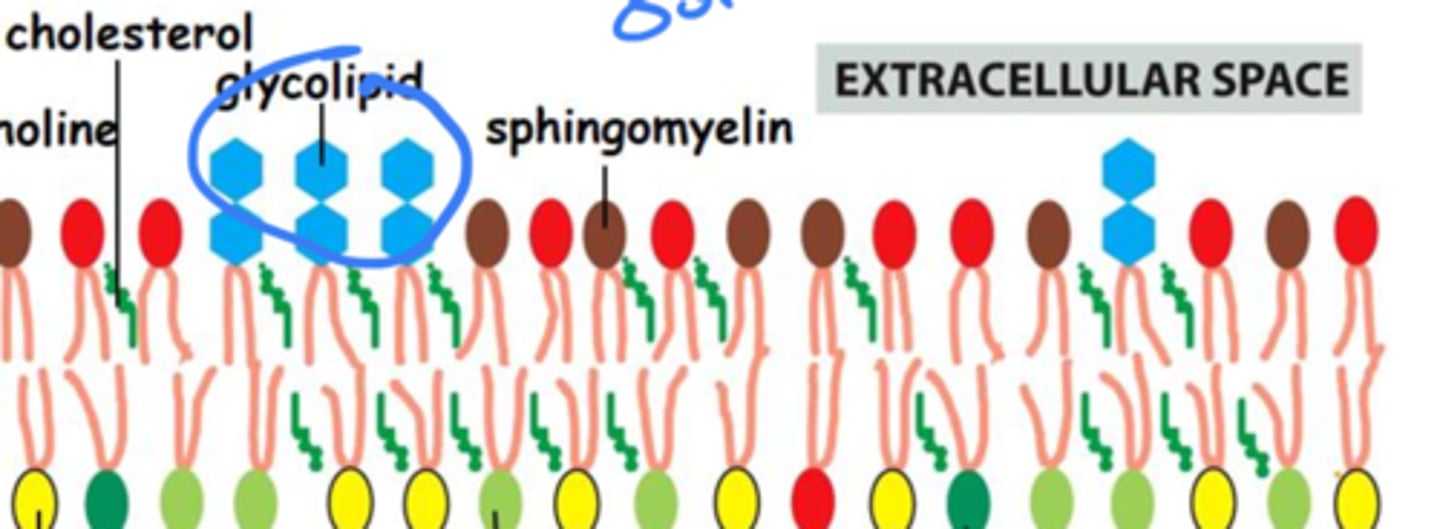
What are glycolipids important for?
Plasma membrane integrity, giving the cell a more structured appearance
Where do glycolipids acquire their sugar groups?
The golgi body
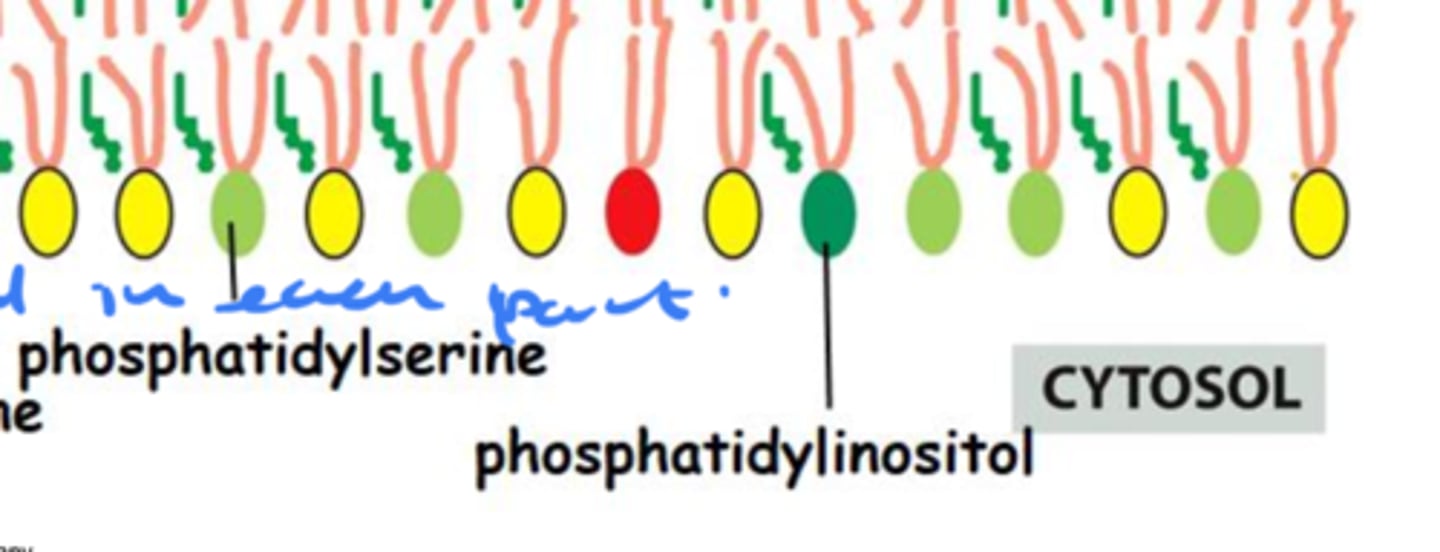
Are phosphatidylinositol lipids usually found in the in the cytosolic or non-cytosolic part of the membrane bilayer? Why?
They are found on the cytosolic side because they are signaling lipids that respond to internal cellular pathways. They can communicate what's happening inside the cell.